Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Time Conjunctions - Past Tenses - Theory
Uploaded by
Jose100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
40 views1 pageThis document provides definitions and examples of time conjunctions used with past tenses. It explains the uses of "as", "while", "when", "as soon as", "by the time", "once", and "until" to indicate sequences of events, parallel situations, interruptions, and specific points in time in the past. Examples are given to illustrate the meaning and usage of each conjunction.
Original Description:
HOW TO USE THEM?
Original Title
TIME CONJUNCTIONS _ PAST TENSES - THEORY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides definitions and examples of time conjunctions used with past tenses. It explains the uses of "as", "while", "when", "as soon as", "by the time", "once", and "until" to indicate sequences of events, parallel situations, interruptions, and specific points in time in the past. Examples are given to illustrate the meaning and usage of each conjunction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
40 views1 pageTime Conjunctions - Past Tenses - Theory
Uploaded by
JoseThis document provides definitions and examples of time conjunctions used with past tenses. It explains the uses of "as", "while", "when", "as soon as", "by the time", "once", and "until" to indicate sequences of events, parallel situations, interruptions, and specific points in time in the past. Examples are given to illustrate the meaning and usage of each conjunction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
TIME CONJUNCTIONS – PAST TENSES
As, while, when As soon as
1) An interruption: a long action interrupted by a short
one 1) Immediately after: the second event happened
immediately after the first
e.g.: As/While/When I was watching a
horror movie, I heard a noise. e.g.: As soon as he had gone outside, it started
raining.
e.g.: It started raining as soon as he had gone
2) Parallel situations: two longer activities happening at outside.
the same time
AS SOON AS + PAST PERFECT
e.g.: As /While/When I was working, my
brother was sitting on the beach.
By the time
When
1) A sequence of events: an instant short action after 1) Before:
another one
e.g.: By the time the police arrived, the robbers
e.g.: When he crossed the finish line, everybody had run away.
cheered. e.g.: The robbers had run away by the time the
police came.
Before, after BY THE TIME + PAST SIMPLE
Once
1) Sequence of events: “before” always goes with the
second action in the sequence. 1) Specific point in time: something has already
happened
e.g.: Before we left, I filled up/had filled up with
petrol. e.g.: Once they got home in the evening, her
e.g.: I filled up/had filled up with petrol before mother had already gone to sleep.
we left.
2) Sequence of events: “after” always goes with the
Until
first action in the sequence.
1) Up to a time in the past: the main clause usually
e.g.: After I filled up/had filled up with petrol, comes first
we left.
e.g.: We left after I filled up/had filled up with e.g.: I’m going to wait until the January sales
petrol. start to buy a new jacket.
e.g.: I thought he was called Damien! Until he
mentioned his name was Doug,
You might also like
- Past Continous Tense: To Talk About An Action Which Was in Progress at A Certain Time in The PastDocument1 pagePast Continous Tense: To Talk About An Action Which Was in Progress at A Certain Time in The PastSherly KuwiatmadjaNo ratings yet
- Grammar English For ScienceDocument104 pagesGrammar English For ScienceRizka Alfi100% (1)
- Narrative Forms (I07)Document11 pagesNarrative Forms (I07)Fabryzio Stefano Espada RiosNo ratings yet
- What Is The Passive Voice?: Vinci. (Agent Leonardo Da Vinci)Document25 pagesWhat Is The Passive Voice?: Vinci. (Agent Leonardo Da Vinci)yuvitaNo ratings yet
- Narrative FormsDocument11 pagesNarrative FormsAriana Cerazo ReymundoNo ratings yet
- Past TensesDocument1 pagePast TensesZineb RahmaniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Passive Voice?: Vinci. (Agent Leonardo Da Vinci)Document25 pagesWhat Is The Passive Voice?: Vinci. (Agent Leonardo Da Vinci)yuvita prasadNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous VS Simple PastDocument5 pagesPast Continuous VS Simple Pastdarwin gualotoNo ratings yet
- For An Action Which Happened Before A Definite Time in The Past Examples: Time in The Past ExamplesDocument1 pageFor An Action Which Happened Before A Definite Time in The Past Examples: Time in The Past ExamplesElsa Ventura BosiNo ratings yet
- 1a Past Tenses CPE Use of English V.evansDocument5 pages1a Past Tenses CPE Use of English V.evansTetiana GumeniukNo ratings yet
- Profa de Engleza - Amintire...Document6 pagesProfa de Engleza - Amintire...Catalin ScorusNo ratings yet
- Passe Compose Vs Imparfait-1Document3 pagesPasse Compose Vs Imparfait-1Loona KKNo ratings yet
- My Parents Often Took Us Sightseeing When We Were Kids. She'd Been Writing Poems For Over 10 Years Before She Had Her First Book PublishedDocument2 pagesMy Parents Often Took Us Sightseeing When We Were Kids. She'd Been Writing Poems For Over 10 Years Before She Had Her First Book PublishedVeronica TimofteNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Past Simple When WhileDocument2 pagesPast Continuous Past Simple When WhileBiljana Petrovska100% (2)
- Meeting 13 Ftik 2020: Noun Clause A Noun Clause Is Used As A Subject or An ObjectDocument7 pagesMeeting 13 Ftik 2020: Noun Clause A Noun Clause Is Used As A Subject or An ObjectRizal RuliyantoNo ratings yet
- Grammar 3 Syllabus 1 Pages 1 6 CompressedDocument6 pagesGrammar 3 Syllabus 1 Pages 1 6 CompressedIinpuspitaa sariiNo ratings yet
- MIND MAP Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument1 pageMIND MAP Past Simple Vs Past Continuoussabineft82No ratings yet
- Engleza An II Sem I - Unit 3Document13 pagesEngleza An II Sem I - Unit 3Ciprian ChelariuNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2. The Past Tense ProgressiveDocument2 pages3.2.2. The Past Tense ProgressiveLivia MoreanuNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Dan Past Simple: Tenses GabunganDocument2 pagesPast Continuous Dan Past Simple: Tenses GabunganVio KartikoNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument2 pagesPast Tenseratih widyaNo ratings yet
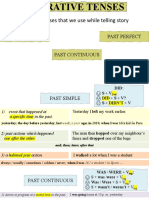
- Grammar Tenses That We Use While Telling Story: Past Simple Past PerfectDocument4 pagesGrammar Tenses That We Use While Telling Story: Past Simple Past PerfectItaliano TimeNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice Science 3Document15 pagesActive and Passive Voice Science 3Rafi FairuzNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument3 pagesGrammarapriliaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple 2. Past ContinuousDocument8 pagesPast Simple 2. Past ContinuousGeraldine QuirogaNo ratings yet
- Verb Form in EnglishDocument2 pagesVerb Form in EnglishAnonymous eKsE5t3wNo ratings yet
- Who Was This Man?: Benjamin FranklinDocument19 pagesWho Was This Man?: Benjamin FranklinFabrizioLupoNo ratings yet
- Ar Guide Past Perfect: Wegot Married in 1990, Just Ayear After Hadfallen in Very Time (Like Breaking A Window)Document1 pageAr Guide Past Perfect: Wegot Married in 1990, Just Ayear After Hadfallen in Very Time (Like Breaking A Window)ireneNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Past TensesDocument2 pagesUnit 2 - Past TensesLaura Luque BruguéNo ratings yet
- Expressing Simultaneity and Anteriority in Time ClausesDocument2 pagesExpressing Simultaneity and Anteriority in Time Clausesjauhar27100% (2)
- We Use The Simple Past For Completed Actions ThatDocument1 pageWe Use The Simple Past For Completed Actions ThatKorchi IlyassNo ratings yet
- Non Finite Clauses 1Document4 pagesNon Finite Clauses 1Cecilia Mercedes MendozaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Past ProgressiveDocument4 pagesSimple Past Past ProgressiveErick FarelNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses. Uses and Examples Eso (Updated)Document3 pagesVerb Tenses. Uses and Examples Eso (Updated)carmenerodriguez2277No ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument9 pagesPassive VoiceLeizl Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Past ProgressiveDocument8 pagesSimple Past Past ProgressiveOscar TaguacundoNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous+Past Simple When WhileDocument2 pagesPast Continuous+Past Simple When WhileKatmadvi100% (29)
- Past Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast Perfect Simple and ContinuousPatricia PerezNo ratings yet
- 3.tenses Gabungan and Pasive VioceDocument6 pages3.tenses Gabungan and Pasive ViocenikNo ratings yet
- ELTIdeas Tenses of English A4 PDFDocument2 pagesELTIdeas Tenses of English A4 PDFJackie YongNo ratings yet
- Time Expressions AfterDocument2 pagesTime Expressions AfterRobi SarmientoNo ratings yet
- English COMPLETE TENSESDocument21 pagesEnglish COMPLETE TENSESPaula FrentoaiaNo ratings yet
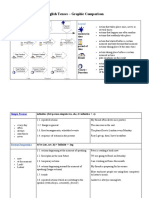
- English Tenses - Graphic Comparison: LegendDocument6 pagesEnglish Tenses - Graphic Comparison: LegendKim AnhNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Diagrams - HS22Document2 pagesVerb Tense Diagrams - HS22Natali OpanasiukNo ratings yet
- What Is The Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Passive VoiceDiraby DrinkNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Past Simple When WhileDocument2 pagesPast Continuous Past Simple When WhileGoga Maria0% (1)
- Presen T Past: 1. Simple PresentDocument3 pagesPresen T Past: 1. Simple PresentAnnisa AnyaNo ratings yet
- English Iii - Simple Past and Time SequencersDocument10 pagesEnglish Iii - Simple Past and Time SequencersMELANY OROSCONo ratings yet
- Tuyet W3 Unit 2 Tenses Adverbial Clause of Time Zalo HSDocument16 pagesTuyet W3 Unit 2 Tenses Adverbial Clause of Time Zalo HSVũ Thanh GiangNo ratings yet
- Adverb, Adjective and Noun ClauseDocument25 pagesAdverb, Adjective and Noun ClauseRaditya FanjasmaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 GrammarDocument4 pagesWeek 4 GrammarstefanoNo ratings yet
- Past Tense and Past Continuous VerbsDocument22 pagesPast Tense and Past Continuous VerbsAndree RosalesNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Genap 24Document6 pagesPassive Voice Genap 24Dora Dorii429No ratings yet
- S+V-ed/V2 S+was/were+V-ing S+ Didn't+v Inf S+wasn't/ Weren't+v-Ing Did+S+V Inf ? Was/Were +S+ V-Ing? Past Simple Past ContinuousDocument6 pagesS+V-ed/V2 S+was/were+V-ing S+ Didn't+v Inf S+wasn't/ Weren't+v-Ing Did+S+V Inf ? Was/Were +S+ V-Ing? Past Simple Past ContinuousRamona DinuNo ratings yet
- L36 - P13 - Past Continuous & Past SimpleDocument1 pageL36 - P13 - Past Continuous & Past SimplePhạm Yến NgọcNo ratings yet
- The Simple Past Tense 1.1.use For The Relation of Past EventsDocument6 pagesThe Simple Past Tense 1.1.use For The Relation of Past EventsDjamal DjannadNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past Continuous Vs Past PerfectDocument2 pagesPast Simple Vs Past Continuous Vs Past PerfectJulián CarlsonNo ratings yet
- Advanced Rev02 GW 01a-1Document2 pagesAdvanced Rev02 GW 01a-1กนกพล ด่านวัฒนพานิชNo ratings yet
- Class Assignment - Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesClass Assignment - Conditional SentencesJoseNo ratings yet
- Work Vs JobDocument3 pagesWork Vs JobJoseNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2JoseNo ratings yet
- Lessons - Oral ReviewDocument3 pagesLessons - Oral ReviewJoseNo ratings yet
- UNIT 05 TV Activity Worksheets PDFDocument2 pagesUNIT 05 TV Activity Worksheets PDFMicael RD50% (6)
- Class Assignment - Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesClass Assignment - Passive VoiceJoseNo ratings yet
- Class Assignment - Writing StoriesDocument1 pageClass Assignment - Writing StoriesJoseNo ratings yet
- Class Assignment - Complete Tense ReviewDocument3 pagesClass Assignment - Complete Tense ReviewJoseNo ratings yet
- Class No. 1: Oral Exam - ReviewDocument1 pageClass No. 1: Oral Exam - ReviewJoseNo ratings yet
- English Language Exam - A2-B1Document10 pagesEnglish Language Exam - A2-B1dule8350% (2)
- Who Do You Feel More IdentifiedDocument8 pagesWho Do You Feel More IdentifiedJoseNo ratings yet
- Sol3e Uppint Cumulative Test Answer Keys BDocument5 pagesSol3e Uppint Cumulative Test Answer Keys BJoseNo ratings yet
- STICKERSDocument2 pagesSTICKERSJoseNo ratings yet
- English Phonemic AlphabetDocument5 pagesEnglish Phonemic AlphabetJoseNo ratings yet
- EXTRA REVIEW - POSSESIVE ADJECTIVES - AnswersDocument1 pageEXTRA REVIEW - POSSESIVE ADJECTIVES - AnswersJoseNo ratings yet
- B1 Coping With Stress BLC001Document102 pagesB1 Coping With Stress BLC001JoseNo ratings yet
- Sol3e Uppint U5 Progress Test ADocument4 pagesSol3e Uppint U5 Progress Test AJose100% (1)
- Intermediate Unit5 Revision BeDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit5 Revision BeJoseNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Unit6 Revision BeDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit6 Revision BeJoseNo ratings yet
- Sol3e Uppint Cumulative Test Answer Keys ADocument5 pagesSol3e Uppint Cumulative Test Answer Keys AJoseNo ratings yet
- EXTRA REVIEW - SUBJECT AND OBECT - AnswersDocument1 pageEXTRA REVIEW - SUBJECT AND OBECT - AnswersJoseNo ratings yet
- Sol3e Uppint U4 Progress Test ADocument7 pagesSol3e Uppint U4 Progress Test AJoseNo ratings yet
- Sol3e Uppint Cumulative Test 6-9 BDocument5 pagesSol3e Uppint Cumulative Test 6-9 BJoseNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Unit4 Revision BeDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit4 Revision BeJoseNo ratings yet
- Online Activities II Year - Entrega 7Document3 pagesOnline Activities II Year - Entrega 7JoseNo ratings yet
- Online Activities II Year - Entrega 9Document5 pagesOnline Activities II Year - Entrega 9JoseNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Unit7 Revision BeDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit7 Revision BeJoseNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Unit8 Revision BeDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit8 Revision BeJoseNo ratings yet
- Online Activities II Year - Entrega 8Document3 pagesOnline Activities II Year - Entrega 8JoseNo ratings yet
- Online Activities II Year - Entrega 10Document4 pagesOnline Activities II Year - Entrega 10JoseNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: When NOT To Use "The"! (Definite Article) : 1. Things in GeneralDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar: When NOT To Use "The"! (Definite Article) : 1. Things in GeneralMatildaNo ratings yet
- Lindenwood University: School of HumanitiesDocument11 pagesLindenwood University: School of HumanitiesClarisse JaymeNo ratings yet
- Verbal and NonVerbal Communication QuizDocument4 pagesVerbal and NonVerbal Communication QuizAngelNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Communication SkillsDocument12 pagesAssignment On Communication SkillsMOHD.ARISH88% (73)
- Code Switching and Code MixingDocument25 pagesCode Switching and Code Mixinganna39No ratings yet
- Bombose - World EnglishDocument8 pagesBombose - World EnglishShirin AfrozNo ratings yet
- LEARNER GUIDE CHCECE007 Develop Positive and Respectful Relationships With ChildrenDocument47 pagesLEARNER GUIDE CHCECE007 Develop Positive and Respectful Relationships With ChildrenSidrah Subdia75% (16)
- GRADE 8 Course Outline Term 1 French 1Document2 pagesGRADE 8 Course Outline Term 1 French 1Beryl bundeNo ratings yet
- CAE (C1) : Rephrasing: 50 Examples of Rephrasing For Cambridge Cae Advanced ExamDocument14 pagesCAE (C1) : Rephrasing: 50 Examples of Rephrasing For Cambridge Cae Advanced ExamLucia DuranNo ratings yet
- Writing A Narrative EssayDocument2 pagesWriting A Narrative EssaycikainNo ratings yet
- RPH Modular Skju Bi Y2 2018Document3 pagesRPH Modular Skju Bi Y2 2018Aimi SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Tag QuestionsDocument7 pagesTag Questionsangelito peraNo ratings yet
- RPH Week 4 2022 (Fazlina) 1Document16 pagesRPH Week 4 2022 (Fazlina) 1fazlina harunNo ratings yet
- 7r Priprema Unit4 TestDocument3 pages7r Priprema Unit4 TestNastavnik DejanNo ratings yet
- 3rdsummative Reading and Writing SkillsDocument3 pages3rdsummative Reading and Writing SkillsKeziah Mae FerrerNo ratings yet
- VRB Didehloqwasgi 2012Document120 pagesVRB Didehloqwasgi 2012Wyman Kirk100% (3)
- Tos FilipinoDocument15 pagesTos FilipinoRoxanne Parbo CariagaNo ratings yet
- May:2017 Level: 2AM Third Term English Exam Time:1h30: Part One. Section One: Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pagesMay:2017 Level: 2AM Third Term English Exam Time:1h30: Part One. Section One: Reading Comprehensionkaimero changNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Negative Questions in English and Vietnamese A Contrastive AnalysisDocument61 pages(123doc) Negative Questions in English and Vietnamese A Contrastive AnalysisĐinh Hồ Mai HoaNo ratings yet
- Active & Passive Voice: The Dog The HurdleDocument10 pagesActive & Passive Voice: The Dog The HurdlebunhuotNo ratings yet
- Tese de Doutorado - Alexandre Peres PDFDocument160 pagesTese de Doutorado - Alexandre Peres PDFAlexandre PeresNo ratings yet
- Noun ClauseDocument6 pagesNoun ClauseDiego De La VegaNo ratings yet
- Bahria Foundation College Kahuta: Islamiat Urdu Social Studies Science English Quranic Studies Computer MathsDocument2 pagesBahria Foundation College Kahuta: Islamiat Urdu Social Studies Science English Quranic Studies Computer MathsYumna ArOojNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Element of Short Story - Litte Joe in Trouble AgainDocument13 pagesIntrinsic Element of Short Story - Litte Joe in Trouble AgainEnrico GiøvanoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Latin Course Workbook PDFDocument4 pagesCambridge Latin Course Workbook PDFbcrbcw6a100% (2)
- EEI Lesson Plan Template: Vital InformationDocument2 pagesEEI Lesson Plan Template: Vital Informationapi-407270738No ratings yet
- English Worksheet Unit 2 7th GradeDocument3 pagesEnglish Worksheet Unit 2 7th GradeBrendaCabreraNo ratings yet
- Texto Bachiller InglesDocument1 pageTexto Bachiller InglesQuil RéjaneNo ratings yet
- The Category of Tense2Document66 pagesThe Category of Tense2Constantin MihaiNo ratings yet
- Asking Questions: Unit 2Document28 pagesAsking Questions: Unit 2Ilham Taufik MunandarNo ratings yet