Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyperloop: Presented by-ARINDAM NANDI Roll No - 1020133200320037 Registration No - KNU18001916 Session - Semester - II
Uploaded by
leo George0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views19 pagesHyperloop ppt
Original Title
hyperlooptansportation3-191003042727
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHyperloop ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views19 pagesHyperloop: Presented by-ARINDAM NANDI Roll No - 1020133200320037 Registration No - KNU18001916 Session - Semester - II
Uploaded by
leo GeorgeHyperloop ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
HYPERLOOP
TRANSPORTATION
THE FIFTH MODE OF TRANPORTATION
Presented by- ARINDAM NANDI
Roll No- 1020133200320037
Registration No- KNU18001916
Session – semester- II
CONTENT
CONVENTIONAL MODES OF TRANSPORTATION
WHAT IS HYPERLOOP?
THE CONCEPT
WHOSE IDEA?
COMPONENTS OF HYPERLOOP TRANSPORT SYSTEM
TUBE
CAPSULE
AIR BEARINGS AND SUSPENSION
PROPULSION
LIM
WORKING PRINCIPLE
HYPERLOOP IN INDIA
ADVANTAGE
DISADVANTAGE
CONCLUSION
REFERENCE
CONVENTIONAL MODES OF TRANSPORTATION
I. RAIL relatively slow and expansive
II. ROAD relatively slow
III. WATER relatively slow
IV. AIR expansive
V. PIPELINE....?
WHAT IS HYPERLOOP?
Existing conventional modes of transportation of people consist of four unique types: rail, road, water
and air. These modes of transport tend to be either relative slow and expensive.
It is the fifth modes of generation of transportation.
Hyperloop is a new modes of transport that seeks to change this paradigm by being both fast and
inexpensive for people and goods.
Hyperloop consist of a low pressure tube with capsules that are transported at both low and high
speed throughout the length of the tube by a number of linear electric motor.
The system can achieve an average speed of 598 mph ( 962 km/h), and a top speed of 760mph (1220
km/h).
THE CONCEPT
A capsule full of people in a low pressure tube elevated on pylon goes really
fast.
Passenger may enter and exit Hyperloop at station located either at the end of
the tube, branching along the tube length.
Accelerated via a linear magnetic accelerator.
Supported on cushion of air.
To be covered from Los Angeles to San Francisco (approx. 560 km) to be
covered in just 35 minute, with capsules leaving end stations every 2 minutes.
WHOSE IDEA?
Hyperloop concept was invented and designed in 1812 by the British Mechanical Engineer
GEORGE WENGER.
The concept of hyperloop is now developed and redesigned by the billionaire ELON
MUSK in 2012.
While the term Hyperloop is in some countries a registered trademark of the space
exploration technologies corporation (SpaceX) for the high speed transportation of
passenger and goods in partially evacuated tubes, the Hyperloop concept has been
explicitly open-sourced by Musk and SpaceX, and others have been encouraged to take
the ideas and further developed them.
COMPONENTS OF HYPERLOOP TRANSPORT SYSTEM
TUBE
CAPSULE
AIR BEARINGS AND SUSPENSION
PROPULSION
LIM
Tube
The tube is made of steel. Two tubes will be welded together in a side by side
configuration to allow the capsules to travel both direction.
Pylons (pillars) are placed every 100 ft (30 m) to support the tube. Which constrain the
tube in the vertical direction but allow longitudinal slip for thermal expansion as well as
dampened lateral slip to reduce the risk posed by earthquake.
Solar arrays will cover the top of the tubes in order to provide power to the system.
Tube are made by new material ‘ VIBRANIUM’.
CAPSULE
The capsule are supported via air bearings that operate using a compressed air reservoir and
aerodynamic lift.
Sealed capsules carrying 28 passenger each that travel along the interior of the tube.
It maximum width is 4.43 ft and maximum height 6.11 ft.
COMPRESSOR:
1. One important feature of the capsule is the onboard compressor, which serves two
purpose. The system allow the capsule to traverse the relatively narrow tube without choking flow
that travels between the capsule and the tube walls by compressing air that is bypassed through the
capsule.
2. It also supplies air to air bearings that support that weight of the capsule throughout the journey.
3. The compressor is powered by a1160 hp (865 kW) onboard electric motor. The motor has estimated
mass of 606 lb (275 kg), which included power electronics.
AIR BEARINGS AND SUSPENSION
Thrust air bearings offer stability and extremely low drag
Compressor pressurized air and aerodynamic lift provide better lift to capsule.(0.5 to 1.3 mm)
Independent mechanical suspension are provided for smooth ride for passenger.
Air bearings (also known as aerostatic or aerodynamic bearings) are bearings that used a thin film of
pressurised air to provide a low friction load-bearing interface between surface. Then the surface do not
touched.
Suspending the capsule within the tube present a substantial technical challenge due to transonic velocities.
Conventional wheel axle system become impractical at high speed due to frictional losses and dynamic
instability.
Externally pressurized and aerodynamic air bearings are well suited for the hyperloop due to exceptionally
high stiffness, which is required to maintain stability at high speed.
Also Suspension is achieve due to magnetic levitation.
PROPULSION
Linear accelerator (linear induction motor) used in hyperloop system accelerate and decelerate
the capsule.
It provide some advantages over a permanent magnet motor.
Stator are located on the capsules to transfer momentum to help the capsule via the linear
accelerator.
An alternating current is ran through electromagnet coils on the guide way. This creates a
magnetic field that attract and repels the magnets on the capsule and propels the train
forward.
Braking is accomplished by sending an alternating current in the reverse direction so that is
slowed by attractive and repulsive force.
LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR
(LIM )
Linear induction motor abbreviated as LIM, is
basically a special purpose motor that is in use to
achieve linear motion rather than rotational motion as
in the case of conventional motors.
Construction of a Linear Induction Motor.
WORKING PRINCIPLE
Simply it have the same working principle of Air Hockey.
The pods would accelerate to cruising speed gradually using a linear electric motor and
glide above their track using passive magnetic levitation or air bearings.
Maglev (derived from magnetic levitation) is a system of train transportation that uses
two sets of magnets, one set to repel and push the train up off the track, then another set
to move the `floating train` ahead at great speed taking advantage of the lack of friction.
The absence of air in the hyperloop will further increase the efficiency by nearly
eliminating losses due to air drag and make it much faster.
The capsules are supported on a cushion of air, featuring pressurized air and
aerodynamic lift. The capsules are accelerated via a magnetic linear accelerator affixed at
various station on the low pressure tube with rotors contained in each capsule.
Residual air in the tube is captured, compressed, and forced through holes in skis
attached to the bottom of the capsule. The gap between the skis and the tube during
operation is between 0.5mm and 1.3mm.
The pressure in the tube is very low, a capsule travelling at 700mhp will cause significant
air pressure at the nose of the vehicle, which must be considered in the design.
HYPERLOOP IN INDIA
During the rest at Nevada desert the CM of Maharashtra (India)
was present at the site.
The company has signed an agreement to built a Hyperloop
route between Mumbai to Pune in under just 35 min, beginning
with an operational demonstration track.
ADVANTAGE
Faster
Lower cost.
Pollution free.
Immune to weather.
Safer
Sustainably self power.
Resistant to Earthquakes.
DISADVANTAGE
Tube pressurization.
Turning will be critical(with large radius).
Insufficient movable space for passenger.
CONCLUSION
As it has number of advantages it will very help full for
transport public as well as goods in a very short period
of time( at a top speed of 1200 km/h) and also lower
cost.
It is a new concept and open source so there is some
future work will be required for development of this
project.
REFERENCE
1. Musk, Elon (August 12, 2013). "Hyperloop
Alpha" (PDF). SpaceX. Retrieved August 13, 2013.
2. ^ "Pando Monthly presents a fireside chat with Elon
Musk". pando.com. PandoDaily. July 13, 2012.
Retrieved July 15, 2017.
3. ^ Jump up to:a b "Beyond the hype of Hyperloop: An
analysis of Elon Musk's proposed transit
system". Gizmag.com. August 22, 2013.
Retrieved August 23, 2013.
4. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/hyperloop
5. https://hyperloop.tamu.edu/
6. https://www.youtube.com/
You might also like
- 2015 Tumbleweed Trailer Study PlansDocument43 pages2015 Tumbleweed Trailer Study PlansMelanie Marie Meighan0% (1)
- Aerodynamic CarsDocument18 pagesAerodynamic CarsArunava RayNo ratings yet
- Be-58 Beech Baron - Normal Procedures: Before Engine Start Through Engine Shutdown - Checklist Will Be VerbalizedDocument2 pagesBe-58 Beech Baron - Normal Procedures: Before Engine Start Through Engine Shutdown - Checklist Will Be VerbalizedVic JJ EerumNo ratings yet
- Frame, Chassis and Body, Specification of AutomobileDocument87 pagesFrame, Chassis and Body, Specification of AutomobilePIET MECHANICAL HOD HODNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshFrom EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNo ratings yet
- A320 Abnormal Notes SummaryDocument13 pagesA320 Abnormal Notes SummaryDevdatt SondeNo ratings yet
- "Hyperloop": Prof. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology & REASEARCH, BADNERA (444701)Document23 pages"Hyperloop": Prof. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology & REASEARCH, BADNERA (444701)Harshal SelkarNo ratings yet
- Toyota's: Globalization StrategiesDocument25 pagesToyota's: Globalization StrategiesitsgouravaroraNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop 140615081435 Phpapp02Document32 pagesHyperloop 140615081435 Phpapp02Vaibhav Koolwal100% (1)
- (IKCO) Manual de Propietario Ikco CentauroDocument175 pages(IKCO) Manual de Propietario Ikco CentauroTiberio Lugo86% (7)
- Hyperloop: Presented By: Aniket DeolikarDocument17 pagesHyperloop: Presented By: Aniket DeolikarHARIKRISHNAN VENUGOPALANNo ratings yet
- Kanhaiya Gupta 8 Sem (EE)Document10 pagesKanhaiya Gupta 8 Sem (EE)R Bhushan100% (1)
- Hyperloop technology: a fast and inexpensive transportation systemDocument6 pagesHyperloop technology: a fast and inexpensive transportation systemVishal VsNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: Presented by Rahul Padol B.E Entc Sub: Computer Network Roll No BE16F04F061 Guided By: Prof. P. BhagatDocument23 pagesHyperloop: Presented by Rahul Padol B.E Entc Sub: Computer Network Roll No BE16F04F061 Guided By: Prof. P. BhagatRahul PadolNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop Technology: Seminar OnDocument24 pagesHyperloop Technology: Seminar OnAditya ThokalNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: The Future of TransportationDocument23 pagesHyperloop: The Future of TransportationSourabh Raorane0% (1)
- Hyper Loop 2Document2 pagesHyper Loop 2Sai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument19 pagesHyperloop: Department of Mechanical EngineeringJinjith P NairNo ratings yet
- HyperloopDocument35 pagesHyperloopjishnuNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: The Fifth Mode of TransportationDocument29 pagesHyperloop: The Fifth Mode of TransportationRafaelLazoPomaNo ratings yet
- SYNOPSISDocument18 pagesSYNOPSISMohd RashidNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSeminar Reportyogesh raoNo ratings yet
- Amit - 2Document24 pagesAmit - 220eebme009No ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Hyperloop OneDocument21 pagesSeminar Report On Hyperloop Onechitran duttaNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR REPORT ON HYPERLOOP TECHNOLOGYDocument21 pagesSEMINAR REPORT ON HYPERLOOP TECHNOLOGYSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Hyper LoopDocument12 pagesHyper LoopSourabh RaoraneNo ratings yet
- Hyperlo OP: The Advanced Mode of TransportationDocument19 pagesHyperlo OP: The Advanced Mode of TransportationPavan Kumar MallarapaNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: Presented byDocument29 pagesHyperloop: Presented bykumar pranavNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Hyperloop: (A Fifth Mode of Transport)Document27 pagesPresentation ON Hyperloop: (A Fifth Mode of Transport)Syed yasearNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop New Project For OriginalDocument15 pagesHyperloop New Project For OriginalSridhar KolluruNo ratings yet
- "Hyperloop Transmision System ": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of Degree ofDocument23 pages"Hyperloop Transmision System ": Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement For The Award of Degree ofSai Vamshi PranayNo ratings yet
- Hyperloopppt 190509183406Document15 pagesHyperloopppt 190509183406ANo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On HyperloopDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On HyperloopSomashekhar SavalajeNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop TechnologyDocument18 pagesHyperloop TechnologyPrashant KuwarNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop Transport: An 800MPH FutureDocument20 pagesHyperloop Transport: An 800MPH FutureGAJULA VENKAT SAI GAJULANo ratings yet
- Rahul HyperloopDocument34 pagesRahul Hyperloopchandan pandeyNo ratings yet
- HyperLoop Report PDFDocument18 pagesHyperLoop Report PDFRohan ShastriNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Under Supervision Of:: Prof. A.K.BarikDocument21 pagesPresented By: Under Supervision Of:: Prof. A.K.BarikTom ChrisNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledyttftfiugiuiuNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop 3Document25 pagesHyperloop 3Viswas KaranamNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: Submitted To - Dr. Shelly Vadhera Submitted by - Robin Singh Roll No. - 11814096 Section - EE-6Document18 pagesHyperloop: Submitted To - Dr. Shelly Vadhera Submitted by - Robin Singh Roll No. - 11814096 Section - EE-6Robin dhankharNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR REPORT ON HYPERLOOPDocument21 pagesSEMINAR REPORT ON HYPERLOOPSai Vamshi PranayNo ratings yet
- Hyp PDFDocument4 pagesHyp PDFHarsh VardhanNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: Fifth Mode of TranspotationDocument5 pagesHyperloop: Fifth Mode of TranspotationDharamveerNo ratings yet
- HYPERLOOPDocument20 pagesHYPERLOOP200625adityakNo ratings yet
- Script (Hyperloop Transportation) :: Script Writer:danish ZCA102 2021/2022 ASSIGN.2 (Group 36)Document3 pagesScript (Hyperloop Transportation) :: Script Writer:danish ZCA102 2021/2022 ASSIGN.2 (Group 36)DanishNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Hyperloop OneDocument21 pagesSeminar Report On Hyperloop Oneanirudh singh solankiNo ratings yet
- Seminar: Presented by Sachin Yadav ROLL NO. 11152571 Group B1 Sakshi SachdevaDocument24 pagesSeminar: Presented by Sachin Yadav ROLL NO. 11152571 Group B1 Sakshi SachdevaSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop Transportation System ExplainedDocument22 pagesHyperloop Transportation System ExplainedPrudhvi PrinceNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: The Fifth Mode of Transportation: Presented By: Akash Singh M.E.-Iv Year 1418731008Document24 pagesHyperloop: The Fifth Mode of Transportation: Presented By: Akash Singh M.E.-Iv Year 1418731008Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Airlock System For Hyperloop With Landing WheelsDocument3 pagesIntelligent Airlock System For Hyperloop With Landing WheelsDharamveerNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On HyperloopDocument7 pagesSynopsis On Hyperlooppeer zainNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Muhammad Danish Ali, 1 SEM, M Phil (Physics), Punjab University LahoreDocument35 pagesPresented By, Muhammad Danish Ali, 1 SEM, M Phil (Physics), Punjab University LahoreDanishDani0% (1)
- Hyperlop Transportation SystemDocument4 pagesHyperlop Transportation SystemIJEMR JournalNo ratings yet
- Hyperlop Transportation SystemDocument4 pagesHyperlop Transportation SystemIJEMR JournalNo ratings yet
- Figure 1.1 HyperloopDocument16 pagesFigure 1.1 HyperloopbkrishnakanthNo ratings yet
- Final HyperloopDocument20 pagesFinal Hyperloopapi-439576124No ratings yet
- High Speed Transport System Hyperloop': PresentedDocument22 pagesHigh Speed Transport System Hyperloop': PresentedAnkur AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Presented By, P Vamsi Krishna Mech Dept Bharath UniversityDocument35 pagesPresented By, P Vamsi Krishna Mech Dept Bharath UniversitynejasifiNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop ReportDocument25 pagesHyperloop ReportAVI RAJNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: Elon Musk's High-Speed Transportation VisionDocument38 pagesHyperloop: Elon Musk's High-Speed Transportation VisionNebin P NelsonNo ratings yet
- 4.seminar Report.Document14 pages4.seminar Report.jagadish shivarajNo ratings yet
- Advantages of A New Hyperloop Transport TechnologyDocument4 pagesAdvantages of A New Hyperloop Transport Technologyreenrabi3342No ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Hyperloop TransportationDocument18 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Hyperloop TransportationJaya sankarNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop: The Future of TransportationDocument10 pagesHyperloop: The Future of TransportationM-18 Manish K GowdaNo ratings yet
- IIP PROJECt (Final Report) PDFDocument20 pagesIIP PROJECt (Final Report) PDFSuhil IrshadNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Training Unit: Atr42-500 T1 Maintenance Course OutlineDocument2 pagesAerospace Training Unit: Atr42-500 T1 Maintenance Course OutlineRiders RoughNo ratings yet
- Coduri Piese Suzuki Ignis 1.2i HybridDocument16 pagesCoduri Piese Suzuki Ignis 1.2i HybridStefan Cel MareNo ratings yet
- Manual John Deere 244JDocument18 pagesManual John Deere 244JYoriel GuzmanNo ratings yet
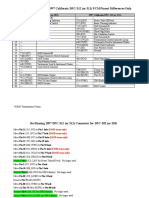
- 1996 Vs 1997 Cali PCM Pinout Differences OnlyDocument2 pages1996 Vs 1997 Cali PCM Pinout Differences OnlyWilliam PeeleNo ratings yet
- Transit.2006.5. (04 2006-)Document306 pagesTransit.2006.5. (04 2006-)asteriskcopNo ratings yet
- XR 250 L 01Document493 pagesXR 250 L 01andrewwitham50% (2)
- Antonio Sanchez Hybrid Engine PDFDocument60 pagesAntonio Sanchez Hybrid Engine PDFAntonio Sánchez100% (2)
- Hydraulic Steering Systems for Marine EnginesDocument40 pagesHydraulic Steering Systems for Marine EnginesЯрослав БогдановNo ratings yet
- Bandenspanningstabel PDFDocument1 pageBandenspanningstabel PDFRiad70No ratings yet
- Sea Doo GTX, RXT, Wake PRO, Fish PRO Series Operator's ManualDocument188 pagesSea Doo GTX, RXT, Wake PRO, Fish PRO Series Operator's ManualDan SimNo ratings yet
- PGODocument2 pagesPGOphilkphilkNo ratings yet
- PERKINS Catalogo Herramientas 2016Document105 pagesPERKINS Catalogo Herramientas 2016Jorge Luis BahamondeAzcarate100% (1)
- ACC0510 - Nissan Silvia-1Document6 pagesACC0510 - Nissan Silvia-1kimchimadNo ratings yet
- MLT 733 105 D St4 s2 Tract Lsu - enDocument16 pagesMLT 733 105 D St4 s2 Tract Lsu - enZsebe-Asztalos KittiNo ratings yet
- d1305 - E4b KUBOTA, Espisificaciones Tecnicas de MotorDocument2 pagesd1305 - E4b KUBOTA, Espisificaciones Tecnicas de MotorLopez GabrielNo ratings yet
- OSK CatalogueDocument29 pagesOSK CatalogueВиктор МушкинNo ratings yet
- Carta de DiagnosticoDocument9 pagesCarta de Diagnosticojosecuellar69No ratings yet
- MAnual Do MotorDocument17 pagesMAnual Do MotorGileno MotaNo ratings yet
- IPD - Lista de Peças Do Motor - 1 PDFDocument3 pagesIPD - Lista de Peças Do Motor - 1 PDFxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx100% (1)
- # Sample Quotation Copy For Go Kart SparesDocument3 pages# Sample Quotation Copy For Go Kart SparessaqibNo ratings yet
- Install 4 and 5 Inch Ram Front Fork Slam KitDocument4 pagesInstall 4 and 5 Inch Ram Front Fork Slam Kitalexp50100% (1)
- Diagramas SC 5200Document52 pagesDiagramas SC 5200Luis Castro BasualtoNo ratings yet