Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bond Polarity and Molecular Polarity
Uploaded by
koko0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe document discusses molecular polarity, which is determined by electronegativity differences between bonded atoms. A polar bond forms when there is a greater than 0.5 difference in electronegativity, creating a partial positive and negative charge. Molecular geometry, including bond and electron pair orientations, also influences overall molecular polarity and properties like solubility. Solubility is determined by whether a substance is polar or nonpolar, with polar substances dissolving in polar solvents and nonpolar dissolving only in nonpolar solvents.
Original Description:
chemistry!
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses molecular polarity, which is determined by electronegativity differences between bonded atoms. A polar bond forms when there is a greater than 0.5 difference in electronegativity, creating a partial positive and negative charge. Molecular geometry, including bond and electron pair orientations, also influences overall molecular polarity and properties like solubility. Solubility is determined by whether a substance is polar or nonpolar, with polar substances dissolving in polar solvents and nonpolar dissolving only in nonpolar solvents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesBond Polarity and Molecular Polarity
Uploaded by
kokoThe document discusses molecular polarity, which is determined by electronegativity differences between bonded atoms. A polar bond forms when there is a greater than 0.5 difference in electronegativity, creating a partial positive and negative charge. Molecular geometry, including bond and electron pair orientations, also influences overall molecular polarity and properties like solubility. Solubility is determined by whether a substance is polar or nonpolar, with polar substances dissolving in polar solvents and nonpolar dissolving only in nonpolar solvents.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Bond Polarity and Molecular
Polarity
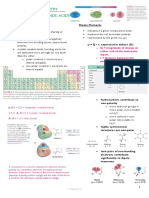
ELECTRONEGATIVITY (EN)
- The tendency (strength of relative
pull) of an atom in a bond to
attract electrons toward itself.
*the higher the EN value, the greater is
the attraction for the electrons.
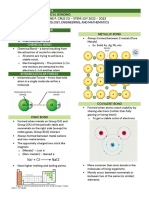
Polar and Nonpolar
Polar
- more electronegative atom
−
becomes partially negative (δ ),
and the other side becomes
+
partially positive (δ );
- This condition results in a dipole
represented as ( ),
with the arrow pointing to the
more electronegative atom.
Nonpolar
- Two atoms with similar electro
negativities creating an even
distribution of electrons in a
chemical bond.
The bond between H and Cl is polar.
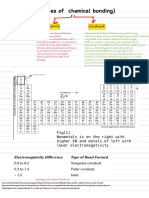
TYPE OF BOND BASED ON ∆EN OF BONDED
ATOMS
∆EN BOND TYPE
The bond between two Cl atoms is 0 NONPOLAR
nonpolar. COVALENT
GREATER THAN 0 UP POLAR COVALENT
TO 1.9
GREATER THAN 1.9 IONIC
ELECTRONEGATIVITY DIFFERENCE (∆EN)
CAN HELP DETERMINE IF THE BOND IS
IONIC, POLAR COVALENT OR
NONPOLAR COVALENT.
- ability of substance to dissolve in
MOLECULAR GEOMETRY a given solvent;
- MOLECULAR GEOMETRY VALENCE - Polar solutes dissolve in polar
SHELL solvents and not in nonpolar;
- ELECTRON PAIR REPULSION (VSEPR) nonpolar solutes can only
THEORY dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
(VSEPR) Theory
- states that a molecule will adjust
its shape so that the valence
electron pairs stay as far apart
from each other as possible;
- Negatively charged electrons
repel one another.
Molecular Geometry
- the arrangements of atoms in a
molecule in three-dimensional;
- Give influence to the physical
and chemical properties of a
compound
(melting and boiling points,
solubility, density, and the types
of chemical reactions).
POLAR MOLECULE: POLAR BONDS
THAT ARE ARRANGED IN A WAY
THAT THERE IS AN ASYMMETRICAL
DISTRIBUTION OF CHARGE.
SOLUBILITY
You might also like
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Polar Covalent BondsDocument10 pagesPolar Covalent BondsParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Lecture03f - Van Der WaalsDocument36 pagesLecture03f - Van Der WaalsKarla B. CamperoNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Monitoring PrimerDocument61 pagesCorrosion Monitoring PrimerShubhodeep SarkarNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document424 pagesBook 2Anonymous DPt7hpiaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument6 pagesGen Chem ReviewerNIKKI GRACE MAGDALI100% (1)
- Physical Science: Ms. Grace Monica P. LebrillaDocument40 pagesPhysical Science: Ms. Grace Monica P. LebrillaGabriel James SedanNo ratings yet
- PolarityDocument27 pagesPolarityGiffNo ratings yet
- Exploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Document18 pagesExploring Polarity of Molecules and Its Properties: Physical Science Quarter 3 Module 2Maricar DimasNo ratings yet
- Annual Product ReviewDocument25 pagesAnnual Product ReviewBhupendra Tomar100% (2)
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleDocument7 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 2: Not For SaleChristien Kate GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Integrity Management MSC (Penspen)Document7 pagesPipeline Integrity Management MSC (Penspen)Majeed Rumani0% (2)
- Instruction Manual: Feel The Energy. Feel The FreshnessDocument12 pagesInstruction Manual: Feel The Energy. Feel The FreshnessShivaprasad Hc PatelNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technology (Vafa Chiragova)Document21 pagesHydrogen and Fuel Cell Technology (Vafa Chiragova)Vəfa ÇıraqovaNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument22 pagesPolarity of MoleculesEstrellita SilvioNo ratings yet
- Properties of Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesProperties of Covalent BondingMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- Polarity & ForcesDocument13 pagesPolarity & ForcesElsayed ElazazyNo ratings yet
- 2 The Chemistry of The ElementsDocument28 pages2 The Chemistry of The ElementsNazmi LatifNo ratings yet
- IMFADocument41 pagesIMFAShaila DelatorreNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculeDocument35 pagesPolarity of MoleculeAlyson Kate CastillonNo ratings yet
- Klein Organic Chemistry Chapter 1: Review of General ChemistryDocument2 pagesKlein Organic Chemistry Chapter 1: Review of General ChemistryJim Xie100% (1)
- Chap 1.2Document47 pagesChap 1.2Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Chemical PolarityDocument6 pagesChemical PolarityPavan TejNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Chem Revieweraldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Chemıcal BondsDocument10 pagesChemıcal BondsDesirie MarceloNo ratings yet
- 02.2 Chapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument12 pages02.2 Chapter 2 - Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BaseselaineustNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds Acids and Bases黃向廷No ratings yet
- Chap-1-1 Intra and Intermolecular ForcesDocument48 pagesChap-1-1 Intra and Intermolecular Forceslishan asefaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesDocument9 pagesLesson 7: Polarity of MoleculesRAENA MARIE PENDRASNo ratings yet
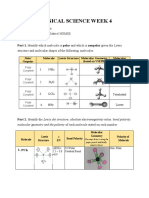
- Physical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSRico R. CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Demo InsetDocument36 pagesDemo InsetSubicAmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LNDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding LNCenjie Niña Hayag SongcalNo ratings yet
- Second Midterm ReviewDocument90 pagesSecond Midterm ReviewEvelyn Montserrat Gómez ZentenoNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Polarity - FactsDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Polarity - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Ii LecturesDocument18 pagesGen Chem Ii LecturesHANNA ROLISH DIGAMONNo ratings yet
- Review Basic Chemical ConceptsDocument4 pagesReview Basic Chemical ConceptsMary♡No ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument19 pagesMolecular PolarityDianne CofinoNo ratings yet
- Ion DipoleDocument18 pagesIon DipoleblessyramasamillanoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesGen Chem ReviewerLawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Chemical BondingJanchel BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Specialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoDocument5 pagesSpecialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Handout 9.1 Electronegativity Differences and PolarityDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Handout 9.1 Electronegativity Differences and PolarityGwyneth CataneNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument41 pagesIntermolecular Forcessuka11blyatNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument11 pagesPhysical ScienceSieg BelfortNo ratings yet
- 02 BondingDocument24 pages02 Bondingiron_trNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Polarity of Molecules: Seventh Course (General Chemistry) by Dr. IstadiDocument23 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Polarity of Molecules: Seventh Course (General Chemistry) by Dr. IstadiBINTANGNo ratings yet
- Molecule Total Number of Valence Electrons Lewis Structure Skeleton Structure CH H 0 HCN OH SODocument3 pagesMolecule Total Number of Valence Electrons Lewis Structure Skeleton Structure CH H 0 HCN OH SOKashika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The EarthDocument58 pagesChemical Composition of The EarthPutik Nurul ArasyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Note 1Document3 pagesChemical Bonding Note 1youservezeropurpose113No ratings yet
- Atoms, Electrons, Chemical Bonding, and Orbitals: Computer Modeling and Visualization in ChemistryDocument33 pagesAtoms, Electrons, Chemical Bonding, and Orbitals: Computer Modeling and Visualization in Chemistryhasib_07No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and Chemical CompoundsDocument8 pagesChemical Bonds and Chemical Compoundsmargareth bumatayNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesIntramolecular ForcesNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- GENCHEMDocument6 pagesGENCHEMangeladmana09No ratings yet
- General Chem 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesGeneral Chem 2 ReviewerBeverly A PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The EarthDocument58 pagesChemical Composition of The EarthPutik Nurul ArasyNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 - MSE312 - Manual - 2021Document14 pagesExp 4 - MSE312 - Manual - 2021Trust IssuesNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 NotesDocument20 pagesGenchem 2 Notesmoss headNo ratings yet
- Bonds in Solid 4 SDocument5 pagesBonds in Solid 4 SS.M. Abdul Mannan MahdiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Polarity of MoleculesDocument56 pagesPhysical Science Polarity of MoleculeskharentaponNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic StructureDocument43 pages2 Atomic StructureRafael ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Luxuricious CompanyNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds&Molecules V2Document9 pagesPolar Bonds&Molecules V2vlattaetaeNo ratings yet
- Chem2 MT 1st LT NotesDocument3 pagesChem2 MT 1st LT NotesnicolassarragaNo ratings yet
- Phys. Sci. Module 5Document3 pagesPhys. Sci. Module 5TE RENo ratings yet
- Comparison On BondsDocument7 pagesComparison On Bondseliastadele7No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument50 pagesUntitledNica Floresta - MendozaNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,651,730 B2: Jiang Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 25, 2003Document10 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,651,730 B2: Jiang Et Al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 25, 2003Vy PhanNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Grade 60-40-18, Low Temperature ServiceDocument2 pagesDuctile Iron Grade 60-40-18, Low Temperature Servicevamsi patnalaNo ratings yet
- Extra ExercisesDocument55 pagesExtra ExercisesCamilo MartinezNo ratings yet
- hướng dẫn sử dụng Lắp Buchi r300Document116 pageshướng dẫn sử dụng Lắp Buchi r300Giáo job vạnNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: Carla M. Oliveira, António S. Barros, António C.S. Ferreira, Artur M.S. SilvaDocument7 pagesFood Chemistry: Carla M. Oliveira, António S. Barros, António C.S. Ferreira, Artur M.S. SilvaElias Torres GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 980.13 Fructose, Glucose, Lactose, Maltose and Sucrose in Milk ChocolateDocument1 page980.13 Fructose, Glucose, Lactose, Maltose and Sucrose in Milk ChocolateJessica triana pinedaNo ratings yet
- Preventing Coil Tubing CorrosionDocument6 pagesPreventing Coil Tubing Corrosionktjayakumar3878No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Ionic and Covalent BondDocument8 pagesLesson 1: The Ionic and Covalent BondJoshua BaldoNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of FiberglassDocument4 pagesHydrolysis of FiberglassMurugan RangarajanNo ratings yet
- SIPOMER Resin Modi ErsDocument7 pagesSIPOMER Resin Modi ErsVictor LopezNo ratings yet
- Chem Int CC CH 19 - Equilibrium - Answers PDFDocument12 pagesChem Int CC CH 19 - Equilibrium - Answers PDFChristal EcheverriaNo ratings yet
- 5Document8 pages5Anwar ALkurayshiNo ratings yet
- Sciencedoze: Science, Education and Technology: Biodegradable Polymers: de Nition, Examples, Properties and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesSciencedoze: Science, Education and Technology: Biodegradable Polymers: de Nition, Examples, Properties and Applicationssantosh chikkamathNo ratings yet
- 65 Liv API 6a 150 To 10000 Psi LT WT FT Check VDocument15 pages65 Liv API 6a 150 To 10000 Psi LT WT FT Check VRiddhesh PatelNo ratings yet
- 2023 Notes CH#3 9thDocument2 pages2023 Notes CH#3 9thhaseebsipio121No ratings yet
- AC II Unit I MCQDocument6 pagesAC II Unit I MCQPRATK DESAINo ratings yet
- Modern Pharmaceutics 4th Edition Chapter 10Document47 pagesModern Pharmaceutics 4th Edition Chapter 10Faysal MasoodNo ratings yet
- Isothermal Batch ReactorDocument5 pagesIsothermal Batch ReactorSrikanthNo ratings yet
- Nutrition EssayDocument2 pagesNutrition EssayJoan SANo ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering, Vol.7, No.6B, 2018-1 - Odysseas KopsidasDocument39 pagesJournal of Environmental Science and Engineering, Vol.7, No.6B, 2018-1 - Odysseas KopsidasAnonymous kqqWjuCG9No ratings yet
- SCI - AC - Elaboración de Hormigón Ligero A Partir de Arcilla Expandida Modificada Con RCGDocument8 pagesSCI - AC - Elaboración de Hormigón Ligero A Partir de Arcilla Expandida Modificada Con RCGEstructuras MetalicasNo ratings yet
- Power PlantDocument17 pagesPower PlantVasu RajaNo ratings yet
- Reinzoplast 300mL: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesReinzoplast 300mL: Safety Data SheetEugenNo ratings yet
- MEEN 20052 - Week 4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.Document4 pagesMEEN 20052 - Week 4 - Salamat, Andre Agassi D.andreagassiNo ratings yet