Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamins: Vitamin Active Form Function RDA Sources Deficiency Signs and Symptoms Vitamin B
Vitamins: Vitamin Active Form Function RDA Sources Deficiency Signs and Symptoms Vitamin B
Uploaded by
BaldogOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vitamins: Vitamin Active Form Function RDA Sources Deficiency Signs and Symptoms Vitamin B
Vitamins: Vitamin Active Form Function RDA Sources Deficiency Signs and Symptoms Vitamin B
Uploaded by
BaldogCopyright:
Available Formats
VITAMINS
Organic molecules essential for normal health and growth.
Required in trace amounts and are obtained from the diet because sufficient amounts are not synthesized in the body.
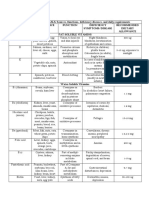
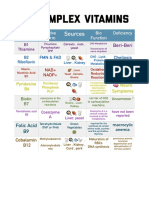
1. WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Not stored in the body since excess amounts are excreted in the urine
Destroyed by heat, oxygen and ultraviolet light
Required by many enzymes as cofactors to carry out certain aspects of catalytic action
ACTIVE
VITAMIN FUNCTION RDA SOURCES DEFICIENCY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
FORM
Beriberi Tachycardia, vomiting, convulsions
Thiamine Liver, yeast, whole grain,
Vitamin B1 Thiamine Decarboxylation 1.2 mg Wernicke-Korsakoff Apathy, loss of memory, eye
pyrophosphate bread, cereals, milk
(alcoholics) movements
Beef, liver, chicken, eggs,
Dermatitis
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin FMN, FAD Electron transfer 1.2-1.8 mg green leafy vegetables, dairy Rare
Angular stomatitis
foods, peanuts, whole grains
Dermatitis
Niacin Brewer’s yeast, chicken,
Oxidation- Pellagra Diarrhea
Vitamin B3 Nicotinic acid NAD+, NADP+ 14-18 mg beef, fish, liver, brown rice,
reduction Dementia
Nicotinamide whole grains
Salmon, beef, liver, eggs,
Pantothenic Acetyl group
Vitamin B5 Coenzyme A 5 mg brewer’s yeast, whole grain, Rare —
acid transfer
fresh vegetables
Pyridoxine Glossitis
Pyridoxal Meat, liver, fish, nuts, whole
Vitamin B6 Pyridoxamine Transamination 1.3-2.0 mg Rare Neuropathy
phosphate grains, spinach
Pyridoxal
Methylcobalam
Pernicious anemia
in Methyl group Liver, beef, kidney, chicken, Megaloblastic anemia
Vitamin B12 Cobalamin 2.0-2.6 μg Dementia
Deoxyadenosyl transfer fish, milk products Neuropsychiatric symptoms
Spinal degeneration
cobalamin
Enzyme-bound
Vitamin H Biotin Carboxylation 30 μg Liver, yeast, nuts, eggs Rare —
protein
Blueberries, oranges,
Collagen Sore, spongy gums
strawberries, cantaloupe, Scurvy
Vitamin C Ascorbic acid Ascorbic acid synthesis, wound 60-95 mg Loose teeth
tomatoes, peppers, broccoli,
healing Poor wound healing
cabbage, spinach
Green leafy vegetables.
Tetrahydrofolic Methyl group Beans, meat, seafood, yeast, Megaloblastic anemia Anemia
Folic acid Folate 400 μg
acid transfer asparagus, whole grains Neural tube defects Birth defects
enriched with folic acid
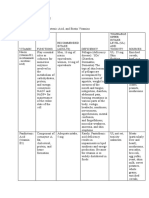
2. FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Carried in lipids & are influenced by the same factors that affect lipid absorption
Fairly resistant to the effects of heat; they are not destroyed by cooking or food processing (Vitamins A, D, E, & K)
Stored in the body and not eliminated toxicity
VITAMIN ACTIVE FORM FUNCTION RDA SOURCES DEFICIENCY SIGNS AND SYMTPTOMS
Retinol Retinol Impotence
Retinal Retinal Vision, RNA Yellow and green fruits and Night blindness Increased visual threshold
Vitamin A 800 μg
Retinoic acid Retinoic acid synthesis vegetables Growth retardation Dryness of cornea
β-Carotene Xerophthalmia
Cholecalciferol 1,25-dihydroxy- Regulation of P Sunlight, cod liver oil, Rickets (children)
Vitamin D3 5-10 μg Soft, pliable bones
Ergocalciferol cholecalciferol and Ca absorption enriched milk, eggs Osteomalacia (adults)
Any of theseveral
Antioxidant, cell Meats, whole grains, RBC fragility leads to hemolytic
Vitamin E α-tocopherol tocopherol 15 mg Rare
protection vegetable anemia
derivatives
Menadione Menadione
Meats, whole grains, Newborn
Vitamin K Menaquinone (K2) Menaquinone Blood clotting 90-120 μg Bleeding
vegetables Rare (adults)
Phylloquinone Phylloquinone
You might also like
- RESEARCH MWTHODS M.ADocument11 pagesRESEARCH MWTHODS M.ADacosta FlectureNo ratings yet
- Efforts For The Revival of Islam in The Sub ContinentDocument3 pagesEfforts For The Revival of Islam in The Sub ContinentS Alam100% (1)
- House Rules and RegulationsDocument1 pageHouse Rules and RegulationsJuliannNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument2 pagesVitamindaroshamchaudhary1237No ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument3 pagesBiology ProjectShaik ShaahidNo ratings yet
- All Vitamins Chmical Name ListDocument3 pagesAll Vitamins Chmical Name ListSanthosh sanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition VITAMIN TABLE CompletedDocument2 pagesNutrition VITAMIN TABLE CompletedGeneralRipphookNo ratings yet
- Deficiency Disease,: Vitamins - Chemical NamesDocument2 pagesDeficiency Disease,: Vitamins - Chemical NamesGirish Waru100% (1)
- Sendy Bullus: Group S1513Document12 pagesSendy Bullus: Group S1513Marin ChianuNo ratings yet
- Sources of Nutrients and Deficiency DiseasesDocument4 pagesSources of Nutrients and Deficiency DiseasesAditya A Strange PersonNo ratings yet
- Tricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31 1 76Document5 pagesTricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31 1 76Pussy catNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsAlisaClarkNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument2 pagesVitamins and MineralsHelen Mae GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Coenzima Función de La Coenzima Vitamina Relacionada Función de La Vitamina Fuente de La Vitamina DeficienciaDocument3 pagesCoenzima Función de La Coenzima Vitamina Relacionada Función de La Vitamina Fuente de La Vitamina DeficienciaCristian PulidoNo ratings yet
- Tricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31Document5 pagesTricks To Remember Vitamins and Their Deficiency 31Cruel SatyaNo ratings yet
- Notes of VitaminsDocument8 pagesNotes of VitaminsEllyNo ratings yet
- Vitamins NotesDocument8 pagesVitamins NotesEllyNo ratings yet
- CNURSING CARE OF A FAMILY WITH A NEWBORN PART 3cDocument43 pagesCNURSING CARE OF A FAMILY WITH A NEWBORN PART 3cJustine Jean GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Their Importance - UPSC Guide PDFDocument1 pageVitamins and Their Importance - UPSC Guide PDFRajesh ManjhiNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument6 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsRan And SanNo ratings yet
- A Few Minutes Series: VitaminsDocument3 pagesA Few Minutes Series: VitaminsPriti MishraNo ratings yet
- Shafiya Fatiha Rahmi 11181330000023Document2 pagesShafiya Fatiha Rahmi 11181330000023Shafiya RahmiNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument17 pagesVitaminsnicholaschungu24No ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Vitamin What It Does Food Sources Symptoms and DiseasesDocument7 pagesVitamin What It Does Food Sources Symptoms and DiseasesNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals: Name: Mahajan, Deepika Sardar Student No: 16-2-21988 Section: BDocument8 pagesVitamins and Minerals: Name: Mahajan, Deepika Sardar Student No: 16-2-21988 Section: BDeepika MahajanNo ratings yet
- Nutritional DeficienciesDocument3 pagesNutritional DeficienciesSara JosephNo ratings yet
- Essential Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesEssential Amino Acidssania ziaNo ratings yet
- IMP BiologyDocument22 pagesIMP Biologyvolesa9875No ratings yet
- Vitamins Ther 201Document2 pagesVitamins Ther 201Jenward HostalleroNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDADocument4 pagesVitamin Chemical Nature Function Solubilit y Sources Coenzymes Formed Deficiency RDAAndy J. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins - DiseasesDocument2 pagesVitamins - DiseasesAakash MathersNo ratings yet
- Deficiency Diseases and Malnutrition GK Notes in PDFDocument5 pagesDeficiency Diseases and Malnutrition GK Notes in PDFvamsiprasannakoduruNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezDocument5 pagesVitamins and Oligoelements Abstract Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezCristhian LozanoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Summary SheetDocument8 pagesVitamin Summary Sheetglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Purpose Deficiency Comments Source Water Soluble: Beriberi: PolyneuropathyDocument1 pageVitamin Purpose Deficiency Comments Source Water Soluble: Beriberi: PolyneuropathyArely CrzNo ratings yet
- Phenylalanine Theonine Histidine Valine Isoleucine Arginine (Semi-Essential in Kids Only) Tryptophan Methionine LysineDocument7 pagesPhenylalanine Theonine Histidine Valine Isoleucine Arginine (Semi-Essential in Kids Only) Tryptophan Methionine LysineApril BasilioNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision of Vitamins and MineralsDocument6 pagesQuick Revision of Vitamins and MineralspriyankamangalkarNo ratings yet
- Nutrients TableDocument1 pageNutrients TableNelson LongsworthNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Synonyms Chemistry Coenzyme Form RDA Sources Properties Physiologic Role DeficiencyDocument9 pagesVitamins Synonyms Chemistry Coenzyme Form RDA Sources Properties Physiologic Role Deficiencykristian markus delos santosNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument5 pagesAnswersBarak KilimoNo ratings yet
- Nur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikDocument7 pagesNur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikSyahirah YusriNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Table FormDocument7 pagesVitamins Table FormR-Chian Jose GermanpNo ratings yet
- Christine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesChristine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument2 pagesVITAMINSthisswannNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 4 - VitaminsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 4 - VitaminsDahria CatalanNo ratings yet
- Ramos - Activity VitaminsDocument7 pagesRamos - Activity VitaminsChristian Vonne B. RamosNo ratings yet
- Vitamin StudentDocument63 pagesVitamin StudenttienesemNo ratings yet
- Vitamin List Sources and FunctioningDocument4 pagesVitamin List Sources and FunctioningAndrew Princely GerhartNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- Desire TO Learn: Nutrients and Their Deficiency DiseasesDocument9 pagesDesire TO Learn: Nutrients and Their Deficiency DiseasesKunal GautamNo ratings yet
- B-Complex VitaminsDocument1 pageB-Complex VitaminsIbrahim JamalNo ratings yet
- Study Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesDocument3 pagesStudy Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesWaseemNo ratings yet
- Study Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesDocument3 pagesStudy Notes of Vitamins: (A) - Fat Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins (Name) Rich Food Source Functions Deficiency DiseasesAnugrah MNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminscolek22100% (2)
- Vitamins: Vitamin What? Where? Deficiency ToxicityDocument6 pagesVitamins: Vitamin What? Where? Deficiency ToxicitybrooklynNo ratings yet
- Summary On Vitamins: Vitamins Aka Category FunctionsDocument2 pagesSummary On Vitamins: Vitamins Aka Category FunctionsnivedbNo ratings yet
- 510 FinalDocument2 pages510 Finalapi-301586234No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- Vitamins ReviewerDocument3 pagesVitamins RevieweroperanacireNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersDocument11 pagesPharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersJuliann100% (1)
- Administered Under The Epidermis, Eg. Forearm, UpperDocument17 pagesAdministered Under The Epidermis, Eg. Forearm, UpperJuliannNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument22 pagesPharmacology NotesJuliann100% (1)
- Pharm Analysis 2 - ECQ RequirementsDocument12 pagesPharm Analysis 2 - ECQ RequirementsJuliannNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - The Hospital and Its OrganizationDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - The Hospital and Its OrganizationJuliannNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Extemporaneous CompoundingDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Extemporaneous CompoundingJuliann100% (1)
- Quality Control Lecture2 2Document74 pagesQuality Control Lecture2 2Juliann50% (2)
- Motor Learning Theory: References: Cole & Tufano, Chapter 19 Reserve Article: Mathiowetz & Bass Haugen (1994) AJOTDocument23 pagesMotor Learning Theory: References: Cole & Tufano, Chapter 19 Reserve Article: Mathiowetz & Bass Haugen (1994) AJOTEdwin BedfordNo ratings yet
- Annual Budget CY 2023Document180 pagesAnnual Budget CY 2023robertson builderNo ratings yet
- EXPANDIT 10 Mortar Comparison TestDocument1 pageEXPANDIT 10 Mortar Comparison TestLaura GarcíaNo ratings yet
- InheretanceDocument8 pagesInheretancefarhan.mukhtiarNo ratings yet
- NCM 210 RLE - 10 Herbal Plants Approved by DOHDocument6 pagesNCM 210 RLE - 10 Herbal Plants Approved by DOHLYRIZZA LEA BHEA DESIATANo ratings yet
- Eternally YoursDocument224 pagesEternally Yourstri_nanaNo ratings yet
- Personal Notes H.E Needle Work EquipmentDocument7 pagesPersonal Notes H.E Needle Work EquipmentThe ExodusNo ratings yet
- Review Article Barium HexaferriteDocument11 pagesReview Article Barium HexaferriteIngrid Bena RiaNo ratings yet
- STM Series Solar ControllerDocument2 pagesSTM Series Solar ControllerFaris KedirNo ratings yet
- Strategic Chain SupplyDocument3 pagesStrategic Chain SupplyRafya ArainNo ratings yet
- (Gender and Well-Being.) Ortiz, Teresa - Santesmases, María Jesús - Gendered Drugs and Medicine - Historical and Socio-Cultural Perspectives-Ashgate Publishing Limited (2014)Document261 pages(Gender and Well-Being.) Ortiz, Teresa - Santesmases, María Jesús - Gendered Drugs and Medicine - Historical and Socio-Cultural Perspectives-Ashgate Publishing Limited (2014)Federico AnticapitalistaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Business Analytics 3rd Edition Cam Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Business Analytics 3rd Edition Cam Solutions Manualwyattcgkzc100% (41)
- Primer DesignDocument37 pagesPrimer DesignRyu- MikaNo ratings yet
- Evaluative Commentary: Integrated Language Skills IiiDocument5 pagesEvaluative Commentary: Integrated Language Skills IiiShawn RizalNo ratings yet
- Power Management GuideDocument101 pagesPower Management GuideDiego MenegazziNo ratings yet
- What Is A Health AssessmentDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Health AssessmentKleeNo ratings yet
- Survey ReportDocument14 pagesSurvey ReportKamila KuźniarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Primary and Permanent TeethDocument15 pagesDifference Between Primary and Permanent TeetharthisaNo ratings yet
- Low Latency Performance Tuning For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7Document31 pagesLow Latency Performance Tuning For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7bakiNo ratings yet
- Stretching Mesh Reduced FileDocument5 pagesStretching Mesh Reduced FileMerlie Fuentes Fiel ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Ceg461 - Tutorial 4a - CompactionDocument4 pagesCeg461 - Tutorial 4a - Compactiondzikryds0% (1)
- An Internship Project On KLN MotorsDocument11 pagesAn Internship Project On KLN MotorsmunirajaffarNo ratings yet
- Johny John Medicine Bill ADocument8 pagesJohny John Medicine Bill Atgohiakri2006No ratings yet
- MakalahDocument6 pagesMakalahOctafianti AriniNo ratings yet
- Cause & Effect WorksheetDocument2 pagesCause & Effect WorksheetAh Gone67% (3)
- Construction-Additives 2019 FinalDocument5 pagesConstruction-Additives 2019 FinalAPEX SONNo ratings yet
- Event Report Insights Into HackathonDocument7 pagesEvent Report Insights Into HackathonSujoy SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lsa 501Document8 pagesLsa 501Lorenzo RossiNo ratings yet