Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural
Uploaded by
Mary Ann FiguerasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural
Uploaded by
Mary Ann FiguerasCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural
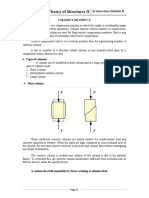
It is an assemblage of framing members designed to support gravity loads and STRUCTURE
1
resists lateral forces?
Occupancies and structures housing or supporting toxic or explosives HAZARDOUS FACILITIES
chemicals or substances; non-building structures storing, supporting or
2
containing quantities of toxic or explosives substances?
3 This consists of the weight of all materials and other fixed or permanent loads? DEAD LOAD
4 A wall design to resist the lateral displacement of soil or other materials? RETAINING WALL
It is a horizontal or nearly horizontal system acting to transmit lateral forces to DIAPHRAGM
5 the vertical-resisting elements, including the horizontal bracing systems.
It is one in which the lateral stiffness is less than 70% of the stiffness of the SOFT STORY
6
story above?
7 It is one in which the story strength is less than 80% of the story above? WEAK STORY
It is the secondary effect on shears, axial forces and moments of frame P-DELTA EFFECT
members due to the action of the vertical induced by horizontal displacement
8
of the structure resulting from various loading.
It is an artificial stone derived from a mixture of properly proportioned CONCRETE
9 amount of hydraulic cement, fine aggregates, coarse aggregates and water,
with or without admixtures.
A material other than aggregate, water, or hydraulic cement used as an ADMIXTURE
10 ingredient of concrete and added to concrete before or during its mixing to
modify its properties.
11 Load that is movable or transferable is called? LIVE LOAD
12 A large beam supporting a smaller beam is called? GIRDER
13 An advantage of steel over concrete? ELESTICITY
14 The sharp bending or buckling when a column is loaded heavily is called? CRIPPLING
15 Usual failure of a long column? BUCKLING
What usually happen to reinforcing steel in a reinforced concrete slab or beam YIELD
16
if such member is about to collapse?
17 Reinforcing bars put in contact to act as a unit is called? BUNDLED BARS
18 Structural member that is subjected to transverse load which bends it? BEAM
What is the purpose of the stirrups aside from resisting vertical and diagonal HOLD LONGITUDINAL
19
tensions in a beam? BARS IN PLACE
The degree to which a location is subjected to earthquake risk, usually refers SEISMEICITY
20 to the frequency of occurrence and magnitude of past earthquake and
expectation of future earthquake activity?
21 Ties are used for what type of structural elements? COLUMNS
22 Stirrups are used for what type of structural elements? BEAMS
23 What do you call a column that is not aligned to a lower floor column? PLANTED COLUMN
Type of pre-stressing for which tension is applied prior to the placing of PRE-TENSIONING
24
concrete?
It is one in which the lateral stiffness is less than 70% of the stiffness of the SOFT STORY
25
story above?
26 A type of concrete floor which has no supporting beams? FLAT SLAB
compiled by: XlX1
Structural
The failure of a base when heavily loaded columns strike a hole through it is PUNCHING SHEAR
27
due to?
The force adhesion per unit area of contact between two bonded surfaces is BOND STRESS
28
called?
29 The distance between two structural supports is called? SPAN LENGTH
What is the temporary force exerted by a device that introduce tension into a JACKING FORCE
30
pre-stressing tendons?
31 Rapid hardening cement is called "early______cement". SETTING
The gradual downward movement of an engineering structure due to SETTLEMENT
32
compression of the soil below the foundation.
33 The ability of soil to allow water to flow through it. PERMEABILITY
34 Slump test is done in fresh concrete in order primarily to determine: WORKABILITY
This has the effect of delaying the onset of hardening and reducing the rate of RETARDER
35
hydration process in concrete:
Inert materials in concrete which occupy more than 75% of the volume of the AGGREGATES
36
hardened concrete:
37 The wall that resist horizontal forces applied in a plane of the wall: SHEAR WALL
It is formed, sawed, or tooled groove in a concrete structure to create a CONTRACTION JOINT
weakened plane and regulate the location of cracking resulting from the
38
dimensional change of different parts of the structure.
It is the length of embedded reinforcement required to develop the design DEVELOPMENT LENGTH
39
strength of reinforcement at critical section.
It is a method of pre-stressing in which tendons are tensioned after concrete POST TENSIONING
40
has hardened.
Newton (N) is the SI unit of force and was named after Isaac Newton in kg m/s2
41 recognition of his contributions to the field of mechanics. It is denoted by N
and is expressed in:
42 What usually happens to steel when stressed? BEND
43 Pascal (Pa), the SI unit of stress, is expressed in: N/m2
44 The unit of stress in the Imperial System. psi
The deformation of a body under the action of an applied force. It is the ratio STRAIN
45 of the change in size and shape to the original size and shape of the body.
46 It is the force per unit are (F/A) on a body that tends to cause it to change shape.STRESS
It is the stress caused by an applied load that acts to reduce the length of the COMPRESSIVE STRESS
47
material along the axis of the applied load.
It is the stress caused by an applied load that tends to elongate the material TENSILE STRESS
48
along the axis of the applied load.
It is the stress caused by pair of opposing forces that acts along parallel lines SHEAR STRESS
49
through the material.
50 It is the change in shape of a material created when stress is applied. DEFORMATION
51 An instrument used to measure deformation. EXTENSOMETER
A term to describe the magnitude to which a structural element is displaced DEFLECTION
52
when subjected to an applied load.
compiled by: XlX2
Structural
It is the amount of stress that a material can undergo before moving from ELASTIC LIMIT
53
elastic deformation into plastic deformation.
Compression/to resist compression. COMPRESSIVE
54
STRENGTH
55 To resist tension. TENSILE STRENGTH
56 To resist cyclic stress FATIGUE STRENGTH
57 The capacity to absorb shock. IMPACT STRENGTH
It is the first stress in a material at which an increase in strain occurs without YIELD POINT
58
an increase in stress.
59 What do you call the point wherein a material is about to rupture? ULTIMATE STRENGTH
The point in the stress-strain curve beyond which the material pemanently ELASTIC LIMIT
60
deforms after removing the load.
It is the ability of a material to return to its previous shape after stress is ELASTICITY
61
released.
62 A material that possesses a very high Young's Modulus is. RIGID
63 What is Modulus of Elasticity? (F/A) / (d L/L)
64 Formula of Modulus of Elasticity? (F/A) / (d L/L)
What do you call ratio Stress/Strain? MODULUS OF
65
ELASTICITY
MODULUS OF
Young's Modulus is the ratio of stress along an axis to the strain along that axis
66 ELASTICITY
in the range of stress in which Hooke's Law holds. It is also known as?
Also called the Shear Modulus, it is the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain MODULUS OF RIGIDITY
67
and is denoted by G.
68 The ratio of lateral strain / longitudinal strain POISSON'S RATIO
The greatest stress at which a material is capable of sustaining the applied PROPORTIONAL LIMIT
69 load without deviating from the proportionality of stress to strain. It is
expressed in psi or kg/mm^2
70 What is the most important determinant of concrete strength? WATER
71 What deformation does a beam contain? DEFLECTION
72 Minimum concrete cover for slab on fill? 75mm
Minimum concrete cover of cast-in-place 2nd floor slabs considering 42mmØ 40mm
73
bars?
Minimum concrete cover of cast-in-place 3rd floor slabs considering 36mmØ 20mm
74
bars?
75 Minimum concrete cover of cast-in-place beams not exposed to wheather? 40mm
76 Minimum concrete cover of cast-in-place beams exposed to wheather? 50mm
77 For columns exposed to wheather? 50mm
78 For columns not exposed to wheather? 40mm
79 Minimum concrete column for column footing? 75mm
A method of mechanically increasing the density of soil. It is a very significant SOIL COMPACTION
part of the building process and if improperly done could cause soil settlement
80 which could result to unnecessary maintenance costs or structure failure:
Static, Impact, Vibrating, Gyrating, rolling and Kneading.
compiled by: XlX3
Structural
81 Main bars for cantilevered slabs are located at? TOP
82 For one way slab, the ratio of the longer span (L) to the shorter span (B) is? L/B>=2
83 For two way slab, the ratio of the longer span (L) to the shorter span (B) is? L/B<2
84 What is the best location of support for a one way slab? END OF SLAB
It is a flaky layer of hardened but weak hydrated cement and fine aggregates LAITANCE
which began as a milky layer on the upper surface of the concrete mass during
85 the curing process which was caused by an excess amount of water used in
the mixture or by too much vibration.
Other term for Tangential Stress? CIRCUMFERENTIAL
86
STRESS
87 Effective length of the column? SLENDERNESS RATIO
88 KL/r<22 SHORT COLUMN
89 KL/r>22 LONG COLUMN
90 A non-vertical support? BATTER PILE
A structural member whose function is to transfer the loads from a building FOOTING
91
safely into the ground?
It is the depth below ground water level multipled by the weight of water. HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE
92
It is the ultimate bearing capacity divided by a factor of safety. However, in ALLOWABLE BEARING
certain situations, usually on soft soil sites, large settlements may occur under CAPACITY
93 loaded foundations without actual shear failure occuring. In such cases "this"
is based on the allowable settlement.
If a project is located on a steep ground, what type of foundation would you CANTILEVER
94
recommend?
What is the main factor that determines the strength of concrete? WATER-CEMENT RATIO
95
A36 Steel is the most common type of steel alloy. What does the number 36 YIELD STRENGTH
96
means?
ASTM stands for? AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR
97 TESTING AND
MATERIALS
98 ASTM standard specification for carbon structural steel is? ASTM A36
The ASTM standard specification for general requirements for rolled structural ASTM A6
99
steel bars, plates, shapes and sheet piling?
ASTM standard specification for structural bolts, steel, heat treated, ASTM A325
100
120/105ksi minimum tensile strength?
101 In I-beam, which part carries most of the weight of a structure? WEB OF I-BEAM
102 In an I-beam, the flanges resist most of the? BENDING MOMENT
103 In reinforced concrete beams, which portion is under tension? BOTTOM
A simplified way to get the economical width of the beam LESS THAN COLUMN
104
WIDTH
At what part of a reinforced concrete beam would you allow a pipe/service AT L/4 OF BEAM SPAN
105
hole to pass through for utility purposes?
compiled by: XlX4
Structural
106 In reinforced concrete beams, which portion is under compression? TOP
107 Formula for beam depth? d=L/16
Identify: LIVE LOAD
108
Identify: DEAD LOAD
109
110 For stairs, the load rests on the? STRINGER
111 It is the product of the nominal load and a load factor. FACTORED LOAD
A support of a fixed-end beam. RESTRAINED SUPPORT
112
A pair of forces, equal in magnitude but opposite in direction and displaced by COUPLE
113
perpendicular distance or moment.
114 What do you call the distance between supports? SPAN LENGTH
Identify: 1=CLEAR SPAN
2=?????
3=SPAN LENGTH
115
It is the distance measured from extreme compression fiber to the centroid of EFFECTIVE DEPTH OF
116
tension reinforcement. SECTION
117 A small beams to support floor and ceiling. JOISTS
118 What loads are considered for high rise buildings? LATERAL LOADS
What do you call the design wherein both steel and concrete fail at the same BALANCE
119
time?
120 A design wherein the steel fails first before crashing. UNDERREINFORCED
121 A design wherein the concrete fails first, it destroyed without warning? OVERREINFORCED
122 In lateral ties & stirrups, longitudinal bars w/ 32mm or smaller. 10mm
123 In lateral ties & stirrups, longitudinal bars w/ 36mm or larger. 12mm
124 Allowable stress for tension in structural steel in terms of gross area. 0.6
Allowable shear stress on structural steel on the cross sectional area effective 0.40 Fy
125
in resisting shear.
126 What supports the shearwall? FOOTING
A structural system used to transfer/transmit lateral forces like wind and DIAPHRAGM
127
earthquake load to the vertical-resisting elements.
A structural system used to counter the effect of lateral forces like wind and SHEAR WALL
128
earthquake load. It is also referred to as a structural wall.
129 Which would enhance the building against lateral forces? RIGID CORE
Is a frame in which members and joints are capable of resisting forces MOMENT RESISTING
130
primarily by flexure. FRAME
compiled by: XlX5
Structural
Driven piles of uniform section shall have a minimum nominal outside 300mm
131
diameter of?
132 What equipment is used for pile driving? PILE HAMMER
Where can we stop pouring ready mixed concrete in the column, slabs, and AT THE MIDDLE THIRD
133
beams if the pouring cannot be done in one setting?
On concrete pouring of beams and slabs, which should be poured first with BEAM FIRST
134
one day interval?
135 What will transmit the loads of the structure to the piles? PILE CAP
136 Most likely failure for a footing. UNSTABLE SOIL
It is a column that is symmetrical to its other axis. SYMMETRICAL COLUMN
137
What do you call a horizontal member of a structure that is fixed at both RESTRAINED FIXED-END
138
ends? BEAM
139 Two fixed supports is indeterminate to what degree? 3RD
140 What is flexural stress? BENDING STRESS
141 What is Torsion stress? TORQUE
142 What is P-Delta Effect? SECONDARY EFFECT
A wall that carries no other load except load its own weight. NON-LOAD BEARING
143
WALL
144 Where will you find the main bars for cantilever beams? TOP
145 A repeated series of stress? FATIGUE
146 In Trusses, it is the process of isolating. METHOD OF JOINT
147 In trusses, it is the process of cutting. METHOD OF SECTION
148 An instrument used to measure velocity & acceleration of an earthquake. ACCELEROGRAPH
The term in working stress design, refers to reinforced concrete beam in BALANCE DESIGN
which the cross-sectional areas of concrete and steel are of such dimensions
149
that each develops its full allowable stress simultaneously:
150 The best Economical Column design? SQUARE COLUMN
151 The best column design in terms of strength? CIRCULAR COLUMN
152 1inch = _____ m 0.0254
153 1feet = _____ m 0.3048
154 Density of steel? 7850kg/cum
It is the length of embedded reinforcement required to develop the design DEVELOPMENT LENGTH
155
strength of reinforcement at critical section.
It is the length of embedded reinforcement provided beyond a critical section. EMBEDMENT LENGTH
156
How is a 90degree bend standard hook for concrete reinforcement 90* BEND+10db
157
constructed? EXTENSION
158 It is the distance between inner face of supports. CLEAR SPAN
A slump cone use to test freshly mixed concrete is a mold in the form of the 12"
159 lateral surface of the frustum of a cone with a base diameter of 8" and a top
diameter of 4", then what is its height?
When do you getsamples for a slump test? MIDDLE OF MIXER
160
DISCHARGE
compiled by: XlX6
Structural
The purpose of a cooncrete slump test is to measure? WORKABILITY &
161
CONSISTENCY
162 Test used to determine the strength of concrete. COMPRESSION TEST
163 It is the most important component in determining the strength of concrete. WATER
The most important factor affecting the strength of concrete. WATER-CEMENT RATIO
164
A complete record of tests of materials and of concrete shall be available for 2YEARS
165 inspection during progress of work anf for how many years after completion
of the project?
Who is responsible for keeping and maintaining a complete record of tests of PROJECT MANAGER /
166
material during and after completion of the project. OWNER
Minimum and maximum spacing of lateral ties in beams. 25mm MINIMUM, NO
167
MAX
A structural system without a complete vertical-load carrying space frame. BEARING WALL SYSTEM
168
Is an essentially vertical truss system of the concentric or eccentric type that is BRACED FRAME
169
provided to resist lateral forces.
170 Minimum thickness for load bearing walls. 150mm
171 Where do shear wall rest? FOOTING
172 It is a wall designed to resist lateral forces parallel to the plane of the wall. BEARING WALL
173 Is the lateral displacement of one level relative to the level above or below. STORY DRIFT
174 Is the story drift divided by the story height. STORY DRIFT RATIO
Failure of a material due to repeated or continued stress. It is more visible and CREEPING
175
severe in materials subjected to heat.
176 It is the more dangerous than underreinforced concrete. OVERREINFORCED
177 A building collapses without any warning. How was the building designed? OVERREINFORCED
A gap between building elements that allows them to move with expansion EXPANSION GAP
178
due to changes in temperature of moisture.
A gap between two buildings that allow them to move during an earthquake. SEISMIC GAP
179
It is a phenomenon whereby soil substantially loses its strength usually due to LIQUEFACTION
180
an earthquake and acts like a fluid.
181 Advantage of steel over concrete. ELASTICITY
182 Bending of column. BUCKLING
The perpendicular distance a spanning member deviates from under DEFLECTION
transverse loading, increasing with load and span and decreasing with an
183
increase in the moment of inertia of the section or the modulus of elasticity of
the material.
What usually happens to steel in a slab or reinforced concrete beam if such YIELDS
184
member is about to collapse?
These are a group of parallel reinfircing bars bundled in contact to act as a unit BUNDLED BARS
185 and is limited to four bars in a bundle. It is enclosed within stirrups or ties.
186 Ties are used for what structural element? COLUMNS
compiled by: XlX7
Structural
A reinforcement used to resist shear and torsion stresses in a structural STIRRUP
member; typically bars either single leg orbent into L,U or rectangular shapes
187
and located perpendicular to or at an angle to longitudinal reinforcement.
A reinforced-concrete-encased structural steel section (rolled ar built-up) or COMPOSITE COLUMN
188 concrete filled steel section used as a column where both steel and concrete
workas a unit is called a.
189 What is the minimum width of a wall footing? .40m
190 What is the minimum thickness of a wall footing? .20m
What do you call bars that are perpendicular to the main reinforcement of TEMPERATURE BARS
191 slabs on fill where they prevent cracking due to contraction brought about by
shrinkage and temperature changes?
It is the height of the wall divided by its thickness (H/t) SLENDERNESS RATIO OF
192
THE WALL
193 It is the general term for forces that act on a building. LOAD
194 What do you call two(2) or more materials that are combined together? COMPOSITE
195 It is a web found in a structural member. ROOF TRUSS
196 It is the middle part of a wide flange. WEB
The architect asks you to order from the supplier a W8x35 wide flange steel 8" DEEP, 35lbs PER
197 section. What do the two numbers used to designate a wide flange describe? LINEAR ft
What is produced on continuous process of cold roll and hot roll steel? WIDE VARIETIES OF
198
STEEL
199 It is used to support the rafters. PURLINS
200 A brick wall is weak in? TENSION
What is the resultant uniform distribution load? CONCENTRATED BEAM
201
202 It is also known as elastic limit. ELONGATION
The section of a beam at which the bending moment changes from positive to INFLECTION POINT
203
negative and at this point, the bending moment is zero.
A property of material that enables it to undergo plastic deformation after DUCTILITY
204 being stressed beyond the elastic limit and before rupturing.
A property of materials that causes it to suddenly rupture under stress with BRITTLENESS
205
little or no evident deformation.
206 What component of steel dictates its ductility? CARBON
207 It is the maximum capacity of a building. ULTIMATE STRENGTH
A slight curve built intentionally into a beam, slab, girder or truss to CAMBER
208
compensate for an anticipated deflection?
209 Camber = 1% of LENGTH
210 For a beam, what is the camber direction? UPWARD
211 For a 3m beam, What will be the allowed camber in mm? .03m
It is the structural system without a complete vertical load carrying space BEARING WALL SYSTEM
212
frame.
compiled by: XlX8
Structural
The maximum axial load that can theoretically be applied to a column without CRITICAL BUCKLING
213
causing it to buckle. LOAD
214 A thick column subject to failure by crushing rather than by buckling? SHORT COLUMN
215 What makes a long column to buckle? AXIAL COMPRESSION
216 Will most likely fail due to buckling. LONG COLUMN
Usually fails by both crushing and buckling. INTERMEDIATE COLUMN
217
218 Pedestals, Piers or Compression Blocks are classified as? SHORT COLUMN
219 L/r is also know as? SLENDERNESS RATIO
220 What does Slenderness Ratio determine? EFFECTIVE LENGTH
221 It is the distance between two supports measured from the inner face. CLEAR SPAN
Soil testing is done during? DURING SITE
222
INVESTIGATION
For the Geotechnical Evaluation (Soil Boring Test) of a jobsite, ASTM requires 1.50m
223 that a Soil Penetration Test (SPT) be performed every how many meters?
224 Up to what depth should a Soil Boring Test be done? BEDROCK
It is removing of earth materials or the depositing of earth materials or the BORROWING
225
combination thereof.
226 It is the main structural member of a wooden floor? JOISTS
A strip of metal or wood attached to a surface to restrain or support an CLEATS
227
element or member.
Any of a series of small parallel beams for supporting floors, ceilings, or flat JOISTS
228
roofs.
229 A brick or stone projecting from within a wall, usually to support a weight? CORBEL
Most likely failure for a retaining wall. FAILURE AT MOMENT
230
ARM
Identify:
231
Identify:
232
Backfill shall be placed in layers and each layer shall be _____mm thick and 200mm
233
compacted.
compiled by: XlX9
Structural
An exterior wall supported wholly by the structural frame of a building and CURTAIN WALL
234 carrying no,loads other than its own weight and wind loads.
A vertical diaphragm acting as a thin, deep cantilever beam in transfering SHEAR WALL
235
lateral loads to the ground foundation.
A wall of treated timber, masonry, concrete for holding in place a mass of RETAINING WALL
236
earth.
The tendency of a force to produce rotation of a body about a point or line, MOMENT
equal in magnitude to the product of the force and the moment arm and
237
acting in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction.
Force that causes one part of the body to slide relative to an adjacent part in a SHEAR
238
direction parallel to their plane of contact.
239 The act of stretching or state of being pulled apart. TENSION
The twisting of an elastic body about its longitudinal axis caused by two equal TORSION
240 and opposite torques, producing shearing stresses in the body.
241 Combination of intermediate moment resisting space frame and shear walls. DUAL
it is a formed, sawed or tooled groove in a concrete structure to create a CONTRACTION JOINT
weakened plane and regulate the location of cracking resulting from the
242
dimensional change of different parts of the structure.
CONSTRUCTION JOINT
When laying concrete, it is sometimes not possible to pour in one setting. It
can be due to wheather, time constraints, lack of materials or even by design.
243
Hence, there will now be a separation between old and newly poured
concrete once concrete pouring resumes. What do you call this?
An undesirable discontinuity in concrete that occurs when a layer of concrete COLD JOINT
244 hardens before the rest of the concrete is poured in what is meant to be a
single, solid mass.
Construction joints in floors shall be located within ______ of spans of slabs, MIDDLE THIRD
245
beams and girders.
Joints in girders shall be offset a minimum distance of how much the width of 2X
246
intersecting beams?
To pre-stress a concrete member by tensioning the reinforcing tendons after POST TENSIONING
247
the concrete has set.
Aconcrete reinforced by pre-tensioning or post tensioning high-strength steel PRE STRESSED
248 tendons within their elastic limit to actively resist a service load.
249 What do you call the wires/cables where jacking force is applied? TENDONS
250 How do you connect pre-stressed concrete to reinforced concrete? DOWEL
What foundation presents the LEAST disturbance & potential damage to ISOLATED FOOTING
251
neighboring lots?
What foundation presents the MOST disturbance & potential daamage to BORED PILE
252
neighboring lots?
253 What are pile placed at an inclination to resist forces that are not vertical? BATTER PILE
compiled by: XlX10
Structural
Driven piles of uniform section shall have a minimum nominal outside 300mm
254
diameter of?
A concrete beam placed directly on the ground to provide foundation for the GRADE BEAM
255
superstructure.
A method used in driving piles in sand, gravel or soft packed clay due to the JETTING
256 high resistance of these materials to hammer driven piles.
257 The soil or rock directly beneath the footing is? FOUNDATION BED
In PERT-CPM, the difference between the scheduled and actual SLIPPAGE
258
accomplishments is reffered to as.
This Truss was patented in 1840 and it includes vertical members and HOWE TRUSS
259 diagonals that slope towards the center. It is the opposite of the Pratt Truss?
These are braces used to provide lateral load resistance in buildings. It reduces CHEVRON BRACING
deflection of the beam it supports above and transfer loads to your support or
foundations. It helps to greatly reduce the sizes of beams. It provides
260
additional stability to your structure, reduces sidesways and deflection and
other serviceability requirement.
Given a 300mmX300mm column with 8-16mmØ main bars and 10mmØ ties, 1032mm
261 what is the length of each tie if the column is nonprestressed and not exposed
to weather?
712mm
In a 300mmX350mm grade beam with 8-16mmØ main bars and 10mmØ
262
stirrups, what is the length of each stirrup if the beam is nonprestressed?
263 The maximum clear spacing between spirals is? 75mm
264 The minimum clear spacing between spirals is? 25mm
The distance between points of zero moment on a compression member is? EFFECTIVE LENGTH OF
265
COLUMN
compiled by: XlX11
You might also like
- SSR 2021-22Document445 pagesSSR 2021-22Avishkar Chikhalikar56% (9)
- BOQ Format Sample Road-R5Document44 pagesBOQ Format Sample Road-R5ParamitaDana77% (13)
- Jecc ReportDocument14 pagesJecc ReportNavneet Zandu100% (2)
- Mechanical Properties of Dental MaterialsDocument40 pagesMechanical Properties of Dental MaterialsRamnarayan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2 Concept of Stress and StrainDocument33 pagesLecture # 2 Concept of Stress and StrainSohaibNo ratings yet
- 07 - Planning and Development of Prewar ManilaDocument23 pages07 - Planning and Development of Prewar ManilaCleo BuendichoNo ratings yet
- Tropical Design LectureDocument14 pagesTropical Design LectureOfeliah100% (1)
- Stowing and CavingDocument14 pagesStowing and CavingPrabhu Prasad100% (1)
- BMED 2 SBA Assignment 5& 6Document6 pagesBMED 2 SBA Assignment 5& 6shondelB 5No ratings yet
- BetonelDocument5 pagesBetonelGaál Csaba NimródNo ratings yet
- Short NotesDocument170 pagesShort NoteskiranNo ratings yet
- SpecsDocument105 pagesSpecsianiroy13No ratings yet
- Structural ConceptualizationDocument130 pagesStructural ConceptualizationNeochel De JesusNo ratings yet
- Structural ReviewerDocument17 pagesStructural ReviewerJireh Grace100% (4)
- Capacity Design: P.Sudha 1061014 Ii M.E. CmaaseDocument66 pagesCapacity Design: P.Sudha 1061014 Ii M.E. CmaasePraveenkumar Shanmugam100% (1)
- Steel 03 PDFDocument9 pagesSteel 03 PDFshane escoteNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument6 pagesMechanicsJeo CajerasNo ratings yet
- Structural elements and concepts for buildingsDocument1 pageStructural elements and concepts for buildingsShara Marimon50% (2)
- The Control of Building Motion by Friction Dampers: Cedric MARSHDocument6 pagesThe Control of Building Motion by Friction Dampers: Cedric MARSHAlam Mohammad Parvez SaifiNo ratings yet
- LAB VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesLAB VIVA Questions and AnswersNilambar YadavNo ratings yet
- Ibc 16Document114 pagesIbc 16Luis Fernando BaqueNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes - StrengthofMaterials Part 1Document201 pagesLectureNotes - StrengthofMaterials Part 1Sir ArtNo ratings yet
- 02 Geenral Intro DuctionsDocument52 pages02 Geenral Intro Ductionsmuhammad irfanNo ratings yet
- Structural ReviewerDocument18 pagesStructural ReviewerjericoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 2 MarksDocument3 pagesUnit 1 2 MarksisaivananNo ratings yet
- StructuralDocument4 pagesStructuralMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Sumsem1-2018-19 Mee1005 Eth Vl2018198000361 Reference Material I 20-May-2019 l28-29 - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument32 pagesSumsem1-2018-19 Mee1005 Eth Vl2018198000361 Reference Material I 20-May-2019 l28-29 - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsADAM ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Python in VtuDocument44 pagesPython in VtuAnand ShivannaNo ratings yet
- Chap. 4Document50 pagesChap. 4gossayeNo ratings yet
- ME 1201 ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERINGDocument33 pagesME 1201 ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERINGBau MandalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction - Theory and BehaviourDocument68 pagesUnit 1 Introduction - Theory and Behavioursanthiamutha0% (1)
- Direct Stresss and Strain - Elasticity and PlasticityDocument5 pagesDirect Stresss and Strain - Elasticity and PlasticityRonald obasieNo ratings yet
- Structural: Question and Answer Samples and TechniquesDocument100 pagesStructural: Question and Answer Samples and TechniquesCasas SweetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Structural Design PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 16 - Structural Design PDFTefera TemesgenNo ratings yet
- 006 StructuralDocument4 pages006 StructuralrcdpreludeNo ratings yet
- Structural Notes: Center of MomentDocument14 pagesStructural Notes: Center of MomentRonaleen Mae PerlasNo ratings yet
- Structural NotesDocument12 pagesStructural NotesCzareena DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Understanding Stress and StrainDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Stress and StrainDivyanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- RC-II- Tutorial NOTE for Exit Exam (1)Document79 pagesRC-II- Tutorial NOTE for Exit Exam (1)znabugrmay20adiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document59 pagesUnit 3P S HARSHITA100% (1)
- Mos Unit-1Document32 pagesMos Unit-1Srinivas EedaraNo ratings yet
- ES3D1 Concrete StrengthDocument28 pagesES3D1 Concrete StrengthMubin Al-ManafNo ratings yet
- Rc1 NotesDocument16 pagesRc1 NotesKyle Russell FabiaNo ratings yet
- TDS III Lec 2Document22 pagesTDS III Lec 2Selam MubarekNo ratings yet
- Properties of ForcesDocument120 pagesProperties of ForcesAnne Felicia Monderin CruzNo ratings yet
- April 7 2009Document67 pagesApril 7 2009Williams AkandiNo ratings yet
- Structural: Properties of Forces Internal Forces Types Tension Compression Shear AstmDocument14 pagesStructural: Properties of Forces Internal Forces Types Tension Compression Shear AstmRjane CañeteNo ratings yet
- Structural DesignDocument14 pagesStructural DesignMiguel Fernando YangNo ratings yet
- Structural Notes: Center of MomentDocument14 pagesStructural Notes: Center of MomentNeochel De JesusNo ratings yet
- Tensile StructuresDocument59 pagesTensile StructuresWendimu TolessaNo ratings yet
- LFRSDocument43 pagesLFRShsnaterNo ratings yet
- Video PDFDocument8 pagesVideo PDFAhmed Ali TahaNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of ConcreteDocument2 pagesElasticity of ConcreteSohaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 - Plastic Analysis Lecture-One FinalDocument60 pagesChapter-1 - Plastic Analysis Lecture-One Finaltelham MNo ratings yet
- Strenght of ShipDocument24 pagesStrenght of ShipSujit DasNo ratings yet
- Elasticity Stress-Strain Curve2222Document20 pagesElasticity Stress-Strain Curve2222mohammad hafodyNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument5 pagesMechanics of Deformable BodiesJera Lunar CaliwanaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Structural DesignDocument48 pagesChapter 16 - Structural DesignAlaym AguilarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties OF Dental MaterialsDocument39 pagesMechanical Properties OF Dental Materialsbukya002No ratings yet
- January 2000 Board Exam quiz helps geometry revisionDocument10 pagesJanuary 2000 Board Exam quiz helps geometry revisionEloisa LauNo ratings yet
- Flow Separation and Its Effect On Drag Fluid MechanicsDocument14 pagesFlow Separation and Its Effect On Drag Fluid MechanicsRUGERO KeslyneNo ratings yet
- AE2030 Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics GuideDocument32 pagesAE2030 Fatigue and Fracture Mechanics Guidelogicvirus100% (1)
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Asha AsokNo ratings yet
- CE 4312 Lecture Part 1Document58 pagesCE 4312 Lecture Part 1Saifaah IslamNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (4)
- Deformation Geometry for Materials Scientists: International Series on Materials Science and TechnologyFrom EverandDeformation Geometry for Materials Scientists: International Series on Materials Science and TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- +wire Size and Ampere CapacityDocument1 page+wire Size and Ampere Capacitynetinetnet78No ratings yet
- Planning: Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesPlanning: Page 1 of 3Mary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Essential Utilities GuideDocument6 pagesEssential Utilities GuideGallardo Nixon100% (2)
- StructuralDocument4 pagesStructuralMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- 003 PlanningDocument3 pages003 PlanningrcdpreludeNo ratings yet
- 006 StructuralDocument4 pages006 StructuralrcdpreludeNo ratings yet
- CCST Conversions Document PDFDocument5 pagesCCST Conversions Document PDFMichael GaydosNo ratings yet
- +reviewr Table PDFDocument3 pages+reviewr Table PDFnetinetnet78No ratings yet
- Acoustics and LightingDocument15 pagesAcoustics and LightingNeslie Joy AgotoNo ratings yet
- Essential Utilities GuideDocument6 pagesEssential Utilities GuideGallardo Nixon100% (2)
- Unesco ListDocument20 pagesUnesco ListMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Landscape Architecture GlossaryDocument12 pagesLandscape Architecture GlossaryGretel Adrianne UmaliNo ratings yet
- Unesco ListDocument20 pagesUnesco ListMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Building Tech SummaryDocument20 pagesBuilding Tech SummaryMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Unesco ListDocument20 pagesUnesco ListMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Unesco List PDFDocument20 pagesUnesco List PDFMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Building Tech SummaryDocument20 pagesBuilding Tech SummaryMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Iconic ArchitectsDocument20 pagesIconic ArchitectsMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURAL BUILDING MATERIALSDocument22 pagesARCHITECTURAL BUILDING MATERIALSMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- (PDF) UAP Doc 401-402Document17 pages(PDF) UAP Doc 401-402stanflynnNo ratings yet
- Hoa SummaryDocument13 pagesHoa SummaryMary Ann Figueras0% (1)
- ORNAMENTSDocument7 pagesORNAMENTSMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Building Tech SummaryDocument20 pagesBuilding Tech SummaryMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- ABM Panel Installation & Trim Guide: A B Martin A B MartinDocument14 pagesABM Panel Installation & Trim Guide: A B Martin A B Martingleber_1No ratings yet
- Japanese Companies in India - 2018Document117 pagesJapanese Companies in India - 2018Geetanjali BarejaNo ratings yet
- Structural Basement CalculationsDocument37 pagesStructural Basement CalculationsdependNo ratings yet
- Boq 546117Document30 pagesBoq 546117pravin kanse0% (1)
- ME302-Syllabus - ME-302 Mechanical Systems IIDocument2 pagesME302-Syllabus - ME-302 Mechanical Systems IIد.محمد كسابNo ratings yet
- Flat Plate Final For CanvaDocument9 pagesFlat Plate Final For CanvaRick SarazaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation For Hexadecagonal Pole: L W W T FDocument3 pagesDesign Calculation For Hexadecagonal Pole: L W W T FsaravqwertyNo ratings yet
- Schedule of HATTI PIT XXV Conference 9-10 Nov 2021Document10 pagesSchedule of HATTI PIT XXV Conference 9-10 Nov 2021deo warouwNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Using Self-Compacting Concrete in C PDFDocument14 pagesFeasibility of Using Self-Compacting Concrete in C PDFAbdelrhman NagyNo ratings yet
- Table For Sampling & Testing Frequency G18-G38Document22 pagesTable For Sampling & Testing Frequency G18-G38Riaz SafdarNo ratings yet
- Jerry El Bazouni - Brief Portfolio-OptimisedDocument15 pagesJerry El Bazouni - Brief Portfolio-OptimisedArch. JB DesignNo ratings yet
- Lean EN 2018Document48 pagesLean EN 2018Karan KarnikNo ratings yet
- Goldblatt Catalogue-Compressed PDFDocument56 pagesGoldblatt Catalogue-Compressed PDFFREE BITCOINSNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures Considerations To Reduce Failures Due To InstabilityDocument157 pagesSteel Structures Considerations To Reduce Failures Due To InstabilityFreddy Millen100% (1)
- Master Format 2004Document5 pagesMaster Format 2004bauemmvssNo ratings yet
- Chemicals - Firma ListesiDocument9 pagesChemicals - Firma ListesiPriska MalvinNo ratings yet
- Sika PDS E SikaProof MembraneDocument2 pagesSika PDS E SikaProof Membranelwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Chisel N BailerDocument51 pagesChisel N BailerAmine Amroun67% (3)
- Structural Analysis of Residence in Addis AbabaDocument40 pagesStructural Analysis of Residence in Addis AbabaKidist MollaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steel Design Course Syllabus and Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesAdvanced Steel Design Course Syllabus and Marking Schemesheikh jamilNo ratings yet
- Material Properties Design Forces: Punching Shear Calculations As Per Aci 318Document12 pagesMaterial Properties Design Forces: Punching Shear Calculations As Per Aci 318ramblrNo ratings yet
- Construction Manual2019 PDFDocument1,157 pagesConstruction Manual2019 PDFHasniati AminNo ratings yet
- Floor design detailsDocument14 pagesFloor design detailsshaimenneNo ratings yet
- Anchor Flange SpecificationDocument9 pagesAnchor Flange SpecificationMamadNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Shed With A Slanted Roof Step-by-Step GuideDocument39 pagesHow To Build A Shed With A Slanted Roof Step-by-Step GuideFederico BarberisNo ratings yet