Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lect. 23 MOSFET Current Source and Active Load PDF
Uploaded by
dipaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lect. 23 MOSFET Current Source and Active Load PDF
Uploaded by
dipaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lect.
23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
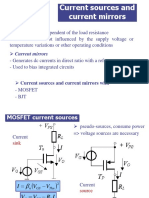
Various bias techniques for MOSFET circuits
How do we make
a constant current source
with MOSFETs?
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
Constant current source: 1 ' ⎛W ⎞
= kn ⎜ ⎟ (VGS − Vt )
2
I D1
2 ⎝ L ⎠1
VDD − VGS
I D1 = I REF =
R
Assuming Q1, Q2 have same properties (kn’),
1 ' ⎛W ⎞
kn ⎜ ⎟ (VGS − Vtn )
2
IO = I D 2 =
2 ⎝ L ⎠2
IO (W / L ) 2
=
Î Current
C t mirror
i
I REF (W / L )1
Limitation on Vo? VO ≥ VGS − Vt
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
Mismatches between IREF and IO
Due to channel-length modulation For two Q1 and Q2
IO = IREF only if VDS1= VDS2 Î V0=VGS
As VO increased, IO increases from IREF
VO − VGS
I O = I REF +
r0
Comparison with BJT current mirror?
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
VDD=3V, Q1 and Q2 are identical with 1 ' ⎛W ⎞
I D1 = I REF = kn ⎜ ⎟ (VGS − Vt )2
L= 1μm, W=100μm, Vt=0.7V, kn’=200μA/V2, 2 ⎝ L ⎠1
ro = 200kΩ
1
100 = × 200 × 10 × (VGS − Vt )2 ,
1. Determine R for IO=100μA. 2
2 What is the lowest value for VO?
2. (VGS − Vt ) = 0.316,
0 316 VGS = 1.016
1 016
3. How much IO changes when VO changes 1V?
VDD − VGS 3 − 1.016
R= = = 19.84kΩ
I REF 0.1mA
0 1mA
VO min = VGS − Vt = VOV = 0.316 V
ΔVO 1V
ΔI O = = = 5μ A
ro 2 200k Ω
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
(W / L ) 2
I 2 = I REF
( W / L )1
(W / L ) 3
I 3 = I REF
( W / L )1
I3 = I4
(W / L ) 5
I5 = I4
(W / L ) 4
Current-steering circuits: current source (Q5), current sink (Q2)
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
CS amplifier
f
Where is RD ?
Current source as a resistor Î Active load
(Remember Q2 has rO)
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
Large change in vO with vI change!
Î Large amplifier gain
Load-line analysis
Q1
Q2
v = VDD-vo
vo= VDD - v
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
Gain for CS amplifier with PMOS current mirror
-gm (rO1 || rO2)
PMOS current mirror provides
large “Drain” resistance (Active Load)
as well as bias current!
Î Good for IC!
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
Lect. 23: MOSFET Current Mirror and Active Load
VDD=3V, Vtn=|Vtp|=0.6V, kn’=200μA/V2, kp’=65μA/V2,
L=0 4μm W=4μm,
L=0.4μm, W=4μm ro1=200kΩ,
=200kΩ ro2,3 = 100kΩ,
100kΩ
IREF=100μA. 1. Aυ = − gm 1 ( ro1 || ro 2 )
' ⎛W ⎞ 4
1. What is the small-signal voltage gain, vO/vI? g m 1 = 2 k n ⎜ ⎟ I REF = 2 × 200 × × 100 = 0.63mA/V
⎝ L ⎠1 0.4
2 What is the maximum vO for which the above is valid?
2.
∴ Aυ = −0.63(mA/V) ⋅ (200 || 100)(kΩ ) = −42
1 ' ⎛W ⎞
( )
2 VSD ,3
2. For Q 3 , I REF = − Vtp +
2 p ⎜⎝ L ⎟⎠ 3 SG ,33
k V
ro
1 ⎛ 4 ⎞ VSG ,3
( )
2
100 = × 65 ⎜ ⎟ SG
V − 0.6 +
2 ⎝ 0.4 ⎠ 100 K
∴VSG ~ 1.12
1 12V
For vO ,max , VSD 2,min = VSG − | Vtp |= 1.12 − 0.6 = 0.52V
∴ vO ,max
max = VDD − VSD 22,min
min = 2.48V
Electronic Circuits 1 (09/2) Prof. Woo-Young Choi
You might also like
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits, Solutions (McGraw) - RAZAVIDocument329 pagesDesign of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits, Solutions (McGraw) - RAZAVImtechsurendra12379% (33)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- DADocument40 pagesDAkrishneel sharmaNo ratings yet
- TFE 731 Chap 74Document6 pagesTFE 731 Chap 74Egor85No ratings yet
- Transformer Fault Current CalculationDocument1 pageTransformer Fault Current CalculationNarasimha RaoNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- EE-215 Lecture 07, 08, 09 DiodeDocument41 pagesEE-215 Lecture 07, 08, 09 DiodeMazoon ButtNo ratings yet
- Mazda 3 6 MZR-CD2.2 Engine PDFDocument46 pagesMazda 3 6 MZR-CD2.2 Engine PDFjorge100% (3)
- Lect05 PDFDocument15 pagesLect05 PDFVan GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Passive and Active Current Mirrors Current MirrorsDocument68 pagesPassive and Active Passive and Active Current Mirrors Current MirrorsDeepanshu Midha5140No ratings yet
- Band GapDocument15 pagesBand GapMoin PashaNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Current Mirror PDFDocument27 pagesMOSFET Current Mirror PDFaliNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics II (Chapter 2)Document29 pagesApplied Electronics II (Chapter 2)Ermias Mesfin100% (2)
- 05 - Current Mirror 11.11.2020Document47 pages05 - Current Mirror 11.11.2020Ashraf YusofNo ratings yet
- Compare Current Sources for Analog CircuitsDocument16 pagesCompare Current Sources for Analog CircuitsVarun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Current Sources and Sinks: V V V V V V VDocument7 pagesCurrent Sources and Sinks: V V V V V V VSyed HyderNo ratings yet
- Lect 22 MOSFET Current Mirror and CS AmplifierDocument10 pagesLect 22 MOSFET Current Mirror and CS AmplifierLoret1086No ratings yet
- Derivation, Design and Simulation of The Single-Ended Primary-Inductor Converter (SEPIC)Document15 pagesDerivation, Design and Simulation of The Single-Ended Primary-Inductor Converter (SEPIC)camilaNo ratings yet
- ESC201T L21 Diode ModelDocument41 pagesESC201T L21 Diode ModelRachit MahajanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 An Not atDocument25 pagesLecture 22 An Not atapi-3721075No ratings yet
- 電子學一 第三章Document24 pages電子學一 第三章電機二 12黃聖祐No ratings yet
- 4 DiodesDocument42 pages4 DiodesPapp RichárdNo ratings yet
- Lecture EEE 447 Chap 5 DC DC ConvertersDocument41 pagesLecture EEE 447 Chap 5 DC DC ConvertersMd. Anisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 마이크로전자회로 ppt 파일Document17 pages마이크로전자회로 ppt 파일강민수No ratings yet
- Exercise Single Phase PWM BBDocument4 pagesExercise Single Phase PWM BBadrian valenciaNo ratings yet
- EE309 Notes 13Document4 pagesEE309 Notes 13Hassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Exam1Document6 pagesSolutions For Exam1TSway100% (1)
- Line commutated rectifiers for particle acceleratorsDocument51 pagesLine commutated rectifiers for particle acceleratorsAniket DasNo ratings yet
- مختبر_الالكترونيك_شبكات_&_معلوماتDocument16 pagesمختبر_الالكترونيك_شبكات_&_معلوماتaddfgh177No ratings yet
- Rectifiers CASWarrington2004Document51 pagesRectifiers CASWarrington2004Pradeepan PoothattaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Microelectronic Circuits, 7th EditionDocument11 pagesPages From Microelectronic Circuits, 7th Editionguduru babuNo ratings yet
- HITEC University Taxila: Power Electronics LabDocument9 pagesHITEC University Taxila: Power Electronics LabNisar Ahmed RanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Switches, Rectifiers and Generators: SP.764, Practical Electronics Dr. James A. BalesDocument5 pagesLecture 2: Switches, Rectifiers and Generators: SP.764, Practical Electronics Dr. James A. BalesFadhilaNo ratings yet
- 05 Current Source Mirror EngDocument12 pages05 Current Source Mirror EngNavanath DarwanteNo ratings yet
- MEL ZG621 VLSI DESIGN (Lect 5)Document32 pagesMEL ZG621 VLSI DESIGN (Lect 5)2023ht80200No ratings yet
- Diode Lecture MineDocument34 pagesDiode Lecture MineSaud AloufiNo ratings yet
- Objective:: Study of The Multistage (Cascaded) AmplifierDocument6 pagesObjective:: Study of The Multistage (Cascaded) Amplifierعلي حسنNo ratings yet
- Task 2 Beta MultiplierDocument10 pagesTask 2 Beta MultiplierMario PajaNo ratings yet
- Active Loads and IC MOS AmplifiersDocument41 pagesActive Loads and IC MOS AmplifiersKamlaNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh: Experiment 10 Lab ManualDocument4 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Experiment 10 Lab ManualAnamNo ratings yet
- EEE109 Midterm Exam II ReviewDocument5 pagesEEE109 Midterm Exam II ReviewkakagoNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifiers 2Document16 pagesDifferential Amplifiers 2Wadih El AwarNo ratings yet
- ch08 1Document44 pagesch08 1zmxncbv08090526No ratings yet
- EECE2412 Final Exam: With SolutionsDocument15 pagesEECE2412 Final Exam: With Solutionsአንድነት togetherNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument9 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab ManualRohan KatkamNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier Analysis and DesignDocument47 pagesDifferential Amplifier Analysis and DesignSwathi BellaryNo ratings yet
- Esc201: Introducton To Electronics: DiodesDocument35 pagesEsc201: Introducton To Electronics: Diodesash jayNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Fully Controlled Rectifier: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument22 pagesSingle Phase Fully Controlled Rectifier: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Ideal Diode Circuits AnalysisDocument15 pagesIdeal Diode Circuits AnalysisAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers CASWarrington2004Document51 pagesRectifiers CASWarrington2004Mohd ShanuNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Representations For Modelling of Power Electronics Structures (Examples of Hybrid 2L Models)Document12 pagesMathematical Representations For Modelling of Power Electronics Structures (Examples of Hybrid 2L Models)Cornel ArageaNo ratings yet
- Single-phase half-bridge inverter operational details and analysisDocument31 pagesSingle-phase half-bridge inverter operational details and analysistintuvrNo ratings yet
- Electronics design II amplifier calculationsDocument14 pagesElectronics design II amplifier calculationsbhanuNo ratings yet
- OC & SC Test On 1-Phase TransformerDocument5 pagesOC & SC Test On 1-Phase TransformerChaitanyavaddigalaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 10 - The Inductive DC-DC Converter: 1 Luiz Augusto Frazatto Fernandes 2 Yasmim de SouzaDocument3 pagesLab Report 10 - The Inductive DC-DC Converter: 1 Luiz Augusto Frazatto Fernandes 2 Yasmim de SouzaYasmim de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4Yanendra SahNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers CASWarrington2004Document51 pagesRectifiers CASWarrington2004hazem ab2009No ratings yet
- Electrical Computer EngineeringDocument49 pagesElectrical Computer EngineeringDƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHNo ratings yet
- L10 Single Phase Fully Controlled RectifierDocument26 pagesL10 Single Phase Fully Controlled Rectifierapi-1995170750% (2)
- CS Amplifier With Diode Connected Load 020303Document23 pagesCS Amplifier With Diode Connected Load 020303mayank_parasrampuriaNo ratings yet
- RFIC Exam Questions and Transistor EquationsDocument6 pagesRFIC Exam Questions and Transistor EquationsAyman Nayef Mahmoud Al AzzamNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document7 pagesLab 1dipaNo ratings yet
- Aim: To Study RANDTOOL and Plot Exponential and Normal Random Variable FunctionDocument7 pagesAim: To Study RANDTOOL and Plot Exponential and Normal Random Variable FunctiondipaNo ratings yet
- AIM:To Study DFITTOOL and EZSURF Random Variable Function. DfittoolDocument10 pagesAIM:To Study DFITTOOL and EZSURF Random Variable Function. DfittooldipaNo ratings yet
- Ap P A P: N I I N I N I N IDocument38 pagesAp P A P: N I I N I N I N ItusharNo ratings yet
- MatlabDocument127 pagesMatlabdipaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lab Manual Contents and ExperimentsDocument82 pagesVLSI Lab Manual Contents and Experimentssuvarna neetiNo ratings yet
- Disttool Distribution Functions:: The Binomial and Beta DistributionsDocument32 pagesDisttool Distribution Functions:: The Binomial and Beta DistributionsdipaNo ratings yet
- SsaDocument6 pagesSsadipaNo ratings yet
- Solving Examples Using Symbolic MathDocument13 pagesSolving Examples Using Symbolic MathdipaNo ratings yet
- JFET Voltage Divider Biasing ExperimentDocument3 pagesJFET Voltage Divider Biasing Experimentdipa0% (1)
- Statistical Signal Analysis Using MatlabDocument65 pagesStatistical Signal Analysis Using MatlabdipaNo ratings yet
- Verilog HDL - Samir PalnitkarDocument403 pagesVerilog HDL - Samir PalnitkarSameer RaichurNo ratings yet
- Datasheet DS1216 DALLASDocument13 pagesDatasheet DS1216 DALLASRICHIHOTS2No ratings yet
- Ina 02184Document6 pagesIna 02184Julio SalazarNo ratings yet
- Measurements LABDocument70 pagesMeasurements LABMustafa MhmoodNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument279 pagesService ManualSarfraz QureshiNo ratings yet
- Emx1 / Umx1N / Imx1: General Purpose Transistor (Dual Transistors)Document9 pagesEmx1 / Umx1N / Imx1: General Purpose Transistor (Dual Transistors)Juan CarlosNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Panel SunPower MAX3 400 390 370Document2 pagesFicha Tecnica Panel SunPower MAX3 400 390 370Juan Perez ArizavalNo ratings yet
- Absolute Standards Inorganic 2012Document80 pagesAbsolute Standards Inorganic 2012AriCalidadNo ratings yet
- Isc N-Channel MOSFET Transistor 2SK638: FeaturesDocument2 pagesIsc N-Channel MOSFET Transistor 2SK638: FeaturesWall PereiraNo ratings yet
- Silicon PNP Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationDocument3 pagesSilicon PNP Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationVitorio LogoNo ratings yet
- STK0765BF: Switching Regulator Applications FeaturesDocument8 pagesSTK0765BF: Switching Regulator Applications Featuresmaksyd2No ratings yet
- Communication Engineering Lab ManualDocument53 pagesCommunication Engineering Lab Manualtharunkumarreddy100% (1)
- X1 / X2 / X3 / X4: Service ManualDocument24 pagesX1 / X2 / X3 / X4: Service ManualOscar Javier DominguezNo ratings yet
- Manual Variador DeltaDocument173 pagesManual Variador DeltaDavid CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Manual Soldering and De-Soldering For Spice Package-VerA PDFDocument6 pagesManual Soldering and De-Soldering For Spice Package-VerA PDFVivek SuranaNo ratings yet
- Faculty Details Proforma For DU Web-Site: Prof./Dr./Mr./Ms./ MrsDocument12 pagesFaculty Details Proforma For DU Web-Site: Prof./Dr./Mr./Ms./ MrsM SRINIVAS RAONo ratings yet
- Solid State Phy-RPDocument39 pagesSolid State Phy-RPAbhijan Carter BiswasNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Home AutomationDocument25 pagesGSM Based Home AutomationVenuVedantNo ratings yet
- MVLC - FolletoDocument2 pagesMVLC - FolletoHoracio BerniNo ratings yet
- Ordering Information: PCB Power Relay - G5NB-EDocument4 pagesOrdering Information: PCB Power Relay - G5NB-ELean Choon SweeNo ratings yet
- LT1083 Power Supply Regulated 7Document3 pagesLT1083 Power Supply Regulated 7Collie de KloeNo ratings yet
- PV+ PV-S COM Input Side Output Side: Voltage Detection CircuitDocument1 pagePV+ PV-S COM Input Side Output Side: Voltage Detection CircuitRamiro BraccoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Logic Gate Devices Characteristics (DBV30023)Document68 pagesUnit 2 - Logic Gate Devices Characteristics (DBV30023)Abd Kadir JailaniNo ratings yet
- Insulated Rail Joint Tester SICO 2046Document18 pagesInsulated Rail Joint Tester SICO 2046mpuskaric1No ratings yet
- Tga4516 TSDocument10 pagesTga4516 TScurzNo ratings yet
- ElectrogoniometerDocument4 pagesElectrogoniometermihaela_moldova9128No ratings yet
- PHY 221 Long Quiz #3 - MagnetismDocument1 pagePHY 221 Long Quiz #3 - MagnetismCatherine Shaina O. PasionNo ratings yet
- Ncer Unit1 WTRMRK PDFDocument5 pagesNcer Unit1 WTRMRK PDFshylaja9No ratings yet