Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DalagUETE National High School Physics Mastery Test Review
Uploaded by
Annabella Quevedo CampomanesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DalagUETE National High School Physics Mastery Test Review
Uploaded by
Annabella Quevedo CampomanesCopyright:
Available Formats
DALAGUETE NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
MASTERY TEST
GENERAL PHYSICS 1
2nd SEMESTER
SY 2019-2020
I. Multiple Choice
Direction: Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write the letter in your answer sheet.
1. What forces are acting on a dropped book that falls to the floor?
A. Gravity only B. Gravity and air resistance C. Air resistance D. Friction only
2. A change to an objects motion is caused by...
A. Balanced forces B. Unbalanced forces C. Acceleration D. Velocity
3. When a car’s velocity is negative and its acceleration is negative, what is happening to the car’s motion?
A. The car slows down. B. The car speeds up C. The car travels at constant speed D. the car is at rest
4. Which of the following statements applies to the motion of a ball rising and then falling in free fall?
I. The ball has constant acceleration as it moves upward.
II. The ball has constant acceleration at the top of its path.
III. The ball has constant acceleration as it moves downward.
A. I only B. III only C. I and III D. I, II, and III
5. A car accelerates at 2 m/s . Assuming the car starts from rest, how much time does it need to accelerate to a
2
speed of 20 m/s?
A. 2 seconds B. 10 seconds C. 20 seconds D. 40 seconds
6. Which of the following explains the difference between speed and velocity?
A. One has motion, and the other does not B. One has direction, and the other does not.
C. One involves time, and the other does not D. One involves acceleration, and the other does not
7. A sled sliding on a flat, icy surface with a constant velocity is best described by _______.
A. Newton’s first law of motion for objects at rest B. Newton’s first law of motion for objects in motion
C. Newton’s second law of motion D. Newton’s third law of motion
8. A ball is thrown straight downward with a speed of 0.50 meter per second from a height of 4.0 meters. What is the speed of the ball
0.70 second after it is released? [Neglect friction.]
A. 0.50 m/s B. 7.4 m/s C. 9.8 m/s D. 15 m/s
9. An object is dropped from rest and falls freely 20 meters to Earth. When is the speed of the object 9.8 meters per second?
A. during the entire first second of its fall B. at the end of its first second of fall
C. during its entire time of fall D. after it had fallen 9.8 meters
10. How many significant figures does the following number have: 4.57 x 107?
A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 7
11. How many miles are there in 10560 ft?
A. 2.5 miles B. 3 miles C. 2 miles D. 1.5 miles
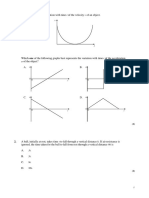
12. According to the graph above, during which interval is the
cat at rest? A. 0.0–5.0 s B. 10.0–15.0 s
C. 5.0–10.0 s D. 15.0–20.0 s
13. According to the graph above, the cat has the fastest speed
during which interval? A. 0.0–5.0 s B. 10.0–15.0 s
C. 5.0–10.0 s D. 15.0–20.0s
14. Where is the cat after 5 seconds?
A. 2 m B. 3 m C. 4m D. 5m
15. Which of the following statements applies to the motion of a ball rising and then falling in free fall?
I. The ball has constant acceleration as it moves upward.
II. The ball has constant acceleration at the top of its path.
III. The ball has constant acceleration as it moves downward.
A. I only B. III only C. I and III D. I,II, and III
16. Which would fall greater acceleration in a vacuum- a leaf or a stone?
A. the leaf B. the stone C. They accelerate at the same rate D. It is difficult to determine
17. The moon has a smaller mass than the Earth. If you were able to travel to the moon your weight would...
A. Increase B. Decrease C. Stay the same D. Vary with day and night
18. Which ball will hit the ground first?
A. Metal first, then plastic, then wood last
B. Wood first , then plastic, then metal last
C. They will all hit at the same time.
D. There is no way to tell.
wood Plastic metal
ball
MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE ( 10pts)
1. Dividing the total distance travelled by the total time is how to calculate average acceleration.
2. A change to an objects motion is caused by balanced forces.
3. Acceleration is the rate of change of an objects velocity in the given period of time.
4. Without any force to change it, an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion according to the law of
interaction.
5. Acceleration which points to the center of a circular path is called centrifugal acceleration.
6. Uniform motion is the motion of an object under the sole influence of gravity
7. The horizontal distance travelled by a projectile is called trajectory.
8. The single vector which represents the sum of the component vectors is called component vector.
9. For an object in Uniform accelerated motion its acceleration is zero.
10. In projectile motion its horizontal acceleration is zero and the vertical is 9.8m/s2
Problem Solving
1. A bike accelerates uniformly from 7.5m/s to a speed of 9.10 m/s over a distance of 50.5 m. Determine the
acceleration of the bike. ( 2pts)
2. Three players on a reality TV show are brought to the center of a large, flat field. Each is given a meter stick, a
compass, a calculator, a shovel, and (in a different order for each contestant) the following three displacements:
Find the resultant vector
( 5pts) A. 72.4 m, 32.0° east of north B. 57.3 m, 36.0° south of west C. 17.8 m due south
3. An airplane is flying 340 km/hr at 120 East of North. The wind is blowing 40 km/hr at 340 South of East. What is the
plane’s actual velocity?
4. A ball is dropped from the roof of a building. The brick strikes the ground in 1.50 s. You may ignore air resistance, so
the brick is in free fall.
A. How tall, in meters, is the building? C. Where is the brick after 1 second after released?
B. What is the magnitude of the brick’s velocity just before it reaches the ground?
5. A cannon fires a cannonball 500.0 m downrange when set at a 45.0 o angle. At what velocity does the cannonball
leave the cannon?
6. A diver plunges head first into a diving pool while travelling at 28.2 m s–1. Upon entering the water, the diver stops
within a distance of 4.00 m from the diving board. Consider the diver to be a single point located at her centre of mass
and assume her acceleration through the water to be uniform.
A. Calculate the average acceleration of the diver as she travels through the water.
B. How long does the diver take to come to a stop?
C. What is the speed of the diver after she has dived for 2.00 m?
7. While exploring a cave, a spelunker starts at the entrance and moves the following distances. She goes 75.0 m North,
250 m east, 125 m at an angle 30.0° north of east, and 150 m south. Find her resultant displacement from the cave
entrance.
8. A ball rolls off a desk at a speed of 3.0 m/s and lands 0.40 seconds later.
a) How far from the base of the desk does the ball land B. How high is the desk?
9. A punter in a football game kicks a ball from the goal line at 60.00 from the horizontal at 25.0 m/s.
A. Find the maximum height. (2pts) B. How far away does it hit the ground? (2pts)
10. Convert 1100 feet per second into miles per hour
You might also like
- Law of Cosines: C A + B - 2 - A - B - Cos Law of Sines: A/sina B/sinß C/sin Fluid, Air Drag: FD 1/2CD - Ar - R - VDocument8 pagesLaw of Cosines: C A + B - 2 - A - B - Cos Law of Sines: A/sina B/sinß C/sin Fluid, Air Drag: FD 1/2CD - Ar - R - VrileyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Past PaperDocument19 pagesChapter 6 Past PaperWahid AzizyNo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- General Physics-1 CPT U2Document4 pagesGeneral Physics-1 CPT U2Tracy Nicole MaurilloNo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 TQDocument9 pagesScience Grade 9 TQLae GadgudeNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 1 Test q4 Version 2-FreeDocument51 pagesGen Physics 1 Test q4 Version 2-FreeJoel PalopeNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics Reviewerfroilance100% (1)
- Physics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseDocument11 pagesPhysics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseCarmen JuranovicNo ratings yet
- UP College of Science Physics 71 1st Long Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesUP College of Science Physics 71 1st Long Exam ReviewAb YZNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest2Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest2Jasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- SemiDocument2 pagesSemiJoanne Diaz JacintoNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter TestDocument5 pages3RD Quarter TestABIGAIL BATALLERNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1 Summative ExamDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 1 Summative ExamLeizel MundoNo ratings yet
- PretestDocument6 pagesPretestEdna Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- 50items EXAM. TUPAG E.Document5 pages50items EXAM. TUPAG E.Erika Mae Tupag0% (1)
- Test BankDocument26 pagesTest Banksani biNo ratings yet
- 4Q Science G9Document3 pages4Q Science G9Kimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension ReviewerDocument15 pagesMotion in One Dimension ReviewerJilliana TumanganNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document26 pagesModule 2James MinaNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Science 9Document3 pages4th Summative Test Science 9odette carzanoNo ratings yet
- LT1.3 Projectile Motion ANSDocument3 pagesLT1.3 Projectile Motion ANSRed GallegoNo ratings yet
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Document4 pagesReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.No ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Kawit 2017Document15 pagesMath 8 Kawit 2017HELMA B. JABELLONo ratings yet
- Unit TestDocument4 pagesUnit TestNicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- G7 - 3rd Quarterly ExamDocument4 pagesG7 - 3rd Quarterly ExamKarina Manalo100% (1)
- Science Revision G7Document17 pagesScience Revision G7Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- PhysicsLAB - 2006 Physics Quiz Bowl (Part 1)Document6 pagesPhysicsLAB - 2006 Physics Quiz Bowl (Part 1)Bishoy AkmalNo ratings yet
- University of The Philippines College of ScienceDocument10 pagesUniversity of The Philippines College of SciencecrizwiseNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter TestDocument2 pages4TH Quarter TestCathyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan MomentumDocument6 pagesLesson Plan MomentumMarie VicNo ratings yet
- Free FallDocument2 pagesFree FallShalom OhNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q3 - Science - 7 - Aster Madalla - ASTERIO MADALLADocument7 pagesTQ - Q3 - Science - 7 - Aster Madalla - ASTERIO MADALLAPhilip Atma100% (2)
- Genphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingDocument5 pagesGenphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingRonilo Rivera CaringalNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd Periodic TestDocument6 pagesScience 3rd Periodic TestRochelle VilelaNo ratings yet
- Module 9 Going PlacesDocument36 pagesModule 9 Going PlacesMelvin Cabonegro100% (1)
- Physics Grade 11 1st Work SheetDocument8 pagesPhysics Grade 11 1st Work SheetMikas TesfuNo ratings yet
- Science 9 4th Quarter Summative Test 1Document2 pagesScience 9 4th Quarter Summative Test 1Yuno KeityNo ratings yet
- Basic PhysicsDocument4 pagesBasic PhysicsDiane Marr Nicolas Dencio100% (1)
- Uclm Cesafi QuestionsDocument1 pageUclm Cesafi QuestionsBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerNeil VelascoNo ratings yet
- Test-Questions-Physics IDocument7 pagesTest-Questions-Physics INheszie Cortez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Summative-1Document4 pagesQ4 Summative-1artNo ratings yet
- Physics 3 Probset 1 2nd 13-14Document2 pagesPhysics 3 Probset 1 2nd 13-14Aaron Paul AguasNo ratings yet
- Ade8 Pilot Test 1ST &2ND Qtr.Document5 pagesAde8 Pilot Test 1ST &2ND Qtr.Mae Biñas AngelesNo ratings yet
- Physics Quiz #2: Forces, Motion, and SpeedDocument20 pagesPhysics Quiz #2: Forces, Motion, and SpeedRovhie FerminNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment For Module 1 and 2 Science 7Document5 pagesSummative Assessment For Module 1 and 2 Science 7Fe GullodNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion: WEEK 3-4Document3 pagesForces and Motion: WEEK 3-4Jerizza ParafinaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Exam in Science 7Document4 pages3rd Periodical Exam in Science 7KeannoNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet One 9th 22Document3 pagesWork Sheet One 9th 22Firaol TegenuNo ratings yet
- Physics 201 (003N) Fall 2010 - Midterm I.AnswersDocument7 pagesPhysics 201 (003N) Fall 2010 - Midterm I.AnswersXiao LinNo ratings yet
- AGA KHAN SCHOOLS PHYSICS EXAMDocument10 pagesAGA KHAN SCHOOLS PHYSICS EXAMHaseeb MirzaNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesPhysics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsNader HijaziNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Tow 9thDocument3 pagesWork Sheet Tow 9thFiraol TegenuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Quiz2Document1 pageUnit 4 Quiz2LuisNo ratings yet
- Governor’s Hills Science School 1st Quarter Physics ExamDocument5 pagesGovernor’s Hills Science School 1st Quarter Physics ExamAriane DionisioNo ratings yet
- Summative Test (Force and Motion)Document3 pagesSummative Test (Force and Motion)Ann ClariceNo ratings yet
- Impulse Momentum QuizDocument1 pageImpulse Momentum QuizAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument7 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Hydrometeorological HazardsAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- DLP Redox Reaction BiologyDocument2 pagesDLP Redox Reaction BiologyAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- DLP Day Molecular Formula Given The Molar MassDocument4 pagesDLP Day Molecular Formula Given The Molar MassAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Honors Physics - Impulse and MomentumDocument48 pagesHonors Physics - Impulse and MomentumAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Vector Addition November 15Document2 pagesVector Addition November 15Annabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- For Observation Polar MoleculesDocument4 pagesFor Observation Polar MoleculesAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Impulse Momentum QuizDocument1 pageImpulse Momentum QuizAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- DLP July Free Body Diagram January 10Document4 pagesDLP July Free Body Diagram January 10Annabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Structures, Functions and ClassificationDocument59 pagesProteins: Structures, Functions and ClassificationAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- DLP Catapult Activity January 6Document4 pagesDLP Catapult Activity January 6Annabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Proteins Problem SetDocument2 pagesProteins Problem SetAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Proteins Problem SetDocument2 pagesProteins Problem SetAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 1 - Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument3 pagesPROBLEM SET 1 - Amino Acids and PeptidesAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Proteins Problem SetDocument2 pagesProteins Problem SetAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET 1 - Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument3 pagesPROBLEM SET 1 - Amino Acids and PeptidesAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Physics Test SpecificationsDocument4 pagesChemistry and Physics Test SpecificationsAnnabella Quevedo CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Upcat Reviewer PhysicsDocument7 pagesUpcat Reviewer PhysicsRogelio EscobarNo ratings yet
- Physicsaholics DPP - 1 SolutionsDocument3 pagesPhysicsaholics DPP - 1 SolutionsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Momento de Inercia-DefinicionDocument4 pagesMomento de Inercia-Definicionluis quitianNo ratings yet
- Magnetism NotesDocument19 pagesMagnetism NotesAnonymous JM62lPsJYp100% (2)
- OCR M1 January 2011 PaperDocument4 pagesOCR M1 January 2011 PaperDan S-RajahNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Practice Problems Target IIT ADVANCE-2019Document4 pagesMechanics Practice Problems Target IIT ADVANCE-2019Shivam JaggiNo ratings yet
- A2 Circular Motion QuestionsDocument11 pagesA2 Circular Motion Questionsaby251188No ratings yet
- Newton's Second Law AccelerationDocument6 pagesNewton's Second Law AccelerationJamie JimenezNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion Chapter 2 Notes Part2Document4 pagesForce and Laws of Motion Chapter 2 Notes Part2A48 SHAIKH WAJIDNo ratings yet
- PT 1Document8 pagesPT 1LOVELESH KHATTERNo ratings yet
- Test 45 - Electric Charges & Fields - Middle of PyramidDocument7 pagesTest 45 - Electric Charges & Fields - Middle of PyramidJay PatelNo ratings yet
- What is weight and mass? The difference explainedDocument13 pagesWhat is weight and mass? The difference explainedPrince SanjiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C MomentumDocument34 pagesAP Physics C MomentumShamanthakNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Adrian CadizNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesCircular Motion Chapter Notes陈伟明No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2021 Physics F4 KSSM 2021Document42 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2021 Physics F4 KSSM 2021MijieyNo ratings yet
- Charged ParticlesDocument19 pagesCharged Particlesjonan_evansNo ratings yet
- Physics 2305 Lab 11: Torsion PendulumDocument14 pagesPhysics 2305 Lab 11: Torsion PendulumJason LeeNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy PDFDocument28 pagesWork Power Energy PDFShabbir KhanNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument38 pagesSpeed and VelocityAlyssa Grace BrandesNo ratings yet
- What Is A Force? How Do Forces Combine? How Does Friction Affect Motion?Document15 pagesWhat Is A Force? How Do Forces Combine? How Does Friction Affect Motion?Gaurav SwamiNo ratings yet
- Physics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesPhysics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsLone50% (2)
- Test 21kinematics20151002Document26 pagesTest 21kinematics20151002laguiiniNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument17 pagesMomentumtomadrenovacNo ratings yet
- LorentzDocument7 pagesLorentzvedakshi sapraNo ratings yet
- BL-PHYC-2122-LEC-1922S General Physics 2 PDFDocument56 pagesBL-PHYC-2122-LEC-1922S General Physics 2 PDFDesiree Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Complete Mechanics QuestionsDocument38 pagesComplete Mechanics QuestionsEdumaaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesPhysics: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelD S A DHAKA SPACE AGENCYNo ratings yet
- KOM Program PracticalDocument7 pagesKOM Program PracticalKeshav PagarNo ratings yet