Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exploring Human Factors: Organisation & Management Job (Task, Environment and Equipment) Person
Exploring Human Factors: Organisation & Management Job (Task, Environment and Equipment) Person
Uploaded by
757rustamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exploring Human Factors: Organisation & Management Job (Task, Environment and Equipment) Person
Exploring Human Factors: Organisation & Management Job (Task, Environment and Equipment) Person
Uploaded by
757rustamCopyright:
Available Formats
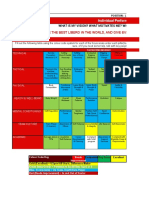
Exploring Human Factors
Person Job (task, environment and equipment) Organisation &
management
SKILL PHYSICAL STATE SKILL PHYSICAL STATE EQUIPMENT & WORKSPACE DESIGN TOP LEVEL MANAGEMENT
Competence Personal health & hygiene, fitness, Competence Personal health & hygiene, fitness, System Design Safety policy
Previous training balanced diet Previous training balanced diet Usability Budgeting
Experience PHYSICAL CAPABILITY Experience PHYSICAL CAPABILITY Human-system interface Resource allocation
Currency Strength, stamina, stress, fatigue, Currency Strength, stamina, stress, fatigue, Human-human, human machine, human- Leadership philosophy
Leadership pain/discomfort, hunger, thirst, Leadership pain/discomfort, hunger, thirst, computer PERSONNEL
CULTURAL DIFFERENCES temperature extremes, vibration, CULTURAL DIFFERENCES temperature extremes, vibration, Anthropometry Selection and check of competence
Religion, national tradition, dress, movement constriction, lack of physical Religion, national tradition, dress, movement constriction, lack of physical Body Size Education and training
language exercise, disruption of circadian rhythm language exercise, disruption of circadian rhythm Body strength & stamina Leadership and supervision
MOTIVATION PSYCHOLOGICAL STATE MOTIVATION PSYCHOLOGICAL STATE Limits of strength and endurance Motivation
Work environment Task speed, task load, threat of Work environment Task speed, task load, threat of Workplace design Modification of attitudes
Temperature, humidity, air quality, lighting, failure/loss of job, monotonous, degrading Temperature, humidity, air quality, lighting, failure/loss of job, monotonous, degrading User capabilities and limitations Development of social climate
noise, vibration, cleanliness or meaningless work, long uneventful noise, vibration, cleanliness or meaningless work, long uneventful Stresses and Hazards OPERATIONAL
Working hours vigilance periods, conflicts of motives Working hours vigilance periods, conflicts of motives Wind, whole body motion, motion induced Inspection methods
Continuous operations, watchkeeping about job performance, reinforcement Continuous operations, watchkeeping about job performance, reinforcement fatigue, vibration, noise, darkness/dazzle, Maintenance methods and procedures
Habitability absent or negative, sensory deprivation, Habitability absent or negative, sensory deprivation, temperature, sleep loss Operations procedures
Adequate tools & equipment distractions (noise, glare, movement, Adequate tools & equipment distractions (noise, glare, movement, Vision and Lighting System documentation
Manning levels flicker, colour), inconsistent cues Manning levels flicker, colour), inconsistent cues Human vision, visual displays and lighting Manning and watch systems
Organization structure PSYCHOLOGICAL CAPABILITY Organization structure PSYCHOLOGICAL CAPABILITY design TECHNICAL
Authority, responsibility, communication Perception, motor requirements (speed, Authority, responsibility, communication Perception, motor requirements (speed, Auditory Information Reliability and availability
Actions by others strength precision), control-display Actions by others strength precision), control-display Transfer of information to human operators System performance
Reward relationships, anticipatory requirements, Reward relationships, anticipatory requirements, using their hearing Instrumentation
Recognition interpretation, decision-making, Recognition interpretation, decision-making, Voice Communication Monitoring
Benefits information load, narrowness of task, Benefits information load, narrowness of task, Characteristics of speech and hearing Automation
Job description frequency & repetitiveness, task criticality, Job description frequency & repetitiveness, task criticality, Face-to-face and electronically assisted speech Man-machine interface
Instructions long/short-term memory; calculation Instructions long/short-term memory; calculation communication Work place conditions
Procedures requirements, feedback (knowledge of Procedures requirements, feedback (knowledge of Controls SAFETY MANAGEMENT
Continuation Training results), dynamic v step-by-step results, Continuation Training results), dynamic v step-by-step results, Optimum size, shape, operating dynamics and Management
KNOWLEDGE team structure & communication, man- KNOWLEDGE team structure & communication, man- spacing Organisation
Education & training machine interface Education & training machine interface Maintainability Routines
Accessibility Inspection and auditing
Tools & equipment Feedback
Handbooks, Procedures Learning
Emergency planning and training
Health
Environment
Safety at work
Photo credits: Bridge - ABS. Others - jalens - joachim affeldt
uman Factors, or The Human Factor, are Human Factors (Fitting the job to the person): • System Safety - The human contribution maintain and sustain a system and provide how they - together with the environment
H terms which are often misinterpreted
and are used as a covers for the Human
Human Resources which is a closely related
activity that addresses the supply of
suitably qualified and experienced staff. • Human Factors Engineering - The
to risk when the system is functioning in a
normal or abnormal manner.
optimum quality and quantity of the crews
to man the ship.
in which the organisation and person are
operating - impact on the behaviour of
comprehensive integration of human
Element or even Human Error. A simple people.This diagram attempts to show the
definition of Human Factors is: the body
When considering the operation or design characteristics into the definition, design Human Resources (Fitting the person to the job): • Training - The instruction or the education, various factors that can influence the inter-
development, and evaluation of a system and on-the-job or part-task or full-mission
of scientific knowledge about people
of any ship and its systems both of these
domains should be considered - Human to optimise Human-Machine performance
• Manpower - the number of personnel training required to provide personnel action between a human and any system
and how they interact with their required, and potentially available, to aboard ship, ie: The Human Element!
Resources for the selection and preparation under specified conditions. operate, maintain, sustain and provide with their essential job skills, knowledge,
environment, especially when working.
training for a system. values and attitudes.
Applying human factors to the design and of staff able to do the required work and
Human Factors to account for the use of
• Health Hazards - The identification, A practical example of how to apply
operation of a ship or its systems means
taking account of human capabilities, people as a component of the system.
assessment and the removal or reduction
of short or long-term hazards to health
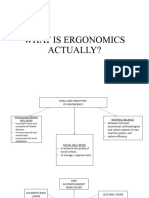
• Personnel - The cognitive (trainability A simple way to view human factors is to
consider three main aspects: the person,the
human factors to the design and
operation of a Ship Control Centre can be
and mental aptitude) and physical (fitness
skills, limitations and needs. Human Factors Both domains contain a number of occurring as a result of normal operation levels, physical size, gender) capabilities job (task, environment and equipment), and downloaded from www.he-alert.org/
should not be confused with the term sub-domains: of a system. required to be able to train for, operate, the organisation and management, and filemanager/root/site_assets/
standalone_articles_not_linked_to_a_bulleti
n/HE00130.pdf
You might also like
- Unit 13: 1. What Is A Negotiable InstrumentDocument7 pagesUnit 13: 1. What Is A Negotiable InstrumentAyas JenaNo ratings yet
- Comfort Control PrinciplesDocument45 pagesComfort Control PrinciplesThanh ThuanNo ratings yet
- Janitorial Safety Training Guide: Ership, ActDocument32 pagesJanitorial Safety Training Guide: Ership, Act757rustam100% (2)
- LBO ModellingDocument22 pagesLBO ModellingRoshan PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Hope 1Document4 pagesHope 1Emily T. Nonato100% (7)
- Point-of-Care: Leadership Tips and Tools For NursesDocument6 pagesPoint-of-Care: Leadership Tips and Tools For Nurses757rustamNo ratings yet
- Stress Talking ToolkitDocument24 pagesStress Talking Toolkit757rustamNo ratings yet
- BPM Team Building Toolkit 2019Document84 pagesBPM Team Building Toolkit 2019757rustamNo ratings yet
- Leading and Managing People Trainers' Toolkit: Building A TeamDocument36 pagesLeading and Managing People Trainers' Toolkit: Building A Team757rustam100% (1)
- Hope 3Document4 pagesHope 3Emily T. NonatoNo ratings yet
- Recognition Toolkit For LeadersDocument2 pagesRecognition Toolkit For Leaders757rustam100% (1)
- BBCMusic201409 PDFDocument102 pagesBBCMusic201409 PDFKadirOzturk100% (1)
- Grbglu TutorDocument82 pagesGrbglu TutorFaizal Ngauge100% (2)
- Physical Preparation of Elite AthletesDocument38 pagesPhysical Preparation of Elite Athletesrafiwingate100% (2)
- Disasters Related To BBSDocument38 pagesDisasters Related To BBSVikram TNo ratings yet
- 1.50pm (H) Fitness For Work - Fatigue Management - IncorporaDocument17 pages1.50pm (H) Fitness For Work - Fatigue Management - IncorporaAndres Lucero LeivaNo ratings yet
- PpeDocument68 pagesPpeoshaptss100% (1)
- Pediatric Rehabilitation FiDocument61 pagesPediatric Rehabilitation FidannisanurmiyaNo ratings yet
- Hope 4Document4 pagesHope 4Emily T. NonatoNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Behaviour Based SafetyDocument11 pagesImplementation of Behaviour Based SafetyAnoop NairNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Risiko Ergonomi Dan Psikososial - Baiduri Widanarko - RevDocument85 pagesPengelolaan Risiko Ergonomi Dan Psikososial - Baiduri Widanarko - RevSafran RochimNo ratings yet
- Social Accounting Concept, Definition, Features and Benefits Financial AnalysisDocument11 pagesSocial Accounting Concept, Definition, Features and Benefits Financial AnalysisPontuChowdhury100% (4)
- Ang Ladlad LGBT Party V Comelec DigestDocument2 pagesAng Ladlad LGBT Party V Comelec DigestAmado Peter Garbanzos80% (5)
- Eating Disorders in AthletesDocument44 pagesEating Disorders in AthletesLaura BaumanNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence In Action: Training and Coaching Activities for Leaders and ManagersFrom EverandEmotional Intelligence In Action: Training and Coaching Activities for Leaders and ManagersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Fina Supply V Abilene National Bank - Deception, Concealment, Fraud On Part of One With Superior KnowledgeDocument40 pagesFina Supply V Abilene National Bank - Deception, Concealment, Fraud On Part of One With Superior KnowledgegoldilucksNo ratings yet
- Strategic Procurement Cloud Integration Options R13Document20 pagesStrategic Procurement Cloud Integration Options R13Sanjeev ThakurNo ratings yet
- Election Law: Election Commission of India Indian Civil Service Indian Administrative ServiceDocument27 pagesElection Law: Election Commission of India Indian Civil Service Indian Administrative ServiceraoNo ratings yet
- DR Luh - Role of PMR in NICUDocument50 pagesDR Luh - Role of PMR in NICUad putraNo ratings yet
- OISD Standard - 181Document28 pagesOISD Standard - 181sanjiv shrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Class Notes QualityDocument31 pagesClass Notes QualitysunnyNo ratings yet
- Pdhpe AcroynmsDocument5 pagesPdhpe AcroynmsJai robboNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Risiko Ergonomi Dan Psikososial - Baiduri WidanarkoDocument74 pagesPengelolaan Risiko Ergonomi Dan Psikososial - Baiduri WidanarkoDaniel SihombingNo ratings yet
- 2.0 HRM FrameworkDocument7 pages2.0 HRM Frameworkemmy.anitagilbertNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics ReviewerDocument12 pagesErgonomics ReviewerJason CamaNo ratings yet
- Paper 13 Ergonomics Issues and ChallengesDocument40 pagesPaper 13 Ergonomics Issues and ChallengesAng chong beng100% (1)
- Geo Individual PlanDocument4 pagesGeo Individual PlanGeoNo ratings yet
- Human FactorDocument14 pagesHuman FactorJoseph Nathan MarquezNo ratings yet
- Minggu 7 - Work PsychologyDocument41 pagesMinggu 7 - Work PsychologyMuhammad IqraqNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics & Human Factors in SafetyDocument42 pagesErgonomics & Human Factors in Safetyhendri setiawanNo ratings yet
- Compre Notes!!!!!!!!!!!Document12 pagesCompre Notes!!!!!!!!!!!Cyenel DeiparineNo ratings yet
- OB End TermDocument188 pagesOB End Termsanskriti.p22No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Approach of Children With Cerebral PalsyDocument55 pagesRehabilitation Approach of Children With Cerebral PalsyridaNo ratings yet
- 1.perform Workplace and Safety PracticesDocument6 pages1.perform Workplace and Safety Practicesalvin manalaysayNo ratings yet
- Parkour PDFDocument16 pagesParkour PDFbonengNo ratings yet
- Clinical Passport 2nd Placement 1Document6 pagesClinical Passport 2nd Placement 1api-584598939No ratings yet
- Organization Theory & BehaviorDocument35 pagesOrganization Theory & Behaviorasad siddiqui71% (7)
- UAS-GIZI ERGONOMIC Risk Factor AssesmentDocument23 pagesUAS-GIZI ERGONOMIC Risk Factor AssesmentIffa Karina PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Notice of HR Policies Annex 2 - EPSRCDocument2 pagesNotice of HR Policies Annex 2 - EPSRCanupkrajakNo ratings yet
- Ergonomic Hazards RENTOYDocument14 pagesErgonomic Hazards RENTOYShailani Hossain100% (1)
- Session 2Document16 pagesSession 2AnkitNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument13 pagesPhysical EducationPedro Arturo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Human Factors OfficialDocument31 pagesHuman Factors Official2056060043No ratings yet
- 5.LP On PhyDocument11 pages5.LP On PhySanjeevNo ratings yet
- Teori Organisasi Dan ManagemenDocument14 pagesTeori Organisasi Dan Managemenmotz100% (2)
- Human Resource Development Management Special TopicsDocument19 pagesHuman Resource Development Management Special TopicsFrancheska LarozaNo ratings yet
- EFPH411-PRELIMDocument5 pagesEFPH411-PRELIMPtrck MgnyNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Ergonomi 2Document16 pagesPengantar Ergonomi 2Maytadewi NegaraNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State UniversityDocument6 pagesMindanao State UniversityJay Carlo BagayasNo ratings yet
- Scope and Sequence (Grade 3)Document2 pagesScope and Sequence (Grade 3)malissa nugeraNo ratings yet
- ECH5514 Chap3 1032017 StudentDocument56 pagesECH5514 Chap3 1032017 Studentmohamad azrilNo ratings yet
- Accommodation and Compliance Series Employees With Anxiety DisorderDocument26 pagesAccommodation and Compliance Series Employees With Anxiety DisorderTess TingNo ratings yet
- Designing The Workplace For The Aging WorkforceDocument26 pagesDesigning The Workplace For The Aging Workforcerizki aryaNo ratings yet
- The Precede-Procede: ModelDocument12 pagesThe Precede-Procede: ModelArda Krisnata100% (1)
- Wellbeing Project - RubyDocument8 pagesWellbeing Project - RubylokirealmegtNo ratings yet
- Leadership and ProfessionalismDocument25 pagesLeadership and ProfessionalismPingLomaadEdulanNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy-RehabilitationDocument26 pagesCerebral Palsy-RehabilitationVarun Thomas PaulNo ratings yet
- Bsbwhs504: Manage Whs Hazards and RisksDocument10 pagesBsbwhs504: Manage Whs Hazards and Riskssimran aroraNo ratings yet
- History Systems Review Tests and MeasuresDocument4 pagesHistory Systems Review Tests and MeasuresorthooNo ratings yet
- HRs AssignmentDocument5 pagesHRs AssignmentPoornima DeviNo ratings yet
- Paper4 ShoDocument46 pagesPaper4 ShoHafiz SabriNo ratings yet
- 2 Total Ergonomic ApproachDocument25 pages2 Total Ergonomic ApproachPande Indra PremanaNo ratings yet
- Io Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesIo Midterm ReviewerMargarita Dave MendozaNo ratings yet
- P E A R: RecognitionDocument9 pagesP E A R: RecognitionIbni UlhusnaNo ratings yet
- Human: - Divya KrishnakumarDocument35 pagesHuman: - Divya KrishnakumarGretchen LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Administrative Office Management ReviewerDocument5 pagesAdministrative Office Management Reviewerroseann mangobaNo ratings yet
- Inner-Defence: Inner Management Skills for First Responders, Security and Risk Management ProfessionalsFrom EverandInner-Defence: Inner Management Skills for First Responders, Security and Risk Management ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- The Desk Jockey's Manifesto: The Practical Guide for Modern Computer/Desk WorkerFrom EverandThe Desk Jockey's Manifesto: The Practical Guide for Modern Computer/Desk WorkerNo ratings yet
- There Is Someone at Work Who Encourages My Development.: Help Me GrowDocument2 pagesThere Is Someone at Work Who Encourages My Development.: Help Me Grow757rustamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Concepts Lesson 3 - Recruiting, Selection, and OrientationDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Concepts Lesson 3 - Recruiting, Selection, and Orientation757rustamNo ratings yet
- Learner Needs Analysis Template: What'S The Point of This Template?Document13 pagesLearner Needs Analysis Template: What'S The Point of This Template?757rustamNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Leaders GuideDocument44 pages2015 - Leaders Guide757rustamNo ratings yet
- Manager'S Guide To Building A Successful Learning Path Using UlearnitDocument1 pageManager'S Guide To Building A Successful Learning Path Using Ulearnit757rustamNo ratings yet
- Action Team Leader ToolkitDocument20 pagesAction Team Leader Toolkit757rustamNo ratings yet
- 2 Wellbeing at Work My Role As A Manager or Team LeaderDocument2 pages2 Wellbeing at Work My Role As A Manager or Team Leader757rustamNo ratings yet
- IICF Volunteer Team Leader Website Guide: Sign Up For Year-Round Volunteer Projects As Well As The Annual Week of Giving!Document6 pagesIICF Volunteer Team Leader Website Guide: Sign Up For Year-Round Volunteer Projects As Well As The Annual Week of Giving!757rustamNo ratings yet
- Team Leader Guide: Thank You For Accepting The Role of Team Leader!Document7 pagesTeam Leader Guide: Thank You For Accepting The Role of Team Leader!757rustamNo ratings yet
- Task Force & Strike Team Leader Guidebook: Updated For 2020 COVID-19 EnvironmentDocument34 pagesTask Force & Strike Team Leader Guidebook: Updated For 2020 COVID-19 Environment757rustamNo ratings yet
- GG202x: Mindfulness and Resilience To Stress at Work: Team Leader GuideDocument10 pagesGG202x: Mindfulness and Resilience To Stress at Work: Team Leader Guide757rustamNo ratings yet
- 20% Off-The-Job Training GuideDocument7 pages20% Off-The-Job Training Guide757rustamNo ratings yet
- Career Conversations: Employee-Driven. Development-Oriented. SimpleDocument12 pagesCareer Conversations: Employee-Driven. Development-Oriented. Simple757rustamNo ratings yet
- Team Leader Guide: Prepared byDocument9 pagesTeam Leader Guide: Prepared by757rustamNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based On-The-Job Training For Aviation Maintenance and Inspection) A Human Factors ApproachDocument11 pagesCompetency-Based On-The-Job Training For Aviation Maintenance and Inspection) A Human Factors Approach757rustamNo ratings yet
- (eBook-EN) Make UX MeasurableDocument34 pages(eBook-EN) Make UX Measurable757rustamNo ratings yet
- The Proper Way To Do On The Job TrainingDocument1 pageThe Proper Way To Do On The Job Training757rustamNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Human Error Probability of Disc Brake Unit Assembly and Wheel Set Maintenance of Railway BogieDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Human Error Probability of Disc Brake Unit Assembly and Wheel Set Maintenance of Railway Bogie757rustamNo ratings yet
- Maritime Educators and Trainers - : Knowledge, Skills & AttributesDocument1 pageMaritime Educators and Trainers - : Knowledge, Skills & Attributes757rustamNo ratings yet
- Centrespread 33 PDFDocument1 pageCentrespread 33 PDF757rustamNo ratings yet
- SIBUR - 1H 2020 - Results - PresentationDocument22 pagesSIBUR - 1H 2020 - Results - Presentation757rustamNo ratings yet
- A Rough Guide To MLC 2006 Regulation 3.1: HabitabilityDocument1 pageA Rough Guide To MLC 2006 Regulation 3.1: Habitability757rustamNo ratings yet
- Abstract DC Bill April-May-2023Document11 pagesAbstract DC Bill April-May-2023jsshaik24No ratings yet
- 10 Ways Human Resources Will Change in 2022Document7 pages10 Ways Human Resources Will Change in 2022Kashish GurnaniNo ratings yet
- Heidelberg Linoprint CV (Ricoh Pro c7100) 69391Document1 pageHeidelberg Linoprint CV (Ricoh Pro c7100) 69391ArlindPacukuNo ratings yet
- CLOXACILLIN (Cloxacillin Sodium) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Document1 pageCLOXACILLIN (Cloxacillin Sodium) : Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Crizzalyn CruzNo ratings yet
- 03-TA80 CONF030 ExtendingEntitiesDocument37 pages03-TA80 CONF030 ExtendingEntitiesathiraviswanath02No ratings yet
- Blended Wing Body Low Speed Flight DynamicsDocument10 pagesBlended Wing Body Low Speed Flight DynamicsARUN.A.J NAIRNo ratings yet
- MSDS Radiator CoolantDocument10 pagesMSDS Radiator CoolantFauzy AL RahmanNo ratings yet
- Od126520774203945000 1 PDFDocument2 pagesOd126520774203945000 1 PDFMuthukumaresan ANo ratings yet
- Erlang - DefinitionDocument19 pagesErlang - DefinitionNathan MillsNo ratings yet
- Citect ModnetDocument5 pagesCitect ModnetKuncoroNuryantoNo ratings yet
- Uson v. Diosomito, 61 Phil. 535 (1935)Document3 pagesUson v. Diosomito, 61 Phil. 535 (1935)Danica GodornesNo ratings yet
- CH #2 NumericalsDocument3 pagesCH #2 NumericalsMs Noor ul AinNo ratings yet
- Host Supervisor Assessment Form Ads667 60%Document11 pagesHost Supervisor Assessment Form Ads667 60%Malabaris Malaya Umar SiddiqNo ratings yet
- HontinDocument28 pagesHontinMaria Theresa Deluna MacairanNo ratings yet
- Course Material 1 The Practice of EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pagesCourse Material 1 The Practice of EntrepreneurshipRenz ZacharielleNo ratings yet
- ELEC4410 Control System Design Revision NotesDocument10 pagesELEC4410 Control System Design Revision Notescjman404No ratings yet
- Small Porch SwingDocument26 pagesSmall Porch SwingEngr Saad Bin SarfrazNo ratings yet
- What To Look For in A OMEGAMON Statistics Report - IBM DocumentationDocument5 pagesWhat To Look For in A OMEGAMON Statistics Report - IBM Documentationamir ghorbaniNo ratings yet