Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knowledge and Behavioral Verbs
Uploaded by
Emerson Mercado GalanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge and Behavioral Verbs
Uploaded by
Emerson Mercado GalanoCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge Categories: Behavioral Verbs:
Remembering identify, retrieve, recognize, duplicate, list,
The learner can recall information and retrieve relevant knowledge from memorize, repeat, describe, reproduce
long-term memory
Understanding interpret, exemplify, classify, summarize,
The learner can construct meaning from oral, written and graphic infer, compare, explain, paraphrase, discuss
messages
Skills Applying execute, implement, demonstrate,
The learner can use information to undertake a procedure in familiar dramatize, interpret, solve, use, illustrate,
situations or in a new way convert, discover
Analyzing differentiate, distinguish, compare, contrast,
The learner can distinguish between parts and determine how they organize, outline, attribute, deconstruct
relate to one another, and to the overall structure and purpose
Evaluating coordinate, measure, detect, defend, judge,
The learner can make judgments and justify decisions argue, debate, describe, critique, appraise,
evaluate
Creating generate, hypothesize, plan, design, develop,
The learner can put elements together to form a functional whole, produce, construct, formulate, assemble,
create a new product or point of view devise
Attitude Categories:
1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention
Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study,
use
2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and reacts to a particular
phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in
responding (motivation).
Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, perform, practice, present, read,
recite, report, select, tell, write
3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from simple acceptance to the more
complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these
values are expressed in the learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable.
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, initiate, invite, join, justify,
propose, read, report, select, share, study
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving conflicts between them, and
creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on comparing, relating, and synthesizing values.
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, explain, formulate, generalize, identify,
integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate, synthesize
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. The behavior is pervasive,
consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with
the student's general patterns of adjustment (personal, social, emotional).
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, practice, propose, qualify, question,
revise, serve, solve, verify
Values Categories:
1. Receiving Phenomena - Awareness, willingness to hear, selected attention
Behavioral Verbs: ask, choose, describe, erect, follow, give, hold, identify, locate, name, point to, reply, select, sit, Study,
use
2. Responding to Phenomena - Active participation on the part of the learners. Attends and reacts to a particular
phenomenon. Learning outcomes may emphasize compliance in responding, willingness to respond, or satisfaction in
responding (motivation).
Behavioral Verbs: aid, answer, assist, comply, conform, discuss, greet, help, label, perform, practice, present, read,
recite, report, select, tell, write
3. Valuing - Attaches to a particular object, phenomenon, or behavior. This ranges from simple acceptance to the more
complex state of commitment. Valuing is based on the internalization of a set of specified values, while clues to these
values are expressed in the learner's overt behavior and are often identifiable.
Behavioral Verbs: work, complete, demonstrate, differentiate, explain, follow, form, initiate, invite, join, justify,
propose, read, report, select, share, study
4. Organization - Organizes values into priorities by contrasting different values, resolving conflicts between them, and
creating a unique value system. The emphasis is on comparing, relating, and synthesizing values.
Behavioral Verbs: adhere, alter, arrange, combine, compare, complete, defend, explain, formulate, generalize, identify,
integrate, modify, order, organize, prepare, relate, synthesize
5. Internalizing values - (Characterization): Has a value system that controls their behavior. The behavior is pervasive,
consistent, predictable, and most importantly, characteristic of the learner. Instructional objectives are concerned with
the student's general patterns of adjustment (personal, social, emotional).
Behavioral Verbs: act, discriminate, display, influence, listen, modify, perform, practice, propose, qualify, question,
revise, serve, solve, verify
You might also like
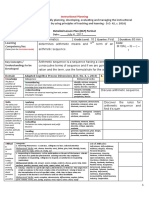
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- OC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyDocument4 pagesOC 13 Identifies Strategies Used by Each Speaker To Convey Hisher Ideas EffectivelyZeen Dee100% (1)
- IPlan DLP Format English-VersionDocument5 pagesIPlan DLP Format English-VersionDina ArcenalNo ratings yet
- IPlan DLP Format v.02Document4 pagesIPlan DLP Format v.02Julie Anne MacuseNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument3 pagesInstructional Planning Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatAntonio CaballeroNo ratings yet
- OC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeDocument4 pagesOC 11.1 Ascertains The Verbal and Nonverbal Cues That Each Speaker Uses To Achieve His Her PurposeZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- IplanDocument4 pagesIplanJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- 10.3.3 DLP RetuyaDocument4 pages10.3.3 DLP RetuyaGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- M11GM Ia 1Document5 pagesM11GM Ia 1Dan Albert Abes67% (3)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningPapellero Villamor GlendaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRendyNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument4 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- OC 12.1 Comprehends Various Kinds of Oral TextsDocument4 pagesOC 12.1 Comprehends Various Kinds of Oral TextsZeen Dee100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJesson AlbaranNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningAnonymous HJlXukJrNo ratings yet
- Nail Care Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesNail Care Lesson PlanMa. Crissa Aboyme100% (1)
- C1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3Document5 pagesC1 - Joey Jabonet-W4-Dlp1-3ludabelle19No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- CS - RS12 Id e 2Document8 pagesCS - RS12 Id e 2Josua GarciaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRemedios Enad CataoNo ratings yet
- M11GM IIc 1Document6 pagesM11GM IIc 1Hordan Jay SalleNo ratings yet
- OC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 11 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- DLP 51Document6 pagesDLP 51Maricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning for Exponential EquationsDocument7 pagesInstructional Planning for Exponential EquationsLionelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJennibeth Garcia Dela RitaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument7 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- DLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarDocument4 pagesDLP - Iplan Template From The Region - Sir ElnarRhona Liza CanobasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- C1 Name Template Sample W4 DLP1 3Document6 pagesC1 Name Template Sample W4 DLP1 3Luda Cababan SanesNo ratings yet
- Solving exponential equationsDocument7 pagesSolving exponential equationsJeger JbTattoo BaguioNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningdanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningRed Zye UbayNo ratings yet
- OC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechDocument4 pagesOC 12 The Learner Distinguishes The Types of SpeechZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- OC 21 Types of Communicative StrategiesDocument7 pagesOC 21 Types of Communicative StrategiesZeen Dee0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- 10.2.4 DLP GealonDocument4 pages10.2.4 DLP GealonGlad Norman LimoconNo ratings yet
- OC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesDocument4 pagesOC 10 Watches and Listens To Sample Oral Communication ActivitiesZeen Dee86% (7)
- Per Dev Week 2Document4 pagesPer Dev Week 2Andrey DyNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Principles and Techniques of Measuring Vital SignsDocument9 pagesDiscuss The Principles and Techniques of Measuring Vital SignsMarielle ContaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningEllorin RANo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJulia Maria LoviteNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: The Characteristics Quantitative ResearchDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: The Characteristics Quantitative ResearchHanelen DadaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningBlessila LopezNo ratings yet
- IPLan TemplateDocument5 pagesIPLan TemplateSigrid Therese CañeteNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 1Document7 pagesOral Comm 1Theresa B.No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science DLP 12Document4 pagesEarth & Life Science DLP 12Bowina KhoNo ratings yet
- DLP FBS 1Document5 pagesDLP FBS 1Christine Rose Villanueva VargasNo ratings yet
- Elucidate Concepts Through Definition, Explication and ClarificationDocument4 pagesElucidate Concepts Through Definition, Explication and ClarificationMa Lou100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Instructional PlanningJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning (iPlan) No. 1 Promotes Primary Education as a Human RightDocument11 pagesInstructional Planning (iPlan) No. 1 Promotes Primary Education as a Human RightFLOREVIL BASAYNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional Planningamy faith susonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningJane Kyu Jung100% (1)
- M11 GM-Ic-1Document5 pagesM11 GM-Ic-1Dan Albert AbesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningReynalyn HernandezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Introduction To 21 Century Literature From The Philippines To World NADocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Introduction To 21 Century Literature From The Philippines To World NAChariza PitogoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Various Models of CommunicationZeen DeeNo ratings yet
- SGC OathDocument1 pageSGC OathEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- CovidDocument1 pageCovidEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Calibungan High School Natural Hazards TestDocument2 pagesCalibungan High School Natural Hazards TestEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- SGC Functionality Assessment Tool Validity Form 2023.v1Document1 pageSGC Functionality Assessment Tool Validity Form 2023.v1Emerson Mercado Galano100% (1)
- Notice of MeetingDocument2 pagesNotice of MeetingEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Eabs CBN 2Document1 pageEabs CBN 2Emerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- UDHR Articles and Labor Rights in the PhilippinesDocument6 pagesUDHR Articles and Labor Rights in the PhilippinesEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Recognition For Guest of Honor and Speaker Template 1Document1 pageCertificate of Recognition For Guest of Honor and Speaker Template 1Emerson Mercado Galano100% (1)
- Calibungan High School Natural Hazards TestDocument2 pagesCalibungan High School Natural Hazards TestEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation LMS Eval Guide 2016-APACDocument59 pagesNext-Generation LMS Eval Guide 2016-APACEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Name: - Score: - Year and Section: - DateDocument2 pagesName: - Score: - Year and Section: - DateEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log in Earth and Life ScienceDocument1 pageDaily Lesson Log in Earth and Life ScienceEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Quarter 1, October 5 - 8, 2020 Class Adviser: Emerson M. GalanoDocument4 pagesWeek 1 - Quarter 1, October 5 - 8, 2020 Class Adviser: Emerson M. GalanoEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- DRRR PDFDocument1 pageDRRR PDFEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Permutation CombinationDocument11 pagesPermutation CombinationEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log in Earth and Life ScienceDocument1 pageDaily Lesson Log in Earth and Life ScienceEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- ENCLOSURE-2.-SDRRM-SELF-EVALUATION-FORM Calibungan HSDocument6 pagesENCLOSURE-2.-SDRRM-SELF-EVALUATION-FORM Calibungan HSEmerson Mercado Galano100% (1)
- PROSPECTUSDocument9 pagesPROSPECTUSEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Lost at Sea Survival Ranking GuideDocument1 pageLost at Sea Survival Ranking GuideEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Script For 2019 MRDocument7 pagesScript For 2019 MREmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Group The Galaxies PDFDocument14 pagesGroup The Galaxies PDFEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Module III Constellations Act 1 Charac of StarsDocument1 pageModule III Constellations Act 1 Charac of StarsEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Lost at Sea Traing GameDocument7 pagesLost at Sea Traing GamejikoljiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam DRRR SY 2018-2019Document6 pagesMidterm Exam DRRR SY 2018-2019Jhen Barnard85% (34)
- BOARDGAMEDocument1 pageBOARDGAMEEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- CAREER GUIDANCE PROGRAM EVALUATIONDocument2 pagesCAREER GUIDANCE PROGRAM EVALUATIONEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- MainDocument23 pagesMainEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- This Planet IsnDocument1 pageThis Planet IsnEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Parabola 10-5 RevDocument8 pagesParabola 10-5 RevEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- Parabola 10-5 RevDocument8 pagesParabola 10-5 RevEmerson Mercado GalanoNo ratings yet
- PDHS New DLL Format 2017Document1 pagePDHS New DLL Format 2017NIÑO E. BELANONo ratings yet
- Darden ResumesDocument87 pagesDarden Resumescyberdevil321No ratings yet
- SCRIPT For GraduationDocument3 pagesSCRIPT For GraduationMinajs PesitoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Vocational and Technical Education - I. OlaitariDocument22 pagesThe Role of Vocational and Technical Education - I. OlaitarioedhieNo ratings yet
- Department of Educational Studies Lewis University Sample Lesson Plan FormatDocument4 pagesDepartment of Educational Studies Lewis University Sample Lesson Plan Formatapi-340704942No ratings yet
- Bài tập mệnh đề quan hệDocument121 pagesBài tập mệnh đề quan hệNguyễn Xuân HoàngNo ratings yet
- Think Mathematics Table of Contents Grades 1 5Document62 pagesThink Mathematics Table of Contents Grades 1 5Toni Hartono50% (2)
- Manisha SinghDocument2 pagesManisha SinghkamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument253 pagesSyllabus PDFVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management in The SchoolDocument13 pagesLeadership and Management in The SchoolSYAHIDATUL IRMA BINTI MOHAMAD ROSLAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Implications For Teaching Literature: Lesson 2Document4 pagesPedagogical Implications For Teaching Literature: Lesson 2Berlyn D. AlmandaresNo ratings yet
- The Craft of StorytellingDocument15 pagesThe Craft of StorytellingJason Blurryeyes100% (1)
- Modern Art Movements Progress ReportDocument6 pagesModern Art Movements Progress ReportERNALYN GEM GEM G. RAFER-PANDINo ratings yet
- Eng8 WLP Q3 Week3Document3 pagesEng8 WLP Q3 Week3ANNABEL PALMARINNo ratings yet
- Pumpkin LessonDocument5 pagesPumpkin Lessonapi-284900448No ratings yet
- Functional TextDocument16 pagesFunctional TextDadi SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material in Mathematics Grade 7Document19 pagesStrategic Intervention Material in Mathematics Grade 7Jovenill Granton VIINo ratings yet
- Stats Proba PDFDocument15 pagesStats Proba PDFCathlyn AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Division Memorandum No. 100, S. 2017Document6 pagesDivision Memorandum No. 100, S. 2017Dee HeiNo ratings yet
- Cbiemapu 05Document10 pagesCbiemapu 05Nikita JainNo ratings yet
- Chronic Absenteeism Lit Review 2018 PDFDocument55 pagesChronic Absenteeism Lit Review 2018 PDFEunsang LeeNo ratings yet
- The Risk Based AuditDocument6 pagesThe Risk Based AuditHana AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Prelim Project in ResearchDocument20 pagesPrelim Project in ResearchJessa Mae GalanidaNo ratings yet
- UNMAC - Mine ActionDocument284 pagesUNMAC - Mine ActionFrancesco100% (1)
- Didactics of Literature AP - 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesDidactics of Literature AP - 2019 PDFAleixo Domingos CaetanoNo ratings yet
- Bomb-Making For Beginners':Inside An Al-Qaeda E-Learning CourseDocument8 pagesBomb-Making For Beginners':Inside An Al-Qaeda E-Learning CourseAleksandar GovnozovicNo ratings yet
- Biodata of S.Khuntia, Scientist - Dec 2012Document29 pagesBiodata of S.Khuntia, Scientist - Dec 2012Dr. SURENDRA KHUNTIANo ratings yet
- All Saints Catholic College Specialist in Humanities: Year 11 InformationDocument2 pagesAll Saints Catholic College Specialist in Humanities: Year 11 Informationjanrocks1No ratings yet
- Stephanie B. Balaga (My Report Lite001)Document15 pagesStephanie B. Balaga (My Report Lite001)Teph BalagaNo ratings yet