Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Uploaded by
N.Nityaini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageOriginal Title
respiration-notes-pdf.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation
Uploaded by
N.NityainiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
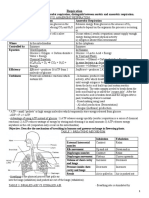
CHAPTER 7-RESPIRATION (FORM 4)
www.sureshkumarbio.wordpress.com
Surface Protozoa Main substrate needed glucose
membrane
RESPIRATION Divided into 1.External:
Gills Fishes
-a mechanical process
-also known as breathing
Lungs Humans
2. Internal: -maintains a continuous
Respiratory
-also called cellular respiration. exchange of CO2 and O2.
Tracheal system Insects Structures
-a biochemical process.
Of Animals
Lungs, skin, Amphibians -energy released from ATP.
mouth cavity
Divided into Divided into
2. Aerobic respiration:
Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalation:
-requires O2.
-O2 taken in through -CO2 released through
-breakdown of glucose is complete.
mouth / nostrils mouth / nostrils
-large amount of energy ↑.
-energy is used toform ATP. (a) Human muscle:
-occur in mitochondria. -happens during vigorous exercise.
(b) yeast / plants:
-CO2 released as waste products. -lactic acid builds up in muscle
-glucose is converted into
causes muscle fatigue.
1.Anaerobic respiration: ethanol + energy + CO2.
process is also called -after exercise, deep and fast breathing
-≠ require O2.
occurs
-breakdown of glucose is not fermentation.
to break down lactic acid.(in muscle
complete. -ethanol is converted back to CO2
and liver)
-less amount of energy↑. and energy when O2 is present.
Occurs in -amount of O2 needed for the
-occur in cytoplasm.
breakdown is called “Oxygen debt”.
-by products are:
-lactic acid is broken down to form CO2
i)lactic acid in animals.
and energy.
ii)ethanol in yeasts & plants.
-energy from this process is less.
You might also like
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationDocument33 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationPau Siew LingNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalationmentos999No ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaeDocument29 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaezulaikhaabdrahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationXuan Deng FamNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Respiration 2023Document8 pagesTopic 10 Respiration 2023nizaizzatiNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Document17 pagesBio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Gillion lordNo ratings yet
- ANSWER Chapter 7 BIO F4Document3 pagesANSWER Chapter 7 BIO F4Izeliwani Haji IsmailNo ratings yet
- DLP Biology F4 Answers Chap 7 (Final)Document3 pagesDLP Biology F4 Answers Chap 7 (Final)deathangel88 GtNo ratings yet
- Bio - Active Learning - Cellular Respiration & FermentationDocument26 pagesBio - Active Learning - Cellular Respiration & FermentationnurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION TheoryDocument8 pagesRESPIRATION TheorySiddi AadiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- Chap7F4 Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesChap7F4 Cellular RespirationSyahir NajmiNo ratings yet
- Production of Urea (14.1.2) - Edexel A Level Biology Revision Notes 2022Document1 pageProduction of Urea (14.1.2) - Edexel A Level Biology Revision Notes 2022Steven FieldsNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument24 pagesCellular RespirationTrinity BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Science - 090820 - Respiration in Organisms Class 7 AssignmentDocument15 pagesScience - 090820 - Respiration in Organisms Class 7 AssignmentDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- Energy Utilization-1Document4 pagesEnergy Utilization-1Henu AryudaNo ratings yet
- Biology Rank Edge Series Neet Sample MaterialDocument111 pagesBiology Rank Edge Series Neet Sample MaterialSam MishraNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Respiration Topic Checklist: C H O + 6O 6CO + 6H ODocument2 pages12.1 Respiration Topic Checklist: C H O + 6O 6CO + 6H Otee sooyeeNo ratings yet
- General Biology NotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology NotesjeayNo ratings yet
- CN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12Document1 pageCN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12Andro RomanoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy: BiologyDocument74 pagesCellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy: BiologyJericho AguilarNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisms and Life ProcessesDocument21 pages2 Organisms and Life ProcessesSagar WaghmareNo ratings yet
- # Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)Document7 pages# Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)VELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer:: - Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer:: - Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesSarah Jane P. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- 14 Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument4 pages14 Respiration in Plants-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesLife Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respirationcarlosgoh246No ratings yet
- Basis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesBasis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationLia JeonNo ratings yet
- The Photosynthesis Equation 6CO + 6H O - C H O + 6ODocument4 pagesThe Photosynthesis Equation 6CO + 6H O - C H O + 6OMicaela SuarezNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab For Practical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Student Name: H ID: BTBTIU21065Document3 pagesPre-Lab For Practical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Student Name: H ID: BTBTIU21065Easper OneNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Concept MapDocument15 pagesRespiration: Concept MapSHAHIDA SAADNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Reviewer in ScienceDocument3 pagesQuarter 4 Reviewer in ScienceHanna Samantha LisingNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Ms. A. BantonDocument18 pagesTeacher: Ms. A. BantonCxsh TvNo ratings yet
- 401-402 Aerobic RespirationDocument9 pages401-402 Aerobic Respirationalirazanqvi310No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- (BIOLOGY) Cellular RespirationDocument12 pages(BIOLOGY) Cellular RespirationHAJIRA RAMLANNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemDocument5 pagesMetabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemFerdinand Arcangel Ebalo IiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FermentationDocument6 pagesChapter 7 FermentationBRENDAN CHIEW CHANG RONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCellular Respirationashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest Chemical EnergyDocument75 pagesHow Cells Harvest Chemical EnergylinNo ratings yet
- Notes Respiration Handout 1Document3 pagesNotes Respiration Handout 1Imran IjazNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- Topic 8-Cellular Respiration PART 1,2,3 - StudentDocument35 pagesTopic 8-Cellular Respiration PART 1,2,3 - StudenthadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document56 pagesChapter 7Norizan DarawiNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument11 pagesCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesEvannaCoronaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Cellular RespirationDocument62 pagesWeek 5 - Cellular RespirationEce YılmazNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document21 pagesLesson 12Swastik Singh 8A 30No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument2 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesLAVKUSH TIWARINo ratings yet
- Biochem PDFDocument7 pagesBiochem PDFNhư NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationDocument3 pagesGen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Bio Respiration Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesBio Respiration Chapter SummaryYoussef Abdurrahman WeinmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes EditedDocument5 pagesBiology Revision Notes EditedAiney MaiNo ratings yet
- Y8 AP2 Revision LesssonsDocument32 pagesY8 AP2 Revision Lesssons4m44r2010No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics HandoutDocument1 pageBioenergetics HandoutRhaven GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellDocument14 pagesOnline Lecture No.4 Class:9 (A, B&C) Subject:Biology Chapter:-Plant CellwatashiwayakinikuNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins WORDDocument6 pages3.2 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins WORDCaitlin Barrett100% (1)