Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expt. 8 Two Port Network
Uploaded by
aditya bunnyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt. 8 Two Port Network
Uploaded by
aditya bunnyCopyright:
Available Formats
Simulation # 8
Two port network – Z Parameters
Electrical Network Simulation Laboratory (EE2701)
Department of Electrical Engineering,
NIT Rourkela
Prepared by Prof. Paresh Kale Page 1
Aim of the Expt.:
Understand two port circuits
Calculate Z parameters for two port networks
Use Multisim to find the Z parameters for given circuit
Theory:
Figure 1 Generalisation of two port network
There are six groups of two-port circuit parameters (e.g., the impedance z-parameters, admittance
y-parameters, hybrid h-parameters, etc) that can be used to relate the input/output voltage & current
variables. Any set of parameters can be derived from the other ones.
The z-parameters are defined by:
V1 = Z11 I1 + Z12I2
V2 = Z21 I1 + Z22I2
These parameters can be measured by the following tests (based on open-circuit input port
condition, and open-circuit output port condition):
Z11 = V1 / I1 when I2 = 0
Z12 = V1 / I2 when I1 = 0
Z21 = V2 / I1 when I2 = 0
Z22 = V2 / I2 when I1 = 0
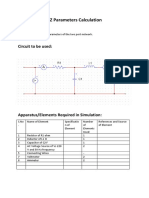
Circuit:
Figure 2 Circuit for experiment
Prepared by Prof. Paresh Kale Page 2
Simulation:
1. Build the circuit of Figure 2 in Multisim Electronics Workbench.
2. Apply a DC voltage test source to the input port with the output port open. Use a
voltmeter and ammeter to read the values of the voltages and currents necessary to
compute Z11 and Z21. Observe the proper polarity of the currents.
3. Repeat a similar procedure with a DC voltage test source applied to the output port with
the input port open. Use a voltmeter and ammeter to read the voltage and current values,
and derive the parameters Z22 and Z12.
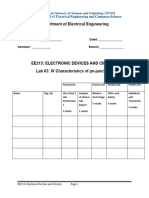
4. Record the values of the Z-parameters in Table 1.
Table 1 Z-parameters for circuit 1
Z-parameters Z11 Z12 Z21 Z22
Simulation
Calculation
Questions:
1. Explain whether this two-port circuit is reciprocal, and why?
2. Explain whether this two-port circuit is symmetric, and why?
3. Run the simulation for a loaded two port network as shown in Figure 3 and find the voltage
and current gain. Vs= 10 V DC, Gv=V2/Vs and current gain Gi=I2/I1.
Figure 3 Loaded two-port network
Prepared by Prof. Paresh Kale Page 3
You might also like
- Expt # 6 Two Port Network - Z ParametersDocument10 pagesExpt # 6 Two Port Network - Z ParametersRohanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 3Document42 pagesElectrical Circuits 3akramul alimNo ratings yet
- Z and Y ParametersDocument6 pagesZ and Y Parameterskudupudinagesh100% (12)
- NETWORK ANALYSIS Chap.8 TWO PORT NETWORK & NETWORK FUNCTIONS PDFDocument34 pagesNETWORK ANALYSIS Chap.8 TWO PORT NETWORK & NETWORK FUNCTIONS PDFsudarshan poojaryNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis-Two Port Network & Network FunctionsDocument34 pagesNetwork Analysis-Two Port Network & Network Functionsanjugadu100% (2)
- Chapter 8 Two Port Network & Network Functions: Learning OutcomesDocument34 pagesChapter 8 Two Port Network & Network Functions: Learning OutcomesKarim Ullah PW ELE BATCH 22No ratings yet
- Two Port Network ReportDocument12 pagesTwo Port Network Reportعبدالعزيز شقحانNo ratings yet
- Experiment No1Document20 pagesExperiment No1Deepanshu Gupta100% (2)
- Network Theory Lab ManualDocument31 pagesNetwork Theory Lab ManualkondraguntajbNo ratings yet
- EEE111 - Lab ManualDocument28 pagesEEE111 - Lab ManualAnindita MishiNo ratings yet
- Index: S.No. Experiment Date RemarksDocument10 pagesIndex: S.No. Experiment Date RemarksYogesjh KalraNo ratings yet
- ET/ Module-5 / DC CIRCUITS / Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument12 pagesET/ Module-5 / DC CIRCUITS / Mesh and Nodal AnalysisSrikanth AllamsettyNo ratings yet
- NT Lab MannualDocument31 pagesNT Lab MannualsagarNo ratings yet
- Two Port Networks - UploadDocument16 pagesTwo Port Networks - UploadkarthikhrajvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document16 pagesChapter 18EL DrickNo ratings yet
- Two Port CircuitsDocument13 pagesTwo Port CircuitsSandaruwan WanninayakaNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Experiment: Apparatus Required:: V1V2 I1I2Document8 pagesAim of The Experiment: Apparatus Required:: V1V2 I1I2lopa_titanNo ratings yet
- EIE324 2portDocument30 pagesEIE324 2portEmmanuel OkoroNo ratings yet
- EEE111+ (Exp+1) +I v+Characteristics+of+DiodeDocument4 pagesEEE111+ (Exp+1) +I v+Characteristics+of+DiodeFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- Electronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesElectronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Aust/Eee: Student Name: Student IDDocument32 pagesAust/Eee: Student Name: Student ID29 - 023 - Abid HasanNo ratings yet
- Practical Task 2Document15 pagesPractical Task 2Kosigar Chelladorai100% (1)
- Two Port NetworkDocument51 pagesTwo Port NetworkPranzal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument69 pagesBee Lab ManualYash AryaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Assignment-X: Simulation of Half Bridge InverterDocument4 pagesPower Electronics Lab Assignment-X: Simulation of Half Bridge InverterAurang ZaibNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Assignment-III: Simulation of Half Wave Uncontrolled Ac-Dc ConverterDocument8 pagesPower Electronics Lab Assignment-III: Simulation of Half Wave Uncontrolled Ac-Dc ConverterAurang ZaibNo ratings yet
- EE230 Lab 0Document8 pagesEE230 Lab 0AnnirudhNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 (3420)Document12 pagesLab 3 (3420)Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Two Port Networks - Impedance and Admitance Parameters-1Document50 pagesTwo Port Networks - Impedance and Admitance Parameters-1SAJJAD AHMAD Jalozai Electrical - Batch 20No ratings yet
- Two Port Networks: Unit - 6Document15 pagesTwo Port Networks: Unit - 6vimalaspl7831No ratings yet
- Lab 03Document11 pagesLab 03afnanmirza106No ratings yet
- Lab 3Document10 pagesLab 3Ahmed Razi UllahNo ratings yet
- Other 22122021211053993Document6 pagesOther 22122021211053993Dhrubajit Acharya Bishal 222-15-6242No ratings yet
- 3947Document7 pages3947Dei PehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Two Port Network AnalysisDocument32 pagesChapter 2 Two Port Network AnalysisBewnet GetachewNo ratings yet
- LabInstr EE320L Lab7Document9 pagesLabInstr EE320L Lab7baig79No ratings yet
- Elvis II y MultisimDocument17 pagesElvis II y MultisimHermes PolancoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDocument27 pagesElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512No ratings yet
- Cercuit NetworkDocument19 pagesCercuit NetworkShivam PandyaNo ratings yet
- Verification of Superposition Theorem.Document6 pagesVerification of Superposition Theorem.Apu SarkarNo ratings yet
- QUT Digital Repository:: Conference (IPEC 2007), Pages Pp. 661-665, SingaporeDocument6 pagesQUT Digital Repository:: Conference (IPEC 2007), Pages Pp. 661-665, SingaporeSheetal VermaNo ratings yet
- ID AND NAME OF THE STUDENT: 3420987 - Katia Santiago Del Rio 2. TOPIC AND NUMBER OF THE LAB: V-I Characteristics of A SemiconductorDocument4 pagesID AND NAME OF THE STUDENT: 3420987 - Katia Santiago Del Rio 2. TOPIC AND NUMBER OF THE LAB: V-I Characteristics of A SemiconductorKati SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1MeghaNo ratings yet
- EE325 Lab 1Document8 pagesEE325 Lab 1williamNo ratings yet
- YZ Parameters CalculationDocument4 pagesYZ Parameters CalculationAnupNo ratings yet
- NAS Lab Manual - Z ParametersDocument7 pagesNAS Lab Manual - Z ParametersPoonam DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Two Port Network ParametersDocument7 pagesTwo Port Network ParametersARVINDNo ratings yet
- Power Diode WorksheetDocument20 pagesPower Diode WorksheetLộc Phạm vănNo ratings yet
- EN3ES1 Basic Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Diode and Zener Diode Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesEN3ES1 Basic Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Diode and Zener Diode Page 1 of 5Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsLab - Manual March2010Document64 pagesElectronicsLab - Manual March2010pnarendrareddy.mscNo ratings yet
- 15 Electric Circuit Analysis: If The Source Is... The Analysis Type Is..Document26 pages15 Electric Circuit Analysis: If The Source Is... The Analysis Type Is..Suresh NikalajeNo ratings yet
- 223 Instrumentation and Measurement - F2016 - 223Document49 pages223 Instrumentation and Measurement - F2016 - 223Vinay MakhijaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1. Diode Characteristics HalfDocument10 pagesLab Report 1. Diode Characteristics HalfayasumireNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document4 pagesExperiment 2tarekabdelhalimsedik555No ratings yet
- Ed - Exp - 1 - Student - Manual - 2Document4 pagesEd - Exp - 1 - Student - Manual - 2fahimsahriar200No ratings yet
- Ece2201 SJB Lab1Document8 pagesEce2201 SJB Lab1Areeba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Application Note 14Document5 pagesApplication Note 14Elbahi DjaalabNo ratings yet
- ATP Daily Report 11 September 2023Document90 pagesATP Daily Report 11 September 2023Hendra W.FNo ratings yet
- EX Series UpRunning PDFDocument291 pagesEX Series UpRunning PDFaykargilNo ratings yet
- CAPsMAN Real-Life ScenariosDocument52 pagesCAPsMAN Real-Life ScenariosKyawNo ratings yet
- Log4j Users GuideDocument299 pagesLog4j Users GuideSigit PamungkasNo ratings yet
- IER 600 TECHNICAL MANUAL N0B612A. ReaderDocument40 pagesIER 600 TECHNICAL MANUAL N0B612A. ReaderzigmanNo ratings yet
- CH 10 - Cyber Threats & Security - NotesDocument2 pagesCH 10 - Cyber Threats & Security - NotesKabir MaskeNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication & Computer Networks: Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument17 pagesTelecommunication & Computer Networks: Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologySaba SaherNo ratings yet
- 100 Eye Opening Facts About Generation ZDocument45 pages100 Eye Opening Facts About Generation ZDerek E. Baird100% (1)
- 1.3.2.4 Lab - Tracing Internet ConnectivityDocument3 pages1.3.2.4 Lab - Tracing Internet Connectivity03Muhammad Raihan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Cisco Routing Switching - Unlocked PDFDocument200 pagesCisco Routing Switching - Unlocked PDFAung Zaw LinNo ratings yet
- Surpass Hix 5635/30 R1.5: Training For OperatorDocument85 pagesSurpass Hix 5635/30 R1.5: Training For OperatorQuocKhanh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Reaktor ManualDocument492 pagesReaktor ManualspaceskipperNo ratings yet
- Wireless Handheld Ordering Terminal Based On Embedded SystemDocument6 pagesWireless Handheld Ordering Terminal Based On Embedded SystemGaurav PohujaNo ratings yet
- Private Employers - New DelhiDocument51 pagesPrivate Employers - New DelhiDavid ThomasNo ratings yet
- 751 Solucion de FallasDocument133 pages751 Solucion de FallasCHRIZSPAULNo ratings yet
- Harga DistributorDocument16 pagesHarga DistributorAta NurdinNo ratings yet
- Cross Culture TrainingDocument5 pagesCross Culture TrainingSaurabh Jain50% (2)
- JSP Interview Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesJSP Interview Questions and AnswersKeerthanaKeerthuNo ratings yet
- SUIT Protocol Description v12.0Document64 pagesSUIT Protocol Description v12.0سعد الطائعNo ratings yet
- Nuvoton 8051 ISP by COM Port: User ManualDocument18 pagesNuvoton 8051 ISP by COM Port: User ManualParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Instalar Pgadmin 4 Cenos - OdtDocument7 pagesInstalar Pgadmin 4 Cenos - OdtbecerrilcacarotoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksM Sachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Sim900 Rs232 GSM Modem OpnDocument19 pagesSim900 Rs232 GSM Modem OpnOlen Borromeo100% (1)
- Access Lists ExercisesDocument36 pagesAccess Lists ExercisesSung Chin TialNo ratings yet
- UPS - Cybersecurity - White Paper PDFDocument4 pagesUPS - Cybersecurity - White Paper PDFThibaut Serge Vianey AkproNo ratings yet
- The Use of Information and Communication Technologies in ConstructionDocument26 pagesThe Use of Information and Communication Technologies in Constructionsara peigeNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) : Raafat Ali Supervisor: Dr. Nizar ZarkaDocument17 pagesGaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) : Raafat Ali Supervisor: Dr. Nizar ZarkahiriNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument121 pagesProject ReportretwickNo ratings yet
- 5th June 2014 Anroid Developer AlkaDocument15 pages5th June 2014 Anroid Developer AlkaSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Domino Cluster Fundamental ImplimatationDocument4 pagesDomino Cluster Fundamental Implimatationmknair101No ratings yet