Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
Uploaded by
Ahmed ElmasryOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
Uploaded by
Ahmed ElmasryCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
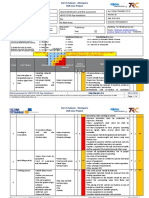
RA Ref Number: 34b Revision: 3 Project/Job Number Reference Insert Job Number Approval Date: 30/03/2018
RA Description: Installing Conduit Next Review Date: 01/04/2019
Notes: Please refer to Safe Working Practices 34b for definitions of items in this assessment. Created by: Lee Davies
Risk Assessment The summary risk assessment is calculated as “Likelihood” x “Consequence” Issued by: Insert Name
Method & Scoring and categorised as follows; 1 to 6 = Low Risk – 7 to 16 = Medium Risk – 17 to 25 = High Risk Issue Date: Insert Date
TASK HAZARDS PERSONS INITIAL CONTROL MEASURES REVISED
AFFECTED RISK RISK LEVEL
LEVEL
Installing PVC Injuries from Engineer Likelihood 4 Only engineers who are trained to do so install / cut conduit. Likelihood 1
conduit. hacksaw used to cut Severity 4 Engineers use hand tools that are in good condition, with sharp blades that are Severity 4
conduit. Total 16 not damaged or prone to snapping. Total 4
Medium Risk Conduit is cut on a flat surface. Low Risk
Conduit is held firmly whilst it is being cut.
Installing PVC Injuries to hands Engineer Likelihood 4 Only engineers who are trained to do so install / set conduit. Likelihood 1
conduit. whilst using a Severity 4 Engineers use hand tools that are in good condition, that are not damaged or Severity 4
bending spring to set Total 16 prone to snapping. Total 4
Medium Risk Bending springs are inspected prior to use, and if found to be over stretched or Low Risk
conduit.
damaged are placed out of use.
Conduit is set typically by bending it over the knee; engineers are trained
in the best working practices of using the spring for this task.
Installing PVC Injuries from Engineer / Likelihood 4 Engineers do not carry bundles of conduit through buildings alone, Likelihood 1
conduit. handling lengths of others present. Severity 4 another person is present to open doors, warn others etc. Severity 4
conduit. Total 16 Conduit is stored safely and not left lying around as a trip hazard. Total 4
Medium Risk Low Risk
Only the amount of conduit to be used straight away is taken to the
workplace, others are left in storage until they are required.
RA Number: 34b - Issue Revision: 3 Page 1 of 5
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
TASK HAZARDS PERSONS INITIAL CONTROL MEASURES REVISED
AFFECTED RISK RISK LEVEL
LEVEL
Installing steel Injuries from Engineer / Likelihood 4 Engineers do not carry bundles of conduit through buildings alone, Likelihood 1
conduit. handling lengths of others present Severity 4 another person is present to open doors, warn others etc. Severity 4
conduit. Total 16 Conduit is stored safely and not left lying around as a trip hazard. Total 4
Medium Risk A dedicated work area is established for the cutting / setting of conduit, Low Risk
and spare tube is kept here.
Only the amount of conduit to be used straight away is taken to the work
area, others are left in storage until they are required.
Installing steel Injuries from cutting, Engineer Likelihood 4 Only engineers who are trained to do so install / cut conduit. Likelihood 1
conduit. setting, bending, Severity 4 Conduit is cut, set, and bent, threaded using a pipe vice to hold the Severity 4
threading steel Total 16 conduit. The correct size-setting wheel is always used. Total 4
conduit. Medium Risk Engineers use hand tools that are in good condition, with sharp blades Low Risk
that are not damaged or prone to snapping.
RA Number: 34b - Issue Revision: 3 Page 2 of 5
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
Safe Working Practice: 34b – Installing Conduit
1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this guide is to highlight safe working practices for: Installing Conduit.
IT MUST NOT BE TREATED AS A SUBSTITUTE FOR TRAINING
2 PROTECTIVE CLOTHING AND EQUIPMENT
Operators must wear
➢ Safety Boots/Shoes incorporating steel toe-caps
➢ CDI issued work wear
➢ Dust masks – where appropriate
➢ Ear protectors - where appropriate.
3 BEFORE WORK
➢ Flexible conduit. To comply with BS 731 / BS 6053.
➢ Flexible conduit (Copex) is only to be used to form short connections between other
containment systems, or where a run is required to be moveable.
➢ Typical examples are linking a steel conduit to a machine where Copex is installed through a
cabling trough in the machine, or linking a basket tray to a floor box in a raised floor where
the floor box may have to move in future.
4 DURING WORK
➢ Where the feeder conduit is steel, or where mechanical damage is possible, steel lined Copex
should be used. All PVC Copex should only be used where risk of mechanical damage is very
low.
➢ Installation of Copex is by loose laying, do not fix as the tube needs to be able to move.
➢ Normal conduit boxes will fit onto Copex, and through boxes are used to form a feed point in
a longer run.
➢ You can use cable base fixings with Tyraps to fix flexible conduit to a wall, or it can be
Trapped direct for other applications.
➢ Be careful not to over tighten the Tyraps and crush the conduit.
➢ Copex termination is by cutting with a hand held junior hacksaw, as for PVC conduit. The
end coupler is fitted to the Copex by threaded gland. Be careful not to over tighten these as
this can cause the thread to strip, and the gland to become loose.
5 AFTER WORK
➢ Check all tools for any damage, and place them out of use if any is found.
➢ Remove all waste materials and place into approved waste containers or remove from site.
CDI GROUP LTD PLACES GREAT IMPORTANCE ON EVERYONE'S SAFETY:
FAILURE TO COMPLY WITH ANY OF THE ABOVE MAY RESULT IN DISCIPLINARY
ACTION
RA Number: 34b - Issue Revision: 3 Page 3 of 5
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
RA Number: 34b - Issue Revision: 3 Page 4 of 5
Risk Assessment & Safe Working Practice
RA Number: 34b - Issue Revision: 3 Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- 2020 Calendar PDFDocument12 pages2020 Calendar PDFHaneef ShaikNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis For: Hcu & Lobs Revamp ProjectDocument6 pagesJob Safety Analysis For: Hcu & Lobs Revamp ProjectShilpiengg SafetyNo ratings yet
- Gas Cutting Work: Hazard Identification and Risk AssessmentDocument3 pagesGas Cutting Work: Hazard Identification and Risk AssessmentAchalere Shekhar Kashinath100% (2)
- RA Confined Space PDFDocument10 pagesRA Confined Space PDFrodman823100% (1)
- Risk Assessment: Pick & Carry CranesDocument36 pagesRisk Assessment: Pick & Carry CranesAbd Ennacer100% (2)
- Permit To Work System Reasons For Its FailureDocument5 pagesPermit To Work System Reasons For Its FailurePraveen AbisakeNo ratings yet
- Risk - Batching Plant OperationsDocument6 pagesRisk - Batching Plant Operationsmechajay2002100% (1)
- Yms Shem P 0810 - (Yms Oms P 31610) - 221216 - 102800Document117 pagesYms Shem P 0810 - (Yms Oms P 31610) - 221216 - 102800vinay kumarNo ratings yet
- Job Activity Hazard Effect Control Measures: Project in ChargeDocument3 pagesJob Activity Hazard Effect Control Measures: Project in Chargeperquino oasanNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor Bearing InspectionDocument3 pagesBelt Conveyor Bearing InspectionKarthikeyan MNo ratings yet
- NEW CL - JLA Steel Hand Tool - SWPDocument3 pagesNEW CL - JLA Steel Hand Tool - SWPAbdul Rafiq100% (1)
- Working at Height Risk Assessment Mar 21Document2 pagesWorking at Height Risk Assessment Mar 21tariq1987No ratings yet
- Hse Risk Register-RaDocument8 pagesHse Risk Register-RaNiraNo ratings yet
- DSM-FRM-0001-27-0, HDPE PE-100 Pipe InstallationDocument4 pagesDSM-FRM-0001-27-0, HDPE PE-100 Pipe Installationkadir tanzaniaNo ratings yet
- SRB-02-2011 - (Welding of Pipes) For Thrust BoringDocument4 pagesSRB-02-2011 - (Welding of Pipes) For Thrust BoringkkalviNo ratings yet
- Design Aspects For Safety IN Electrical System: ' OISD-RP-149 Draft-III For Restricted Circulation OnlyDocument48 pagesDesign Aspects For Safety IN Electrical System: ' OISD-RP-149 Draft-III For Restricted Circulation OnlyArunava Chakraborty100% (5)
- Pressure Relief Device Maintenance QC ManualDocument10 pagesPressure Relief Device Maintenance QC ManualMohammed ZubairNo ratings yet
- Clariant SDS Hostagel PH1 Argentina EnglishDocument16 pagesClariant SDS Hostagel PH1 Argentina Englishkunal agiwaleNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicle Repair ShopDocument4 pagesMotor Vehicle Repair Shopapuesto726100% (1)
- TR Local Guiding Services NC IIDocument52 pagesTR Local Guiding Services NC IIleijulia75% (4)
- Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesRisk AssessmentBishop Ojonuguwa AmehNo ratings yet
- Method Statement: QC InspectorDocument7 pagesMethod Statement: QC InspectorCobbinah MarkNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Excavation SafetyDocument72 pagesGroup 3 Excavation SafetyRohadzma N. NajebNo ratings yet
- SOP SOP0022 Concrete Core DrillDocument3 pagesSOP SOP0022 Concrete Core Drillkristian08No ratings yet
- Hira - 01Document3 pagesHira - 01Angw BasumataryNo ratings yet
- Workplace Policy and Program On Hepatitis B and D.ODocument7 pagesWorkplace Policy and Program On Hepatitis B and D.OAldrin AguasNo ratings yet
- Form 72-Fire Hydrant and Sprinkler System Periodic Testing and MaintenanceDocument3 pagesForm 72-Fire Hydrant and Sprinkler System Periodic Testing and MaintenanceSatrio Budi Prakosa RachmanNo ratings yet
- Method Statement and Risk Assessment For General Stone Masonry Including Dry Stone WallingDocument8 pagesMethod Statement and Risk Assessment For General Stone Masonry Including Dry Stone WallingMatin Hamid FaqiriNo ratings yet
- ARA - For Emergency Diesel GeneratorDocument4 pagesARA - For Emergency Diesel GeneratorShaikh AftabNo ratings yet
- Ppe Al JaberDocument20 pagesPpe Al JaberImtiyaz AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Safe Working PracticeDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment & Safe Working Practicekamranshamoo1100% (1)
- 2.0 en-US 2016-05 SR.2190 2201Document96 pages2.0 en-US 2016-05 SR.2190 2201Edgar IbañezNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Safe Working PracticeDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment & Safe Working Practicemonik_atabaresNo ratings yet
- Carpentry, Forming, Framing or Wood WorkingDocument1 pageCarpentry, Forming, Framing or Wood Workingchirese2000No ratings yet
- Carpentry, Forming, Framing or Wood WorkingDocument1 pageCarpentry, Forming, Framing or Wood WorkingAlex DcostaNo ratings yet
- Method Statement & Risk Assessment: Industrial Security Doors LTDDocument8 pagesMethod Statement & Risk Assessment: Industrial Security Doors LTDNathi MaphangaNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Forming Framing or Wood WorkingDocument1 pageCarpentry Forming Framing or Wood WorkingPrakash PavuralaNo ratings yet
- Carpentry, Forming, Framing or Wood Working PDFDocument1 pageCarpentry, Forming, Framing or Wood Working PDFnaraNo ratings yet
- Exhibitor RAMS Example - LDB 23Document11 pagesExhibitor RAMS Example - LDB 23BocirneaNo ratings yet
- Honda Petrol GensetDocument3 pagesHonda Petrol Gensetmanishadash009No ratings yet
- Term Contract For Gas Transmission Pipe Lines and Facilities Project Works, CONTRACT NO: 9140339 (TC5)Document22 pagesTerm Contract For Gas Transmission Pipe Lines and Facilities Project Works, CONTRACT NO: 9140339 (TC5)quocphong199No ratings yet
- WWETB Waterford TC - Metal Fabrication 2015Document9 pagesWWETB Waterford TC - Metal Fabrication 2015DEVIL々 Gamers FFNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment FormDocument8 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Assessment FormMOHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Sener/Sepcoiii Consortium Noor Iii Project: Risk AssessmentDocument7 pagesSener/Sepcoiii Consortium Noor Iii Project: Risk AssessmentmessaoudiNo ratings yet
- Welding Robots Technology System Issues and Applications - J Norberto PiresDocument76 pagesWelding Robots Technology System Issues and Applications - J Norberto PireshetpinNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 11 Safety Services Guidance Lead Contact: Safety ServicesDocument11 pagesPage 1 of 11 Safety Services Guidance Lead Contact: Safety ServicesJoseph Ryan ManandegNo ratings yet
- SOP-22 AC Compressore Replacement WorkDocument4 pagesSOP-22 AC Compressore Replacement WorkNarendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Risk RegisterDocument8 pagesRisk RegisterStephenNo ratings yet
- 01-01b Safety BoomerDocument30 pages01-01b Safety BoomerJorge Luis Guerreros RamosNo ratings yet
- HSE Risk Register 2Document8 pagesHSE Risk Register 2Shazayn KhanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Maintenance: L - Likelihood S - Severity RL - Risk LevelDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment Maintenance: L - Likelihood S - Severity RL - Risk LevelMohamed ElnagdyNo ratings yet
- Risk Register: Hazards Identified Risk Control Measures Residual Risk by Whom L S R L S RDocument8 pagesRisk Register: Hazards Identified Risk Control Measures Residual Risk by Whom L S R L S Rzae nuddinNo ratings yet
- Tuaman Engineering Limited: Job Safety Analysis (Jsa)Document6 pagesTuaman Engineering Limited: Job Safety Analysis (Jsa)abhijit janaNo ratings yet
- 7.5 Risk Assessment and Safety Measures:: 7.5.1 Classification of The Hazards in The Cement IndustryDocument28 pages7.5 Risk Assessment and Safety Measures:: 7.5.1 Classification of The Hazards in The Cement IndustryjohnNo ratings yet
- Electric Submersible PumpDocument2 pagesElectric Submersible Pumpneyazy abdelmonemNo ratings yet
- MPS - Fail Safe PDFDocument1 pageMPS - Fail Safe PDFNABEILNo ratings yet
- Post Hole Borer Risk Assessment: September 2015 //1Document2 pagesPost Hole Borer Risk Assessment: September 2015 //1Rajendra0% (1)
- Hand Grinder IncidentDocument1 pageHand Grinder IncidentMohammedNo ratings yet
- Final Method Statement v2Document13 pagesFinal Method Statement v2sheebaNo ratings yet
- Ra Operating and Testing Weber Hydraulic EquipmentDocument4 pagesRa Operating and Testing Weber Hydraulic EquipmentMicky PlumbNo ratings yet
- CHEMSAFE Warehouse Risk Assessment ExampleDocument6 pagesCHEMSAFE Warehouse Risk Assessment ExampleMatthew LeeNo ratings yet
- Trenching Safety Training: Department of Administrative Services Loss Control ServicesDocument32 pagesTrenching Safety Training: Department of Administrative Services Loss Control Services김원재No ratings yet
- Safe Work Method Statement: Excavation, Trenching and Underground ServicesDocument8 pagesSafe Work Method Statement: Excavation, Trenching and Underground ServicesComsip400No ratings yet
- Paper IV: Part 2 Oral Presentation Report of Hazards in The Construction Site of Nestle Manufacturing (M) SDN BHDDocument18 pagesPaper IV: Part 2 Oral Presentation Report of Hazards in The Construction Site of Nestle Manufacturing (M) SDN BHDMuhd NaqibNo ratings yet
- OCP - 4 Handling of Reinforced SteelDocument3 pagesOCP - 4 Handling of Reinforced Steelbabu541No ratings yet
- Safety Procedure RammerDocument2 pagesSafety Procedure RammerAura SantosNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For Risk Assessment in Cement Plants - Part2Document10 pagesTraining Manual For Risk Assessment in Cement Plants - Part2Kamran ZafarNo ratings yet
- Culvert and Multi Plate Installation 2016 VerisonDocument3 pagesCulvert and Multi Plate Installation 2016 VerisonJæy JåýNo ratings yet
- RA Covid 19.1 Cleaning General Area and Office Rooms Covid 19 Update 1.4.20Document7 pagesRA Covid 19.1 Cleaning General Area and Office Rooms Covid 19 Update 1.4.20Vimal ThomasNo ratings yet
- FP ManualDocument444 pagesFP ManualRajiv ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) : Extremely Unpleasant OdourDocument2 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) : Extremely Unpleasant OdourdhaktodesatyajitNo ratings yet
- D618 12087Document4 pagesD618 12087xavicojmNo ratings yet
- Evaluate The Organisation'S Health, Safety and Security EffectivenessDocument2 pagesEvaluate The Organisation'S Health, Safety and Security EffectivenessGladys CaramoanNo ratings yet
- F109 SchlumbergerDocument9 pagesF109 Schlumbergersajad gohariNo ratings yet
- TrafficDocument21 pagesTrafficNazhirin DisiniNo ratings yet
- YK-X/XH Series: Yamaha Scara RobotDocument370 pagesYK-X/XH Series: Yamaha Scara RobotDavid MurilloNo ratings yet
- 5 - Development of A Risk-Based Maintenance Strategy Using FMEA For A Continuous Catalytic Reforming PlantDocument8 pages5 - Development of A Risk-Based Maintenance Strategy Using FMEA For A Continuous Catalytic Reforming PlantNur Azizah NasutionNo ratings yet
- PCMDocument14 pagesPCMcyrawrNo ratings yet
- One Direct Method Statement: Main Hazards Preventative MeasuresDocument4 pagesOne Direct Method Statement: Main Hazards Preventative MeasuresAyu Wanda SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- VM Checklist - Manufacturing: Peracha Engineering CoDocument2 pagesVM Checklist - Manufacturing: Peracha Engineering CoPeracha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- GC3 - Exam TemplateDocument10 pagesGC3 - Exam TemplateSiddharthNo ratings yet
- 266dsh Instructions PDFDocument76 pages266dsh Instructions PDFCarlos VidelaNo ratings yet
- Flame Scanner Durag Ig200Document117 pagesFlame Scanner Durag Ig200Hiên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bosiet With Ebs: DurationDocument2 pagesBosiet With Ebs: DurationjijinsNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Pulse TrainDocument409 pagesYaskawa Pulse Traincorrecaminos69No ratings yet
- CL 2871Document8 pagesCL 2871makhrufNo ratings yet
- Functional Academics Science 3Document13 pagesFunctional Academics Science 3Riza Pearl LlonaNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Hexafluoride sf6 Safety Data Sheet Sds p4657Document9 pagesSulfur Hexafluoride sf6 Safety Data Sheet Sds p4657Terkel GinaNo ratings yet