Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Type of Incenerator: Inceneration Technology
Uploaded by
AlohaaSwezz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageWaste incineration is a process that involves burning organic waste materials in a furnace to reduce their volume and weight by approximately 90% and 75% respectively. There are different types of incinerators like fixed grate, moving grate, rotary kiln, and fluidized bed incinerators. Incineration provides advantages such as immediate waste reduction with no long-term storage needed, and the production of sterile ash residues. However, it also has disadvantages like high capital and operating costs, and the need for air pollution control devices to mitigate harmful emissions.
Original Description:
Original Title
INCENERATION TECHNOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWaste incineration is a process that involves burning organic waste materials in a furnace to reduce their volume and weight by approximately 90% and 75% respectively. There are different types of incinerators like fixed grate, moving grate, rotary kiln, and fluidized bed incinerators. Incineration provides advantages such as immediate waste reduction with no long-term storage needed, and the production of sterile ash residues. However, it also has disadvantages like high capital and operating costs, and the need for air pollution control devices to mitigate harmful emissions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views1 pageType of Incenerator: Inceneration Technology
Uploaded by
AlohaaSwezzWaste incineration is a process that involves burning organic waste materials in a furnace to reduce their volume and weight by approximately 90% and 75% respectively. There are different types of incinerators like fixed grate, moving grate, rotary kiln, and fluidized bed incinerators. Incineration provides advantages such as immediate waste reduction with no long-term storage needed, and the production of sterile ash residues. However, it also has disadvantages like high capital and operating costs, and the need for air pollution control devices to mitigate harmful emissions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Waste treatment process that involves the
combustion of organic substances
contained in waste materials
In a simple term, it is a furnace where waste
Burn pile is burnt
Burn barrel Volume and weight reduced (approx. 90% vol. and 75% wt reduction)
Fluidized bed Waste reduction is immediate, no long term residency required
Specialized Inceneration Type of Incenerator Incineration can be done at generation site
Fixed grate Advantages Small disposal area required
Moving grate Info
Air discharges can be controlled
Rotary kiln Ash residue is usually non-putrescible, sterile, inert
Cost can be offset by heat recovery/ sale of energy
Acid gases Skilled operators are required (particularly for boiler operations)
Particulates High capital cost
Metal hazardous air pollutants Disadvantages Public disapproval
Flue gas pollutants INCENERATION TECHNOLOGY
Organic hazardous air pollutants Some material require supplemental fuel
NOx Some materials are noncombustible
CO
waste collect by local authority
Good Combustion Practices mostly of household waste and
Remove certain waste components some commercial and industrial
Municipal waste
Electrostatic Precipitator Solid Waste
(MSW) Becoming a problem for
Selective Non-catalytic Reduction Air pollution control
authorities due to the fact landfill
Baghouses Emission control device is becoming less
and does not recover energy
Activated Carbon
Acid Gas Scrubbers
Oxygen
Combustion will take
Combustion Theory place if all three Heat
elements are present
Fuel
You might also like
- Trace Element Contamination of the EnvironmentFrom EverandTrace Element Contamination of the EnvironmentDavid PurvesNo ratings yet
- Bio Filtration OverviewDocument5 pagesBio Filtration OverviewLarry BothamNo ratings yet
- Waste Management ProcedureDocument4 pagesWaste Management Proceduresyamimi balkhisNo ratings yet
- Concord Blue W2H2 General Overview v15Document14 pagesConcord Blue W2H2 General Overview v15Andra PratamaNo ratings yet
- Clean Coal Technologies Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) DisadvantagesDocument2 pagesClean Coal Technologies Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) DisadvantagesLaudemhir Jan ParelNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Waste Management in BangladeshDocument36 pagesRadioactive Waste Management in BangladeshMd. Hasibul HasanNo ratings yet
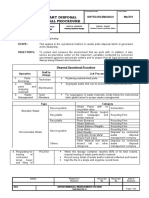
- 3.2c Waste Parts DisposalDocument2 pages3.2c Waste Parts DisposalJaime jr MillanNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Concepts: Soil Pollution Land PollutionDocument2 pagesMiscellaneous Concepts: Soil Pollution Land PollutionYuvraj ShivalkarNo ratings yet
- Air and Air Pollution by - 240206 - 175818Document45 pagesAir and Air Pollution by - 240206 - 175818chelseaabiola1No ratings yet
- S.No. Technology + + + - + - 1 Mass BurnDocument6 pagesS.No. Technology + + + - + - 1 Mass BurnShubham MaindarkarNo ratings yet
- Incineration and Thermal Treatment MSWDocument47 pagesIncineration and Thermal Treatment MSWterlojitan100% (1)
- Lect 14 Week 14 Industerial Wastages P IIDocument29 pagesLect 14 Week 14 Industerial Wastages P IIAsad MehboobNo ratings yet
- Incinerator Scenario Week Urban PhysicsDocument6 pagesIncinerator Scenario Week Urban PhysicsAna??⭐️???No ratings yet
- Kawaski Waste To Biogas GenerationDocument6 pagesKawaski Waste To Biogas GenerationjorgebwongNo ratings yet
- Biomass Combustion System - COENDocument3 pagesBiomass Combustion System - COENonooruddin100% (1)
- Brochure Oil and Gas PurificationDocument5 pagesBrochure Oil and Gas Purificationjast1111No ratings yet
- MR Jayaraman Rajavel, Thermax PDFDocument21 pagesMR Jayaraman Rajavel, Thermax PDFselva pNo ratings yet
- "Leaching of Copper From Waste Pcbs Using Aspergillus Niger andDocument14 pages"Leaching of Copper From Waste Pcbs Using Aspergillus Niger andRachna SinhaNo ratings yet
- 1 Term 2017-2018: AdnievaDocument3 pages1 Term 2017-2018: AdnievaTENBENTENTENNo ratings yet
- CLP Dki WasteDocument94 pagesCLP Dki WasteayyishNo ratings yet
- Changes On Mesoscale & Microscale: Air QualityDocument1 pageChanges On Mesoscale & Microscale: Air QualityAfiq JohariNo ratings yet
- Steel Industry StudyDocument3 pagesSteel Industry StudyLiu TinghuiNo ratings yet
- Removal of Mercury From Flue Gas Using Activated CarbonDocument1 pageRemoval of Mercury From Flue Gas Using Activated CarbonactivatedcarbonsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Integrated w2r TrainingDocument28 pagesIntegrated w2r Trainingworkpractice283No ratings yet
- Linde WAO TechnologyDocument30 pagesLinde WAO Technologyrzlisk01No ratings yet
- CP AddressEnvironProbDocument2 pagesCP AddressEnvironProbSa'dilah FauziNo ratings yet
- Pollution - Pengantar Teknik Kimia - 2018Document22 pagesPollution - Pengantar Teknik Kimia - 2018Annisah MardiyyahNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument34 pagesProject ReportAnkita KolekarNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument5 pagesWaste ManagementFaiqoh NahareyNo ratings yet
- SWM 150317051042 Conversion Gate01Document10 pagesSWM 150317051042 Conversion Gate01manisha deivandranNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument21 pagesSolid Waste Management123No ratings yet
- Poster EUBCE 2015 - Modèle CIRADDocument1 pagePoster EUBCE 2015 - Modèle CIRADTjandra LiemNo ratings yet
- Solid and Hazardous WasteDocument22 pagesSolid and Hazardous WasteEUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- CompostingDocument30 pagesCompostingedit16No ratings yet
- Typical Composition: Classification of Gaseous FuelsDocument3 pagesTypical Composition: Classification of Gaseous FuelsHamza AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Reducing Dioxin Emissions in Electric Steel Mills PDFDocument4 pagesReducing Dioxin Emissions in Electric Steel Mills PDFJames DuNo ratings yet
- 19 - Fdr-Irrmi - Brief SWM Operations - Nea Aug32017Document22 pages19 - Fdr-Irrmi - Brief SWM Operations - Nea Aug32017rehnegibbNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Economic Analysis For The Optimal Conceptual Design of Biomass Gasification Energy Conversion SystemsDocument29 pagesThermo-Economic Analysis For The Optimal Conceptual Design of Biomass Gasification Energy Conversion SystemsAdriana Rocio Palencia SalgarNo ratings yet
- JETIR2205802Document27 pagesJETIR2205802Arnav MoulikNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment SystemsDocument7 pagesWastewater Treatment SystemsBrent SanPedroNo ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter: 01: PollutionDocument13 pagesBiology - Chapter: 01: PollutionYash PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Flexible Mechanisms: Emission Trading Joint Implementation CDMDocument85 pagesFlexible Mechanisms: Emission Trading Joint Implementation CDMNarender SinghNo ratings yet
- CL 618 - 2023 - Sweetening ProcessDocument12 pagesCL 618 - 2023 - Sweetening Processhp7772858No ratings yet
- (Kemenperin) Sampangan Fundraising Deck 9 Nov 21-1Document28 pages(Kemenperin) Sampangan Fundraising Deck 9 Nov 21-1Imaniar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Boiler Ra1: Environmental Risk Assessment:: Summary Information: Make Location Fuel Area To Be ServicedDocument5 pagesBoiler Ra1: Environmental Risk Assessment:: Summary Information: Make Location Fuel Area To Be ServicedRajesh gp100% (1)
- FDR PresentationDocument16 pagesFDR Presentationjeicg21No ratings yet
- ECC PresentationDocument66 pagesECC PresentationAdroit ConsultantNo ratings yet
- W6L2 - Sweeting of Natural GasDocument10 pagesW6L2 - Sweeting of Natural GasHarish RajNo ratings yet
- Laxminarayan Institute of Technology, Nagpur: Tyre OilDocument3 pagesLaxminarayan Institute of Technology, Nagpur: Tyre OilKHAN AQSANo ratings yet
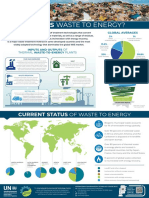
- What Is Waste To Energy?: Global AveragesDocument3 pagesWhat Is Waste To Energy?: Global AverageslightsonsNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy-Lecture 2B-Cleaner Fossil Energy System-2022 - CompressedDocument102 pagesSustainable Energy-Lecture 2B-Cleaner Fossil Energy System-2022 - Compressedsatrio wekaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Villaganas, Mary Rose P. Verganio, Jasmin DDocument23 pagesSubmitted By:: Villaganas, Mary Rose P. Verganio, Jasmin DNina Rose VerganioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Fundamentals of Wastewater Engineering - IntroductionDocument26 pagesLesson 10 - Fundamentals of Wastewater Engineering - IntroductionPheletso Andrias MoloantoaNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste IncinerationDocument15 pagesSolid Waste IncinerationGOWTHAM GUPTHANo ratings yet
- MixtureDocument18 pagesMixtureadvaitc07No ratings yet
- MO32 Formative Assessment SasakiDocument2 pagesMO32 Formative Assessment SasakiarsenicshinyaNo ratings yet
- Waste To Energy: Summary For PolicymakersDocument6 pagesWaste To Energy: Summary For PolicymakersppourmoghaddamNo ratings yet
- Sludge Management: Treatment and Disposal of SludgeDocument108 pagesSludge Management: Treatment and Disposal of SludgeRishu RajNo ratings yet
- Energy Production From Wastewater: Barış ÇALLIDocument30 pagesEnergy Production From Wastewater: Barış ÇALLIEslam ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Debashis SeminarDocument10 pagesDebashis Seminar2108010eeNo ratings yet
- Test LawDocument1 pageTest LawAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Type of Gaifier Process & Concept: GasificationDocument1 pageType of Gaifier Process & Concept: GasificationAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Components of An Infectious Waste Management PlanDocument1 pageComponents of An Infectious Waste Management PlanAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Created by Unlicensed Version: How To Make An OfferDocument1 pageCreated by Unlicensed Version: How To Make An OfferAlohaaSwezz100% (1)
- Categories of Consideration: CaseDocument1 pageCategories of Consideration: CaseAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Capacity: Requirement As To CapacityDocument1 pageCapacity: Requirement As To CapacityAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Condition For Valid Acceptance: Section 2 (B) "When The Person To Whom The Proposal Is MadeDocument1 pageCondition For Valid Acceptance: Section 2 (B) "When The Person To Whom The Proposal Is MadeAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- List of Tables List of Figures List of Abbreviations 1Document75 pagesList of Tables List of Figures List of Abbreviations 1AlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Report On Sungai KimkimDocument13 pagesReport On Sungai KimkimAlohaaSwezz100% (1)
- Assignment 1 (Managerial Skills) : 31 January 2019Document5 pagesAssignment 1 (Managerial Skills) : 31 January 2019AlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Successful Entrepreneurs in MalaysiaDocument8 pagesSuccessful Entrepreneurs in MalaysiaAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Managerial SkillDocument5 pagesManagerial SkillAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ENT300Document52 pagesBusiness Plan ENT300AlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Soduim Borohydride Reduction of CyclohexanoneDocument10 pagesSoduim Borohydride Reduction of CyclohexanoneAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Bernouli's Theorem DemonstrationDocument14 pagesBernouli's Theorem DemonstrationAlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption ReportDocument16 pagesGas Absorption ReportAlohaaSwezz100% (1)
- Cooling Tower (From Apparatus To Calculation Only) )Document13 pagesCooling Tower (From Apparatus To Calculation Only) )AlohaaSwezzNo ratings yet
- FA21 - Lec23 - 2021-12-08 - PWM - Part2 and SPIDocument24 pagesFA21 - Lec23 - 2021-12-08 - PWM - Part2 and SPIMahreenNo ratings yet
- Research On The Aerodynamics of Intermediate Turbine DiffusersDocument31 pagesResearch On The Aerodynamics of Intermediate Turbine DiffusersleizongqiNo ratings yet
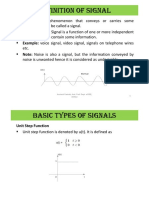
- Signals and Systems Module 1Document35 pagesSignals and Systems Module 1ASUTOSH PATNAIKNo ratings yet
- Apps and Social MediaDocument25 pagesApps and Social Mediaaaron canoyNo ratings yet
- City of New Boston V NetflixDocument12 pagesCity of New Boston V NetflixTHROnlineNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Year 9 Algebra Question and NotesDocument20 pages5.3 Year 9 Algebra Question and Notesprimalp6105No ratings yet
- 06 Assistant DoctypeDocument166 pages06 Assistant DoctypeChristal Rae Tac-anNo ratings yet
- Dc6Cautp4P3X: Product DatasheetDocument3 pagesDc6Cautp4P3X: Product DatasheetKailash KumarNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Influence of Preventive MaintenanceDocument14 pagesAssessment of The Influence of Preventive MaintenancemaulanahafishNo ratings yet
- Distillation Optimization Through Atomospheric DistillationDocument3 pagesDistillation Optimization Through Atomospheric DistillationAyoub GhabriNo ratings yet
- Registration User GuideDocument20 pagesRegistration User GuideMelody ShekharNo ratings yet
- Complementary ProductsDocument2 pagesComplementary ProductsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- Derruba DCDocument12 pagesDerruba DCdono da nikeNo ratings yet
- DM 246 Division Research TrainingDocument7 pagesDM 246 Division Research Traininglsh AshNo ratings yet
- Clinical Experience With The Constellation Vision SystemDocument16 pagesClinical Experience With The Constellation Vision SystemMohammad Abdullah BawtagNo ratings yet
- sd8 Valve Overall DetailsDocument1 pagesd8 Valve Overall DetailsVEERAMANINo ratings yet
- Ascential DataStage Director Guide121Document96 pagesAscential DataStage Director Guide121B MUNIRAJANo ratings yet
- 1.2.5. UCP Board Instruction Manual PDFDocument16 pages1.2.5. UCP Board Instruction Manual PDFHabibulla Bavaji100% (1)
- Arabic OCR ReportDocument20 pagesArabic OCR ReportAmirNo ratings yet
- ComputerScienceD9PaperII - 12th - For - StudentDocument11 pagesComputerScienceD9PaperII - 12th - For - Student31 Sahil shete XII ANo ratings yet
- Catia Tips & TricksDocument3 pagesCatia Tips & TrickschuranjitNo ratings yet
- Electric Suspended MagnetsDocument5 pagesElectric Suspended MagnetsedgarlimasNo ratings yet
- Magelis GTO - HMIGTO3510Document3 pagesMagelis GTO - HMIGTO3510DarwinVillegas2790No ratings yet
- Pedestrian Stacker Truck: W-SeriesDocument4 pagesPedestrian Stacker Truck: W-SeriesXb ZNo ratings yet
- Understanding Mathematics in The Digital AgeDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Mathematics in The Digital Ageuser0xNo ratings yet
- 10 Full Dual HVDCDocument21 pages10 Full Dual HVDCmohamedNo ratings yet
- Lab 6B - Datum - PL-CR-CR CAD (H-1000-5304-01-A)Document22 pagesLab 6B - Datum - PL-CR-CR CAD (H-1000-5304-01-A)adolfoNo ratings yet
- Complaint BoxDocument12 pagesComplaint BoxChetan MasramNo ratings yet
- Mazda 626 MX6 GE Factory Service Manual 1991 1997Document1,730 pagesMazda 626 MX6 GE Factory Service Manual 1991 1997Julio100% (1)
- Visa Interview Question and Answers - PDF - Arizona State University - Academic DegreeDocument16 pagesVisa Interview Question and Answers - PDF - Arizona State University - Academic Degreesig20arshiyanaanjumNo ratings yet