Professional Documents
Culture Documents
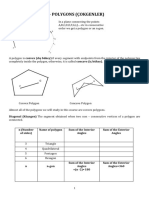
Angles of Polygons 7.1: Essential Question
Uploaded by
avrahamscOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Angles of Polygons 7.1: Essential Question
Uploaded by
avrahamscCopyright:
Available Formats
7.
1 Angles of Polygons
Essential Question What is the sum of the measures of the interior
angles of a polygon?
The Sum of the Angle Measures of a Polygon
Work with a partner. Use dynamic geometry software.
a. Draw a quadrilateral and a pentagon. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
angles of each polygon.
Sample
B
G
F
A C
H
E
I
D
b. Draw other polygons and find the sums of the measures of their interior angles.
Record your results in the table below.
CONSTRUCTING Number of sides, n 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
VIABLE ARGUMENTS
To be proficient in math, Sum of angle measures, S
you need to reason
c. Plot the data from your table in a coordinate plane.
inductively about data.
d. Write a function that fits the data. Explain what the function represents.
Measure of One Angle in a Regular Polygon
Work with a partner.
a. Use the function you found in Exploration 1 to write a new function that gives the
measure of one interior angle in a regular polygon with n sides.
b. Use the function in part (a) to find the measure of one interior angle of a regular
pentagon. Use dynamic geometry software to check your result by constructing a
regular pentagon and finding the measure of one of its interior angles.
c. Copy your table from Exploration 1 and add a row for the measure of one interior
angle in a regular polygon with n sides. Complete the table. Use dynamic geometry
software to check your results.
Communicate Your Answer
3. What is the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon?
4. Find the measure of one interior angle in a regular dodecagon (a polygon with
12 sides).
Section 7.1 Angles of Polygons 359
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 359 1/19/15 11:50 AM
7.1 Lesson What You Will Learn
Use the interior angle measures of polygons.
Use the exterior angle measures of polygons.
Core Vocabul
Vocabulary
larry
diagonal, p. 360 Using Interior Angle Measures of Polygons
equilateral polygon, p. 361
In a polygon, two vertices that are endpoints of Polygon ABCDE
equiangular polygon, p. 361
the same side are called consecutive vertices.
regular polygon, p. 361 A diagonal of a polygon is a segment that
C
Previous joins two nonconsecutive vertices.
B D
polygon
As you can see, the diagonals from one vertex
convex diagonals
divide a polygon into triangles. Dividing a
interior angles polygon with n sides into (n − 2) triangles A E
exterior angles shows that the sum of the measures of the A and B are consecutive vertices.
interior angles of a polygon is a multiple Vertex B has two diagonals, —
BD and — BE .
of 180°.
Theorem
Theorem 7.1 Polygon Interior Angles Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles
REMEMBER ⋅
of a convex n-gon is (n − 2) 180°.
1
2
3
A polygon is convex when m∠1 + m∠2 + . . . + m∠n = (n − 2) 180° ⋅ 6 5
4
no line that contains a side
of the polygon contains Proof Ex. 42 (for pentagons), p. 365 n=6
a point in the interior of
the polygon.
Finding the Sum of Angle Measures in a Polygon
Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles
of the figure.
SOLUTION
The figure is a convex octagon. It has 8 sides.
Use the Polygon Interior Angles Theorem.
⋅
(n − 2) 180° = (8 − 2) 180°⋅ Substitute 8 for n.
⋅
= 6 180° Subtract.
= 1080° Multiply.
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of the figure is 1080°.
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
1. The coin shown is in the shape of an 11-gon. Find
the sum of the measures of the interior angles.
360 Chapter 7 Quadrilaterals and Other Polygons
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 360 1/19/15 11:50 AM
Finding the Number of Sides of a Polygon
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon is 900°. Classify
the polygon by the number of sides.
SOLUTION
Use the Polygon Interior Angles Theorem to write an equation involving the number
of sides n. Then solve the equation to find the number of sides.
⋅
(n − 2) 180° = 900° Polygon Interior Angles Theorem
n−2=5 Divide each side by 180°.
n=7 Add 2 to each side.
The polygon has 7 sides. It is a heptagon.
Corollary
Corollary 7.1 Corollary to the Polygon Interior Angles Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
Proof Ex. 43, p. 366
Finding an Unknown Interior Angle Measure
108° 121° Find the value of x in the diagram.
SOLUTION
x° 59°
The polygon is a quadrilateral. Use the Corollary to the Polygon Interior Angles
Theorem to write an equation involving x. Then solve the equation.
x° + 108° + 121° + 59° = 360° Corollary to the Polygon Interior Angles Theorem
x + 288 = 360 Combine like terms.
x = 72 Subtract 288 from each side.
The value of x is 72.
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
2. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon is 1440°.
Classify the polygon by the number of sides.
3. The measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral are x°, 3x°, 5x°, and 7x°.
Find the measures of all the interior angles.
In an equilateral polygon, In an equiangular A regular polygon is
all sides are congruent. polygon, all angles in the a convex polygon that
interior of the polygon are is both equilateral and
congruent. equiangular.
Section 7.1 Angles of Polygons 361
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 361 1/19/15 11:50 AM
Finding Angle Measures in Polygons
A home plate for a baseball field is shown. A B
a. Is the polygon regular? Explain your reasoning.
b. Find the measures of ∠C and ∠E. E C
SOLUTION D
a. The polygon is not equilateral or equiangular. So, the polygon is not regular.
b. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles.
⋅ ⋅
(n − 2) 180° = (5 − 2) 180° = 540° Polygon Interior Angles Theorem
Then write an equation involving x and solve the equation.
x° + x° + 90° + 90° + 90° = 540° Write an equation.
2x + 270 = 540 Combine like terms.
x = 135 Solve for x.
So, m∠C = m∠E = 135°.
Q Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
P R
156°
93° 85° 4. Find m∠S and m∠ T in the diagram.
5. Sketch a pentagon that is equilateral but not equiangular.
T S
Using Exterior Angle Measures of Polygons
Unlike the sum of the interior angle measures of a convex polygon, the sum of the
exterior angle measures does not depend on the number of sides of the polygon. The
diagrams suggest that the sum of the measures of the exterior angles, one angle at each
vertex, of a pentagon is 360°. In general, this sum is 360° for any convex polygon.
2 1
360°
5 1 5 1 5
3 4
2
4 2 4 3
JUSTIFYING STEPS 3
To help justify this Step 1 Shade one Step 2 Cut out the Step 3 Arrange the
conclusion, you can exterior angle exterior angles. exterior angles
visualize a circle containing at each vertex. to form 360°.
two straight angles. So,
there are 180° + 180°,
or 360°, in a circle. Theorem
Theorem 7.2 Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem
180° 2
The sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a 3
convex polygon, one angle at each vertex, is 360°.
180° 4
m∠1 + m∠2 + · · · + m∠n = 360° 1
5
Proof Ex. 51, p. 366 n=5
362 Chapter 7 Quadrilaterals and Other Polygons
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 362 1/19/15 11:50 AM
Finding an Unknown Exterior Angle Measure
Find the value of x in the diagram. 89°
2x° 67°
x°
SOLUTION
Use the Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem to write and solve an equation.
x° + 2x° + 89° + 67° = 360° Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem
3x + 156 = 360 Combine like terms.
x = 68 Solve for x.
The value of x is 68.
REMEMBER
A dodecagon is a Finding Angle Measures in Regular Polygons
polygon with 12 sides
and 12 vertices. The trampoline shown is shaped like a
regular dodecagon.
a. Find the measure of each interior angle.
b. Find the measure of each exterior angle.
SOLUTION
a. Use the Polygon Interior Angles Theorem to
find the sum of the measures of the interior angles.
⋅
(n − 2) 180° = (12 − 2) 180° ⋅
= 1800°
Then find the measure of one interior angle. A regular dodecagon has
12 congruent interior angles. Divide 1800° by 12.
1800°
— = 150°
12
The measure of each interior angle in the dodecagon is 150°.
b. By the Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem, the sum of the measures of the exterior
angles, one angle at each vertex, is 360°. Divide 360° by 12 to find the measure of
one of the 12 congruent exterior angles.
360°
— = 30°
12
The measure of each exterior angle in the dodecagon is 30°.
Monitoring Progress Help in English and Spanish at BigIdeasMath.com
6. A convex hexagon has exterior angles with measures 34°, 49°, 58°, 67°, and 75°.
What is the measure of an exterior angle at the sixth vertex?
7. An interior angle and an adjacent exterior angle of a polygon form a linear pair.
How can you use this fact as another method to find the measure of each exterior
angle in Example 6?
Section 7.1 Angles of Polygons 363
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 363 1/19/15 11:50 AM
7.1 Exercises Dynamic Solutions available at BigIdeasMath.com
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
1. VOCABULARY Why do vertices connected by a diagonal of a polygon have to be nonconsecutive?
2. WHICH ONE DOESN’T BELONG? Which sum does not belong with the other three? Explain
your reasoning.
the sum of the measures of the interior the sum of the measures of the exterior
angles of a quadrilateral angles of a quadrilateral
the sum of the measures of the interior the sum of the measures of the exterior
angles of a pentagon angles of a pentagon
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3–6, find the sum of the measures of the In Exercises 15–18, find the value of x.
interior angles of the indicated convex polygon.
15. 16.
(See Example 1.) 102° 146° 140°
3. nonagon 4. 14-gon 120° 86° 138°
5. 16-gon 6. 20-gon 124°
x° 158° x° 59°
In Exercises 7–10, the sum of the measures of the
interior angles of a convex polygon is given. Classify the 17. 96° 18.
121° 2x° 152°
polygon by the number of sides. (See Example 2.) 143° 116°
x° x° 125°
7. 720° 8. 1080° 101°
139° 140°
162°
9. 2520° 10. 3240°
In Exercises 19 –22, find the measures of ∠X and ∠Y.
In Exercises 11–14, find the value of x. (See Example 3.)
(See Example 4.)
11. X 12. H
J 19. X Z 20.
100° Y 103°
133° 164° V W Y
130°
102° 47°
x° 66° Z
x° 58°
W Z G K 119°
Y X
W V
13. M 14. B
x° 92° 21. 22. W
L Z Y
154° A V Y 110°
x° 171°
99°
88°
K 29°
V 100° 149° U
101° 68° X
N 159°
D C 91°
W U
X Z
364 Chapter 7 Quadrilaterals and Other Polygons
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 364 1/19/15 11:51 AM
In Exercises 23–26, find the value of x. (See Example 5.) 34. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS The floor of the
gazebo shown is shaped like a regular decagon.
23. 24.
x° Find the measure of each interior angle of the
48°
50° regular decagon. Then find the measure of each
65° 59°
exterior angle.
39°
78°
106° 58° x°
x°
25. 26.
85° 40°
x°
71° 45°
44°
2x° 77°
3x° 2x°
35. WRITING A FORMULA Write a formula to find the
number of sides n in a regular polygon given that the
measure of one interior angle is x°.
In Exercises 27–30, find the measure of each interior
angle and each exterior angle of the indicated regular
36. WRITING A FORMULA Write a formula to find the
polygon. (See Example 6.)
number of sides n in a regular polygon given that the
27. pentagon 28. 18-gon measure of one exterior angle is x°.
29. 45-gon 30. 90-gon REASONING In Exercises 37– 40, find the number of
sides for the regular polygon described.
ERROR ANALYSIS In Exercises 31 and 32, describe and
37. Each interior angle has a measure of 156°.
correct the error in finding the measure of one exterior
angle of a regular pentagon.
38. Each interior angle has a measure of 165°.
✗
31.
⋅
(n − 2) 180° = (5 − 2) 180° ⋅ 39. Each exterior angle has a measure of 9°.
⋅
= 3 180°
40. Each exterior angle has a measure of 6°.
= 540°
41. DRAWING CONCLUSIONS Which of the following
The sum of the measures of the
angle measures are possible interior angle measures
angles is 540°. There are five
of a regular polygon? Explain your reasoning. Select
angles, so the measure of one
540° all that apply.
exterior angle is —5
= 108°.
A 162°
○ B 171°
○ C 75°
○ D 40°
○
✗
32.
There are a total of 10 exterior 42. PROVING A THEOREM The Polygon Interior Angles
angles, two at each vertex, so the Theorem (Theorem 7.1) states that the sum of the
measure of one exterior angle is measures of the interior angles of a convex n-gon is
360°
—10
= 36°. ⋅
(n − 2) 180°. Write a paragraph proof of this
theorem for the case when n = 5.
A
33. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS The base of a
jewelry box is shaped like a regular hexagon. What E B
is the measure of each interior angle of the jewelry
box base?
D C
Section 7.1 Angles of Polygons 365
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 365 1/19/15 11:51 AM
43. PROVING A COROLLARY Write a paragraph proof of 49. MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS The formula for the
the Corollary to the Polygon Interior Angles Theorem measure of each interior angle in a regular polygon
(Corollary 7.1). can be written in function notation.
a. Write a function h(n), where n is the number of
44. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that to
sides in a regular polygon and h(n) is the measure
find the interior angle measures of a regular polygon,
of any interior angle in the regular polygon.
you do not have to use the Polygon Interior Angles
Theorem (Theorem 7.1). You instead can use the b. Use the function to find h(9).
Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem (Theorem 7.2) and
c. Use the function to find n when h(n) = 150°.
then the Linear Pair Postulate (Postulate 2.8). Is your
friend correct? Explain your reasoning. d. Plot the points for n = 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8. What
happens to the value of h(n) as n gets larger?
45. MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS In an equilateral
hexagon, four of the exterior angles each have a
measure of x°. The other two exterior angles each 50. HOW DO YOU SEE IT? Is the hexagon a regular
have a measure of twice the sum of x and 48. Find the hexagon? Explain your reasoning.
measure of each exterior angle.
59°
60°
46. THOUGHT PROVOKING For a concave polygon, is
it true that at least one of the interior angle measures
60°
must be greater than 180°? If not, give an example.
59°
If so, explain your reasoning.
61°
61°
47. WRITING EXPRESSIONS Write an expression to find
the sum of the measures of the interior angles for a
concave polygon. Explain your reasoning.
51. PROVING A THEOREM Write a paragraph proof of
the Polygon Exterior Angles Theorem (Theorem 7.2).
(Hint: In a convex n-gon, the sum of the measures of
an interior angle and an adjacent exterior angle at any
vertex is 180°.)
52. ABSTRACT REASONING You are given a convex
polygon. You are asked to draw a new polygon by
increasing the sum of the interior angle measures by
540°. How many more sides does your new polygon
48. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS Polygon ABCDEFGH have? Explain your reasoning.
— and CD
is a regular octagon. Suppose sides AB — are
extended to meet at a point P. Find m∠BPC. Explain
your reasoning. Include a diagram with your answer.
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Reviewing what you learned in previous grades and lessons
Find the value of x. (Section 3.2)
53. 54. 55. 56.
113° (3x + 10)°
x° (8x − 16)°
(6x − 19)°
x° (3x + 20)°
79°
366 Chapter 7 Quadrilaterals and Other Polygons
hs_geo_pe_0701.indd 366 1/19/15 11:51 AM
You might also like
- Math-7 Q3 Week-5-6 Module-4 Polygons For-ReproductionDocument24 pagesMath-7 Q3 Week-5-6 Module-4 Polygons For-Reproductionzaijhon magallanesNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 7 q3 - w3 - d4 With Hots-SoloDocument7 pagesDLP Math 7 q3 - w3 - d4 With Hots-SoloJL Teope IcaoNo ratings yet
- EnhancedWS 2A04 03beDocument3 pagesEnhancedWS 2A04 03beOwen LiNo ratings yet
- Polygon Angle Sum GizmoDocument5 pagesPolygon Angle Sum GizmoEthan BostickNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Measurement UnitDocument74 pagesGeometry and Measurement UnitmesfinNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 7Document4 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 7Jamaica Ikan AquinoNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Angle in PolygonsDocument4 pages4.4 Angle in PolygonsRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- 6 1 Angles of PolygonsDocument23 pages6 1 Angles of PolygonsidkjittrippinNo ratings yet
- Handout 1.5 Polygons 1Document3 pagesHandout 1.5 Polygons 1james.ebardolazaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Geometry of Shape and Size-1Document21 pagesModule 2 - Geometry of Shape and Size-1bernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Visualizing PolygonsDocument32 pagesVisualizing PolygonsAllen Abegando BitterNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Angles of PolygonsDocument24 pages6-1 Angles of PolygonsDarwin VargasNo ratings yet
- ROQUE Lesson-PlanDocument12 pagesROQUE Lesson-PlanCHRISTIAN RHEY NEBRENo ratings yet
- Math7 Q3 Week 5Document21 pagesMath7 Q3 Week 5Francis TudlongNo ratings yet
- Angle Relationships - Part5Document8 pagesAngle Relationships - Part5dias.hugoNo ratings yet
- Angle Relationships - Part1Document8 pagesAngle Relationships - Part1dias.hugoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Geometry of Shape and SizeDocument20 pagesModule 2 - Geometry of Shape and SizepolotanNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument23 pagesPolygonsMary Ann TimbalNo ratings yet
- Designing Polygons: The Angle ConnectionDocument4 pagesDesigning Polygons: The Angle ConnectionjackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Deductive Geometry PDFDocument46 pagesChapter 4 - Deductive Geometry PDFauroraNo ratings yet
- 4 Angles in Polygons WsDocument2 pages4 Angles in Polygons WsYesNo ratings yet
- 1-Polygons HandoutDocument7 pages1-Polygons Handoutf.eylul3333No ratings yet
- q3 Week 6Document15 pagesq3 Week 6Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Module Interior and Exterior Angle of PolygonsDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Module Interior and Exterior Angle of PolygonsLawrence CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document21 pagesLesson 5Arnel ManaleNo ratings yet
- Form 3Document15 pagesForm 3Atikah Mat SaminganNo ratings yet
- DLP Interior & ExteriorDocument4 pagesDLP Interior & ExteriorAngie A. DerialNo ratings yet
- DLP ConvexDocument5 pagesDLP ConvexAngie A. DerialNo ratings yet
- Polygons 6Document96 pagesPolygons 6AshleyNo ratings yet
- LeaP Math G7 Week 5 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Math G7 Week 5 Q3JovelynNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Quarter3 Week5Document11 pagesGrade7 Quarter3 Week5midnight skyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2.5introduction To Polygon FillingDocument18 pagesUnit 1.2.5introduction To Polygon Filling20BCA1382 GYAN VARDHANNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument2 pagesPolygonsrinaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - 3 Quarter: Sarah May O. AcabadoDocument61 pagesMath 7 - 3 Quarter: Sarah May O. AcabadoBab SitaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7Gianmarie Sumagaysay Hilado100% (4)
- Geometría Taller 8 8vo 2019 2020 QuizDocument2 pagesGeometría Taller 8 8vo 2019 2020 QuizMILLER MARTINEZ CÁRDENASNo ratings yet
- Angles in PolygonsDocument24 pagesAngles in PolygonsPranav SathyanNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument8 pagesMathematicsSkyler MontalvoNo ratings yet
- ANGLES AND POLYGONSDocument20 pagesANGLES AND POLYGONSNoor HayatiNo ratings yet
- Triangle TheoremsDocument14 pagesTriangle TheoremsAiden ChristensenNo ratings yet
- (457756) 15 Identify and Calculate With Co-Interior Alternate and Corresponding AnglesDocument2 pages(457756) 15 Identify and Calculate With Co-Interior Alternate and Corresponding AnglesJaniceNo ratings yet
- Polygons and Their Angles MeasuresDocument16 pagesPolygons and Their Angles MeasuresRaymark MagatNo ratings yet
- Math 7-Q3-Module-5Document16 pagesMath 7-Q3-Module-5Joseff Rey PizonNo ratings yet
- Esolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroDocument33 pagesEsolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroNate WoolfNo ratings yet
- Math 7 3rd Grading ExamDocument3 pagesMath 7 3rd Grading ExamRickrick EspinaNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Angles of PolygonsDocument33 pages6-1 Angles of Polygonsjamaica almazanNo ratings yet
- Workbook 3.4 Reflected Light - Mirrors FILLABLEDocument8 pagesWorkbook 3.4 Reflected Light - Mirrors FILLABLETim DaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Polygons - 1: Polygons Are Closed Figures Made Only of Line SegmentsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Polygons - 1: Polygons Are Closed Figures Made Only of Line SegmentsAnkit SultaniyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Math 7Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Math 7Cirilyn CincoNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Polygons - Interior AnglesDocument20 pages3.3 Polygons - Interior AnglesFathima SbNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Q3 Module 5Document22 pagesMath 7 Q3 Module 5yt prem67% (3)
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Quiz (Quarter 3)Document11 pagesWeekly Quiz (Quarter 3)Shiela Marie ColloNo ratings yet
- Workbook 3.4 Reflected Light - Mirrors FILLABLEDocument8 pagesWorkbook 3.4 Reflected Light - Mirrors FILLABLEkun jiangNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument16 pagesMathematicsKeisha LeighNo ratings yet
- KSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 PolygonsDocument7 pagesKSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygonsnorfatimah zaharahNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Polygon Formulas: Mental Floss: Mon, Jan 8Document4 pages7.1 Polygon Formulas: Mental Floss: Mon, Jan 8Jhon Lou Raña ManuelNo ratings yet
- 7.1 - Key Polygon Concepts and FormulasDocument4 pages7.1 - Key Polygon Concepts and FormulasJhon Lou Raña ManuelNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument3 pagesPolygonasep habibulohNo ratings yet
- In-Service Teachers' Training Creative Physics Workshops at The National Polytechnic Institute in MexicoDocument10 pagesIn-Service Teachers' Training Creative Physics Workshops at The National Polytechnic Institute in MexicoavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Hiperbola - EjerciciosDocument26 pagesHiperbola - EjerciciosavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Maxima MinimaDocument34 pagesMaxima MinimaSridhar DvNo ratings yet
- Boost Your Brainstorm Effectiveness With The Why HabitDocument2 pagesBoost Your Brainstorm Effectiveness With The Why HabitavrahamscNo ratings yet
- FGGDocument6 pagesFGGMaxela Azi CastroNo ratings yet
- Refinement of Logico-Mathematical Intelligence in The Context of Physics EducationDocument1 pageRefinement of Logico-Mathematical Intelligence in The Context of Physics EducationavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Polygons and Angles PDFDocument4 pagesPolygons and Angles PDFavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Circle Sectors PDFDocument6 pagesCircle Sectors PDFavrahamsc100% (1)
- Missionaries of ScienceDocument7 pagesMissionaries of ScienceavrahamscNo ratings yet
- PoincareDocument10 pagesPoincareIndra Budhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- GovernanceDocument29 pagesGovernanceavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Electroscopio ElectronicoDocument3 pagesElectroscopio ElectronicoavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - Substitution MethodsDocument34 pagesIntegral Calculus - Substitution MethodsVillamorchard0% (2)
- Integral Calculus - Substitution MethodsDocument34 pagesIntegral Calculus - Substitution MethodsVillamorchard0% (2)
- Solutions of Schrodinger EquationDocument4 pagesSolutions of Schrodinger EquationavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus - Substitution MethodsDocument34 pagesIntegral Calculus - Substitution MethodsVillamorchard0% (2)
- Money Vs Performance PDFDocument4 pagesMoney Vs Performance PDFavrahamscNo ratings yet
- GovernanceDocument29 pagesGovernanceavrahamscNo ratings yet
- OptimizationDocument107 pagesOptimizationavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Torah Bereshit PDFDocument795 pagesTorah Bereshit PDFavrahamsc100% (2)
- Money Vs Performance PDFDocument4 pagesMoney Vs Performance PDFavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Money Vs Performance PDFDocument4 pagesMoney Vs Performance PDFavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Electroscopio ElectronicoDocument3 pagesElectroscopio ElectronicoavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Torah Bereshit PDFDocument795 pagesTorah Bereshit PDFavrahamsc100% (4)
- The Circle of Profit PDFDocument230 pagesThe Circle of Profit PDFVictor Manuel Gallegos Cortes100% (1)
- Misioneros de La CienciaDocument30 pagesMisioneros de La CienciaavrahamscNo ratings yet
- PoincareDocument10 pagesPoincareIndra Budhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Einstein's Secret To Amazing Problem Solving (And 10 Specific Ways You Can Use It)Document5 pagesEinstein's Secret To Amazing Problem Solving (And 10 Specific Ways You Can Use It)Saad MemonNo ratings yet
- Measuring G: An Inexhaustible Source of Instruction and CreativityDocument7 pagesMeasuring G: An Inexhaustible Source of Instruction and CreativityavrahamscNo ratings yet
- Michele Capovilla-Searle, Keiko Kawamuro, and Rebecca SorsenDocument47 pagesMichele Capovilla-Searle, Keiko Kawamuro, and Rebecca SorsenDainXBNo ratings yet
- Data Exchange Between CAD/CAM/CAE SystemsDocument34 pagesData Exchange Between CAD/CAM/CAE SystemsHarsheel PanchasaraNo ratings yet
- Polyhedral Formula (Sometimes Called Euler's Formula)Document11 pagesPolyhedral Formula (Sometimes Called Euler's Formula)Mohammad AdamNo ratings yet
- Efficient Computation of Regularized Boolean Operations On The Extreme Vertices Model in The N-Dimensional Space (nD-EVM)Document19 pagesEfficient Computation of Regularized Boolean Operations On The Extreme Vertices Model in The N-Dimensional Space (nD-EVM)hnmhernandezNo ratings yet
- Spatial Data TypesDocument54 pagesSpatial Data TypesNnelg Dlorah SelaromNo ratings yet
- Generate Unstructured Triangular Meshes for FVCOM ModelsDocument27 pagesGenerate Unstructured Triangular Meshes for FVCOM ModelsMeddyDanial100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - Math5 - Visualizing Solid FiguresDocument6 pagesLesson Plan - Math5 - Visualizing Solid FiguresMarieBosangitCasilao100% (2)
- 3 Reasons Why Optimal Solution to Linear Programming Lies at Extreme PointDocument2 pages3 Reasons Why Optimal Solution to Linear Programming Lies at Extreme PointRahulRajRanaNo ratings yet
- PLY Format PLY Format Description Description Plus VCG Extensions Plus VCG ExtensionsDocument15 pagesPLY Format PLY Format Description Description Plus VCG Extensions Plus VCG ExtensionsPaolo CignoniNo ratings yet
- 1.how Can Scaling With Respect To A Point P (.X, y Z) Be Defined in Terms of Scaling With Respect To The Origin?Document16 pages1.how Can Scaling With Respect To A Point P (.X, y Z) Be Defined in Terms of Scaling With Respect To The Origin?LoveBabbarNo ratings yet
- Collision Detection and Response For Computer AnimationDocument10 pagesCollision Detection and Response For Computer AnimationFred J. BeansNo ratings yet
- 2 D 3 D Shapes WorkbookDocument26 pages2 D 3 D Shapes Workbooknia rahmayantiNo ratings yet
- Plexus 2 DocumentationDocument29 pagesPlexus 2 DocumentationHeberto MonroyNo ratings yet
- Voro++ Overview PDFDocument16 pagesVoro++ Overview PDFSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SPII - Grade 8 Mathematics - Curriculum REVISEDDocument50 pagesSPII - Grade 8 Mathematics - Curriculum REVISEDJay B Gayle0% (1)
- Importing Spatial Data Into Tableau Using FMEDocument6 pagesImporting Spatial Data Into Tableau Using FMEYogender KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is TessellationDocument55 pagesWhat Is Tessellationazirah90100% (1)
- Kalsar College Graphics Lab Bresenham's Line AlgorithmDocument37 pagesKalsar College Graphics Lab Bresenham's Line AlgorithmNiranjanNo ratings yet
- IMO 2005 ShortlistDocument51 pagesIMO 2005 ShortlistAdnan GobeljićNo ratings yet
- A Coder's Guide To Spline-Based Procedural GeometryDocument85 pagesA Coder's Guide To Spline-Based Procedural GeometrychessgeneralNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics VIDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics VIPaul Bryan Bron100% (2)
- San Pablo Q3 M7 Week 5 MSEMontanaDocument4 pagesSan Pablo Q3 M7 Week 5 MSEMontanaPaul Marwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- How To Create A Realistic 3D Diamond Ring With 3DS Max TutorialDocument10 pagesHow To Create A Realistic 3D Diamond Ring With 3DS Max Tutorialchinu074160% (1)
- NotesDocument220 pagesNotessteveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 State Management and Drawing Geometric Objects PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 06 State Management and Drawing Geometric Objects PDFprincejiNo ratings yet
- Tesseract Magick I of IIIDocument3 pagesTesseract Magick I of IIIseparatus367100% (2)
- DLP Gr. 6 Module 54 Identifying The Faces Edges, and Vertices of Solids PDFDocument12 pagesDLP Gr. 6 Module 54 Identifying The Faces Edges, and Vertices of Solids PDFCyrell Castroverde PapauranNo ratings yet
- Mobile Topographer GIS: App LicalityDocument79 pagesMobile Topographer GIS: App LicalityMarca NéstorNo ratings yet
- Easy ICDocument201 pagesEasy ICMohamed RayanyNo ratings yet
- Assura Metal Slotting PDFDocument26 pagesAssura Metal Slotting PDFkien diepNo ratings yet