Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic Outline: Plasma
Uploaded by
Christian AlacarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic Outline: Plasma
Uploaded by
Christian AlacarCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY 7: BLOOD HISTOLOGY LABORATORY
092319
PLEASE ASK PERMISSION BEFORE REPRODUCING A COPY/TAKING A PHOTO
TOPIC OUTLINE
Plasma
Introduction
Differentiation and Maturation: Overview - Aqueous (92% H2O) solutions, pH 7.4.
Composition: Whole Blood Composition usually an indicator of the mean of
o Plasma the extracellular fluids in plasma.
o Erythrocyte - Supernatant light coloured (pale yellow to
Blood smear preparation yellow) produced after centrifugation.
Peripheral blood smear - 7% (by weight) proteins – Albumin, Globulin,
Leukocytes Fibrinogen, Regulatory proteins.
o Neutrophils - 1% (by weight) dissolved components – inorganic
o Eosinophils ions (elcetrolytes, eg., Na+, K+, Cl-, etc.),
o Basophils nutrients, respiratory gases, metabolic products.
o Lymphocyte
o Monocyte
o Thrombocytes
Introduction
Blood is a specialised CT consists of formed elements
(cells) and fluid extracellular material— plasma.
General functions:
1. Distribution of nutrients
2. Regulation of body temperature
3. Maintenance of acid-based and osmotic
balance
4. Carries and transports O2, Co2, metabolites,
hormones, etc.
5. Defense – leukocytes
Differentiation and Maturation: Overview
Buffy Coat
- Thin layer of leukocytes and platelets in between
of an anti-coagulated WB-centrifuged sample
(ie., EDTA tube)
Erythrocyte
- Constitutes for 44% of whole blood (WB).
- Referred to as “hematocrit” in an anti-
Composition: Whole Blood coagulated WB-centrifuged sample (ie., EDTA-
coated capillary tube).
General characteristics:
Lacks nucleus and organelles; with Hgb as the
main component.
Carry out O2 and transport CO2 via its
specialized membrane; survives in the circulation
for ~120d.
Shape: biconcave disc – facilitates O2-CO2
transport function via its surface are: volume ratio
Deformity (flexibility) – allows passage to small
vessels in the microvasculature while maintaining
a constant surface area: volume ratio
COLLATED BY ALACAR, CHRISTIAN
MIDTERM
PLEASE ASK PERMISSION BEFORE REPRODUCING A COPY/TAKING A PHOTO
ACTIVITY 7: BLOOD HISTOLOGY LABORATORY
092319
PLEASE ASK PERMISSION BEFORE REPRODUCING A COPY/TAKING A PHOTO
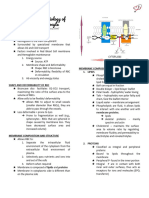
MEMBRANE UNTRASTRUCTURE - In an “RBC ATP-depletion state” , Ca++ and Na+
accumulate intracellularly, K+ and H2O are lost –
General composition: dehydrated rigid cell, subsequently sequestrated
Semipermeable lipid layer supported by a by the spleen (decrease RBC survival)
meshwork of protein
Compose of 40% lipids and 52% protein, 8% Blood Smear Preparation: Overview
carbohydrate.
Non chemical composition, structural
arrangement, and molecular interactions- crucial
to the normal length of RBC survival in the
circulation of 120 days
RBC Membrane components
Phospholipid- main component
o External layer rich in glycolipids and
choline phospholipids
o Cytoplasmic (internal) rich in amino
phospholipids.
Proteins:
o Integral:
GP-A, GP-B, GP-C, & anion-
exchange-channel protein (band
3)
o Peripheral
Spectrin, Actin (band 5), Ankyrin
(band 2.1), Band 4.1 and 4.2, Band 6,
& Adducin
PERMEABILITY
General characteristics and morphology:
Permeability
- This property together with “active RBC cation
transport” prevent “colloid hemolysis” & “control
the volume of the RBC”. Leukocytes
- RBC membrane is freely permeable to H2O, Cl- &
HCO3- and can transverse in <1 second.
- Na+ and K+ are relatively impermeable – control Classification:
H2O volume & maintains homeostasis via cellular
cationic pumps & requires ATP. Granulocytes
- Erythrocyte intracellular: extracellular (EI:E) ration - Characterize by abundant cytoplasmic granules
o EI:E – Na+1:12 such as azurophilic granules (lysosomes), specific
o EI:E – K+ 25:1 granules that bind neutral, basic or acidic stains.
- Ca++ , is also actively pumped from RBC interior - Polymorphic nuclei (multi-lobes)
via energy dependent Ca-ATPase pumps. - Neutrophils (segmenters), eosinophils, basophils)
- Calmodulin – cytoplasmic Ca-binding protein, - Golgi complexes and rough ER are poorly
controls the activity to prevent excessive developed and few mitochondria- glycolysis as
intracellular Ca++ buildup – rigidity. energy source.
- Most undergo apoptosis in the CT
COLLATED BY ALACAR, CHRISTIAN
MIDTERM
PLEASE ASK PERMISSION BEFORE REPRODUCING A COPY/TAKING A PHOTO
ACTIVITY 7: BLOOD HISTOLOGY LABORATORY
092319
PLEASE ASK PERMISSION BEFORE REPRODUCING A COPY/TAKING A PHOTO
Agranulocytes
- Lack specific granules, but do not contains
azurophilic granules.
- Characterise by spherical or intended nucleus
but not lobulated.
- Lymphocytes and monocytes
COLLATED BY ALACAR, CHRISTIAN
MIDTERM
PLEASE ASK PERMISSION BEFORE REPRODUCING A COPY/TAKING A PHOTO
You might also like
- Physio Blood TransDocument7 pagesPhysio Blood TransRoderick PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Cellular PhysiologyDocument32 pagesCellular Physiologyانس ابوهيبة0% (1)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (2)
- Platelet Count ManualDocument2 pagesPlatelet Count ManualAli Ahmad Khameini100% (1)
- Hema 2 - Prelim Topic 1-Intro To HemostasisDocument4 pagesHema 2 - Prelim Topic 1-Intro To HemostasisLowenstein JenzenNo ratings yet
- Hematology ReviewerDocument12 pagesHematology ReviewerPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCM112 MS 1 Week 1Document11 pagesNCM112 MS 1 Week 1Lerry Claire LimosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Histology of BloodDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Histology of BloodRazmine RicardoNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument38 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Chapter Blood: RBC Platelet HemostasisDocument89 pagesChapter Blood: RBC Platelet Hemostasisapi-19916399100% (1)
- Practice Exam - Qats PDFDocument53 pagesPractice Exam - Qats PDFsdfbgshfgNo ratings yet
- ALK-positive Lung Cancer: A Moving TargetDocument16 pagesALK-positive Lung Cancer: A Moving TargetcerbulcarpatinNo ratings yet
- Membrane Enzyme SystemsDocument2 pagesMembrane Enzyme SystemsAngelaHernandezNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Cardiovascular SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- PDF Blood Lympha 2 PDFDocument12 pagesPDF Blood Lympha 2 PDFArianne KimNo ratings yet
- PDF Blood LymphaDocument12 pagesPDF Blood LymphaArianne KimNo ratings yet
- Anhydrase, An Enzyme That Catalyzes TheDocument15 pagesAnhydrase, An Enzyme That Catalyzes TheJohnny eawNo ratings yet
- PDF Blood LymphaDocument13 pagesPDF Blood LymphaGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- The Living CellDocument3 pagesThe Living CellJanjan GarcesNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument6 pagesBloodCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Cell MembraneThea MillanesNo ratings yet
- Background Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesBackground Fluids and ElectrolytesHannah Leigh CastilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-B5Document28 pagesUnit 1-B5Jan Marsha Marie DomiquelNo ratings yet
- Anph Cells and TissuesDocument6 pagesAnph Cells and Tissues屋鈴No ratings yet
- Topic 3Document12 pagesTopic 3Ria AccadNo ratings yet
- Basic Dialysis Theory SweenyDocument28 pagesBasic Dialysis Theory SweenyAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument7 pagesCell Transportako parin itoNo ratings yet
- Hematology: AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesHematology: AbbreviationsReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesBlood TransfusionDocument6 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesBlood TransfusionMaria Erica Jan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument25 pagesCell MembranerajaijahNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument7 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesKarren FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 53 and 54 - RBCS and WBCS RatxamgDocument8 pagesChapter 53 and 54 - RBCS and WBCS Ratxamgt4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- 1 Parcial Ingles CientificoDocument7 pages1 Parcial Ingles Cientificobelemleyva03No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes NCEDocument8 pagesFluid and Electrolytes NCENevea CariñoNo ratings yet
- The Body Fluid Compartments & HomeostasisDocument7 pagesThe Body Fluid Compartments & HomeostasisEstellaNo ratings yet
- Mohammedali Sajun Sem IIDocument48 pagesMohammedali Sajun Sem IIMallika JollyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Cell Structures and Their Functions CellDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 3: Cell Structures and Their Functions CellCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Prelecture Questions 2Document7 pagesPrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNo ratings yet
- The Hematology SectionDocument4 pagesThe Hematology SectionVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - : Gateway To The Cell Gateway To The CellDocument60 pagesThe Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - : Gateway To The Cell Gateway To The CellJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Physiology A - Blood Physiology: RBC and Blood Typing: School of MedicineDocument3 pagesPhysiology A - Blood Physiology: RBC and Blood Typing: School of MedicineGabrielle SerranoNo ratings yet
- M2F Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesM2F Cardiovascular SystemMeteor 858No ratings yet
- Structural Components of The Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesStructural Components of The Cell MembraneYumiNo ratings yet
- Hema Lec #6 (1 - 2) RBC StructureDocument3 pagesHema Lec #6 (1 - 2) RBC StructurenadeslemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2, Plasma MembraneDocument51 pagesTutorial 2, Plasma MembranesureshbabubnysNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Cells & Tissues: Lab Goals and GuidelinesDocument14 pagesLab 2: Cells & Tissues: Lab Goals and GuidelinesAmy BalicagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Hema OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 8 Hema OutlinestaezyeNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its ComponentsDocument8 pagesBlood and Its ComponentsMyat NyanNo ratings yet
- 02 CB Membrane 2019Document34 pages02 CB Membrane 2019Мөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document3 pagesWeek 3naomimarielleNo ratings yet
- The Cell DR - Hegazy: Type The Document TitleDocument25 pagesThe Cell DR - Hegazy: Type The Document Titlemaha mohammdNo ratings yet
- Cellular Organization NotesDocument6 pagesCellular Organization NotesGrayson JamesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument127 pagesCardiovascular Systembreanna coyneNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell and Electrophysiology Part 1 (Barbon) PDFDocument3 pages1.1 Cell and Electrophysiology Part 1 (Barbon) PDFArman Carl DulayNo ratings yet
- ImmunohematologyDocument26 pagesImmunohematologyHanna MaraeNo ratings yet
- Biom1070 L5+6 2022Document45 pagesBiom1070 L5+6 2022Kevin ZhangNo ratings yet
- Physio EssenceDocument602 pagesPhysio EssencePhonogaming XNo ratings yet
- PHY LE 2 Finals ReviewerDocument22 pagesPHY LE 2 Finals Reviewerroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument1 pageBloodmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Cells AnatomyDocument16 pagesCells AnatomyHoneylaine MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Tonsilitis Kronis Dengan Eksaserbasi AkutDocument30 pagesCase Report: Tonsilitis Kronis Dengan Eksaserbasi AkutRara SudibyoNo ratings yet
- New IG SubclassDocument13 pagesNew IG SubclassBrîndușa PetruțescuNo ratings yet
- MDS - Basic Science Question PaperDocument11 pagesMDS - Basic Science Question PaperPorkodi Sudha100% (1)
- 38054 台北市聯合醫院抗生素商品名對照表 PDFDocument99 pages38054 台北市聯合醫院抗生素商品名對照表 PDFka timNo ratings yet
- Mid Module 3rd Year MBBSDocument8 pagesMid Module 3rd Year MBBSShahzaib Ullah ChatthaNo ratings yet
- Pathogen Frequencies (CFAD Ch. 17) - Zapper Wiki - FandomDocument14 pagesPathogen Frequencies (CFAD Ch. 17) - Zapper Wiki - FandomluisNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of The NewbornDocument1 pageHemolytic Disease of The NewbornMASIINo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Bio Class XIIDocument3 pagesLESSON PLAN Bio Class XIISunita Hingar100% (2)
- Basic Concepts of EpigeneticsDocument10 pagesBasic Concepts of EpigeneticsRaju MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ivy Jean MartinezDocument11 pagesIvy Jean MartinezmarjmarjNo ratings yet
- RBC AnomaliesDocument5 pagesRBC AnomaliesThe16LoverrNo ratings yet
- Analysis Prediction and Evaluation of CO PDFDocument6 pagesAnalysis Prediction and Evaluation of CO PDFSurfer LeoNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer Teniques in PlantDocument21 pagesGene Transfer Teniques in PlantRakesh GedalaNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatics in Association With Sex HormonesDocument76 pagesThe Lymphatics in Association With Sex HormonesBryan ZeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Genetic DiversityDocument6 pagesChapter 3: Genetic DiversityNur Bahiyah Binti Abdul Wahab IPGKTINo ratings yet
- Ctni Rapid Quantitative Test: Limitations of ProcedureDocument2 pagesCtni Rapid Quantitative Test: Limitations of ProcedureTrần Thanh Viện100% (1)
- STS Midterms ReviewerDocument19 pagesSTS Midterms ReviewerJaela Rebekah TotañesNo ratings yet
- Enterocolitis NecrosanteDocument21 pagesEnterocolitis NecrosantedenisNo ratings yet
- ChleraDocument26 pagesChleraadelekeyusufNo ratings yet
- Shigella MCQDocument7 pagesShigella MCQSonia ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Entrelazamiento (Amir Aczel)Document8 pagesEntrelazamiento (Amir Aczel)Memento MoriNo ratings yet
- June 2017 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel Biology (B) AS-levelDocument28 pagesJune 2017 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel Biology (B) AS-levelbgtes123No ratings yet
- Antibody StructureDocument9 pagesAntibody StructureNikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- M6a Rna MethylationDocument14 pagesM6a Rna Methylation畏No ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisJhaziel BermejoNo ratings yet
- KP White Blood Cell DisordersDocument15 pagesKP White Blood Cell DisorderssaskiakonitaNo ratings yet
- I. IDENTIFICATION: Write Your Answers On The Space Provided Before Each NumberDocument1 pageI. IDENTIFICATION: Write Your Answers On The Space Provided Before Each NumberKristela Mae ColomaNo ratings yet