Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture - 9 - Secondary & Primary Data
Lecture - 9 - Secondary & Primary Data
Uploaded by
ayush singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views14 pagesThe document discusses data collection and different types of data sources. It defines data collection as the systematic gathering of data from various sources for a particular purpose. Data is collected to obtain information, keep records, make decisions, and pass information to others. Researchers can use secondary data, which includes previously collected qualitative and quantitative data, or primary data collected directly by the researcher through methods like observation, interviews, and questionnaires. The advantages and disadvantages of secondary data are outlined.
Original Description:
hi
Original Title
Lecture_9_Secondary & Primary Data
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses data collection and different types of data sources. It defines data collection as the systematic gathering of data from various sources for a particular purpose. Data is collected to obtain information, keep records, make decisions, and pass information to others. Researchers can use secondary data, which includes previously collected qualitative and quantitative data, or primary data collected directly by the researcher through methods like observation, interviews, and questionnaires. The advantages and disadvantages of secondary data are outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views14 pagesLecture - 9 - Secondary & Primary Data
Lecture - 9 - Secondary & Primary Data
Uploaded by
ayush singhThe document discusses data collection and different types of data sources. It defines data collection as the systematic gathering of data from various sources for a particular purpose. Data is collected to obtain information, keep records, make decisions, and pass information to others. Researchers can use secondary data, which includes previously collected qualitative and quantitative data, or primary data collected directly by the researcher through methods like observation, interviews, and questionnaires. The advantages and disadvantages of secondary data are outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Data Collection
Dr. Devkant Kala
UPES Dehradun
Data Collection
Data Collection is a term used to describe a
process of preparing an collecting data.
Systematic gathering of data for a particular
purpose form various sources, that has been
systematically observed, recorded and
organized.
Data are the basic inputs to any decision
making process in business.
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Data, Information & Knowledge
Human Information
Data Interpretation
Human Knowledge
Information Use
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Knowledge Hierarchy
Enriching through experience,
training and education
Transforming through personal
application, values and beliefs
Adding meaning, understanding,
relevance and purpose
Source: Bender and Fish (2000).
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Purpose of Data Collection
To obtain information.
To keep on record.
To make decision about important issues.
To pass information to others.
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Which type of Data?
Most researches use some combination of
secondary and primary data. How about
your research?
Usually researchers refer to secondary
data first. Why?
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Secondary Data
Previously Collected data by someone else.
They include both qualitative and
quantitative data and they can be used in
both descriptive and exploratory research.
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
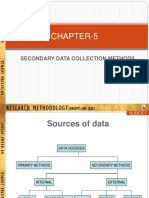
Sources of Secondary Data
Organization’s record
Organization’s website
Reports
Books
Journals
Newspapers
Tape, video recordings, CD
Pictures
Films and TV programs
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Advantages of Secondary Data
1. Less expensive and time saving.
2. Longitudinal and comparative studies became
possible.
3. Permanent and available.
4. Wide Geographical Area.
5. Clarification of Research Questions.
6. Leading to find primary data.
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Disadvantages of Secondary Data
1. May be collected for a purpose that does not
match your need.
2. Access may be difficult or costly when data is
collected for commercial reason.
3. No real control for data quality.
4. Incomplete information
5. Not updated Data.
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Evaluating Secondary Data
Sources
Review the secondary data with caution:
1. They will enable you to answer your research
question and meet your objectives. (Validity)
2. Reliability and Credibility
3. Clearly defined methodology
4. Adequate Coverage and measured variables.
5. Their benefits greater than their cost.
6. You will be allowed access to the data.
7. Updated Data
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Primary Data
First Hand Data; Collected by researcher
for specific purpose.
Observation
Interviews
Questionnaire
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Observation
Observation may be defined as systematic
viewing, coupled with consideration of seen
phenomenon.
Structured and Unstructured
Participant and Non-participant
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
Interview
A purposeful discussion between two or more
people. It can help you to gather valid and reliable
data that are relevant to your research question
and objectives.
Structured interview
Unstructured interview
Semi-structured interview
Telephonic Interview
Group Interview
Dr. Devkant Kala, UPES Dehradun
You might also like
- Criminal Intelligence Training - UN Analyst ManualDocument88 pagesCriminal Intelligence Training - UN Analyst Manualgrorwin100% (1)
- Chapter-5: Research MethodologyDocument17 pagesChapter-5: Research MethodologyShilpa SulekhNo ratings yet
- What Are The Essential Features of Effective CommunicationDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Essential Features of Effective CommunicationRishi Joshi100% (1)
- A Cognitive-Affective System Theory of Personality - ZZZDocument23 pagesA Cognitive-Affective System Theory of Personality - ZZZCristina DiaconuNo ratings yet
- The Art of Counter-Strike Volume 1Document204 pagesThe Art of Counter-Strike Volume 1Joep KulderijNo ratings yet
- CBC ForkliftDocument57 pagesCBC Forkliftconnie vitacion50% (2)
- Reading Data Information Knowledge WisdomDocument4 pagesReading Data Information Knowledge WisdomPrabath Withanage100% (1)
- Notes QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE METHODSDocument4 pagesNotes QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE METHODSDavid LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Systematic Layout Planning - Richard MutherDocument416 pagesSystematic Layout Planning - Richard MutherAlberto Trejo92% (13)
- Methodology, Scope, Limitatio, Significance, Data Collection and ChapterizationDocument37 pagesMethodology, Scope, Limitatio, Significance, Data Collection and ChapterizationWZ HakimNo ratings yet
- Research Orientation YsraDocument16 pagesResearch Orientation YsraMobasser HosainNo ratings yet
- Q2 Modules 4 To 7Document46 pagesQ2 Modules 4 To 7Mikyla DulinNo ratings yet
- 데이터큐레이션 0515Document10 pages데이터큐레이션 0515ynjrwdt4s5No ratings yet
- Enhance Your Team-BasedDocument5 pagesEnhance Your Team-BasedGh AsNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Study - ResearchDocument4 pagesQualitative Study - ResearchSam kNo ratings yet
- Data Collection, Survey, Design Experiments: Classification of Data According To SourceDocument2 pagesData Collection, Survey, Design Experiments: Classification of Data According To SourceSvan CodmNo ratings yet
- Educational Data Miningphd ThesispdfDocument6 pagesEducational Data Miningphd ThesispdfPaperWritingServiceCheapCanada100% (2)
- 1 Running Head: RESEARCH DESIGNDocument6 pages1 Running Head: RESEARCH DESIGNPROFESSOR HANAHNo ratings yet
- Resume of Nidheesh Sreedharan (11 Aug 2014)Document3 pagesResume of Nidheesh Sreedharan (11 Aug 2014)Srinivas KotaNo ratings yet
- Filosopi Penelitian Dan Konstruksi Artikel Publikasi BereputasiDocument43 pagesFilosopi Penelitian Dan Konstruksi Artikel Publikasi BereputasiSipenmaru AkbidNo ratings yet
- A Perfect Time For Data Use: Using Data-Driven Decision Making To Inform PracticeDocument16 pagesA Perfect Time For Data Use: Using Data-Driven Decision Making To Inform PracticeMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Research Notes 5Document8 pagesResearch Notes 5Myangel LoiseNo ratings yet
- IOP3705 Unit 5 Chap 7 Collecting and Analysing Diagnostic InformationDocument6 pagesIOP3705 Unit 5 Chap 7 Collecting and Analysing Diagnostic Informationsyeda salmaNo ratings yet
- TYBBA - RM - Topic No 3Document59 pagesTYBBA - RM - Topic No 3Vikas PabaleNo ratings yet
- Concept and Sources of Primary Data and SecondaryDocument47 pagesConcept and Sources of Primary Data and SecondaryNeenu M.HNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing 2: Philip Jerome A. Flores, RN, MSN LecturerDocument20 pagesCommunity Health Nursing 2: Philip Jerome A. Flores, RN, MSN LecturerAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranNo ratings yet
- Bhel HR ProjectDocument70 pagesBhel HR Projectvipul tandonNo ratings yet
- Knowledge ManagementDocument28 pagesKnowledge Managementrafida athaNo ratings yet
- Collecting Qualitative DataDocument24 pagesCollecting Qualitative DataEdi Hendri MNo ratings yet
- A Perfect Time For Data Use: Using Data-Driven Decision Making To Inform PracticeDocument17 pagesA Perfect Time For Data Use: Using Data-Driven Decision Making To Inform PracticeVictor ManzanoNo ratings yet
- DelphiDocument9 pagesDelphihaslindaNo ratings yet
- Article 6Document6 pagesArticle 6Abiy MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ResearchDocument12 pagesIntroduction To ResearchLaiba AslamNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Aecp3Document3 pagesModule 2 Aecp3Maria Crista Mae UmaliNo ratings yet
- QualiDocument3 pagesQualiCharisse Aleli DoyonganNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering Procedure Report (Richard D. Valdez)Document4 pagesData Gathering Procedure Report (Richard D. Valdez)Richard Divina ValdezNo ratings yet
- ARTIFACTs IN BASIC RESEARCH WRITINGDocument6 pagesARTIFACTs IN BASIC RESEARCH WRITINGlloviajuliusvonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3-Week 1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument6 pagesMODULE 3-Week 1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarsha MGNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (RM) UpdatedDocument13 pagesUnit 1 (RM) UpdatedSachitaa SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology LECTURE - NOTEDocument485 pagesResearch Methodology LECTURE - NOTESimaleeNo ratings yet
- BRM 1Document35 pagesBRM 1Digital teamNo ratings yet
- Focus Group Discussion Tehnique in Qualitative ResearchDocument11 pagesFocus Group Discussion Tehnique in Qualitative ResearchSuci AlfarystaNo ratings yet
- Identifying A Research ProblemDocument19 pagesIdentifying A Research ProblemTwelve Forty-fourNo ratings yet
- Chreswell CH 2 - Identifying A Research ProblemDocument19 pagesChreswell CH 2 - Identifying A Research ProblemTashika LewisNo ratings yet
- Research Data Management by DR RC GaurDocument29 pagesResearch Data Management by DR RC Gaursudheer babu arumbakaNo ratings yet
- Sources of DataDocument4 pagesSources of DataHarleigh SyneNo ratings yet
- Loudon 2015Document11 pagesLoudon 2015Deep AhireNo ratings yet
- Business Research Method: DR Rajeshwari PatilDocument42 pagesBusiness Research Method: DR Rajeshwari Patilsakshi raiNo ratings yet
- MKT 426 ExploratoryDocument18 pagesMKT 426 ExploratoryAminul NadimNo ratings yet
- Week 1 AssignmentDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Assignmentmutoro fredNo ratings yet
- Research Guidelines For The Delphi SurveyDocument8 pagesResearch Guidelines For The Delphi SurveyTheGimhan123No ratings yet
- Od Lesson 6-7Document3 pagesOd Lesson 6-7Pia Izella Meulio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Business ResearchDocument17 pagesBusiness Researchsejal chowhanNo ratings yet
- Comparing Open-Book and Closed-Book Examinations: A Systematic ReviewDocument17 pagesComparing Open-Book and Closed-Book Examinations: A Systematic ReviewMayurkumar patilNo ratings yet
- Thesis Data Gathering ProcedureDocument7 pagesThesis Data Gathering Procedureamberrodrigueznewhaven100% (2)
- An Open Conversation On Using Eye-Gaze Methods in Studies of Neurodevelopmental DisordersDocument14 pagesAn Open Conversation On Using Eye-Gaze Methods in Studies of Neurodevelopmental DisordersAndrea Gallo de la PazNo ratings yet
- Jdinh ResumeDocument3 pagesJdinh Resumeapi-352681904No ratings yet
- Knowledge MGMTDocument23 pagesKnowledge MGMTsuryamonNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ketan VeeraDocument20 pagesDr. Ketan VeeraHare Ram SinghNo ratings yet
- PR 2 GuideDocument11 pagesPR 2 GuideSetch PalmaNo ratings yet
- Module1 RDM PresentationDocument15 pagesModule1 RDM PresentationBose LogoNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document65 pagesWeek 2theresita raval100% (1)
- Res. Methodology-2 - 111917Document14 pagesRes. Methodology-2 - 111917Allen Davis JamesNo ratings yet
- Exploring Security, Privacy, and Reliability Strategies To Enable The Adoption of IotDocument201 pagesExploring Security, Privacy, and Reliability Strategies To Enable The Adoption of IotKashif KhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesEngineering Data AnalysisMaoi ReyesNo ratings yet
- Communication Manual Automatic Exchange of Tax Arrangements (DAC 6)Document72 pagesCommunication Manual Automatic Exchange of Tax Arrangements (DAC 6)RuthNo ratings yet
- Concept, Issues and Importance of Library Consortium: Problems and Prospects of University Library Consortium in BangladeshDocument23 pagesConcept, Issues and Importance of Library Consortium: Problems and Prospects of University Library Consortium in BangladeshMd. Anwarul Islam100% (1)
- BSE Synopsis Edited 22.03.2021Document48 pagesBSE Synopsis Edited 22.03.2021abdrhmn200377No ratings yet
- Four Ethical Issues of The Information AgeDocument7 pagesFour Ethical Issues of The Information AgeMithinga NarzaryNo ratings yet
- OG - Audit Report - Part 2 - Group No. 9Document24 pagesOG - Audit Report - Part 2 - Group No. 9Karan BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Global E-Business and Collaboration: Management Information Systems, 13e (Laudon/Laudon)Document23 pagesChapter 2 Global E-Business and Collaboration: Management Information Systems, 13e (Laudon/Laudon)HermanNo ratings yet
- QUIZ Purposive CommsDocument7 pagesQUIZ Purposive CommsJanica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Display and Control DesignDocument19 pagesDisplay and Control DesignLorenz ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Medi Help: A System Design Project Report OnDocument36 pagesMedi Help: A System Design Project Report OnAakash VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Technology and Internet EssaysDocument7 pagesTechnology and Internet EssaysAshwiniNo ratings yet
- Multimodal Smartphone - Millennial Student Learning - M Bayu FirmansyahDocument11 pagesMultimodal Smartphone - Millennial Student Learning - M Bayu FirmansyahbayuNo ratings yet
- Social Media Marketing Strategy: Definition, Conceptualization, Taxonomy, Validation, and Future AgendaDocument21 pagesSocial Media Marketing Strategy: Definition, Conceptualization, Taxonomy, Validation, and Future Agendaniharika singhNo ratings yet
- Quản trị họcDocument10 pagesQuản trị họcPhạm Chi MaiNo ratings yet
- Aurora Pioneers Memorial Ollege: Teaching Guides Template (2019)Document2 pagesAurora Pioneers Memorial Ollege: Teaching Guides Template (2019)mae joy saysipNo ratings yet
- Notes IMC451Document6 pagesNotes IMC451Muhammad HilmiNo ratings yet
- E PKS: XperionDocument207 pagesE PKS: XperionAnkoosh MandanNo ratings yet
- Accepted ManuscriptDocument22 pagesAccepted ManuscriptNUR SUKMAWATINo ratings yet
- 3is Q4 Week 1 Module 5Document22 pages3is Q4 Week 1 Module 5yanyanoligo0902No ratings yet
- 2021 Van Gool and MichelDocument22 pages2021 Van Gool and MichelDimaNo ratings yet
- The Electronic Library: Article InformationDocument16 pagesThe Electronic Library: Article InformationSakshi RNo ratings yet
- Genre Analysis of Business Letters of Negotiation - SantosDocument33 pagesGenre Analysis of Business Letters of Negotiation - SantosZack RandalNo ratings yet
- Early Literacy and Brain Development PDFDocument35 pagesEarly Literacy and Brain Development PDFcojoneraxNo ratings yet
- Wa0121.Document592 pagesWa0121.Shawon Moshiur RahamanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Chapter 2: Logistics and Information Technology Multiple Choice Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)Document12 pagesTest Bank Chapter 2: Logistics and Information Technology Multiple Choice Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)ewalied2800No ratings yet