Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood
Uploaded by
mehal guptaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood
Uploaded by
mehal guptaCopyright:
Available Formats
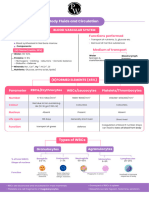
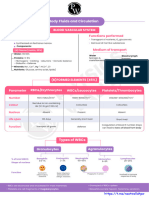
1. INTERSTITIAL FLUID ECF 5.
6.
DIGESTIVE FLUID
URINARY TRACT FLUID
2. CSF
7. SYNOVIAL FLUID
3.
4.
INTRAOCCULAR FLUID
BLOOD PLASMA BLOOD 30 - 35% of ECF 8. SEROUS FLUID
1. Mobile connective tissue • 70 Kg body weight has 5.5 Lts of blood. 9. LYMPH PLASMA
2. River of life • Slight alkaline (pH 7.4)
FLUID - Plasma 3. Softest tissue of the body • pH in artery > vein CELLS - Formed elements
Pale yellow, clear 55% of Blood 45% of Blood
translucent
Blood Corpuscles
Composition Composition
A. Water - 90 - 92%
A. Erythrocytes (RBC) B. Leucocytes (WBC) C. Thrombocytes (Platelets)
B. Solids - 8%
1. Anti-coagulant: Heparin - conjugated polysaccharide Heading RBC WBC Platelets
Counts 4.5 million/mm3 in F 6000-8000/mm3 1,50,000 -
- prevent coagulation of blood inside vessels 3,50,000/mm3
5 million/mm3 in M WBC: RBC:: 1:600
2. Blood clotting factors: present in plasma in inactive ↑Counts Erythrocytosis Leucocytosis Thrombocytosis
form. Plasma - Clotting Factors = SERUM* ↓ Counts Erythrocytopenia Leucopenia Thrombocytopenia
3. Compounds for self-defense: Abnormal↑ Polycythemia Leukemia (Malignancy)
Formation Stimulus →↑EPO from Grnulocytes & Monocytes - Formed from
a. Immunoglobulins (Igs) - act as antibodies Anti-bacterial
kidney cells → ↑EPO formed in bone marrow, megakaryocytes (very
b. Lysozyme - a polysaccharide Anti viral hormone in blood → Lymphocytes - Lymph Nodes, large cells of the bone
c. Properdin - a large protein Destroys toxins stimulates bone marrow spleen, thymus, tonsils, bone marrow)
4. Discharging / Excretory substances: → ↑production of RBCЖ marrow, Peyer’s patches [THROMBOPOIESIS]
[ERYTHROPOIESIS] [LEUCOCYTOSIS / LEUCOPOIESIS]
Urea, Uric acid, Creatin, Cratinine etc.
Size 7-8𝜇𝑚 diameter, 1-2 𝜇𝑚 12-20𝜇𝑚 in diameter 2-3𝜇𝑚 in diameter
5. Enzymes, Vitamins & hormones: thick near rim
6. Minerals: Na+, Ca++, Mg++, HCO3-, Cl- Shape Biconcave circular - gas Round or irregular, can Rounded or oval disc
exchange advantage b/c it change shape like amoeba -
7. Nutrients: Glucose, AA, Lipids has more SA than sphere. amoeboid movement -
8. Proteins: (6-8% of plasma) - Enucleated - in all adult squeeze out of the capillaries
mammals into tissue - diapedesis
a. Albumin - for osmotic balance (Oncotic pressure)
Structure Do not have cell organelles It has Cell membrane, Flat and non-
b. Globulin - for defense mechanism & nucleus, thus Cytoplasm & Nucleus nucleated fragments
c. Fibrinogen - for blood clotting • Instead of sphere it a. Agranulocyte - L / M of cell; bits of
C. Dissolved gases: 1- 2%: O2, CO2, N2 become biconcave → b. Granulocyte - E / B / N protoplasm bound by
more SA → enables to a membrane with
have ↑Hb in cytoplasm. few organelles &
*खुरंट हटने के बाद जो पानी जैसा पदार्थ ननकलता है नजसमे क्लॉनटं ग फैक्टसथ नहीं होते
• Less O2 demand. secretary basophilic
Anemia - ↓ in Hb due to less iron reserves
• Anaerobic respi in RBC granules in centreǂ
Erythrocytosis: Exercise, High altitude - to meet ↑ demand of O2.
Haemoglobin = Heme + Globin
EPO = Erythropoietin
Ж Life span 120 days Granulocytes - 4-5 hr in blood 7 days (1 week)
Site of RBC production: Early few weeks embryonic - yolk sac;
circulation then 4-5 days in
Late embryonic - liver & Spleen & Birth onward - bone marrow
ǂGp of basophilic granules in the centre give appear of a nucleus tissue; M - 10-20 hrs; L : few
days/months/years as body’s
need.
You might also like
- MLS305 Hema Lab PrelimsDocument11 pagesMLS305 Hema Lab PrelimsEvanka BaguistanNo ratings yet
- DR Otodo BloodDocument19 pagesDR Otodo BloodOluwapelumi DimejiNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument197 pagesBloodNimesh Sharma100% (1)
- Body Fluids N CirculationDocument74 pagesBody Fluids N CirculationChinmaya SNo ratings yet
- 1.07 - The BloodDocument5 pages1.07 - The Blood13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument4 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationINTERESTING RECOVERSNo ratings yet
- Mtle - Hema 1Document50 pagesMtle - Hema 1Leogene Earl FranciaNo ratings yet
- Hema Lec Cover2coverDocument61 pagesHema Lec Cover2coverPrincheska TallaNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument26 pagesHematologyScolaNo ratings yet
- Hematology: AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesHematology: AbbreviationsReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- Selflearning Kit Blood and Its Components2019Document18 pagesSelflearning Kit Blood and Its Components2019Jeff Bryan Arellano HimorNo ratings yet
- BLOOD TransesDocument7 pagesBLOOD TransesBianca Paulyn CastilloNo ratings yet
- Physiology A - Blood Physiology: RBC and Blood Typing: School of MedicineDocument3 pagesPhysiology A - Blood Physiology: RBC and Blood Typing: School of MedicineGabrielle SerranoNo ratings yet
- Human Blood s2Document46 pagesHuman Blood s2Nita SaragihNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Histology of BloodDocument4 pagesLecture 7 Histology of BloodRazmine RicardoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System TransesDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Hematology CHapter 1Document3 pagesHematology CHapter 1Rheila DuyaNo ratings yet
- Blood CompositionDocument17 pagesBlood Compositionkaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid and CirculationDocument5 pagesBody Fluid and Circulationanshuroy524No ratings yet
- Hema 11-ReviewerDocument59 pagesHema 11-ReviewerMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Hematology System Lec. 1Document17 pagesHematology System Lec. 1xqfs2cd44sNo ratings yet
- Circulatory 1.1Document26 pagesCirculatory 1.1Ashianna SmithNo ratings yet
- Hbioana Le3Document3 pagesHbioana Le3bitangyarahNo ratings yet
- Midterm Topics Hema 1 LecDocument37 pagesMidterm Topics Hema 1 Lec4jzbxz64kqNo ratings yet
- Circulatory PathwaysDocument5 pagesCirculatory Pathwaysaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Document5 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024aashish.tskauthNo ratings yet
- Bloodhana 2019 PDFDocument41 pagesBloodhana 2019 PDFAngelica Parreñas BayonaNo ratings yet
- PDF Blood LymphaDocument12 pagesPDF Blood LymphaArianne KimNo ratings yet
- PDF Blood Lympha 2 PDFDocument12 pagesPDF Blood Lympha 2 PDFArianne KimNo ratings yet
- 642e7dcceb519600186072f6 - ## - Body Fluids and Circulations Mind Maps 04-FN11M (Only PDFDocument5 pages642e7dcceb519600186072f6 - ## - Body Fluids and Circulations Mind Maps 04-FN11M (Only PDFagrimkarmakar500No ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation: BloodDocument2 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation: Bloodswayam bhosaleNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Chpter 10Document8 pagesBiology Notes Chpter 10Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Chpter 10Document8 pagesBiology Notes Chpter 10Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- ErythropoiesisDocument51 pagesErythropoiesisKevin Leo100% (1)
- 1 Parcial Ingles CientificoDocument7 pages1 Parcial Ingles Cientificobelemleyva03No ratings yet
- BloodDocument70 pagesBloodbookaccountNo ratings yet
- Cardio WhatsoeverDocument12 pagesCardio WhatsoeverFernando DisuNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics: C. PlateletsDocument6 pagesPhysical Characteristics: C. PlateletsGwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- 4 Blood Physiology (FINAL)Document8 pages4 Blood Physiology (FINAL)kath-kathNo ratings yet
- Bloodphysiology LECTUREDocument58 pagesBloodphysiology LECTUREShfici AdanNo ratings yet
- VSP-UG-1 (Blood)Document70 pagesVSP-UG-1 (Blood)Samartha SamdarshiNo ratings yet
- Blood 2Document4 pagesBlood 2Jhes D.No ratings yet
- Chapter Blood: RBC Platelet HemostasisDocument89 pagesChapter Blood: RBC Platelet Hemostasisapi-19916399100% (1)
- HematologyDocument22 pagesHematologyytmdrayushdubeyNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reticulocyte Release Rate of Removal of Spent Rbcs by Spleen & LiverDocument4 pagesRate of Reticulocyte Release Rate of Removal of Spent Rbcs by Spleen & Liverraiansuyu2495gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Z-05 Digest Part EVDocument49 pagesZ-05 Digest Part EVXaveer AzadNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology LectureDocument174 pagesBlood Physiology Lectureemmanuelakinola2006No ratings yet
- BCH102 Unit - III: Physiology Topic: BloodDocument18 pagesBCH102 Unit - III: Physiology Topic: Blooddivya vajpayeeNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocument10 pagesBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Erythropoiesis 150731072608 Lva1 App6891Document51 pagesErythropoiesis 150731072608 Lva1 App6891shinigami07700254100% (1)
- Haematology PhysiologyDocument15 pagesHaematology PhysiologyOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Presentation Hematology Analyzer SAM MedanDocument135 pagesPresentation Hematology Analyzer SAM MedanJeffry NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument20 pagesCirculatory SystemsuryanshNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument3 pagesTransport in Humans『bhargavi』No ratings yet
- Histo by DR - Ahmed Zahra (Blood)Document13 pagesHisto by DR - Ahmed Zahra (Blood)Abedelaal MohamedNo ratings yet
- (PHY) 2.01 Introduction To Hematology and Red Blood Cells-Bareng FINALDocument8 pages(PHY) 2.01 Introduction To Hematology and Red Blood Cells-Bareng FINALJerylle Lynch Gallinero LazaNo ratings yet
- Booklet 2 Donador de SangreDocument16 pagesBooklet 2 Donador de SangreKatherine QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Comprehensive-OverviewDocument71 pagesCardiovascular System - Comprehensive-OverviewMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- BLOODDocument175 pagesBLOODJohn JimsNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument11 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationDwi rahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Test AnalysisDocument14 pagesLab Test Analysismehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Icu ProtocolDocument4 pagesIcu Protocolmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- 303EnvironmentalEducation& DisastermanagementDocument217 pages303EnvironmentalEducation& DisastermanagementdihuNo ratings yet
- AMU Board Exam Q Papers Class 11Document19 pagesAMU Board Exam Q Papers Class 11mehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Environmental ChemistryDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Chemistrymehal guptaNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY Class 11Document25 pagesENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY Class 11mehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Phe Assignment Anatomy Physology of Human and KinesiologyDocument26 pagesPhe Assignment Anatomy Physology of Human and Kinesiologymehal guptaNo ratings yet
- List of Important Medicinal Plants - Uses of Medicinal Plant - Buy Medicinal Plant - OFDCDocument4 pagesList of Important Medicinal Plants - Uses of Medicinal Plant - Buy Medicinal Plant - OFDCmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Enthalpies For Different Types of Reactions - Enthalpy, Videos, Examples FinalDocument3 pagesEnthalpies For Different Types of Reactions - Enthalpy, Videos, Examples Finalmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument55 pagesHydrogenmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Solomons' Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesSolomons' Organic Chemistrymehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Supw Project Medicinal PlantsDocument7 pagesSupw Project Medicinal Plantsmehal gupta75% (4)
- Tabular FormDocument3 pagesTabular Formmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- 1 DevelopmentDocument14 pages1 Developmentmehal guptaNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Mohamad H Qari, MD, FRCPADocument49 pagesHematology: Mohamad H Qari, MD, FRCPASantoz ArieNo ratings yet
- Tendon HealingDocument46 pagesTendon Healingirsan100% (2)
- Muscular System - Lesson 19Document17 pagesMuscular System - Lesson 19Gamer0092No ratings yet
- Bid Number Work Description Open DateDocument2 pagesBid Number Work Description Open DateTender 247No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Clinical Hematology and Fundamentals of Hemostasis 5th Edition HarmeningDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Clinical Hematology and Fundamentals of Hemostasis 5th Edition HarmeningWilbur Penny100% (29)
- Packed Cell Volume (Hematocrit) : PlasmDocument3 pagesPacked Cell Volume (Hematocrit) : PlasmS ANo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusions in Dogs and Cats 2. Practicalities of Blood Collection and AdministrationDocument7 pagesBlood Transfusions in Dogs and Cats 2. Practicalities of Blood Collection and AdministrationSamantha Orozco PinedaNo ratings yet
- 1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalDocument27 pages1 Sistem MuskuloskeletalAshar AbilowoNo ratings yet
- Jeevan Daan - Community ServiceDocument4 pagesJeevan Daan - Community ServiceDr. Khusboo MuniNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders: Morey A. Blinder, M.DDocument49 pagesBleeding Disorders: Morey A. Blinder, M.DpallavberiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Test Study GuideDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System Test Study GuideEstherThompsonNo ratings yet
- Karring 1975Document12 pagesKarring 1975Juan Pablo FloresNo ratings yet
- Hematology UQU 2022Document94 pagesHematology UQU 2022Elyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- RBC PathologyDocument7 pagesRBC PathologyKent CruzNo ratings yet
- APEA Hematology 2020 PDFDocument14 pagesAPEA Hematology 2020 PDFAdams ZarawuNo ratings yet
- Articulations and Body Movements: ExerciseDocument4 pagesArticulations and Body Movements: ExerciseKyle Vincent PulaNo ratings yet
- Hematology MCQ 2007Document6 pagesHematology MCQ 2007Li-Yana ZeE50% (2)
- Divyasparshi: Healer Suresh NagarsekarDocument19 pagesDivyasparshi: Healer Suresh Nagarsekarprashant borge100% (1)
- Avian Hematology SlidesDocument22 pagesAvian Hematology Slidesandry pratamaNo ratings yet
- HEMOSTASISDocument12 pagesHEMOSTASISRyan PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy Dic 1 1Document25 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy Dic 1 1api-394684626No ratings yet
- Anaphy - Chapter 4Document16 pagesAnaphy - Chapter 4Deanne Joyce AdelantarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document26 pagesLesson 2Janielle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Reagent Red Blood Cells 2015-03-19Document4 pagesReagent Red Blood Cells 2015-03-19cesareNo ratings yet
- The Exact Manual Calculation of The Erythrocyte IndicesDocument11 pagesThe Exact Manual Calculation of The Erythrocyte IndicesTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Building A Medical Vocabulary 7th Edition by Leonard Full DownloadDocument22 pagesTest Bank For Building A Medical Vocabulary 7th Edition by Leonard Full Downloaddanielnelsonstziebqjyp100% (37)
- Orca Share Media1668581887938 6998539686907204385Document5 pagesOrca Share Media1668581887938 6998539686907204385Mavrix AgustinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of BloodDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Bloodaoi_rachelle100% (1)
- @MBS MedicalBooksStore 2019 CardiovascularDocument273 pages@MBS MedicalBooksStore 2019 CardiovascularAhmad FitriawanNo ratings yet
- Biochem Experiment 3Document3 pagesBiochem Experiment 3Julius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet