Professional Documents
Culture Documents
16 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 05 2012 - Practice Problems
Uploaded by
Eng-Ahmed ShabellOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
16 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 05 2012 - Practice Problems
Uploaded by
Eng-Ahmed ShabellCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 3125 ~ ECE 3242 - Practice Problems - Dec 05, 2012
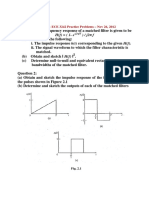
1. Consider the correlation receiver shown in Fig 1 with input y(t) = s(t) + w(t).
s(t) is a pulse of arbitrary shape of duration T sec and energy Es Joules.
w(t) is white noise with double-sided power spectral density N0/2 W/Hz.
Denote the MF output to be z(t) = m(t) + n(t); m(t) denoting the integrator output to
the signal s(t) and n(t) denoting the integrator output to the noise w(t). The sampler
output is z(T) = m(T) + n(T).
Fig 1
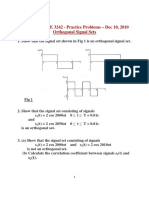
2. Consider the correlation receiver shown in Fig 2 with input y(t) = s(t) + w(t).
s(t) is a pulse of arbitrary shape of duration T sec and energy Es Joules.
w(t) is white noise with double-sided power spectral density N0/2 W/Hz.
Denote the integrator output to be z(t) = m(t) + n(t); m(t) denoting the integrator
output to the signal s(t) and n(t) denoting the integrator output to the noise w(t). The
sampler output is z(T) = m(T) + n(T).
Fig 2
Obtain expression for the following:
(a) output signal power S = m2(T)
(b) output noise power N = mean square value of n(T)
(c) output SNR = S/N
3. Consider the matched filter shown in Fig 3 with input y(t) = s(t) + w(t).
s(t) is a pulse of arbitrary shape of duration T sec and energy Es Joules.
w(t) is white noise with double-sided power spectral density N0/2 W/Hz.
y(t) → hMF(t) = Ks(T-t) → z(t) Fig. 3
K is a constant
The filter output z(t) = m(t) + n(t) is sampled at t = T to give z(T) = m(T) + n(T).
Note that m(t) is the filter output to the signal s(t) while n(t) is the filter output to
the noise w(t).
Obtain expressions for the following:
(a) output signal power S = m2(T)
(b) output noise power N = mean square value of n(T)
(c) output SNR = S/N
4. Consider the matched filter shown in Fig 4 with input y(t) = s(t) + w(t).
s(t) is a Manchester pulse of duration T sec and energy Es Joules.
w(t) is white noise with double-sided power spectral density N0/2 W/Hz.
The filter output z(t) = m(t) + n(t) is sampled at t = T to give z(T) = m(T) + n(T).
Note that m(t) is the filter output to the signal s(t) while n(t) is the filter output to
the noise w(t).
y(t) → hMF(t) =y(t) → →z(t)
Ks(T-t) Fig 4
K is a constant
Obtain expressions for the following:
(a) output signal power S = m2(T)
(b) output noise power N = mean square value of n(T)
(c) output SNR = S/N
5. Problem 3.4 (Text Book – Sklar)
6. Problem 3.5 (Text Book – Sklar)
7. Problem 3.6 (Text Book – Sklar)
You might also like
- Audi A4 Clutch SystemDocument315 pagesAudi A4 Clutch SystemNP100% (1)
- Aops PDFDocument3 pagesAops PDFHaryNo ratings yet
- 1G FUEL SYSTEM (DOHC) - Service Adjustment ProceduresDocument40 pages1G FUEL SYSTEM (DOHC) - Service Adjustment ProceduresAgus Prasetyanto100% (1)
- Matched FilterDocument30 pagesMatched FilterLavanya GangadharanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Fiber Optic Cables Underground InstallationDocument22 pagesGuidelines Fiber Optic Cables Underground Installationmatgar100% (1)
- Lecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureDocument20 pagesLecture 04 - Signal Space Approach and Gram Schmidt ProcedureKhoa PhamNo ratings yet
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDocument110 pagesEe602 Fourier SeriesSyaa MalyqaNo ratings yet
- PPT-302 How Return Loss Gets Its RipplesDocument9 pagesPPT-302 How Return Loss Gets Its RipplesDivya ShyamalaNo ratings yet
- DC 5 Receiver NewDocument228 pagesDC 5 Receiver NewersimohitNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series NOTESDocument67 pagesFourier Series NOTESAzue RamliNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsDocument37 pagesContinuous-Time Signals and SystemsJoseph IbrahimNo ratings yet
- D25 Brochure-EB356 PDFDocument8 pagesD25 Brochure-EB356 PDFSalvador FayssalNo ratings yet
- Group7 - Apple's Future - Apple Watch, Apple TV, and - or Apple CarDocument7 pagesGroup7 - Apple's Future - Apple Watch, Apple TV, and - or Apple CarRuchi Yadav50% (2)
- EE2010Notes+Tutorials of PartI (For EEE Club)Document118 pagesEE2010Notes+Tutorials of PartI (For EEE Club)Leonard TanotoNo ratings yet
- TE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesDocument27 pagesTE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Signals Sampling TheoremDocument3 pagesSignals Sampling TheoremDebashis TaraiNo ratings yet
- Filtros Adaptados PDFDocument3 pagesFiltros Adaptados PDFJimeNucha CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Signals and Systems: F F 0 and FDocument29 pagesCharacterization of Signals and Systems: F F 0 and FEhsan Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- III. Fourier Series and Fourier TransformDocument20 pagesIII. Fourier Series and Fourier TransformEduard Cosmin UngureanuNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Classification of SignalsDocument37 pages1.1 Classification of SignalsIbrahim MansourNo ratings yet
- Signals 1Document15 pagesSignals 1Rupesh SushirNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2Document4 pagesExperiment No. 2ashish pandeyNo ratings yet
- EE635 Solutions Set#3:: RN TN HN TKHNKDocument3 pagesEE635 Solutions Set#3:: RN TN HN TKHNKDhoorjati VommiNo ratings yet
- Signal SystemsDocument40 pagesSignal SystemsscribdsunilNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Harry WillsmithNo ratings yet
- Ee4501f18 HW 3Document7 pagesEe4501f18 HW 3al-muntheral-mairikiNo ratings yet
- Adc Module-3 Part1Document173 pagesAdc Module-3 Part1Nabeel HashimNo ratings yet
- 3 Signal Space Representation of WaveformsDocument5 pages3 Signal Space Representation of WaveformssfjkdlNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Fourier Series & Fourier Series Properties: Spring 2014 Type The Document TitleDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Fourier Series & Fourier Series Properties: Spring 2014 Type The Document TitleAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Signals&System Lab7Document3 pagesSignals&System Lab7Muhamad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 00d Matched FilterDocument39 pages00d Matched FilterabunesanNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication 601 - TutorialDocument12 pagesDigital Communication 601 - TutorialHemanth Vinay Kumar0% (1)
- Homework1 PDFDocument3 pagesHomework1 PDFYuanhao LiuNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems 01Document10 pagesSignals and Systems 01nvbondNo ratings yet
- University of Manchester CS3291: Digital Signal Processing '05-'06 Section 7: Sampling & ReconstructionDocument12 pagesUniversity of Manchester CS3291: Digital Signal Processing '05-'06 Section 7: Sampling & ReconstructionMuhammad Shoaib RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Description and PropertiesDocument42 pagesDescription and Propertiesabhinavmkrishna2020No ratings yet
- Baseband Pulse TransmissionDocument39 pagesBaseband Pulse TransmissionBalaram MullapudiNo ratings yet
- Signals Are Variables That Carry Information - Systems Process Input Signals To Produce Output SignalsDocument10 pagesSignals Are Variables That Carry Information - Systems Process Input Signals To Produce Output Signalsking_hhhNo ratings yet
- Midterm EE456 11Document4 pagesMidterm EE456 11Erdinç KayacıkNo ratings yet
- TE311 Lecture07 AMDocument29 pagesTE311 Lecture07 AMIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam19-20 PartBDocument4 pagesComprehensive Exam19-20 PartBAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Matched FilterDocument15 pagesMatched FilterjMcLean99No ratings yet
- DSP-Chapter1 Student 28062015Document45 pagesDSP-Chapter1 Student 28062015NguyenThaoNo ratings yet
- Exam of Digital Communications 26/06/2013Document2 pagesExam of Digital Communications 26/06/2013pnkc80No ratings yet
- Lect NB NoiseDocument8 pagesLect NB NoiseIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Sistemas SinalesDocument43 pagesSistemas SinalesAlfonso LugoNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Trigonometric Fourier SeriesDocument8 pages4.1 Trigonometric Fourier SeriesAiden An CamreNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam2021 PartBDocument2 pagesComprehensive Exam2021 PartBAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mit6 003f11 Lec19Document43 pagesMit6 003f11 Lec19api-246008426No ratings yet
- Analog Communication Exam Paper T2Document7 pagesAnalog Communication Exam Paper T2DharmendraDixit100% (3)
- ECE1004 - Signals and Systems: Facilitator: Dr.T.VigneswaranDocument14 pagesECE1004 - Signals and Systems: Facilitator: Dr.T.VigneswaranSruthi GNo ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument14 pagesFourier Seriesshahroz12No ratings yet
- Chapter 4.4-4.5, S. Haykin, Communication Systems, Wiley.: ReferenceDocument12 pagesChapter 4.4-4.5, S. Haykin, Communication Systems, Wiley.: ReferenceOMSURYACHANDRANNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication: Modulation and Coding CourseDocument22 pagesDigital Communication: Modulation and Coding CourseAbu Bakar AsifNo ratings yet
- 416 Assignment 1Document5 pages416 Assignment 1mahmab70No ratings yet
- DC Digital Communication PART1Document218 pagesDC Digital Communication PART1ARAVINDNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Laboratory 5Document11 pagesSignals and Systems Laboratory 5Kthiha CnNo ratings yet
- Rutgers: College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDocument8 pagesRutgers: College of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringRiad Al JuboriNo ratings yet
- 6725all 7th Semester Electrical EngineeringDocument161 pages6725all 7th Semester Electrical EngineeringPubg MobilNo ratings yet
- 2022 Lec 01bDocument24 pages2022 Lec 01bMuskan KapoorNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document2 pagesPs 1baolanNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document3 pagesHW 1znNo ratings yet
- EE 220: Signals and Systems Tutorial-8Document3 pagesEE 220: Signals and Systems Tutorial-8Manikanta KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- 03 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Practice Problems - Feb 29 2012Document2 pages03 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Practice Problems - Feb 29 2012Eng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 14 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 26 2012 - Practice ProblemsDocument2 pages14 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 26 2012 - Practice ProblemsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 05 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - March 5 2012 - Review of Random SignalsDocument34 pages05 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - March 5 2012 - Review of Random SignalsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 04 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Assignment 1 - Due March 14 2012Document2 pages04 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Assignment 1 - Due March 14 2012Eng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 12 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 19 2012 - Practice ProblemsDocument3 pages12 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 19 2012 - Practice ProblemsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 13 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 21 2012 - Baseband Demodulation and DetectionDocument18 pages13 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 21 2012 - Baseband Demodulation and DetectionEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 21 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 17 2012 - Practice Problems - Chap 4Document2 pages21 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 17 2012 - Practice Problems - Chap 4Eng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 07 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 05 2012 - Formatting and Baseband Pulse ModulationDocument30 pages07 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 05 2012 - Formatting and Baseband Pulse ModulationEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 22 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 17 2012 - Additional Practice ProblemsDocument1 page22 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 17 2012 - Additional Practice ProblemsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 20 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 17 2012 - Bandpass Signalling - (4b)Document16 pages20 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 17 2012 - Bandpass Signalling - (4b)Eng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 18 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 10 2012 - Practice Problems Orthogonal Signal SetsDocument1 page18 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Dec 10 2012 - Practice Problems Orthogonal Signal SetsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 09 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 07 2012 - Nyquist Transmission Theory & Duo-Binary SignalingDocument34 pages09 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 07 2012 - Nyquist Transmission Theory & Duo-Binary SignalingEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 09 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 07 2012 - Nyquist Transmission Theory & Duo-Binary SignalingDocument34 pages09 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 07 2012 - Nyquist Transmission Theory & Duo-Binary SignalingEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaDocument3 pagesCourse Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 07 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 05 2012 - Formatting and Baseband Pulse ModulationDocument30 pages07 ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Nov 05 2012 - Formatting and Baseband Pulse ModulationEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- ECE 3125 Communication Engineering II ECE 3242 Digital CommunicationDocument22 pagesECE 3125 Communication Engineering II ECE 3242 Digital CommunicationEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- 03 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Oct 08, 2012 - Practice ProblemsDocument2 pages03 - ECE 3125 ECE 3242 - Oct 08, 2012 - Practice ProblemsEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- Micro 4 Prob Sol 5Document40 pagesMicro 4 Prob Sol 5Eng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- ECE 3125 Communication Engineering II ECE 3242 Digital CommunicationDocument22 pagesECE 3125 Communication Engineering II ECE 3242 Digital CommunicationEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- NodeMCU PDFDocument40 pagesNodeMCU PDFNIKHIL ARORA100% (1)
- VHDL Type Conversion - BitWeenieDocument5 pagesVHDL Type Conversion - BitWeenieAaditya ku marNo ratings yet
- 2 - Detailed Project Recoveryrec Schedule As of May2014Document46 pages2 - Detailed Project Recoveryrec Schedule As of May2014raza.slietNo ratings yet
- Z Source Inverter Topologies-A SurveyDocument12 pagesZ Source Inverter Topologies-A SurveyViswanathanBalajiNo ratings yet
- Phase Sequence Relay PFN Mecotron: OperationDocument1 pagePhase Sequence Relay PFN Mecotron: Operationhonafa- R.O.N.ONo ratings yet
- Microprocessors CSE - 341: 8086/8088 Hardware SpecificationDocument26 pagesMicroprocessors CSE - 341: 8086/8088 Hardware SpecificationIrum SabaNo ratings yet
- P NPDocument68 pagesP NPTraian SerbanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsDocument25 pagesSemiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple CircuitsAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Rane Fpm44 Mixer ManualDocument4 pagesRane Fpm44 Mixer ManualtubegeekNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Mixers and Detectors PDFDocument31 pagesCh7 Mixers and Detectors PDFaurybNo ratings yet
- BUS-Connection Trouble Shooting Fault (BCS Screen) Possibility Check 1. Master BUS OffDocument3 pagesBUS-Connection Trouble Shooting Fault (BCS Screen) Possibility Check 1. Master BUS Offjc villongcoNo ratings yet
- Capacity Controller EKC 331 PDFDocument8 pagesCapacity Controller EKC 331 PDFabdur rafayNo ratings yet
- R15 Ind780 TM enDocument538 pagesR15 Ind780 TM envm8119No ratings yet
- ZedBoard HW UG v1 1 PDFDocument38 pagesZedBoard HW UG v1 1 PDFHammad Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Headlamp Aiming GuideDocument5 pagesHeadlamp Aiming Guideshu2uNo ratings yet
- Labo III Appendix A Gunt Ce602eDocument26 pagesLabo III Appendix A Gunt Ce602eMijhael Anatholi Romero MamaniNo ratings yet
- Ingersoll Rand System Automation X12I Operator's Manual: More Than Air, AnswersDocument91 pagesIngersoll Rand System Automation X12I Operator's Manual: More Than Air, AnswersMike DavidNo ratings yet
- Acoustical Design of Rooms For Speech: by J.S. BradleyDocument6 pagesAcoustical Design of Rooms For Speech: by J.S. BradleystesagNo ratings yet
- XGAUGEDocument4 pagesXGAUGEngt881No ratings yet
- Guitar Buyer Magazine Issue 112Document2 pagesGuitar Buyer Magazine Issue 112oysterhouseNo ratings yet
- MAC Address Conflict PDFDocument2 pagesMAC Address Conflict PDFwahidNo ratings yet
- Samsung La32c590h1r Chassis N88aDocument59 pagesSamsung La32c590h1r Chassis N88anikhiltwinNo ratings yet
- Samsung 2220WM Service ManualDocument49 pagesSamsung 2220WM Service ManualMalay K GhoshNo ratings yet































































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)