Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer Lecture
Uploaded by
Safaa Hameed Al NaseryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer Lecture
Uploaded by
Safaa Hameed Al NaseryCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr.
Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer Lecture
HW-5-
1- A wall 40 mm thick has its surfaces maintained at 0°C and 100°C. The heat generation rate is 3.25 ×
105 W/m3. If the thermal conductivity of the material is 2 W/mK, determine the temperature at the mid
plane, the location and value of the maximum temperature and the heat flow at either end. The data are
shown in Fig. Ans(xmax = 0.01538 m, Tmax = 101.74°C , 1500 W/m2, 11500 W/m2)
2- A plate shaped nuclear fuel element of 24 mm thickness exposed on the sides to convection at 200°C
with a convective heat transfer coefficient of 900 W/m2K generates heat at 20 MW/m3. Determine (i) the
surface temperature, (ii) the maximum temperature in the plate and (iii) the temperature gradient at the
surface. Thermal conductivity of the material is 25 W/mK. Ans(Tw = 466.7°C, To = 524.3°C, –
9600°C/m.)
3- A plate shaped nuclear fuel element of 24 mm thickness exposed on the sides to convection at 200°C
with a convective heat transfer coefficient of 900 W/m2K generates heat at 20 MW/m3. Determine (i) the
surface temperature, (ii) the maximum temperature in the plate and (iii) the temperature gradient at the
surface. Thermal conductivity of the material is 25 W/mK. (Ans: 524 °C, – 9600°C/m)
4-A 10 cm thick plane wall (k = 45 W/m· K) generates heat at a uniform rate of 8 * 10 6 W/m3. The two
sides of the wall are maintained at 180°C and 120°C. calculate for A=1m2 the
(i) Temperature distribution across the plate.
(ii) Position and magnitude of the maximum temperature.
(iii) Heat flow rate from each surface of the plate.
Answ(T(x) = -88888.89x2+ 9488.89x + 180; x = 0.0533 m; 433.23°C; 427 kW; 373 kW)
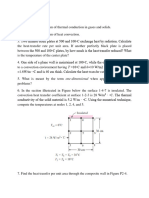
5- Large electrical currents are often carried in aluminum
conductors. Consider a long, 2-cm diameter cable covered
by insulation 2-mm thick. For a particular application, the
outside insulation temperature is limited to 35 ºC, and none
of the insulation can exceed 50 ºC. The cable is in an
environment in which the convective heat transfer
2
coefficient is 25 W/m ·K, the air temperature is 24 ºC, the
insulation thermal conductivity is 0.10 W/m·K, and the
-4
electrical resistance per unit length of the wire is 3.9 × 10
Ω/m. Determine the maximum current allowed (in A).
6- A3.2-mm-diameter stainless-steel wire 30 cm long has a voltage of 10 V impressed on it. The outer
surface temperature of the wire is maintained at 93◦C. Calculate the center temperature of the wire. Take
the resistivity of the wire as 2.611*10-3 Ω and the thermal conductivity as 22.5 W/m.◦C. answ(138C)
7-The outside of a copper wire (k=386W/m.K) having a diameter of 2 mm is exposed to a convection
environment with h=5000 W/m2 ・ ◦C and T∞ =100◦C. What current must be passed through the wire
to produce a center temperature of 150◦C? Repeat for an aluminum wire of the same diameter. The
resistance of copper is 5.315*10-3Ω. Take L=1m. Answ(542A)
Page(1)
You might also like
- Heat Transfer Equations and Critical Insulation RadiusDocument18 pagesHeat Transfer Equations and Critical Insulation RadiusPon ShanmugakumarNo ratings yet
- ME209 Heat Transfer Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesME209 Heat Transfer Solved ProblemsWilliam Hernan HenaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power Plant EngineeringDocument9 pagesIntroduction to Power Plant EngineeringSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant KC ExplainedDocument49 pagesEquilibrium Constant KC ExplainedJagmohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Contoh Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesContoh Second Law of ThermodynamicsBaihaqi Bahrin100% (2)
- BS 5422 PDFDocument82 pagesBS 5422 PDFAnitha Mj75% (4)
- Temprature Hand Book - TempsensDocument182 pagesTemprature Hand Book - TempsensTempsens InstrumentsNo ratings yet
- Practical Boiler Operation Engineering and Power PlantDocument581 pagesPractical Boiler Operation Engineering and Power Plantferez pasaribuNo ratings yet
- CIBSE Module 143 - Variable Air Volume (VAV) Air Conditioning Matures, Adapts and Flourishes - CIBSE JournalDocument13 pagesCIBSE Module 143 - Variable Air Volume (VAV) Air Conditioning Matures, Adapts and Flourishes - CIBSE JournalStephenBrammerNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer: "Solved Problems"Document16 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer: "Solved Problems"qiritical99No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Unit - I: 2 Conductivity 0 0Document14 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Unit - I: 2 Conductivity 0 0Christopher MillerNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Prob Sheet S S C With Heat GenerationDocument2 pages4.1 Prob Sheet S S C With Heat GenerationAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Practice Questions 1Document2 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Practice Questions 1Lucky 230503No ratings yet
- Tutorial - Conduction Heat TransferDocument3 pagesTutorial - Conduction Heat TransferDayanidiNo ratings yet
- HMT Qp-IDocument2 pagesHMT Qp-IPoyyamozhi Nadesan RanjithNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Kunal YadavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems-Unit 1-75 PercDocument5 pagesTutorial Problems-Unit 1-75 PercSuseel Jai Krishnan0% (1)
- Heat Transfer Practice ProblemDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Practice ProblemmkbNo ratings yet
- Sheets of Heat Transfer CourseDocument11 pagesSheets of Heat Transfer CourseSamir YehyaNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Mechanism of Heat ConvectionDocument3 pagesDiscuss The Mechanism of Heat Convectionarul mozhiNo ratings yet
- (An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaDocument2 pages(An Autonomous Institute Under VTU) Manandavadi Road, Mysore-570008, Karnataka, IndiaMohammed Maaz100% (1)
- HMT16 MarksDocument12 pagesHMT16 MarkstagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D EDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D ERotten AppleNo ratings yet
- 1492Document15 pages1492_Anggyaa_No ratings yet
- HT Notes For ESEDocument25 pagesHT Notes For ESEM BhurleNo ratings yet
- MECE 411 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet 3Document4 pagesMECE 411 Heat & Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet 3Thebe Tshepiso MaitshokoNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 1 2022Document6 pagesWork Sheet 1 2022Fikadu GonfaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial One Heat Conduction: 5 2. A P M º N 0Document7 pagesTutorial One Heat Conduction: 5 2. A P M º N 0kookoNo ratings yet
- HT Important Questions For End ExamDocument10 pagesHT Important Questions For End ExamSandeepKattaNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sathyabama University-Aeronautical Engineering 6th Sem Heat Transfer Sample Paper 1Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sathyabama University-Aeronautical Engineering 6th Sem Heat Transfer Sample Paper 1manipsgNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 (Generation)Document4 pagesSheet 4 (Generation)Rafi Mahmoud SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Abinesh GNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 With AnswersDocument2 pagesSheet 2 With Answers01156295293cNo ratings yet
- HT AssignmentDocument12 pagesHT AssignmentCollano M. Noel RogieNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer MechanismsDocument2 pagesSheet 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer MechanismsAhmed YousryNo ratings yet
- 4363 112 Heat TransferDocument6 pages4363 112 Heat Transferyogesh_b_kNo ratings yet
- Northern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferDocument2 pagesNorthern Border University College of Engineering 1403-342 Heat TransferAj ZNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1-13 PDFDocument27 pagesTutorial 1-13 PDFPavanNo ratings yet
- Lecture RadiationDocument16 pagesLecture Radiationzakibrant23No ratings yet
- HW 01Document2 pagesHW 01Potatoes123No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer ProblemsDocument3 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer ProblemsRiyasNo ratings yet
- Holman 1Document4 pagesHolman 1Kumar SamyanaikNo ratings yet
- ME8693-Heat and Mass Transfer IAE 1 Important Questions Part-A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12Document2 pagesME8693-Heat and Mass Transfer IAE 1 Important Questions Part-A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12kanalababsssoNo ratings yet
- Che 342 Practice Set I IDocument4 pagesChe 342 Practice Set I IDan McNo ratings yet
- 4.tutorial HMTDocument5 pages4.tutorial HMTdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDocument4 pages9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Sheet4 231203 210023Document2 pagesSheet4 231203 210023osamaahmedc7No ratings yet
- HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER SOLUTIONSDocument11 pagesHEAT AND MASS TRANSFER SOLUTIONSanithayesurajNo ratings yet
- Home Exam 1Document3 pagesHome Exam 1htbd 1995No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Practice QuestionsLucky 230503No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document0 pagesTutorial 2xhotdogzxNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5-1Document2 pagesTutorial 5-1chandan rajNo ratings yet
- Sheet Three ConductionDocument3 pagesSheet Three ConductionMichael EmadNo ratings yet
- ME5101 2020 Assignment 01Document2 pagesME5101 2020 Assignment 01palash_shrivastava6282058No ratings yet
- 34 Tutorial 1 HT1Document2 pages34 Tutorial 1 HT1jameeloNo ratings yet
- Updated ProblemsDocument3 pagesUpdated Problemsmahmoud koriemNo ratings yet
- nullDocument3 pagesnulldoddi.ajith2003No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer AssignmentDocument7 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer AssignmentAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- HT Assignment-1Document1 pageHT Assignment-1Karthikeya Kvs0223No ratings yet
- Assignments HMTDocument2 pagesAssignments HMTPiyush AgarawalNo ratings yet
- HT Problems-1Document25 pagesHT Problems-1abhiram pasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 19 (Fins)Document2 pagesPractice Set 19 (Fins)Nibir SahaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4Document3 pagesSheet 4Yasmin RedaNo ratings yet
- HMTDocument4 pagesHMTsumeetsharma270% (1)
- An Approach To Calculate Transient Heat Flow Through Multilayer Spherical StructuresDocument8 pagesAn Approach To Calculate Transient Heat Flow Through Multilayer Spherical StructuresSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Second Virial Coefficient of Nonspherical Molecules N2O, CH4, C2H4, C2Document8 pagesCalculation of The Second Virial Coefficient of Nonspherical Molecules N2O, CH4, C2H4, C2Safaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Entropy Generation Inside Concentric Cylindrical Annuli With Relative RotatioDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Entropy Generation Inside Concentric Cylindrical Annuli With Relative RotatioSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- A Ea Ss e W y - G e A A), A: Q1 A Steam Power Plant InstallDocument1 pageA Ea Ss e W y - G e A A), A: Q1 A Steam Power Plant InstallSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Emission and Performance Analysis of A Diesel Engine Burning CashewDocument9 pagesEmission and Performance Analysis of A Diesel Engine Burning CashewSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer HW ProblemsDocument1 pageHeat Transfer HW ProblemsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer HW ProblemsDocument1 pageHeat Transfer HW ProblemsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- A Method For Obtaining Performance Correlations of Absorption MachinesDocument6 pagesA Method For Obtaining Performance Correlations of Absorption MachinesSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer HW NO-6Document1 pageDR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer HW NO-6Safaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction: T T Ha QDocument10 pages1-Introduction: T T Ha QSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer HW ProblemsDocument1 pageHeat Transfer HW ProblemsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Power PlantDocument8 pagesPower PlantSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- DR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer LectureDocument1 pageDR - Safaa Hameed Faisal Heat Transfer LectureSafaa Hameed Al Nasery100% (1)
- Rankine cycle analysis and efficiency calculationsDocument3 pagesRankine cycle analysis and efficiency calculationsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Transient Heat Conduction LectureDocument7 pagesTransient Heat Conduction LectureSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- HW-4-sphere WithoutDocument1 pageHW-4-sphere WithoutSafaa Hameed Al Nasery100% (1)
- Answ:: Coefficient ConducDocument1 pageAnsw:: Coefficient ConducSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- My Lecturenozle - NewDocument10 pagesMy Lecturenozle - NewSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- 2013 683157Document8 pages2013 683157Safaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- HW-1 - Wall WithoutDocument1 pageHW-1 - Wall WithoutSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency of Refrigeration Systems PDFDocument11 pagesEnergy Efficiency of Refrigeration Systems PDFSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument6 pagesThermal Power PlantsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lecture HW-2 Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageHeat Transfer Lecture HW-2 Problems and SolutionsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide As A Natural RefrigerantDocument25 pagesCarbon Dioxide As A Natural RefrigerantSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- GE Power SystemsDocument20 pagesGE Power SystemsSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- Calculation Exercise-Combined Cycle3Document6 pagesCalculation Exercise-Combined Cycle3inno danNo ratings yet
- Calculation Exercise-Combined Cycle3Document6 pagesCalculation Exercise-Combined Cycle3inno danNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Exergy CostDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Exergy CostSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2015 P2Document20 pagesCSEC Physics June 2015 P2Is IbrahimNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems Guide for Comfort and EfficiencyDocument8 pagesHVAC Systems Guide for Comfort and EfficiencySiddhant Vijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Rate and Temperature CalculationsDocument9 pagesHeat Transfer Rate and Temperature CalculationsHectorCabzNo ratings yet
- Energies: Investigation of Stratified Thermal Storage Tank Performance For Heating and Cooling ApplicationsDocument15 pagesEnergies: Investigation of Stratified Thermal Storage Tank Performance For Heating and Cooling ApplicationsRicardo Chegwin HillembrandNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Thermometry, Thermal Expansion & Gas LawsDocument56 pagesTemperature, Thermometry, Thermal Expansion & Gas Lawsedidiong idiongNo ratings yet
- Max PlanckDocument1 pageMax Planckmr personalNo ratings yet
- Entropy 23 01095Document29 pagesEntropy 23 01095semabayNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Kathmandu UniversityDocument38 pagesIntroduction of Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics: Kathmandu UniversityUrgen TamangNo ratings yet
- Vernier-Mixing Warm ColdDocument4 pagesVernier-Mixing Warm ColdOeng BunhakNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer FormulaeDocument9 pagesMass Transfer FormulaeMarisa KirisameNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Numerical Simulation and Investigation of System Parameters of Sonochemical ProcessDocument15 pagesResearch Article: Numerical Simulation and Investigation of System Parameters of Sonochemical ProcessSutanwi LahiriNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Assignment 1Document3 pagesRefrigeration Assignment 1Diganta HatibaruahNo ratings yet
- II SemDocument28 pagesII SemkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument16 pagesRefrigerationKundan sharma100% (1)
- MEG507 Advanced Heat TransferDocument3 pagesMEG507 Advanced Heat TransferAkmal XusanovNo ratings yet
- Etanol-Víz Egyensúly SzámításaDocument30 pagesEtanol-Víz Egyensúly SzámításapseesheNo ratings yet
- EntropiaDocument3 pagesEntropiaMargarida PereiraNo ratings yet
- ε -pH diagrams), other predominance areaDocument56 pagesε -pH diagrams), other predominance areasepura cpmtcNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Staged Operations: A1 SlotDocument18 pagesEquilibrium Staged Operations: A1 SlotErmias NigussieNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 20.11.2017Document32 pagesQuestion Bank 20.11.2017tagoreboopathy0% (1)
- ESCI 341 - Ideal Gas LawDocument7 pagesESCI 341 - Ideal Gas Lawbenedy fajarNo ratings yet
- Proceeding 8th IMAT3Document118 pagesProceeding 8th IMAT3Edy SusantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFAroon KumarNo ratings yet
- Phase Changes - QuizizzDocument7 pagesPhase Changes - QuizizzMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet