Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Internal Combustion Engines
Uploaded by
Rahul Kumar Chauhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views4 pagesINTRODUCTION TO IC ENGINES
Original Title
1-INTRODUCTION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentINTRODUCTION TO IC ENGINES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views4 pagesInternal Combustion Engines
Uploaded by
Rahul Kumar ChauhanINTRODUCTION TO IC ENGINES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
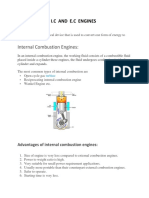
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
An Engine is a device which transforms the chemical energy of a fuel into
thermal energy and uses this thermal energy to produce mechanical work.
Engines normally convert thermal energy into mechanical work and therefore
they are called heat engines.
Heat engines can be broadly classified into :
i) External combustion engines ( E C Engines)
ii) Internal combustion engines ( I C Engines )
External combustion engines are those
in which combustion takes place outside
the engine. For example, In steam engine
or steam turbine the heat generated due
to combustion of fuel and it is employed
to generate high pressure steam, which
is used as working fluid in a
reciprocating engine or turbine. See
Figure 1 : External Combustion Engine
Figure 1.
Internal combustion engines can be classified as Continuous IC engines and
Intermittent IC engines.
In continuous IC engines products of be used again in the cycle.
combustion of the fuel enters into the
prime mover as the working fluid. For
example : In Open cycle gas turbine plant.
Products of combustion from the
combustion chamber enters through the
turbine to generate the power
continuously . See Figure 2.
In this case, same working fluid cannot
Figure 2: Continuous IC Engines
In Intermittent internal
combustion engine
combustion of fuel takes
place inside the engine
cylinder. Power is
generated intermittently
(only during power stroke)
and flywheel is used to
provide uniform output
torque. Usually these
engines are reciprocating
engines. The reciprocating
engine mechanism
consists of piston which
moves in a cylinder and
forms a movable gas tight
seal. By means of a
connecting rod and a crank
shaft arrangement, the
reciprocating motion of
piston is converted into a
rotary motion of the
crankshaft. They are most
popular
because of their use as main prime mover in
commercial vehicles.
ADVANTAGES OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION
ENGINES
1. Greater mechanical simplicity.
2. Higher power output per unit weight because of absence of
auxiliary units like boiler , condenser and feed pump
3. Low initial cost
4. Higher brake thermal efficiency as only a small fraction of heat
energy of the fuel is dissipated to cooling system
5. These units are compact and requires less space
6. Easy starting from cold conditions
DISADVANTAGES OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
1. I C engines cannot use solid fuels which are cheaper. Only liquid or
gaseous fuel of given specification can be efficiently used.
These fuels are relatively more expensive.
2. I C engines have reciprocating parts and hence balancing of
them is problem and they are also susceptible to mechanical
vibrations.
You might also like
- Internal Combustion Engines ExplainedDocument49 pagesInternal Combustion Engines ExplainediswardiidrusNo ratings yet
- Principle of Operation:: Unit IiiDocument20 pagesPrinciple of Operation:: Unit Iiilakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Ci Engine Book ModifyDocument167 pagesCi Engine Book ModifyARUMUGA NAINARNo ratings yet
- Introduction ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntroduction ReviewerIuhence VergaraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Construction and Operation: External Combustion EngineDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Construction and Operation: External Combustion Enginekrishna samNo ratings yet
- Basics of EnginesDocument7 pagesBasics of EnginesMian AsimNo ratings yet
- Types of Heat Engines: What Is The Heat Engine?Document46 pagesTypes of Heat Engines: What Is The Heat Engine?Mozammel HossainNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance of SUZUKI Generator SV1400LDocument30 pagesOperation and Maintenance of SUZUKI Generator SV1400LWeb FlowNo ratings yet
- Te Unit 2Document22 pagesTe Unit 2krishnansriNo ratings yet
- Unit I (IC Engines)Document13 pagesUnit I (IC Engines)prasanthiNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Internal Combustion Power PlantDocument19 pages1-2 Internal Combustion Power PlantGeethika NayanaprabhaNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine & IC EnginesDocument26 pagesHeat Engine & IC EnginesVeeresh Kumar G BNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument14 pagesEnergyNirmal DharavathNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1Shivajee YadavNo ratings yet
- FC01 UpdatedDocument13 pagesFC01 UpdatedSOLAIMANNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument7 pagesInternal Combustion Enginescgalang44No ratings yet
- What Is EngineDocument25 pagesWhat Is EngineSajib Chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- Types and components of heat enginesDocument11 pagesTypes and components of heat enginesjoshua jan allawanNo ratings yet
- Unit5 - Heat Engine-Notes1Document17 pagesUnit5 - Heat Engine-Notes1Krishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Types of EngineDocument11 pagesTypes of Enginejoshua jan allawanNo ratings yet
- Heat EnginesDocument4 pagesHeat EnginesZaib RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-ICE UpdateDocument69 pagesChapter 1-ICE UpdateMahesh LohanoNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument23 pagesIc EngineGanesh kumar100% (1)
- ICE Seminar on Internal Combustion EnginesDocument18 pagesICE Seminar on Internal Combustion EnginesNagapavan MarisettyNo ratings yet
- ICE Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesICE Lecture NotesRajueswar100% (1)
- Icgt Unit-II MaterialDocument34 pagesIcgt Unit-II MaterialA Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 01: B.Tech. 7Th Sem.-Me 7me5-11 (Internal Combustion Engine)Document4 pagesLecture - 01: B.Tech. 7Th Sem.-Me 7me5-11 (Internal Combustion Engine)Kalyan SinghNo ratings yet
- Combustion Ass 1Document6 pagesCombustion Ass 1Shane Michael BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Lab Session 3Document14 pagesLab Session 3Shahid FarooqNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Basics of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument18 pagesUnderstanding the Basics of Internal Combustion Engineschincha chuNo ratings yet
- Engine and Its TypeDocument6 pagesEngine and Its TypeNoumanAwanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Types of EngineDocument14 pagesAssignment-1: Types of EngineRaj SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 Lab Manual ICE 3171923 Odd 2021Document24 pages3 Lab Manual ICE 3171923 Odd 2021Akhilesh NavikNo ratings yet
- I.C Engines LectureDocument127 pagesI.C Engines LectureusamakaleemNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Power Transmission: Module ContentDocument8 pagesIC Engines Power Transmission: Module ContentVinayaka GpNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument44 pagesIC EnginesIbrahim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Diesel Power PlantDocument13 pagesChapter 6-Diesel Power PlantbaseakelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document41 pagesChapter 2Ibrahim KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Internal Combustion Engine UpdatedDocument20 pagesModule 1 Internal Combustion Engine UpdatedMehrab Rabbi RatinNo ratings yet
- ConceptsDocument8 pagesConceptsLouis Feliph RuelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ic EnginesDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Ic EnginesSai Sudheer100% (1)
- IC Engines GuideDocument47 pagesIC Engines GuidearulNo ratings yet
- Mini Project PresentationDocument24 pagesMini Project PresentationHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction IC EnginesDocument8 pagesIntroduction IC EnginesSarmad Altaf Hafiz Altaf HussainNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine & Internal Combustion EngineDocument42 pagesHeat Engine & Internal Combustion EngineFaiz TalpurNo ratings yet
- Motor de Combustión InternaEnglish - CopiaDocument4 pagesMotor de Combustión InternaEnglish - Copiaapazayanquigustavo1234No ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesDocument4 pagesInternal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesTariq AslamNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesDocument4 pagesInternal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesTariq AslamNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesDocument4 pagesInternal Combustion Engines:: I.C and E.C EnginesTariq AslamNo ratings yet
- PJM Auto NotesDocument18 pagesPJM Auto NotesAswin PrasannanNo ratings yet
- Engine TechnlogyDocument44 pagesEngine Technlogykadooliian257No ratings yet
- 1.1 I.C Engines: 1.1.1 Definition of EngineDocument54 pages1.1 I.C Engines: 1.1.1 Definition of EngineANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- IC Engines and Reciprocating Machines Chapter 1: Thermodynamic Cycles and Performance of IC EnginesDocument71 pagesIC Engines and Reciprocating Machines Chapter 1: Thermodynamic Cycles and Performance of IC EnginesYohanis AgumaseNo ratings yet
- About EngineDocument2 pagesAbout Enginesrujanyadav12No ratings yet
- ICE Components LabDocument78 pagesICE Components Labvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Project Intro Internal Combustion EngineDocument4 pagesProject Intro Internal Combustion EngineAmit Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument54 pagesThesisANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Modelling and Analysis 1Document35 pagesModelling and Analysis 1Larry SmithNo ratings yet
- Lec2 PDFDocument28 pagesLec2 PDFJaco MarketlandNo ratings yet
- Ata Reducida 2Document9 pagesAta Reducida 2juankwiesnerteeiNo ratings yet
- 2007 Wartsila Engines For Panamax ContainershipsDocument8 pages2007 Wartsila Engines For Panamax ContainershipsThomas CuerqNo ratings yet
- PC130 7Document220 pagesPC130 7Fernando Sabino94% (54)
- UPSRTC Summer Training Report on Bus MaintenanceDocument44 pagesUPSRTC Summer Training Report on Bus MaintenanceRiya JadaonNo ratings yet
- D E F Op InstDocument85 pagesD E F Op Instwilber100% (2)
- UNIT 16 - Prime Movers and Engines (Q121) PDFDocument22 pagesUNIT 16 - Prime Movers and Engines (Q121) PDFRajesh Gupta100% (1)
- Worksheet SolnDocument3 pagesWorksheet Solnahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- STEAM ENGINE DEMONSTRATIONDocument5 pagesSTEAM ENGINE DEMONSTRATIONMuhammad Nouman RashidNo ratings yet
- Refrigration Saving HeatDocument39 pagesRefrigration Saving HeatTanviNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 10: A. Reciprocating CompressorDocument4 pagesPractical No. 10: A. Reciprocating CompressorJyoti Ben PatelNo ratings yet
- Pump Part 2Document35 pagesPump Part 2Amit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Piston Engine SyllabusDocument3 pagesPiston Engine SyllabusRaul DeonarainNo ratings yet
- KTA19-G8 Advantage Data Sheet SpecsDocument4 pagesKTA19-G8 Advantage Data Sheet SpecsYosi DarmawansyahNo ratings yet
- Test code 805 answer sheet instructionsDocument78 pagesTest code 805 answer sheet instructionsSandeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- HonningDocument13 pagesHonningSyed Danish FayazNo ratings yet
- 91 Introduction To Internal Combustion EnginesDocument35 pages91 Introduction To Internal Combustion Enginesraghu.entrepreneurNo ratings yet
- Pipe Terms PDFDocument109 pagesPipe Terms PDFLourdes Marie Rosalejos OrtegaNo ratings yet
- I.C EnginesDocument58 pagesI.C EnginesvndeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Basics of IC EnginesDocument79 pagesBasics of IC EnginesNikola PetrovićNo ratings yet
- Dae Mechanical Technology (Revised 3rd Year) Course Outline.Document113 pagesDae Mechanical Technology (Revised 3rd Year) Course Outline.Hassan Raza53% (15)
- Flow Profile For Reciprocating PumpsDocument2 pagesFlow Profile For Reciprocating PumpsbtjajadiNo ratings yet
- Four Cylinder Gas EngineDocument7 pagesFour Cylinder Gas EngineJelli Anne Vistal MillanesNo ratings yet
- M15 - (Compressed Air) RevGBDocument25 pagesM15 - (Compressed Air) RevGBVAN VIET NGONo ratings yet
- MMZ Catalog PDFDocument28 pagesMMZ Catalog PDFSecret64No ratings yet
- Me 313b Fluid Machineries Module Week 10 13 PDF FreeDocument60 pagesMe 313b Fluid Machineries Module Week 10 13 PDF FreeChris TopherNo ratings yet
- KTA38-G9 Advantage Data SheetDocument3 pagesKTA38-G9 Advantage Data SheetAnjelyn SaltingNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2: 2.0 Rankine Cycle As A Two-Phase Power SystemDocument23 pagesThermodynamics 2: 2.0 Rankine Cycle As A Two-Phase Power SystemMarianne DevillenaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Sheet 2 ICEDocument10 pagesSolution of Sheet 2 ICEMahmoud NaderNo ratings yet