Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Purcom Reviewer
Uploaded by
gimboongaling4890 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesPurcom Reviewer
Uploaded by
gimboongaling489Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PURCOM Consistency- Maintain a uniform message
across various communications.
Communication - It is the mutual exchange of
Courtesy- Be polite and respectful in your
information, ideas, and understanding by any effective
interactions.
means.
Concreteness- Use specific facts and details to
Verbal Communication - It includes face-to-face enhance understanding.
conversations, speech, telephonic conversation, video, Completeness- Provide all necessary
radio, television, voice over internet. information for a comprehensive
understanding.
Non-Verbal - Is the sending or receiving of wordless
Consideration- Take into account the needs
messages. Such as gestures, body language, posture,
and perspectives of your audience.
tone of voice or facial expressions.
Correctness- Ensure accuracy in your message
Elements of Communication to build trust and credibility.
Feedback- Encourage and be receptive to
1. Sender - She/He may be called the source,
feedback for effective communication.
encoder, speaker, or communicator
Listening- Actively listen to understand others
2. Message - It may consist of ideas, opinion,
and respond appropriately.
information, feeling or attitude of the sender.
3. Chanel - A pathway or medium through which Communication Ethics
the message travels to reach its destination.
Ethics - deals with values relating to human conduct,
4. Receiver - A person or medium through which
with respect to the rightness and wrongness of certain
the message travels to reach its destinations.
actions and to the goodness and badness of the motives
5. Feedback - The receiver's response that
and ends of such actions
provides information to the sender
6. Noise - A form of distortion, barrier, or obstacle Fundamental of ethical communication
that occurs in an of the oral communication
process. Responsible thinking
7. Adjustment - Done if the message is distorted Decision making
or is not clearly understood by the receiver. Development of relationships and communities
8. Context - It is the situation from which the 1. Contexts
communication is done. 2. Cultures
3. Channels
Impacts of Globalization on Communication 4. Media
1. Virtual Interaction Unethical communication – threatens the quality of all
2. Cultural awareness in speech communication and consequently the individuals and
3. Cultural awareness in Body language the society.
4. Time Differences
Types of unethical communication
Impacts of Globalization on Global Communication
1. Coercive
1. Availability of information 2. Destructive
2. Business Conduct 3. Deceptive
3. Social awareness 4. Intrusive
4. The problem 5. Secretive
6. Manipulative-exploitative
Communication Principles
Principles of Ethical Communication
Clarity - Ensure your message is clear and easy
to understand. Advocate
Conciseness- Express your ideas in a brief and Truthfulness, Accuracy, Honesty
to-the-point manner. Endorse freedom of expression
Strive to understand 2. Physical Disabilities
Promote Access to communication 3. Psychological Barriers
Promote communication climates of caring and Lack of attention
mutual understanding Poor retention of communication
Condemn Communication Lack of trust
Closed mind
CODE OF ETHICS - are moral guidelines that are used to
4. Interpersonal Barriers
help assist people in making decisions, to tell the
Gender issues
difference between 'right' and 'wrong' and to utilize this
Completion on environment
understanding to make ethical choices
Culture
3 Level of code of ethics
Ethics in Communication
1. Code of ethics (social issues)
respect privacy and confidentiality
2. Code of conduct (influence to behavior of
Actively listen
employees)
Strive to understand
3. Code of practice (professional responsibility)
Avoid negative tone
Types of communication Do not interrupt
Speak from your own experience
Verbal
Speak from the truth
Non-Verbal
Accept responsibility
Intrapersonal
Interpersonal Forms of Non-Verbal communication
Extended
1. Kinesis – body movement, facial expression
Intercultural
2. Chronemics – value in space and structure
Organization
of time
Written
3. Proxemics – interpersonal intimate contact
General Purpose of effective communication when socialization happens
4. Paralinguistic – tone of your voice and
Purpose
volume
Audience 5. Haptics – communication in touch
Topic 6. Oculesics – communication through eyes.
Adjust your speech/writing to the context of the
situation
Work with your feedback
Principles of effective oral communication
Be clear with your purpose
Be complete with the message
Be concise
Be natural
Be specific and timely
Barriers of communication
1. Physical Barriers
Noise
Temperature
Medium Disturbance
Work place
You might also like
- Oral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Document6 pagesOral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Katleya Balitaan75% (8)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesPurposive CommunicationMiguel Jude Espanto Bautista Jr.100% (1)
- Purposive CommDocument3 pagesPurposive CommCherith May DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication - ReviewerDocument4 pagesOral Communication - ReviewerSamsamNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerDesiree QuinioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Ged 106 CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer in Ged 106 Communicationmeanantig08No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (GNED05)Document3 pagesLesson 1 (GNED05)Ralph ChavezNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument7 pagesPurposive CommunicationKathlene NañawaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LECTUREDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication LECTUREJazzel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business CorrespondenceDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Business CorrespondenceRoberto Velasco MabulacNo ratings yet
- Purcomm ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurcomm ReviewerkiaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LectureDocument18 pagesPurposive Communication LectureRandolf MartinezNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationScythe RyuNo ratings yet
- SCRAPBOOKDocument4 pagesSCRAPBOOKRachel Curato100% (1)
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument2 pagesOral Communication Reviewerralpharchie01No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 on Communication Noise and ProcessDocument3 pagesLesson 1 on Communication Noise and ProcessRalph ChavezNo ratings yet
- Social Context - The Relationship That ExistsDocument16 pagesSocial Context - The Relationship That ExistsAnonymous x1onhdRNo ratings yet
- Purcomm - Lesson 1-3Document3 pagesPurcomm - Lesson 1-3GGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Comm Reviewerdingomez01No ratings yet
- C06Document9 pagesC06Claire ElyseNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Prelim ReviewerDocument3 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Prelim ReviewerkyladimaanoNo ratings yet
- Anna BSTM Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesAnna BSTM Purposive CommunicationespeletatiftciNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context ReviewDocument37 pagesOral Communication in Context ReviewArnez Jewell Dotillos100% (8)
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument2 pagesOral Communication ReviewereukiNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesOral Communicationshoti lahNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesReviewer - Purposive CommunicationHannah May CapitinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For The 1ST Summative Examination For English 1Document8 pagesReviewer For The 1ST Summative Examination For English 1FrancisIanNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Listening Skills With These Active Listening TechniquesDocument5 pagesImprove Your Listening Skills With These Active Listening TechniquesLory TenorioNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION NotesDocument9 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION NotesRuth Micabalo AmistosoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument9 pagesREVIEWERAtty Joven Allen AsidoNo ratings yet
- (Gec06) Purposive Communication Chapter 1 3Document11 pages(Gec06) Purposive Communication Chapter 1 3alexburguetaNo ratings yet
- Eng 3a - Note1Document3 pagesEng 3a - Note1chezyl cadinongNo ratings yet
- Oral Com and Fabm ReviewerDocument6 pagesOral Com and Fabm ReviewerEzra Mae ValdezNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationABM - TOLENTINO, JOANNA MARIE DC.No ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer For GE 5Document3 pagesMidterms Reviewer For GE 5Aquino, Jasmine C.No ratings yet
- 1 The Components of The Communication ProcessDocument3 pages1 The Components of The Communication ProcessColleena CortesNo ratings yet
- PurCom Reviewer For FinalsDocument8 pagesPurCom Reviewer For FinalsTheaNo ratings yet
- Pointers Oral Comm.Document2 pagesPointers Oral Comm.Rose Ann Bereber100% (3)
- Hand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommDocument4 pagesHand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommRoland John MarzanNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Notes - MOD1-7Document8 pagesOral Comm Notes - MOD1-7Ryan Kyle HamoayNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Communication for StudentsDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Communication for StudentsJohara BayabaoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Communication ReviewerReychel LunaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument4 pagesOral CommunicationJuliene Ermie Parel BerameNo ratings yet
- PComm Lesson 1 Ethics and PrinciplesDocument10 pagesPComm Lesson 1 Ethics and PrinciplesShanley ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesReviewer Oral CommunicationRyanNo ratings yet
- Nature and process of communicationDocument3 pagesNature and process of communicationRyan100% (1)
- Oral Com ReviewerDocument4 pagesOral Com ReviewerLee Andrei AlarconNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Cor 001Document14 pagesNote Taking Cor 001Clitz Myle Ochea YmbongNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument4 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationJean De PabloNo ratings yet
- 2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationDocument27 pages2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationNoemie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Principles of CommunicationDocument3 pagesPrinciples of CommunicationDhmi yassinNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Topic 5Document3 pagesOral Communication Topic 5jaja rumbaoaNo ratings yet
- Communication and DocumentationDocument4 pagesCommunication and DocumentationCamille SanguyoNo ratings yet
- Prelims Eng Notes CHP 1 3Document8 pagesPrelims Eng Notes CHP 1 3PadreRon AlquisadaNo ratings yet
- OC HandoutDocument6 pagesOC HandoutMarc Anthony FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument8 pagesOral Communication ReviewerLeonard SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Influence Message Quality, Accuracy, Clarityinclude Age, Gender, Values, Beliefs, Culture, Experiences, NeedsDocument5 pagesInfluence Message Quality, Accuracy, Clarityinclude Age, Gender, Values, Beliefs, Culture, Experiences, NeedsFrenzy PopperNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument8 pagesOral CommunicationAlliah ManilaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Definition and Process of Communication 1Document23 pagesWeek 1 Definition and Process of Communication 1alexancog456No ratings yet
- Talk with Confidence: A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless Communication with Anyone, Anytime, About AnythingFrom EverandTalk with Confidence: A Comprehensive Guide to Effortless Communication with Anyone, Anytime, About AnythingNo ratings yet
- Cogent Arguments and Psychological Impediments To Them: Week 8Document36 pagesCogent Arguments and Psychological Impediments To Them: Week 8Mohamed K MarahNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour Set 17Document5 pagesOrganisational Behaviour Set 17SUNIL SONAWANENo ratings yet
- Teacher Student RelationshipDocument3 pagesTeacher Student RelationshipHuma AliNo ratings yet
- Building Effective Youth TeamsDocument3 pagesBuilding Effective Youth TeamsRocris Glenn Aldave IdulNo ratings yet
- Profed04 Chapter 8Document6 pagesProfed04 Chapter 8RobNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 SociologyDocument29 pagesLecture 11 SociologyMehar ShaniNo ratings yet
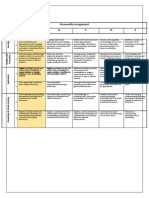
- Example Personality AssigmentDocument6 pagesExample Personality Assigmentapi-461452779No ratings yet
- Cross-Cultural Management - Case StudiesDocument9 pagesCross-Cultural Management - Case StudiesMohammed AldhaheriNo ratings yet
- Stages of Child Development from Early to Middle ChildhoodDocument16 pagesStages of Child Development from Early to Middle ChildhoodwintermaeNo ratings yet
- Bolton Leadership StylesDocument2 pagesBolton Leadership StylesShashveena Shamira A/P KanapathyNo ratings yet
- Counselling in Case WorkDocument6 pagesCounselling in Case Worknjsince1998No ratings yet
- Observation ToolsDocument4 pagesObservation ToolsLeodigaria ReynoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Culture: What Shapes a Company's CultureDocument18 pagesOrganizational Culture: What Shapes a Company's CultureweirdwolfvortexNo ratings yet
- Various Mental Illness Caused by Social MediaDocument3 pagesVarious Mental Illness Caused by Social Mediaapi-597656089No ratings yet
- Impact of Gender Stereotype On Secondary School Students' Self-Concept and Academic AchievementDocument10 pagesImpact of Gender Stereotype On Secondary School Students' Self-Concept and Academic AchievementMayNo ratings yet
- Job SatisfactionDocument4 pagesJob SatisfactionPeniel NisperosNo ratings yet
- The in Uence of Parenting Style On Academic Achievement and Career PathDocument6 pagesThe in Uence of Parenting Style On Academic Achievement and Career PathELLEE LEENo ratings yet
- Perdev Finals ShsDocument6 pagesPerdev Finals ShsRizah HernandezNo ratings yet
- Enclosure For SY - 2022-2023 - School Based Consolidated - AllDocument10 pagesEnclosure For SY - 2022-2023 - School Based Consolidated - AllMimi Ng PinasNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Stigma - EditedDocument8 pagesMental Health Stigma - EditedRoman -No ratings yet
- HBO Lesson 4 - Values, Attitude, and Job SatisfactionDocument9 pagesHBO Lesson 4 - Values, Attitude, and Job SatisfactionJoe P PokaranNo ratings yet
- Individual Development Planning: Competency Self-AssessmentDocument10 pagesIndividual Development Planning: Competency Self-AssessmentmeandmNo ratings yet
- QuestionnairesDocument6 pagesQuestionnairesAriel OyardoNo ratings yet
- Obiora and Osuoha PDFDocument13 pagesObiora and Osuoha PDFjudipatNo ratings yet
- Guide To Crisis Intervention 5th Edition Kanel Test BankDocument4 pagesGuide To Crisis Intervention 5th Edition Kanel Test Bankquachhaitpit100% (36)
- Preschoolers' Socio-Emotional DevelopmentDocument11 pagesPreschoolers' Socio-Emotional DevelopmentPrincess Crisha VelascoNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument10 pagesNotesZhira SingNo ratings yet
- Interview ProcessDocument8 pagesInterview ProcessPulkit GargNo ratings yet
- Lack of Parental Guidance Is Responsible For Children Being ViolentDocument10 pagesLack of Parental Guidance Is Responsible For Children Being ViolentGaspar GuedesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Leadership Qualities Through Role Model StudyDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Leadership Qualities Through Role Model StudyAvnish AhalawatNo ratings yet