100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesSCRAPBOOK
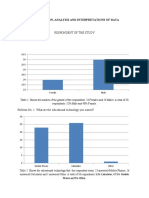
1. Communication is a complex process involving a sender encoding a message, a receiver decoding the message, and potential interference or context that can distort the message.
2. There are several models that describe the communication process, including Shannon and Weaver's model which involves encoding, transmitting, receiving and decoding a message, and Schramm's model which focuses on how meanings are transferred between individuals.
3. Effective communication requires strong listening skills like being engaged, paying attention to nonverbal cues, managing stress, and asserting yourself, as well as verbal communication skills that can vary across cultures.
Uploaded by
Rachel CuratoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views4 pagesSCRAPBOOK
1. Communication is a complex process involving a sender encoding a message, a receiver decoding the message, and potential interference or context that can distort the message.
2. There are several models that describe the communication process, including Shannon and Weaver's model which involves encoding, transmitting, receiving and decoding a message, and Schramm's model which focuses on how meanings are transferred between individuals.
3. Effective communication requires strong listening skills like being engaged, paying attention to nonverbal cues, managing stress, and asserting yourself, as well as verbal communication skills that can vary across cultures.
Uploaded by
Rachel CuratoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Communication Overview: Explores the importance of communication in everyday life, highlighting its characteristics and processes involved in message delivery.
- Listening Skills: Provides insights into effective listening principles and techniques to enhance communication engagement.
- Intercultural Communication: Discusses the dynamics of communicating across different cultures, focusing on verbal and non-verbal communication.
- Types of Speech Context: Examines various speech contexts observed in communication and their distinct characteristics.
- Self-Concept and Self-Awareness: Highlights the links between self-concept, self-awareness, and communication, emphasizing strategies for improvement.