Professional Documents
Culture Documents
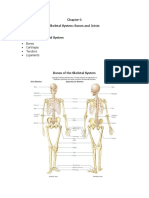
Skeletal System
Uploaded by
Melanie Galedo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Skeletal System.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views3 pagesSkeletal System
Uploaded by
Melanie GaledoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Skeletal System
Major Bones of the Skeletal System
The bone, cartilage,
tendons, and
ligaments of the
skeletal system
are all connective
tissues. Their
characteristics are
largely determined
by the composition
of their extracellular Yellow marrow consists mostly of adipose
matrix. Tissue
Red marrow consists of blood-forming cells and is the
only site of blood formation in adults. Children’s
bones have proportionately more red marrow than do
Type of connective tissue.
adult bones because, as a person ages, red marrow is
Proteoglycans- are large molecules consisting of mostly replaced by yellow marrow.
polysaccharides attached to core proteins Periosteum- Most of the outer surface of bone is
Cartilage- contains collagen and proteoglycans. covered by dense connective tissue
The matrix always contains collagen, ground substance, Endosteum- is a thin vascular membrane of connective
and other organic tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue that
Collagen-is a tough, ropelike protein.it makes forms the medullary cavity of long bones
cartilage tough, Histology of Bone
Four categories of bone The periosteum and endosteum contain osteoblasts
-Long bones are longer than they are wide. Most which function in the formation of bone, as well as in
of the bones of the upper and lower limbs are long the repair and remodeling of bone.
bones. Osteoclasts- bone-eating cells are also present and
- Short bones are approximately as wide as they are contribute to bone repair and remodeling by removing
long; examples are existing bone.
the bones of the wrist and ankle. Lamellae- Bone is formed in thin sheets of extracellular matrix
- Flat bones have a relatively thin, flattened shape. called lamellae
Examples of flat bones are certain skull bones, the Lacunae- with osteocytes located between the
ribs, the scapulae (shoulder blades), and the sternum. lamellae within spaces called lacunae. a cavity or
- Irregular bones include the vertebrae and facial depression
Canaliculi- little canal
bones, which have shapes
Compact bone- is mostly solid matrix and cells.
that do not fit readily into the other three categories.
Spongy bone, or cancellous bone, consists of a lacy network
Structure of a Long Bone of bone with many small, marrow-filled spaces.
Diaphysis- long bone consists of a central shaft, Compact Bone
Epiphysis- the end part of a long bone, initially growing Compact bone (figure 6.3) forms most of the diaphysis of a
separately from the shaft.\ long bone and the thinner surfaces of all other bones.
articular cartilage covers the ends of the epiphyses Osteons- Each osteon consists of concentric rings of lamellae
where the bone articulates (joins) with other bones. surrounding a central canal.
epiphyseal plate, or growth plate- composed of
cartilage, between each epiphysis and the diaphysis The
epiphyseal plate is where the bone grows in length
Epiphyseal line- When bone growth stops, the cartilage
of each epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone and
becomes an epiphyseal line
Bones contain cavities, such as the large medullary
cavity in the diaphysis, as well as smaller cavities in the
epiphyses of long
bones and in the interior of other bones.
Spongy Bone
Spongy bone- is located mainly in the epiphyses of long
bones.Spongy bone consists of delicate interconnecting
rods or plates of bone called trabeculae
Trabeculae-Spongy bone consists of delicate
interconnecting rods or plates of Bone. which
resemble the beams or scaffolding of a building. Like
scaffolding, the trabeculae add strength to a bone
without the added weight that would be present if the
bone were solid mineralized matrix.
Bone Ossification
Ossification-( to make) is the
formation of bone by osteoblasts. After an osteoblast
becomes completely surrounded by bone matrix, it
becomes a mature bone cell, or osteocyte.
Skull
The 22 bones of the skull are divided into those of the
braincase and those of the face.
braincase, which encloses the cranial cavity, consists
of 8 bones that immediately surround and protect the
brain.
facial bones- 14 bones form the structure of the
face. Thirteen of the facial bones are rather solidly
connected to form the bulk of the face. The mandible,
however, forms a freely movable joint with the rest of
the skull. There are also three auditory ossicles (in
each middle ear (six total).
You might also like
- Davao Doctors College Nursing Graduates EmployabilityDocument130 pagesDavao Doctors College Nursing Graduates EmployabilityMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- 01 Human Head Anatomy Defining StructureDocument35 pages01 Human Head Anatomy Defining StructureMarcio de Freitas100% (10)
- Anatomy Note PDFDocument67 pagesAnatomy Note PDFanon_251667476No ratings yet
- Skeletal System: WorksheetsDocument8 pagesSkeletal System: WorksheetsAbigailBarrionGutierrezNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms-1Document65 pagesAnaphy Midterms-1kiann130405No ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesThe Skeletal SystemCharlie CharlesNo ratings yet
- (W9) The Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages(W9) The Skeletal SystemReign Heart HayahayNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesIntoduction To The Skeletal SystemDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Skeletal SystemArlen Joy V. AMPARONo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument15 pagesSkeletal SystemRaven LacsonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Document67 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 4Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Bone AnatomyDocument11 pagesBone AnatomyLiam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 (Skeletal System)Document27 pagesUNIT 2 (Skeletal System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - System AnatomyDocument89 pagesSkeletal - System AnatomysanayaNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Skeletal SystemDocument45 pages7.0 Skeletal System[R2A] Khadijah Azlan100% (1)
- Bone Tissue Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue) Is A Hard Tissue, A Type of Dense Connective Tissue. It HasDocument1 pageBone Tissue Bone Tissue (Osseous Tissue) Is A Hard Tissue, A Type of Dense Connective Tissue. It HasDean PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Physiology (Chapter 6 - Skeletal System)Document39 pagesAnatomy - Physiology (Chapter 6 - Skeletal System)Avi ZychNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MusclesDocument20 pagesSkeletal MusclesDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MariebDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Mariebmissy23papNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesReading Material Skeletal SystemShamel CurrayNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemArra BeatrizNo ratings yet
- ALVEOLAR BoneDocument72 pagesALVEOLAR BoneArchana50% (2)
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMatthew YoungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Skeletal 1Document196 pagesIntroduction To Skeletal 1Earl TrinidadNo ratings yet
- SkeletonDocument15 pagesSkeletonPlacido Edgar MagaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - System AnatomyDocument130 pagesSkeletal - System Anatomyhamnafaisall8No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Skeletal System: Skeleton Dried Up BodyDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of The Skeletal System: Skeleton Dried Up BodyKenn yahweexNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pages3.1 Skeletal SystemAndriy GarcíaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 6 ANAPHY TransesHoly HaeinNo ratings yet
- (Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages(Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Movement (Human Skeleton)Document65 pagesMovement (Human Skeleton)Keyondre McBeanNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Persepsi MGG I-1Document19 pagesPersamaan Persepsi MGG I-1mariaqibtyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cartilage and BoneDocument27 pages1.2 Cartilage and BonePema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Bones and Bone Tissues: Chapter 6Document86 pagesBones and Bone Tissues: Chapter 6humag143No ratings yet
- Unit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Document78 pagesUnit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Gifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Zoo LecDocument27 pagesReviewer Zoo LecayeyedumpNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument27 pagesSkeletal SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- THE SKELETAL SYSTEM I - Bone TissueDocument2 pagesTHE SKELETAL SYSTEM I - Bone TissueAmirah AnfNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal Systemnichole2anne2rodriguNo ratings yet
- Types of Bones Long BonesDocument20 pagesTypes of Bones Long BonesBharat Singh BanshiwalNo ratings yet
- Bone StructureDocument21 pagesBone Structuresapnakumarigurjar108No ratings yet
- Bone Physiology: Structure and FunctionsDocument75 pagesBone Physiology: Structure and FunctionsAnalhaq ShaikhNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 pagesHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System ReviewerDocument14 pagesSkeletal System ReviewerDaniel DanielNo ratings yet
- 02 Skeletal SystemDocument32 pages02 Skeletal SystemHarshika KDGNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesThe Skeletal SystemrizzamaearancesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: CartilageDocument20 pagesSkeletal System: CartilageGrace PascualNo ratings yet
- 6 SkeletalDocument14 pages6 SkeletalprincessstephNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Skeletal SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- PhysioDocument14 pagesPhysioEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal 6Document28 pagesSkeletal 6BSN-2F Neutral Axis SiazonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesDocument90 pagesUnit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesAbi .JNo ratings yet
- TARI ReferensiDocument13 pagesTARI ReferensitariNo ratings yet
- Osteomalacia, Bones Are Mineral-Deficient and Easily DeformedDocument16 pagesOsteomalacia, Bones Are Mineral-Deficient and Easily DeformedVarel JoanNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone DR DeepakDocument107 pagesAlveolar Bone DR DeepakDeepak Kumar100% (2)
- Skeletal System LectureDocument3 pagesSkeletal System LectureFrederick ManaigNo ratings yet
- Bones & Cartilage: Components of the Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesBones & Cartilage: Components of the Skeletal SystemPriyanjali SainiNo ratings yet
- Bone TissueDocument66 pagesBone TissueFunikawati Baldiyah100% (1)
- Anaphy Prelims ReviewerDocument11 pagesAnaphy Prelims ReviewerMariz Elizabeth TaytayNo ratings yet
- Espartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDocument7 pagesEspartero Chapter3, Individual TaskDanelleNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System - JaniDocument20 pagesSkeletal System - Janijanijannahh17No ratings yet
- Bone, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandBone, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- NRES1WEEK2Document17 pagesNRES1WEEK2Melanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesPostoperative Case AnalysisMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Signs and symptoms of heart failureDocument9 pagesSigns and symptoms of heart failureMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing: Mammoplasty PlasticDocument10 pagesPerioperative Nursing: Mammoplasty PlasticMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocument15 pagesAn Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Maiso LawsprogramsDocument58 pagesMaiso LawsprogramsMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument3 pagesQUIZMelanie Galedo100% (1)
- An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocument15 pagesAn Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document23 pagesPresentation 1Melanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument3 pagesQUIZMelanie Galedo100% (1)
- Discover self-love through music's healing powerDocument1 pageDiscover self-love through music's healing powerMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- New CPDocument3 pagesNew CPMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Logo QuizDocument1 pageLogo QuizMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Labs 2Document12 pagesLabs 2Melanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Labs 2Document6 pagesLabs 2Melanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Benefits of BreastfeedingDocument2 pagesBenefits of BreastfeedingMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Nursing's Evolution from Nightingale to TodayDocument3 pagesNursing's Evolution from Nightingale to TodayMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- New CPDocument3 pagesNew CPMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Galedo. CHNDocument9 pagesGaledo. CHNMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- The Philippines Is Primarily Considered A Newly Industrialized CountryDocument3 pagesThe Philippines Is Primarily Considered A Newly Industrialized CountryMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Purpose AiraDocument1 pagePurpose AiraMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- MCN PartialDocument9 pagesMCN PartialMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation BenefitsDocument1 pageBlood Donation BenefitsMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Article IDocument3 pagesArticle IMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Bad ThingDocument1 pageBad ThingMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Blood DonationDocument2 pagesImportance of Blood DonationMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- IsoimmunisationDocument12 pagesIsoimmunisationMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Rumah Sakit Medina: Data Tarif RadiologiDocument5 pagesRumah Sakit Medina: Data Tarif Radiologirsmedina adminNo ratings yet
- Lecture Activity #5 - 2Document2 pagesLecture Activity #5 - 2ReneeNo ratings yet
- Asthi Dhatu - Ayurveda and Modern Perspective: World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchDocument5 pagesAsthi Dhatu - Ayurveda and Modern Perspective: World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical ResearchKirti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Muscle Energy Technique NotesDocument3 pagesCervical Muscle Energy Technique NotesLana Naila AmerieNo ratings yet
- Norma Lateralis: SkullDocument4 pagesNorma Lateralis: SkullJack Marlow0% (1)
- Landmarks in Panoramic RadiographyDocument10 pagesLandmarks in Panoramic RadiographyShailah Leilene Arce BrionesNo ratings yet
- Müller AO Classification of Fractures: Long BonesDocument8 pagesMüller AO Classification of Fractures: Long BonesBruno OhashiNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionDocument81 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- The Total Number of Bones in The Human BodyDocument3 pagesThe Total Number of Bones in The Human BodyImam SetiabudiNo ratings yet
- Gross Veterinary Anatomy: Binarao, Maria Beatriz L. DVM Ii-A 1Document3 pagesGross Veterinary Anatomy: Binarao, Maria Beatriz L. DVM Ii-A 1BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning and Special Procedure1Document38 pagesRadiographic Positioning and Special Procedure1renred1225No ratings yet
- Intro Bone With TypesDocument15 pagesIntro Bone With TypesKiranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Midterm 2Document92 pagesAnatomy Midterm 2Cassandra DavisNo ratings yet
- Kamar Identitas Diagnosis Lab / EKG / Xfoto Thoraks Terapi: List Pasien OrthopediDocument6 pagesKamar Identitas Diagnosis Lab / EKG / Xfoto Thoraks Terapi: List Pasien OrthopediCathy KarundengNo ratings yet
- VISWASS SCHOOL & COLLEGE OF NURSING: THE SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument33 pagesVISWASS SCHOOL & COLLEGE OF NURSING: THE SKELETAL SYSTEMshubham vermaNo ratings yet
- Thorax BonesDocument59 pagesThorax BonesMido TooNo ratings yet
- Middle Ear AnatomyDocument28 pagesMiddle Ear AnatomySriharsha TikkaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFserenafinnodx100% (9)
- Anatomy of TMJ and Its Role in ProsthodonticsDocument72 pagesAnatomy of TMJ and Its Role in ProsthodonticsBaishali GhoshNo ratings yet
- Holter Test Electrode Placement GuideDocument17 pagesHolter Test Electrode Placement GuideancaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Maturity Indicators: Assessing Growth PotentialDocument38 pagesSkeletal Maturity Indicators: Assessing Growth PotentialSamreen SuzairkhanNo ratings yet
- AO Classification of FracturesDocument62 pagesAO Classification of FracturesEka Sutiono100% (1)
- Anaphy Module 4 PDFDocument38 pagesAnaphy Module 4 PDFJosh MagatNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic PathologyDocument2 pagesOrthopedic PathologyvetpathforumNo ratings yet
- FESSDocument52 pagesFESShwalijeeNo ratings yet
- Veterinary AnatomyDocument49 pagesVeterinary AnatomyAdeel SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Mendonca Derick Fronto-Orbital Advancement RevisitedDocument9 pagesMendonca Derick Fronto-Orbital Advancement Revisitedraden chandrajaya listiandokoNo ratings yet