0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views5 pagesReview Problems in Solid Geometry-1
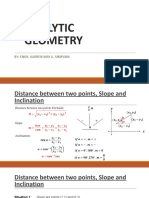
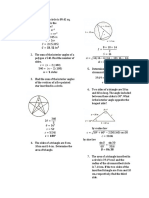
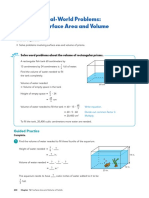
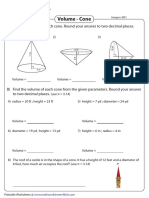
This document contains 42 multiple choice questions reviewing concepts in solid geometry. The questions are divided into 12 situations involving topics like volumes and surface areas of cones, spheres, cylinders, and other solids. The correct answers to each question are provided as multiple choice options.
Uploaded by
Jenesis de GuzmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views5 pagesReview Problems in Solid Geometry-1
This document contains 42 multiple choice questions reviewing concepts in solid geometry. The questions are divided into 12 situations involving topics like volumes and surface areas of cones, spheres, cylinders, and other solids. The correct answers to each question are provided as multiple choice options.
Uploaded by
Jenesis de GuzmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Situation 1
- Situation 4
- Situation 7
- Situation 9
- Situation 12