Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 - SPSF1 12 B9 PDF
Uploaded by
vt.subraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 - SPSF1 12 B9 PDF
Uploaded by
vt.subraCopyright:
Available Formats
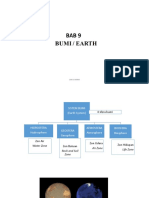
BAB Bumi
9 The Earth
Anda akan mempelajari…
Bumi/THE EARTH
terdiri daripada/consists of
ada
Atmosfera Hidrosfera Geosfera has Mineral ekonomi Biosfera
Atmosphere Hydrosphere Geosphere Economic minerals Biosphere
contoh contoh contoh contoh habitat bagi
example example examples examples habitat of
Stratosfera Taburan air Litosfera, Emas dan perak Semua hidupan
Stratosphere Water distribution astenosfera dan Gold and silver All living things
berlakunya contoh
mesosfera
occurs examples Lithosphere, berlakunya
asthenosphere and occurs
mesosphere
Penipisan Lautan, glasier
lapisan ozon dan awan mengandungi Gempa bumi dan tanah
The depletion of Ocean, glacier contain runtuh
the ozone layer and clouds Earthquakes and landslides
Batuan igneus,
sedimen (enapan) dan
mengalami metamorfik
Luluhawa dan hakisan undergo Igneous, sedimentary and
Weathering and erosion metamorphic rocks
162
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 162 8/9/16 5:58 PM
Standard Kandungan
9.1 Sistem dan struktur Bumi Tarikh:
9.1 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Sfera utama Bumi
Main spheres of the Earth
DSKP
Masteri
1 Kenal pasti empat sfera yang utama bagi struktur Bumi.
Identify four main spheres of the Earth structure. TP2
Biosfera
Biosphere (a) Atmosfera/Atmosphere
Atmosfera Lapisan gas yang berada
Atmosphere di atas permukaan bumi.
Hidrosfera The layer of gas located
Hydrosphere above the Earth’s surface
Geosfera
Geosphere (b) Biosfera/Biosphere
Bahagian Bumi yang
(d) Hidrosfera didiami oleh semua
Hydrosphere benda hidup.
The part of the Earth
Bahagian air which is inhabited by all
di Bumi seperti living things.
awan, sungai
dan salji.
The water part of (c) Geosfera/Geosphere
the Earth, such Bahagian pepejal Bumi.
as clouds, rivers The solid part of the Earth.
and snow.
2 Kaji rajah di bawah tentang stratifikasi atmosfera. Kemudian, jawab soalan-soalan yang diberi.
Study the diagram below on the stratification of the atmosphere. Then, answer the given questions.
Eksosfera (a) Label lapisan-lapisan atmosfera dalam rajah
Exosphere dengan perkataan di bawah.
Label the layers of the atmosphere in the diagram with
the words below. TP2
Ionosfera 500 km
Ionosphere Stratosfera/Stratosphere Eksosfera/Exosphere
Troposfera/Troposphere Ionosfera/Ionosphere
Stratosfera
Stratosphere (b) Lapisan yang manakah mengandungi sebahagian
50 km
besar gas atmosfera seperti oksigen dan mengalami
Troposfera 10 km perubahan cuaca? TP4/KBAT
Troposphere altitud Which layer contains a big portion of atmospheric gases
altitude such as oxygen, and experiences weather changes?
Troposfera/Troposphere
BAB
9
(c) Lapisan yang manakah mengalami fenomena yang berikut:
Which layers experience the following phenomena: TP4/KBAT
(i) Kesan rumah hijau/The greenhouse effect:
Troposfera/Troposphere
(ii) Penipisan lapisan ozon/The depletion of ozone layer:
Stratosfera/Stratosphere
(d) Apakah hubungan antara altitud dengan tekanan
udara? TP3/KBAT Galeri Info
fo
What is the relationship between the altitude and air pressure? Kapal angkasa mengorbit Bumi di eksosfera.
Semakin tinggi altitud, semakin rendah tekanan Ion-ion dalam ionosfera memantulkan
gelombang radio.
higher lower
udara./The the altitude is, the the air Spaceships orbit the Earth in the exosphere. Ions
in the ionosphere reflect radio waves.
pressure will be.
163
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 163 8/9/16 5:58 PM
Tarikh:
9.2 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Stratifikasi dalam lautan (hidrosfera)
Stratification of ocean (hydrosphere)
DSKP
Kontekstual
Kaji rajah tentang lautan di bawah. Jawab soalan-soalan yang diberikan.
Study the diagram about the ocean. Answer the given questions.
X: Zon sinar matahari Y: Zon senja Z: Zon gelap
Sunlight zone Twilight zone Midnight zone
200 m
200 m –
1 000 m
1 000 m –
4 000 m
1 Label lapisan-lapisan lautan dalam rajah di atas dengan perkataan di bawah.
Label the layers of the ocean with the words given below. TP2
Zon senja Zon gelap Zon sinar matahari
Twilight zone Midnight zone Sunlight zone
2 Pada pendapat anda, mengapakah zon sinar matahari mengandungi sebahagian besar daripada
hidupan laut?
In your opinion, why does the sunlight zone contain a large portion of marine life? TP4/KBAT
Proses fotosintesis berlaku di zon ini yang menerima banyak cahaya Matahari .
Makanan yang mencukupi dan suhu laut yang sesuai dapat menampung
banyak hidupan laut.
photosynthesis sunlight
The process of takes place in this zone which receives a lot of . Sufficient
food temperature
and a suitable support marine life.
3 Zon yang manakah proses fotosintesis tidak dapat berlaku? Terangkan mengapa.
In which zone is photosynthesis unable to take place? Explain why. TP4/KBAT
Zon gelap . Cahaya Matahari tidak dapat menembus ke zon ini.
BAB
midnight zone Sunlight cannot
The . penetrate this zone.
9 4 Kadangkala paus sperma menjunam ke dalam zon gelap yang
kekurangan oksigen dan tekanan air yang sangat tinggi. Apakah
pendapat anda tentang kejadian ini?
Sometimes sperm whales dive into the midnight zone that lacks
oxygen and is under very high water pressure. What is your opinion on
this? TP5/KBAT
Paus sperma mencari makanan seperti sotong raksasa.
The sperm whales look for food such as giant squids.
5 Selain lautan, senarai lima taburan air di Bumi.
Other than the ocean, list five sources of water on the Earth. TP1
Sungai, glasier, awan, air bawah tanah dan salji.
Rivers, glaciers, clouds, underground water and snow.
164
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 164 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Tarikh:
9.3 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Komposisi dan sifat fizik lapisan Bumi
Composition and physical characteristics of Earth
DSKP
Masteri
Kaji rajah lapisan Bumi di bawah dan jawab soalan yang diberikan.
Study the diagram of the Earth’s layers and answer the given questions.
P: Litosfera/Lithosphere
X: Kerak/Crust
Q: Astenosfera
Asthenosphere
Y: Mantel/Mantle R: Mesosfera
Mesosphere
teras luar
outer core cecair
liquid
teras
Z: Teras/Core dalam
inner pepejal
core solid
1 Namakan tiga lapisan utama Bumi, X, Y dan Z dalam rajah di atas dengan menggunakan perkataan
di bawah.
Name the three main layers of the Earth which are labelled X, Y and Z in the above diagram by using the
words below. TP2
Mantel Teras Kerak
Mantle Core Crust
2 Berdasarkan maklumat di bawah, namakan tiga lapisan Bumi, P, Q dan R dalam rajah di atas
dengan menggunakan perkataan di bawah.
Based on the given information, name the three layers of the Earth which are labelled P, Q and R in the above
diagram by using the words below. TP4/KBAT
Mesosfera Litosfera Astenosfera
Mesosphere Lithosphere Asthenosphere
Kerak dan bahagian pepejal paling atas mantel (65 – 100 km).
P
The crust and the solid outermost part of the mantle (65 – 100 km).
BAB
Bahagian tengah mantel dan mempunyai batuan separa cecair (200 – 235 km).
9
Q
The centre part of the mantle and contains semi-liquid rock (200 – 235 km).
Bahagian pepejal mantel di bawah astenosfera and di atas teras luar (660 km).
R
The solid part of the mantle below the asthenosphere and above the outer core (660 km).
3 Bumi adalah satu-satunya rumah bagi semua hidupan. Tandakan ( ✓ ) bahagian yang merupakan
biosfera yang didiami oleh semua hidupan di Bumi.
The Earth is the only home for all living things. Tick ( ✓ ) the parts that are the biosphere and are inhabited
by all living things on the Earth. TP2
Litosfera Atmosfera Mantel Hidrosfera
✓ ✓ ✓
Lithosphere Atmosphere Mantle Hydrosphere
165
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 165 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Standard Kandungan
9.2 Bahan Bumi Tarikh:
9.4 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Jenis dan ciri batuan
The types and characteristics of rocks
DSKP
Masteri
A. Kelaskan batuan yang diberikan kepada tiga kumpulan dalam peta pokok di bawah.
Classify the given rocks into three groups in the tree map below. TP2
Syal/Shale Pumis/Pumice Gneis/Gneiss Granit/Granite
Slat/Slate Basalt/Basalt Marmar/Marble Batu pasir/Sandstone
Kuarzit/Quartzite Batu kapur/Limestone Konglomerat/Conglomerate
Jenis bantuan/Types of rock
Bantuan igneus Bantuan sedimen Bantuan metamorfik
Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
Granit/Granite Syal/Shale Gneis/Gneiss
Pumis/Pumice Batu kapur/Limestone Marmar/Marble
Basalt/Basalt Batu pasir/Sandstone Kuarzit/Quartzite
Konglomerat/Conglomerate Slat/Slate
B. Berdasarkan maklumat yang diberikan, kenal pastikan jenis batuan.
Based on the given information, identify the types of rock. TP4/KBAT
1 magma (batuan lebur) 2 batuan
3
magma (molten rocks)
rocks tekanan/pressure
kerak bumi laut
crust sea
batuan/rock
ruang magma
magma chamber haba/heat (magma)
Batuan igneus Batuan sedimen Batuan metamorfik
Igneous rock Sedimentary rock Metamorphic rock
Penyejukan magma daripada Enapan batuan yang Batuan igneus atau sedimen
mantel yang keluar ke kerak. mengalami luluhawa dan yang mengalami suhu dan
The cooling of magma from the hakisan secara berlapis-lapis tekanan yang sangat tinggi
mantle which comes out to the di laut atau tasik. serta tindak balas kimia.
crust. Sedimentation of rock that The igneous or sedimentary rock
undergoes weathering and erosion which is subjected to a very high
in layers, normally occurs in seas heat and pressure and chemical
or lakes. reactions.
BAB
9
C. Tuliskan jenis batuan dalam kitar batuan di bawah untuk menunjukkan proses pembentukannya.
Write the types of rock in the rock cycle below to show the process of formation. TP3/KBAT
erii Innfo
aleer
Gal fo
suhu dan tekanan tinggi,
tindak balas kimia Batuan igneus suhu tinggi
high temperature Igneous rock (lebur dan sejuk)
and pressure, chemical high temperature Batuan metamorfik
reactions suhu tinggi (melt and cool) Metamorphic rock
(lebur dan sejuk) luluhawa Granit Gneis
high temperature weathering Granite Gneiss
(melt and cool)
Batu kapur Marmar
Limestone Marble
luluhawa/weathering
Batuan metamorfik Batuan sedimen Batu pasir Kuarzit
Metamorphic rock Sedimentary rock Sandstone Quartzite
Syal Slat
suhu dan tekanan tinggi, tindak balas kimia Shale Slate
high temperature and pressure, chemical reactions
166
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 166 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Standard Kandungan
9.3 Proses utama Bumi Tarikh:
9.5 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Proses utama Bumi
The major Earth’s processes
DSKP
Masteri
1 Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan proses eksogen?/What is meant by exogenic process? TP2
Proses yang berlaku pada permukaan bumi yang menyebabkannya terhakis . Proses
ini digerakkan oleh tenaga yang berpunca daripada Matahari .
Earth’s surface wear away
A process that takes place at the , that makes the surface . This
energy Sun
process is driven by the in the .
2 Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan proses endogen?/What is meant by endogenic process? TP2
Proses yang berpunca dari dalam Bumi dan mampu mengubah bentuk
permukaan bumi. Proses ini digerakkan oleh haba dalaman bumi.
interior shapes
The process that originates from the of the Earth which the
internal heat
Earth’s surface. This process is driven by the of the Earth.
3 Kelaskan proses Bumi yang mempengaruhi perubahan pada Bumi kepada dua kumpulan iaitu
proses eksogen dan endogen./Classify the Earth’s processes that affect changes in the Earth, into two groups,
i.e. exogenic and endogenic processes. TP2
Angkutan Hakisan Luluhawa Susutan jisim Aktiviti magma
Transport Erosion Weathering Mass wasting Magmatic activity
Pengenapan Olakan mantel Susutan darat Pergerakan kerak bumi (tektonik plat)
Deposition Mantle convection Mass movement Earth crust movement (plate tectonic)
Proses Bumi/Earth’s processes
Proses eksogen/Exogenic process Proses endogen/Endogenic process
Angkutan/Transport Olakan mantel/Mantle convection
Hakisan/Erosion Aktiviti magma/Magmatic activity
Luluhawa/Weathering Pergerakan kerak bumi (tektonik plat)
Susutan jisim/Mass wasting Earth crust movement (plate tectonic)
Pengenapan/Deposition
Susutan darat/Mass movement
4 Berdasarkan maklumat yang diberikan, kenal pasti jenis proses Bumi. Tuliskan sama ada proses
itu adalah eksogen (Ek) atau endogen (En) dalam petak yang diberikan.
Based on the given information, identify the types of Earth’s processes. Write whether the processes are exogenic
(Ex) or endogenic (En) in the boxes provided. TP4/KBAT
(a) (b)
Ek/Ex Ek/Ex
BAB
Luluhawa/Weathering Hakisan/Erosion
Pemecahan atau kelarutan batuan dan Pemecahan (secara fizikal) dan pemindahan
mineral di permukaan kerak bumi (secara batuan dan tanah dari satu tempat ke
fizikal, kimia dan biologi). tempat lain di kerak Bumi.
The breaking down or dissolving of rocks and The breaking down (physical) and transportation
minerals in the surface of the Earth’s crust of rocks and soil from one location to another on
(physical, chemical and biological). the Earth’s crust
167
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 167 8/9/16 5:59 PM
(c) (d)
Ek/Ex En
Pengenapan/Deposition Aktiviti magma/Magmatic activity
Pengenapan bahan batuan terhakis yang Transformasi magma daripada
diangkut oleh angin atau air pada dasar pembentukannya, melalui letusan dan
tasik atau laut. penyejukan di bawah kerak, sehingga
The deposition of eroded rock materials, carried pemejalan menjadi batuan.
by wind or water at the bottom of lakes or seas. The transformation of magma from its creation,
through eruption and cooling down under crust,
until solidification into rock.
(e) (f)
Ek/Ex Ek/Ex
Susutan jisim dan susutan darat Angkutan/Transport
Mass wasting and mass movement Pemindahan bahan-bahan batuan hakisan.
Pergerakan tanah, pasir atau serpihan Angin, sungai, ombak dan sungai adalah
batuan ke bawah cerun akibat tarikan contoh-contoh agen angkutan./The transfer
graviti./Downhill movement of soil, sand or of eroded rock materials. The wind, river and
rock fragments caused by the pull of gravity. wave are examples of transporting agents.
(g)
En/En
Teori yang menyatakan bahawa
kerak luar Bumi dibahagikan kepada
beberapa plat yang menggelongsor di
atas mantel, disebabkan arus dalam
mantel. Semua benua berasal daripada
satu benua besar.
The theory which states that the Earth’s
outer shell is divided into several plates that
glide over the mantle, due to the currents in
BAB
the mantle. The continents were originated
Pergerakan kerak bumi (tektonik plat) from a super continent.
9
Earth crust movement (plate tectonic)
(h) Pergerakan perlahan bahan mantel akibat
En
arus perolakan yang membawa haba daripada
bahagian dalam Bumi ke permukaan. Arus
mantel
ini menyebabkan pergerakan kerak Bumi
mantle dan mengakibatkan fenomena seperti gunung
arus berapi dan gempa bumi.
current Slow creeping motion of mantle materials caused
by convection currents carrying heat from the
interior of the Earth to the surface. These currents
cause the tectonic plates to move resulting in
phenomena such as volcanos formation and
Olakan mantel/Mantle convection earthquakes.
168
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 168 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Standard Kandungan
9.4 Fenomena geobencana Tarikh:
9.6 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Geobencana
Geo-disasters
DSKP
Masteri
1 Foto di bawah menunjukkan suatu geobencana.
The photo below shows a geo-disaster.
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan geobencana?
What is meant by the geo-disaster? TP2
Proses semula jadi bumi yang boleh menyebabkan
kehilangan nyawa , kerosakan harta benda
dan boleh menjejaskan kuantiti alam sekitar.
natural
The phenomena of the Earth which can cause loss
life property
of , damage to and affect
quality
the of the environment.
2 Berdasarkan maklumat yang diberikan, kenal pastikan jenis geobencana.
Based on the given information, identify the types of geo-disaster. TP4/KBAT
Tanah terjerlus Pemanasan global Lubang benam Volkanisme
Land subsidence Global warming Sinkhole Volcanism
Gempa bumi Tanah runtuh Hujan asid Tsunami
Earthquake Landslide Acid rain Tsunami
(a) (b) (c)
Gempa bumi Pemanasan global Tanah runtuh
Earthquake Global warming Landslide
Gegaran di permukaan Peningkatan suhu Sejenis susutan jisim di
kerak bumi akibat anjakan atmosfera Bumi mana tanah bergerak
plat-plat teknonik. disebabkan oleh kesan menuruni cerun akibat
The shaking of the surface rumah hijau. tarikan graviti.
of the Earth’s crust caused The increase in the Earth’s A form of mass wasting where
by the displacement of the atmospheric temperature due the ground moves downhill
tectonic plates. to the greenhouse effect. due to the pull of gravity.
(d) (e) (f) terhakis/corroded
BAB
9
Tsunami/Tsunami Volkanisme/Volcanism Hujan asid/Acid rain
Kejadian ombak raksasa Kejadian letusan batuan Air hujan bersifat asid
disebabkan oleh gempa lebur (magma) di mana disebabkan kelarutan
bumi di dasar laut, lava dan gas gunung gas berasid seperti sulfur
letusan gunung berapi berapi terbebas melalui dioksida di dalamnya.
di dasar laut atau tanah rekahan di permukaan The rain water has an
runtuh di tepi laut./A huge Bumi./The eruption of molten acidic property due to the
wave caused by an undersea rock (magma) where lava and dissolving of acidic gases
earthquake, a volcanic volcanic gases erupt through a such as sulphur dioxide in it.
eruption, or coastal landslide. break in the Earth’s surface.
169
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 169 8/9/16 5:59 PM
(g) (h)
Tanah terjerlus/Land subsidence Lubang benam/Sinkhole
Penenggelaman secara perlahan atau Lubang besar dalam tanah disebabkan
mendadak permukaan Bumi disebabkan keruntuhan lapisan di permukaan Bumi
kehilangan air bawah tanah atau aktiviti ke dalam rongga kosong di bawahnya
perlombongan. terutamanya berlaku di kawasan batu
A gradual settling or sudden sinking of the kapur./A big hole in the ground caused by the
Earth’s surface caused by the removal of collapse of the Earth’s surface layer into the
underground water or mining activity. empty space beneath, especially occuring in
limestone areas.
3 Kaji pernyataan yang diberikan. Kemudian, jawab soalan tentang bagaimana kemajuan sains dan
teknologi boleh menyediakan manusia untuk menghadapi kejadian geobencana.
Answer the questions below about how the progress of science and technology has enabled humans to prepare
themselves to face the occurrences of geo-disasters. TP5/KBAT
(a) Wajarkan penggunaan satelit kaji cuaca dalam pengurusan geobencana.
Justify
fy the use of weather satellites in managing geo-disasters
Geobencana Meramal Angin Suhu
Geo-disasters Forecast Wind Temperature
Mengatasi Tekanan Awal Amaran awal
Overcome Pressure Eary Eary warning
Satelit kaji cuaca membantu kita meramal keadaan cuaca dengan tepat.
Satelit jenis ini dapat mengesan perubahan suhu , angin , dan
tekanan di atmosfera. Maklumat yang diterima daripada satelit ini dapat membantu
kita meramal tempat dan masa berlakunya geobencana seperti ribut taufan, banjir,
siklon, kemarau dan puting beliung. Amaran awal dapat diberi kepada penduduk di
kawasan yang terlibat. Dengan ini, langkah-langkah awal dapat diambil untuk
mengatasi masalah tersebut.
forecast
A weather satellite helps to weather conditions accurately. This type of satellite
temperature wind pressure
can detect changes in the , and
in the atmosphere. The information received from this satellite can help in forecasting the place and
geo-disasters
BAB
the occurring time of such as typhoons, floods, cyclones, drought and tornado.
Early warning
can be given to residents in the affected areas. With this, early steps can be taken
9 to
overcome
the problem.
(b) Foto di bawah menunjukkan satu peralatan untuk mengesan suatu geobencana. Labelkan
peralatan itu./The photo below shows an instrument which detects geo-disasters. Label the instrument.
Apakah kegunaan alat ini?
What is the use of this instrument? TP2
Mengukur pergerakan Bumi seperti gelombang
yang dihasilkan oleh gempa bumi dan letusan
gunung berapi .
motion
It measures the of the ground such as
waves earthquakes
the produced by and
Seismometer/Seismometer volcanic
eruptions.
170
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 170 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Standard Kandungan
9.5 Usia Bumi Tarikh:
9.7 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Kaedah penentuan usia Bumi
Method to determine the age of the Earth
DSKP
Masteri
1 Rajah di bawah menunjukkan satu skala masa geologi yang dipetik daripada laman web yang
berikut:/The diagram below shows a geological time scale which is taken from the following website:
http://geographyclassroom2014.weebly.com
CENOZOIC MESOZOIC PALEOZOIC
PENNSYLVANIAN
MISSISSIPPIAN
ORDOVICIAN
CRETACEOUS
DEVONIAN
CAMBRIAN
PERMIAN
SILURIAN
JURASSIC
TRIASSIC
66.4 245 570
0 100 200 300 400 500
Masa dalam juta tahun dahulu/Time in millions of years ago
Apakah kegunaan skala masa geologi?/What is the use of the geological time scale? TP2
Skala masa ini digunakan oleh ahli geologi untuk menjelaskan masa
dan hubungan antara peristiwa yang terjadi di sepanjang sejarah Bumi.
geologists timing relationship
This time scale is used by to describe the and
events
between that have occurred throughout the Earth’s history.
2 Bahan dalam foto di bawah merupakan bangkai atau kesan tinggalan hidupan yang terawet sejak
zaman purba.
The substance in the photo below is the preserved remains or traces of living things from ancient times.
(a) Namakan bahan ini./Name this substance. TP1
Fosil/Fossil.
(b) Namakan bidang kajian ini./Name this field of study. TP1
Arkeologi/Archaeology
(c) Apakah unsur yang digunakan untuk mengkaji usia artifak
purba?
What is the element used for studying the age of ancient artefacts? TP2
Karbon-14/Carbon-14 BAB
(d) Apakah kaedah yang digunakan untuk mengkaji usia artifak purba ini?
What is the method used for studying the age of ancient artefacts? TP2
9
Pentarikhan karbon/Pentarikhan radiokarbon/Carbon dating/Radiocarbon dating
(e) Apakah kaitan usia fosil dengan sejarah Bumi?
What is the relationship between the age of fossils and the history of the Earth? TP3/KBAT
Daripada usia fosil dan rujukan pada
skala masa geologi , jenis hidupan yang pernah
hidup Usia/Age
pada zaman dahulu dan ciri-cirinya seperti Hidup/Lived
bentuk dan struktur dapat ditentukan. Bentuk/Shape
age Struktur/Structure
From the of the fossils and the reference on the
geological time scale lived Skala masa geologi
, the types of living things that Geological time scale
before in ancient times and the characteristics of the living things such as the
shape structure
and the , can be determined.
171
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 171 8/11/16 5:07 PM
Standard Kandungan
9.5 Sumber Bumi dan geologi gunaan Tarikh:
9.8 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Sumber air dan risikonya
The sources of water and their risks
DSKP
Kontekstual
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan sumber air di Bumi.
The diagram below shows the sources of water on the Earth.
(a) Senaraikan semua air permukaan.
List all the surface water. TP1
Tasik, sungai dan laut.
Lakes, rivers and seas.
tasik
lake laut (b) Apakah risiko yang akan dihadapi jika:
sungai sea What risks will be faced if: TP5/KBAT
river
air bawah tanah
groundwater
(i) kekurangan air permukaan?/there is a lack of surface water?
Kejadian kemarau yang akan menjejaskan kehidupan benda hidup.
drought lives
The occurrence of which will affect the of living things.
(ii) berlebihan air permukaan?/there is an excessive amount of surface water?
Kejadian banjir yang boleh menjejaskan kehidupan hidupan dan
kemusnahan harta benda.
floods lives
The occurrence of which will affect the of living things and
damage
properties.
(c) Apakah jenis air yang terbentuk apabila sebahagian air hujan meresap ke dalam tanah di bawah
permukaan bumi?/What is the type of water formed when a part of rainwater penetrates into the ground
under the Earth’s surface? TP2
Air bawah tanah/Groundwater.
(d) Apakah kepentingan air bawah tanah?/What is the importance of groundwater? TP5/KBAT
Air bawah tanah Tasik Semula jadi Bekalan Kegunaan Sungai
Groundwater Lakes Natural Supply Use Rivers
Air bawah tanah adalah salah satu sumber semula jadi
yang sangat penting. Air bawah
tanah ini merupakan sumber bekalan utama air untuk kegunaan harian
bagi sesetengah negara. Air bawah tanah juga membekalkan air kepada tasik dan
sungai .
natural
Groundwater is one of the most important resources. Groundwater is the main source of
BAB
supply use Groundwater
water to households in some countries for daily .
9
lakes rivers
also supplies water to and .
(e) Apakah risiko yang dihadapi oleh air bawah tanah?/What is the risk faced by groundwater? TP5/KBAT
Pencemaran daripada bahan-bahan seperti baja dan racun perosak from
agriculture.
Pollution fertilisers pesticides
by substances such as and from agriculture.
(f) Lapisan batuan atau bahan seperti kerikil dan pasir yang boleh menakung air bawah tanah.
Layers of rock or materials such as gravel and sand which can hold groundwater.
Berdasarkan pernyataan di atas, tandakan ‘ ✓ ’ lapisan batuan atau bahan itu.
Based on the statement above, tick ‘ ✓ ’ the layers of rock or materials. TP2
✓ Akuifer/Aquifer Lubang benam/Sinkhole Batuan sedimen/Sedimentary rock
172
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 172 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Tarikh:
9.9 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Mineral ekonomi
Economic minerals
DSKP
Masteri
1 Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan mineral?/What is meant by minerals? TP2
Unsur atau sebatian pepejal yang terdapat secara semula jadi di dalam kerak
Bumi.
elements compounds
Solid or that are naturally found on the Earth’s crust.
2 Kaji pernyataan di bawah./Study the statement below.
Mineral yang mempunyai nilai ekonomi yang digunakan secara meluas dalam bidang-bidang
seperti industri, pembinaan dan pengeluaran barangan.
Minerals of commercial value which are used widely in fields such as industrial, construction and
manufacturing.
Namakan mineral ini./Name the minerals. TP2
Mineral ekonomi/Economic minerals.
3 Kelaskan mineral ekonomi mengikut jenisnya.
Classify the types of economic minerals. TP2
Skandium Emas Karbon Itrium Perak Sulfur Batu kapur
Scandium Gold Carbon Yttrium Silver Sulphur Limestone
Platinum Galena Hematit Marmar Mika Bauksit Tanah liat
Platinum Galena Haematite Marble Mica Bauxite Clay
Mineral ekonomi/Economic minerals
Mineral logam Mineral bukan logam Mineral nadir bumi
Metallic minerals Non-metallic minerals Rare earth minerals
Emas, perak, platinum, galena, Karbon, sulfur, batu kapur, Skandium, itrium
hematit, bauksit marmar, mika, tanah liat Scandium, yttrium
Gold, silver, platinum, galena, Carbon, sulphur, limestone.
haematite, bauxite Marble, mica, clay
4 Padankan jenis logam yang dapat diekstrak daripada mineral logam yang diberikan.
Match the metals with the metallic minerals from which they are extracted. TP2
BAB
Logam Mineral logam Logam
Metals Metallic minerals Metals
Timah
Tin
(a) Bauksit
Bauxite
(d) Magnesit
Magnesite
Kuprum
Copper 9
Aluminium (b) Hematit (e) Malakit Plumbum
Aluminium Haematite Malachite Lead
Besi (c) Kasiterit (f) Galena Magnesium
Iron Cassiterite Galena Magnesium
Galeri Info
fo
Mineral nadir bumi digunakan dalam banyak peralatan seperti DVD, batteri
boleh dicas semula dan telefon bimbit.
Rare earth metals are used in many devices such as DVDs, rechargeable
batteries and cell phones.
173
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 173 8/9/16 5:59 PM
Tarikh:
9.10 AKTIVITI
PERBINCANGAN
Sumber semula jadi
Natural resources
DSKP
Masteri
1 Berdasarkan rajah yang diberikan, terangkan pembentukan petroleum dan gas asli.
Based on the given diagram, explain the formation of petroleum and natural gas. TP4/KBAT
P
haiwan dan tumbuhan laut yang mati
dead sea animals and plants Tekanan/Pressure
Petroleum/Petroleum
Q Tumbuhan/Plants
tekanan dan haba tinggi
high pressure and heat
Haba/Heat
R
Gas asli/Natural gas
gas asli
natural gas Haiwan/Animals
Batuan tidak telap
petroleum
petroleum
Impermeable rocks
Haiwan dan tumbuhan laut yang mati tertanam dalam lumpur dan pasir dalam
P animals plants
dasar laut berjuta-juta tahun dahulu./Dead sea and were buried
under mud and sand in the sea bed millions of years ago.
Tekanan dan haba yang tinggi bertindak pada sisa hidupan dalam lumpur dan
Q
pressure heat
pasir/High and were exerted on the remains of the living things
Sisa hidupan berubah menjadi petroleum dan gas asli yang terperangkap di antara
dua lapisan batuan tidak telap yang terbentuk daripada lumpur dan pasir.
R
petroleum natural gas
The remains of the living things changed into and which are trapped
in between two layers of impermeable rock formed from the mud and sand.
2 Berdasarkan rajah yang diberikan, terangkan pembentukan arang batu.
Based on the given diagram, explain the formation of coal. TP4/KBAT
Tumbuhan/Plants
hutan paya Tekanan/Pressure
mangrove swamp
Tanah/Earth
Haba/Heat
arang batu Dimampatkan
coal Compressed
Arang batu terbentuk daripada tumbuhan yang mati berjuta-juta tahun dahulu dan telah
dimampatkan oleh lapisan tanah di atasnya. Tekanan dan haba tinggi
yang bertindak ke atas tumbuhan ini menukarkannya kepada arang batu.
plants compressed
BAB
Coal is formed from that died millions of years ago and have been by layers
earth pressure heat plants
of on top. High and that acted on these
9
changed them into coal.
3 (a) Dihasilkan oleh air panas terutamanya air yang dipanaskan oleh haba daripada bahagian
dalam Bumi. Tenaga boleh dijana menggunakan air panas pada Bumi seperti geiser, untuk
menjana tenaga elektrik./Produced by hot water, especially water heated by the Earth’s internal heat.
Energy can be generated by using the Earth’s hot water such as geysers, to generate electrical energy.
Apakah yang dimaksudkan oleh pernyataan di atas?/What does the above statement refer to? TP2
Hidroterma/Hydrothermal energy.
(b) Bulatkan satu contoh tenaga hidroterma./Circle one example of hydrothermal energy. TP2
Tenaga hidro Bahan radioaktif Geoterma
Hydro energy Radioactive substances Geothermal energy
174
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 174 8/9/16 5:59 PM
REVISI EKSPRES 9
1 Sfera yang utama bagi struktur Bumi ialah atmosfera , biosfera , geosfera dan
hidrosfera .
The main spheres of the Earth structure are the atmosphere , biosphere , geosphere and
hydrosphere .
2 Label empat lapisan atmosfera. Kemudian, padankan lapisan atmosfera dengan pernyataan yang betul.
Label the four layers of the atmosphere. Then, match the layers of the atmosphere with the correct statements.
Atmosfera Pernyataan
Atmosphere Statement
(a) Eksosfera Memantulkan gelombang radio
Exosphere Reflects radio waves.
(b) Ionosfera Perubahan cuaca
Ionosphere Changes in the weather
(c) Stratosfera Kapal angkasa mengorbit Bumi.
Stratosphere Spaceships orbit the Earth.
(d) Troposfera Penipisan lapisan ozon.
Troposphere Depletion of the ozone layer.
3 Lengkapkan peta alir di bawah dengan zon-zon yang berlainan untuk menunjukkan stratifikasi dalam
lautan./Complete the flow map below by writing the different zones to show the stratification of the ocean.
Zon sinar matahari Zon senja Zon gelap
Sunlight zone Twilight zone Midnight zone
Kedalaman bertambah/Increasing depth
4 Taburan air di Bumi termasuk lautan , sungai , awan , salji dan
air bawah tanah/glasier .
The water distribution on the Earth includes oceans , rivers , clouds ,
snow and groundwater/glaciers .
5 Label lapisan Bumi di bawah. Kemudian, labelkan bahagian Bumi berdasarkan pernyataan yang diberikan.
Label the layers of the Earth below. Then, label the parts of the Earth based on the given statements.
Lapisan Bumi (d) Litosfera/Lithosphere
BAB
Earth’s layer Kerak dan bahagian pepejal
9
paling atas mantel.
(a) Kerak/Crust The crust and solid outermost
part of the mantle.
(b) Mantel/Mantle
(e) Astenosfera/Asthenosphere
(c) Teras/Core Batuan separa cecair di
bahagian tengah mantel.
Semi-liquid rock at the centre
(f) Mesosfera/Mesosphere part of the mantle.
Bahagian pepejal mantel di bawah
astenosfera and di atas teras luar.
The solid part of the mantle below the
asthenosphere and above the outer core.
175
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 175 8/9/16 5:59 PM
6 Kenal pasti jenis batuan sama ada batuan igneus (I), batuan sedimen (S) atau batuan metamorfik (M)
dalam petak yang diberikan./Identify the types of rock whether igneous rock (I), sedimentary rock (S) or meta-
morphic rock (M).
(a) Syal (f) Kuarzit (k) Konglomerat
S M S
Shale Quartzite Conglomerate
(b) Gneis (g) Pumis (l) Arang batu
M I S
Gneiss Pumice Coal
(c) Granit (h) Basalt (m) Serpentin
I I M
Granite Basalt Serpentinite
(d) Batu kapur (i) Slat (n) Diorit
S M I
Limestone Slate Diorite
(e) Marmar (j) Batu pasir (o) Gabro
M S I
Marble Sandstone Gabbro
7 Kenal pastikan jenis batuan berdasarkan penerangan yang diberikan.
Identify the types of rock based on the given explanations.
Jenis batuan Penerangan
Types of rock Explanation
(a) Batuan metamorfik Batuan yang mengalami suhu dan tekanan yang sangat tinggi serta tindak
Metamorphic rock balas kimia./The rock which is subjected to a very high heat and pressure and
chemical reactions
(b) Batuan igneus Penyejukan magma daripada semua jenis batuan.
Igneous rock The cooling of magma from all kinds of rock.
(c) Batuan sedimen Enapan batuan yang mengalami luluhawa dan hakisan.
Sedimentary rock Sedimentation of rock that undergoes weathering and erosion.
8 Berdasarkan penerangan yang diberikan, nyatakan proses Bumi. Tuliskan jenis proses Bumi sama ada
eksogen (Ek) atau endogen (En) dalam petak yang disediakan.
Based on the given explanations, state the Earth’s processes. Write the types of Earth’s processes, whether exogenic
(Ex) or endogenic (En) process in the boxes provided.
(a) Pemecahan (secara fizikal) dan pemindahan batuan dan
tanah dari satu tempat ke tempat lain. Hakisan Ek
The breaking down (physically) and transportation of rock and Erosion Ex
soil from one location to another.
(b) Transformasi magma daripada pembentukannya sehingga
pemejalan menjadi batuan. Aktiviti magma
En
The transformation of magma from its creation until solidification Magmatic activity
into rock.
(c) Pemecahan batuan di kerak bumi (secara fizikal, kimia
Luluhawa Ek
BAB
dan biologi)./The breaking down of rock in the Earth’s crust
Weathering Ex
(physical, chemical and biological).
9 (d) Pengenapan batuan terhakis pada dasar tasik atau laut./The
deposition of eroded rock materials at the bottom of lakes or seas.
Pengenapan
Deposition
Ek
Ex
(e) Pemindahan bahan-bahan batuan hakisan. Angkutan Ek
The transfer of eroded rock materials. Transport Ex
(f) Pergerakan bahan mantel daripada bahagian dalam Bumi ke
Olakan mantel
permukaan./The motion of mantle materials from the interior to En
Mantle convection
the Earth’s surface.
(g) Teori yang menyatakan bahawa kerak luar Bumi Pergerakan kerak
dibahagikan kepada beberapa plat yang menggelongsor di bumi (tektonik
atas mantel, disebabkan arus dalam mantel./The theory which plat)/Earth crust En
states that the Earth’s outer shell is divided into several plates movement (plate
that glide over the mantle, due to the currents in the mantle tectonic)
176
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 176 8/9/16 5:59 PM
6 Kenal pasti jenis batuan sama ada batuan igneus (I), batuan sedimen (S) atau batuan metamorfik (M)
dalam petak yang diberikan./Identify the types of rock whether igneous rock (I), sedimentary rock (S) or meta-
morphic rock (M).
(a) Syal (f) Kuarzit (k) Konglomerat
S M S
Shale Quartzite Conglomerate
(b) Gneis (g) Pumis (l) Arang batu
M I S
Gneiss Pumice Coal
(c) Granit (h) Basalt (m) Serpentin
I I M
Granite Basalt Serpentinite
(d) Batu kapur (i) Slat (n) Diorit
S M I
Limestone Slate Diorite
(e) Marmar (j) Batu pasir (o) Gabro
M S I
Marble Sandstone Gabbro
7 Kenal pastikan jenis batuan berdasarkan penerangan yang diberikan.
Identify the types of rock based on the given explanations.
Jenis batuan Penerangan
Types of rock Explanation
(a) Batuan metamorfik Batuan yang mengalami suhu dan tekanan yang sangat tinggi serta tindak
Metamorphic rock balas kimia./The rock which is subjected to a very high heat and pressure and
chemical reactions
(b) Batuan igneus Penyejukan magma daripada semua jenis batuan.
Igneous rock The cooling of magma from all kinds of rock.
(c) Batuan sedimen Enapan batuan yang mengalami luluhawa dan hakisan.
Sedimentary rock Sedimentation of rock that undergoes weathering and erosion.
8 Berdasarkan penerangan yang diberikan, nyatakan proses Bumi. Tuliskan jenis proses Bumi sama ada
eksogen (Ek) atau endogen (En) dalam petak yang disediakan.
Based on the given explanations, state the Earth’s processes. Write the types of Earth’s processes, whether exogenic
(Ex) or endogenic (En) process in the boxes provided.
(a) Pemecahan (secara fizikal) dan pemindahan batuan dan
tanah dari satu tempat ke tempat lain. Hakisan Ek
The breaking down (physically) and transportation of rock and Erosion Ex
soil from one location to another.
(b) Transformasi magma daripada pembentukannya sehingga
pemejalan menjadi batuan. Aktiviti magma
En
The transformation of magma from its creation until solidification Magmatic activity
into rock.
(c) Pemecahan batuan di kerak bumi (secara fizikal, kimia
Luluhawa Ek
BAB
dan biologi)./The breaking down of rock in the Earth’s crust
Weathering Ex
(physical, chemical and biological).
9 (d) Pengenapan batuan terhakis pada dasar tasik atau laut./The
deposition of eroded rock materials at the bottom of lakes or seas.
Pengenapan
Deposition
Ek
Ex
(e) Pemindahan bahan-bahan batuan hakisan. Angkutan Ek
The transfer of eroded rock materials. Transport Ex
(f) Pergerakan bahan mantel daripada bahagian dalam Bumi ke
Olakan mantel
permukaan./The motion of mantle materials from the interior to En
Mantle convection
the Earth’s surface.
(g) Teori yang menyatakan bahawa kerak luar Bumi Pergerakan kerak
dibahagikan kepada beberapa plat yang menggelongsor di bumi (tektonik
atas mantel, disebabkan arus dalam mantel./The theory which plat)/Earth crust En
states that the Earth’s outer shell is divided into several plates movement (plate
that glide over the mantle, due to the currents in the mantle tectonic)
176
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 176 8/11/16 5:07 PM
PT3 PRAKTIS PENGUKUHAN 9
Arahan: Jawab semua soalan.
Instructions: Answer all questions.
1 (a) Foto di bawah menunjukkan ikan yang menghasilkan cahaya sendiri.
The photo below shows a fish which produces its own light.
Wajarkan zon lautan yang ikan ini hidup di dalamnya.
Justify the zone of the ocean in which the fish lives. TP5/K5 Menilai
Ikan ini hidup di dalam zon gelap. Tiada cahaya dapat menembusi zon ini. Ikan itu menghasilkan
cahaya untuk membantu pergerakannya.
This fish lives in the midnight zone. No light penetrates this zone. This kind of fish produces light to help them
in their movement.
[3 markah/3 marks]
(b) Foto di bawah menunjukkan peranan tumbuhan dalam luluhawa.
The photo below shows the role of plants in weathering.
BAB
Organisma lain seperti haiwan dan mikroorganism juga memainkan peranan dalam proses luluhawa.
9 Huraikan luluhawa secara biologi yang disebabkan oleh hidupan tersebut.
Other organisms such as animals and microorganisms also play roles in the process of weathering. Describe
biological weathering caused by the mentioned living things. TP4/K4 Menganalisis
Akar tumbuhan yang membesar mengenakan tekanan pada batuan dan dapat memecahkan batuan.
Sesetengah mikroorganisma dapat menghasilkan asid organik yang dapat melarutkan mineral dalam
batuan. Asid organik yang terhasil dapat menguraikan mineral dalam batuan dengan mengubah
komposisi kimia dalam batuan.
Growing plant roots can exert stress or pressure on rock and can break the rock. Certain microorganisms can
produce organic acids which help to dissolve minerals in rock. The organic acids that are produced can break
down rock minerals by altering the chemical composition of the rock,
[5 markah/5 marks]
178
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 178 8/9/16 5:59 PM
2 (a) Photo di bawah menunjukkan satu geobencana, iaitu tsunami yang mengakibatkan kemusnahan.
The photo below shows a geo-disaster, i.e. tsunami which causes destruction.
Huraikan kesan-kesan tsunami terhadap alam sekitar.
Describe the effects of tsunami on the environment. TP5/K5 Menilai
Tsunami raksasa boleh menyebabkan kemusnahan apabila melanda darat. Beribu-ribu orang terbunuh
dalam tsunami. Keruntuhan bangunan, pemutusan elektrik dan letupan disebabkan gas adalah sebab-sebab
lain kematian. Kawasan berdekatan pantai dibanjiri air laut dan infrastruktur termusnah seperti
tempatan rawatan kumbahan dan tempat bekalan air bersih. Air minum yang tercemar boleh
menyebabkan jangkitan penyakit di kawasan tsunami. Tsunami juga membawa kesan buruk kepada
serangga, haiwan, tumbuhan dan sumber-sumber semula jadi. Mangsa tsunami sering menghadapi
masalah psikologi yang berlanjutan selama beberapa hari, beberapa tahun atau seumur hidup.
A huge tsunami can cause large destruction when it strikes land. Thousands of people are killed by tsunamis.
The collapse of buildings, electrocution, and gas explosions are other causes of death. Areas that are close to the
coast are flooded with sea water, damaging the infrastructure such as sewage treatment and fresh water supply
areas. Contamination of drinking water can cause diseases to spread in tsunami-hit areas. Tsunamis also have a
bad effect on insects, animals, plants, and natural resources. Victims of tsunami events often suffer psychological
problems which can last for days, years or the entire lifetime.
[6 markah/6 marks]
(b) Foto di bawah menunjukkan beberapa ketul arang batu./The photo below shows some coal.
BAB
Diketahui bahawa arang batu berasal daripada tumbuhan yang mati berjuta-juta tahun dahulu. Kenal
pastikan jenis batuan bagi arang batu. Terangkan jawapan anda. TP4/K4 Menganalisis
9
It is found that coal originated from plants millions of years ago. What type of rock is coal? Explain your answer.
Arang batu adalah sejenis batu sedimen. Arang batu terbentuk daripada tumbuhan paya yang mati
berjuta-juta tahun dahulu dan dimampatkan oleh lapisan tanah di atasnya. Tekanan dan suhu tinggi
yang bertindak ke atas tumbuhan tersebut menukarkannya kepada arang batu.
Coal is a type of sedimentary rock. Coal is formed from swamp plants that died millions of years ago and had
been compressed by layers of earth on top. High pressure and temperature that acted on these plants changed
them into coal.
[4 markah/4 marks]
179
09 SC PROCESS SKILL'17-F1-BAB9-Emie2LP.indd 179 8/9/16 5:59 PM
You might also like
- Topic 9 f1 PDFDocument16 pagesTopic 9 f1 PDFNg Imm Khuan60% (5)
- 05 - SPSF1 08 B6Document19 pages05 - SPSF1 08 B6Zulkifli Yusof100% (1)
- Jadual Berkala: Periodic TableDocument15 pagesJadual Berkala: Periodic TableAnonymous RfKC0LciBK100% (2)
- 05 - SPSF1 07 B5Document14 pages05 - SPSF1 07 B5Anonymous RfKC0LciBK0% (1)
- 05 - SPSF2 05 B3Document18 pages05 - SPSF2 05 B3Norzamani NordinNo ratings yet
- Daya Dan Gerakan: Force and MotionDocument21 pagesDaya Dan Gerakan: Force and MotionzinziemeewahNo ratings yet
- Conquer! Pendidikan Moral Tingkatan 3 - ALLDocument111 pagesConquer! Pendidikan Moral Tingkatan 3 - ALLDEEVYA SRI0% (1)
- Sel Sebagai Unit Asas HidupanDocument20 pagesSel Sebagai Unit Asas HidupanAbby Haizul100% (1)
- OMG 5 English Form 2 - Unit 4Document6 pagesOMG 5 English Form 2 - Unit 4maaran sivam100% (1)
- Modul Fizik Tingkatan 4 Modul Fizik Tingkatan 4 Jawapan - Answer Jawapan - Answers. Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.Document25 pagesModul Fizik Tingkatan 4 Modul Fizik Tingkatan 4 Jawapan - Answer Jawapan - Answers. Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.Nur FadzilahNo ratings yet
- Pengangkutan: TransportationDocument22 pagesPengangkutan: TransportationsuhanaNo ratings yet
- TEMA 1: Kaedah SaintifikDocument20 pagesTEMA 1: Kaedah SaintifikAnonymous RfKC0LciBK100% (2)
- Form 5 Biology Notes C1 & C2Document18 pagesForm 5 Biology Notes C1 & C2m-7940668No ratings yet
- Answers: Pembelajaran Abad Ke-21 Activity Topic 1: Directed WritingDocument37 pagesAnswers: Pembelajaran Abad Ke-21 Activity Topic 1: Directed WritingIzyana BokhoriNo ratings yet
- Air Dan Larutan: Water and SolutionDocument16 pagesAir Dan Larutan: Water and SolutionxL1U BusinessNo ratings yet
- Model Answers: Chapter 2 Cell Biology and OrganizationDocument4 pagesModel Answers: Chapter 2 Cell Biology and Organizationsyed ali100% (1)
- 05 - SPSF3 04 B2 PDFDocument20 pages05 - SPSF3 04 B2 PDFCikgu RoshailaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 & 2.2: Biology Experiment ReportDocument1 page2.1 & 2.2: Biology Experiment ReportZhi WeiNo ratings yet
- Pelangi F3 AnswersDocument25 pagesPelangi F3 AnswersYusri Yahya50% (2)
- Answers: CHAPTER 1 Stimuli and ResponsesDocument22 pagesAnswers: CHAPTER 1 Stimuli and Responses林柄洲No ratings yet
- 04 Sps Sains Tg3-Bab4-EmiefDocument14 pages04 Sps Sains Tg3-Bab4-EmiefEve Ngew100% (1)
- Answers: Short TextsDocument4 pagesAnswers: Short TextsYashini BubalanNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Project (Water Audit Project)Document10 pagesForm 2 Science Project (Water Audit Project)Kanmane100% (1)
- 05 - SPSF1 03 B1Document26 pages05 - SPSF1 03 B1Abby Haizul100% (1)
- Moral ValuesDocument3 pagesMoral ValuesDamiafazirah100% (3)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 9Document5 pagesScience Form 3 Chapter 9Noor Azila25% (4)
- 05 - SPSF3 03 B1Document16 pages05 - SPSF3 03 B1maza260399No ratings yet
- Jawapan Kertas Model Pt3 Modul AktivitiDocument2 pagesJawapan Kertas Model Pt3 Modul AktivitiRed Kite0% (1)
- Nilam Module F5 Biology AnswersDocument34 pagesNilam Module F5 Biology Answerskazin yuen kah zingNo ratings yet
- 03 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB3-Emie2LP PDFDocument22 pages03 SPS SAINS Tg2 2018-BAB3-Emie2LP PDFEve NgewNo ratings yet
- 9 Sains PPC 2023 Putrajaya Set 2 (Skema)Document12 pages9 Sains PPC 2023 Putrajaya Set 2 (Skema)syahiddan87No ratings yet
- 02 - Physics Module Chapter 2.1Document9 pages02 - Physics Module Chapter 2.1ZazaNo ratings yet
- Air Dan Larutan: Water and SolutionDocument22 pagesAir Dan Larutan: Water and SolutionNUR SUHAIDAH BINTI SUKOR -No ratings yet
- Preparing and Examining Slides of Plant CellsDocument1 pagePreparing and Examining Slides of Plant CellsIzwahaneIbrahim50% (2)
- Science Project Form 1Document4 pagesScience Project Form 1Sivamalar Thyagarajah100% (3)
- Form 3 Chapter 10.2 ScienceDocument5 pagesForm 3 Chapter 10.2 ScienceTan Soong WeiNo ratings yet
- Answers: Unit 1 Reading WritingDocument6 pagesAnswers: Unit 1 Reading Writingpzah0% (1)
- Biology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)Document2 pagesBiology Practical Reports For Form 4 Experiment 9.2 (Practical Textbook Page 128)ke20% (1)
- Form 2 Science Project Syuen YeeDocument13 pagesForm 2 Science Project Syuen YeeKanmaneNo ratings yet
- Folio Chemistry F4 (Manufactured Substances in Industry)Document31 pagesFolio Chemistry F4 (Manufactured Substances in Industry)JackOss93No ratings yet
- Form 1 Science NotesDocument19 pagesForm 1 Science NotesTanYeeTingNo ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF3 07 B5 PDFDocument7 pages05 - SPSF3 07 B5 PDFCikgu Roshaila100% (1)
- Correct Common MistakesDocument17 pagesCorrect Common MistakesliniNo ratings yet
- PEKA Experiment Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 To 5Document9 pagesPEKA Experiment Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2 To 5James Chua Hong Kheng67% (6)
- English Form 2 AnswersDocument4 pagesEnglish Form 2 Answerskhairul53% (15)
- Cell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)Document2 pagesCell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)jrpyroNo ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF3 05 B3 PDFDocument26 pages05 - SPSF3 05 B3 PDFCikgu Roshaila100% (1)
- Blood Circulation and Transport DocumentDocument24 pagesBlood Circulation and Transport Documentmaza260399100% (1)
- Rangsangan Dan Gerak Balas: Stimuli and ResponsesDocument26 pagesRangsangan Dan Gerak Balas: Stimuli and ResponsesSin Ling WongNo ratings yet
- Revisi Ekspres 9Document3 pagesRevisi Ekspres 9LEE LEE LAUNo ratings yet
- Bab 9 Tingkatan 1Document16 pagesBab 9 Tingkatan 1DANAL YEAP VII ZENN MoeNo ratings yet
- BAB 9 BumiDocument6 pagesBAB 9 BumiNur Hana SyamsulNo ratings yet
- F1 Sains Bab 9 BumiDocument43 pagesF1 Sains Bab 9 BumiHANA HUMAIRA BINTI ALIF FAISAL MoeNo ratings yet
- Mataias Contreiras - Science4 - U5 - FORM-3-8Document6 pagesMataias Contreiras - Science4 - U5 - FORM-3-8mcontrerasaNo ratings yet
- Spherical Earth Activities KeyDocument3 pagesSpherical Earth Activities KeyLeah AquinoNo ratings yet
- Elements of the Climate System Explained in 4 PartsDocument1 pageElements of the Climate System Explained in 4 PartsMelvin Jake ManaogNo ratings yet
- Earth: Exploration of Earth and SpaceDocument104 pagesEarth: Exploration of Earth and SpaceNursaiyidah RoniNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEBrynn EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Activity 2-Investigating Four Spheres of EarthDocument7 pagesActivity 2-Investigating Four Spheres of EarthAlpha SalcepuedesNo ratings yet
- Edited - LESSON 2: EARTH AND EARTH SYSTEMSDocument2 pagesEdited - LESSON 2: EARTH AND EARTH SYSTEMSVinczent Jade B. SumayloNo ratings yet
- 2 Carbon CompoundDocument8 pages2 Carbon Compoundvt.subraNo ratings yet
- 1 Acid Base SaltDocument13 pages1 Acid Base Saltvt.subraNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Revision - Chapter 2Document5 pagesForm 4 Revision - Chapter 2vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Revision Ch 4 Ops on SetsDocument6 pagesForm 4 Revision Ch 4 Ops on Setsvt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 5 Revision - Chapter 2 MatrixDocument6 pagesAssignment - Form 5 Revision - Chapter 2 Matrixvt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 3 Revision - CIRCLES AnswerDocument4 pagesAssignment - Form 3 Revision - CIRCLES Answervt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 5 Revision - Chapter 5Document2 pagesAssignment - Form 5 Revision - Chapter 5vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 4 Revision - Chapter 9 AnswerDocument1 pageAssignment - Form 4 Revision - Chapter 9 Answervt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 5 Revision - Chapter 5Document2 pagesAssignment - Form 5 Revision - Chapter 5vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Prefect Inauguration (Buku Program) 2019Document8 pagesPrefect Inauguration (Buku Program) 2019vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 4 Revision - Chapter 8Document5 pagesAssignment - Form 4 Revision - Chapter 8vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Form 4 Revision - Chapter 9Document3 pagesAssignment - Form 4 Revision - Chapter 9vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Prefect Inauguration (Buku Program) 2019Document8 pagesPrefect Inauguration (Buku Program) 2019vt.subraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FunctionsDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - FunctionsWan Shahirah100% (2)
- Prefect Inauguration (Buku Program) 2019Document8 pagesPrefect Inauguration (Buku Program) 2019vt.subraNo ratings yet
- 3D Holographic Techonology PPT - 1Document17 pages3D Holographic Techonology PPT - 1rajesh mangena100% (1)
- Measurement Methods: Direct vs Indirect Level SensingDocument24 pagesMeasurement Methods: Direct vs Indirect Level Sensingrom10000% (1)
- RADIOSS: Screwing Process Sample: Erwan MestresDocument6 pagesRADIOSS: Screwing Process Sample: Erwan Mestresdotiep88No ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch2 1Document6 pages9 Science Imp ch2 1Er- WALTAR Sir, INNOVATIVE & SMART CLASSESNo ratings yet
- A Shortcut To Optimize Pipe Diameters by Economic CriteriaDocument4 pagesA Shortcut To Optimize Pipe Diameters by Economic CriteriaBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- Introduction To Second-Quantization IDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Second-Quantization IWilliamNo ratings yet
- IPS e El 110Document105 pagesIPS e El 110alinaghibNo ratings yet
- ROLLED PRODUCT DEFECTS AND REMEDIESDocument32 pagesROLLED PRODUCT DEFECTS AND REMEDIESamit gajbhiye100% (2)
- Comparison of SorptionDocument11 pagesComparison of SorptionRicardo Alonso Rocano SalazarNo ratings yet
- Electrowinning and Electrorefining of Copper (Murdoch University)Document76 pagesElectrowinning and Electrorefining of Copper (Murdoch University)Victor100% (8)
- Ni Cad Block KBH HighDocument11 pagesNi Cad Block KBH Highruben egeaNo ratings yet
- Calculation For 450Mm Pipe Culvert Capacity: Velocity, V Capacity, QDocument11 pagesCalculation For 450Mm Pipe Culvert Capacity: Velocity, V Capacity, QAnonymous O404LiV4CNo ratings yet
- MCQ LasersDocument9 pagesMCQ LasersMADHAVNo ratings yet
- Cat 3Document13 pagesCat 3Sebastian LopezNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of Brass and PLADocument10 pagesThermal Conductivity of Brass and PLAJonathan WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Flash Dryer CatalogueDocument4 pagesFlash Dryer CatalogueGantulga TogtokhNo ratings yet
- EML 6155 Convection Heat TransferDocument4 pagesEML 6155 Convection Heat TransfermasumehtfNo ratings yet
- SP Grade 2 SB Course MaterialsDocument23 pagesSP Grade 2 SB Course MaterialsChia Hock ChuanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Engineers Lab ReviewerDocument10 pagesChemistry for Engineers Lab ReviewerCarl Tyrone DizonNo ratings yet
- Valve CaterpillarDocument5 pagesValve CaterpillarЯрослав Валько100% (1)
- 235 Practice Exam 1Document11 pages235 Practice Exam 1bamforNo ratings yet
- 3 Unit EMDocument5 pages3 Unit EMS.Sampath Chemistry Ghss GurubarapalliNo ratings yet
- Elder 1967Document22 pagesElder 1967ALEJANDRO GANCEDO TORALNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon Fibers From Silkworm Cocoon Waste For Congo Red AdsorptionDocument12 pagesActivated Carbon Fibers From Silkworm Cocoon Waste For Congo Red AdsorptionVũ Văn NguyênNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document10 pagesLecture 4Abdullah SubbirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6a Pavement DesignDocument20 pagesLecture 6a Pavement DesignEngr Asad Ahmad ShahNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- NEET MATERIAL Circular MotionDocument27 pagesNEET MATERIAL Circular MotionApex Institute100% (5)
- Standard Practice For Conducting Force Controlled Constant Amplitude Axial Fatigue Tests of Metallic MaterialsDocument7 pagesStandard Practice For Conducting Force Controlled Constant Amplitude Axial Fatigue Tests of Metallic MaterialsviverefeliceNo ratings yet
- ANGLEDocument3 pagesANGLEskorut100% (2)
- The Secret of the Golden Flower: A Chinese Book Of LifeFrom EverandThe Secret of the Golden Flower: A Chinese Book Of LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Essence of the Bhagavad Gita: Explained by Paramhansa Yogananda as remembered by his disciple, Swami KriyanandaFrom EverandThe Essence of the Bhagavad Gita: Explained by Paramhansa Yogananda as remembered by his disciple, Swami KriyanandaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeFrom EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosFrom EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Essence of Self-Realization: The Wisdom of Paramhansa YoganandaFrom EverandThe Essence of Self-Realization: The Wisdom of Paramhansa YoganandaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (43)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersFrom EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- Timefulness: How Thinking Like a Geologist Can Help Save the WorldFrom EverandTimefulness: How Thinking Like a Geologist Can Help Save the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- Chemtrails, HAARP, and the Full Spectrum Dominance of Planet EarthFrom EverandChemtrails, HAARP, and the Full Spectrum Dominance of Planet EarthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeFrom EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Buddha to Thomas Merton: Wisdom from the Great Mystics, Sages, and Saints, FromFrom EverandBuddha to Thomas Merton: Wisdom from the Great Mystics, Sages, and Saints, FromRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- God As Nature Sees God: A Christian Reading of the Tao Te ChingFrom EverandGod As Nature Sees God: A Christian Reading of the Tao Te ChingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)