Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emulsions Questions and Answers
Uploaded by
Ahmad Farhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views3 pagesThis document discusses emulsions, colloidal dispersions, gels, and rheology. It provides definitions and examples of emulsions, factors that affect emulsion stability, and methods to measure stability. It defines a colloidal dispersion and distinguishes between sols and emulsions and sols and aerosols. The document also defines rheological concepts like viscosity, shear stress, and shear rate. It describes reversible and irreversible gels and factors that affect gel stability. Examples of common gelling agents used in food are also provided.
Original Description:
Original Title
368274563-Emulsions-Questions-and-Answers.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses emulsions, colloidal dispersions, gels, and rheology. It provides definitions and examples of emulsions, factors that affect emulsion stability, and methods to measure stability. It defines a colloidal dispersion and distinguishes between sols and emulsions and sols and aerosols. The document also defines rheological concepts like viscosity, shear stress, and shear rate. It describes reversible and irreversible gels and factors that affect gel stability. Examples of common gelling agents used in food are also provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views3 pagesEmulsions Questions and Answers
Uploaded by
Ahmad FarhanThis document discusses emulsions, colloidal dispersions, gels, and rheology. It provides definitions and examples of emulsions, factors that affect emulsion stability, and methods to measure stability. It defines a colloidal dispersion and distinguishes between sols and emulsions and sols and aerosols. The document also defines rheological concepts like viscosity, shear stress, and shear rate. It describes reversible and irreversible gels and factors that affect gel stability. Examples of common gelling agents used in food are also provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
QUESTION BANK Dr Velliou
Emulsions-Colloidal dispersions-Gels-Rheology
1) What is an emulsion?
A fine dispersion of minute droplets of one liquid in another in which it
is not soluble or miscible.
2) Which are the different types of emulsions?
oil droplets in water (milk, ice cream, salad cream, mayonnaise)
water droplets in oil (margarine, butter, skin cream, moisturizing
lotion).
3) Provide 4 examples of food emulsions
Milk, ice-cream, sausage, mayonnaise
4) How can we increase the stability of an emulsion?
Add an emulsifier or stabilizer
5) How can we prepare/create an emulsion?
Hydrogenize oil and water, then add emulsifier
6) Describe the role of an emulsifier in an emulsion
Lower surface (interfacial) tension between phases
Lessen the work/energy needed to produce particles
7) Which factors can affect the stability of emulsions?
Temperature
Droplet size
Electrostatic force between particles
8) How can we assess/measure the stability of an emulsion?
Drop size analysis by microscopy
Turbidimetric measurements
Charge on droplets by electrophoresis
Application of stress centrifugation, heat
9) What is the difference between a sol and an emulsion? Provide examples
for both
Sol – continuous phase is a liquid but disperse phase is a solid
(milk, syrup)
Emulsion – inmiscible liquid dispersed in another inmiscible liquid
(mayonnaise)
10) What is the difference between a sol and an aerosol? Provide examples for
both
Aerosol – liquid/solid dispersed into a gas medium (smoke)
11) What is the definition of a colloidal dispersion?
Colloidal system or colloidal dispersion is a heterogeneous system
which is made up of Dispersed phase and Dispersion medium. In
colloidal dispersion one substance is dispersed as very fine particles
in another substance called dispersion medium. In case of dust,
solid particles are dispersed in air as dispersion medium.
12) What is viscosity?
Resistance to flow/sheer stress
13) What is shear stress?
Resistance to applied force and can be described as force/area
sheared
14) What is shear rate?
Gradient of velocity in flowing material
15) Describe and sketch the different types of flows, based on the
evolution/progression of their rheological properties.
16) What is the difference between reversible and irreversible gels?
Reversible – has non-covalent bonds
Irreversible – covalent bonds and disulphide links
17) Provide a food system in which gelation might occur following exposure to
high temperature.
18) Which factors affect the stability of gels?
Temperature
pH
addition of water competitive compounds (sugar)
19) Give a few examples of gelling agents currently used in the food industry.
Pectin, carrageenan, gelatin, modified starch.
You might also like
- EmulsionsDocument24 pagesEmulsionsRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- 634798775670659161Document41 pages634798775670659161Suvin PsNo ratings yet
- Emulsions Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesEmulsions Questions and AnswersSalomon Morales100% (3)
- Unit Processes in Pharmacy: Pharmaceutical MonographsFrom EverandUnit Processes in Pharmacy: Pharmaceutical MonographsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Multiple Emulsion: AssignmentDocument10 pagesMultiple Emulsion: AssignmentMD REFATNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Emulsions: (DR.) Mirza Salman BaigDocument41 pagesPharmaceutical Emulsions: (DR.) Mirza Salman BaigSantosh PayghanNo ratings yet
- TMP D210Document9 pagesTMP D210FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Emulsions GuideDocument50 pagesPharmaceutical Emulsions GuideChrisNo ratings yet
- Technical Tablet CoatingDocument11 pagesTechnical Tablet CoatinglaszlobeneszNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Pharmacy EXIT Exam SyllabusDocument14 pagesDiploma in Pharmacy EXIT Exam SyllabusRoshan KashyapNo ratings yet
- A Thesis About BiosurfactantDocument25 pagesA Thesis About BiosurfactantSandeep Kumar SaiNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy: Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaDocument6 pagesPhysical Pharmacy: Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaAishwarya PawarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Disperse SystemsDocument94 pagesLecture 2 - Disperse Systemsapi-370729792% (12)
- Emulsion and Foam IntroductionDocument14 pagesEmulsion and Foam IntroductionJose Fernando Solanilla Duque0% (1)
- Question Paper B Pharmacy 2nd Sem BP104TDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper B Pharmacy 2nd Sem BP104TNeeru MalikNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument13 pagesLecturesHaroon RahimNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Application of Polymers in Dosage FormsDocument16 pagesSeminar On Application of Polymers in Dosage FormskeyurNo ratings yet
- Aerosol Components and Testing MethodsDocument3 pagesAerosol Components and Testing MethodsSwaroopSinghJakharNo ratings yet
- Emulsion LectureDocument55 pagesEmulsion Lecturehermella tegegneNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical SuspensionsDocument52 pagesPharmaceutical SuspensionsUsman Akhtar100% (1)
- Pharmaceutics-Chapter-2-Packaging-Materialsxgchbu Gyvy-NotesDocument7 pagesPharmaceutics-Chapter-2-Packaging-Materialsxgchbu Gyvy-NotesBEST OF BESTNo ratings yet
- Multiple Emulsion NewDocument39 pagesMultiple Emulsion NewRohit Verma100% (2)
- 06 - Emulsion 1Document41 pages06 - Emulsion 1amirNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Granulation Equipment GuideDocument19 pagesPharmaceutical Granulation Equipment GuideJoslin RozNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Pharmaceutical ProductsDocument14 pagesPolymers in Pharmaceutical Productsstudent910112No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Solutions (Zara Khan BP0950212)Document30 pagesPharmaceutical Solutions (Zara Khan BP0950212)Zara KhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Information 1414 - AEROPERL® 300 Pharma Improving The Dissolution of Poorly Soluble APIs PDFDocument16 pagesTechnical Information 1414 - AEROPERL® 300 Pharma Improving The Dissolution of Poorly Soluble APIs PDFvinayNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Emulsions2 151213073721 PDFDocument50 pagesPharmaceutics Emulsions2 151213073721 PDFDuc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument32 pagesOriginalAlexandra MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- Liquid OralsDocument55 pagesLiquid OralsShraddha RNo ratings yet
- Stains and Stain RemovalDocument6 pagesStains and Stain Removallucymuchiri797No ratings yet
- Composition of Suspension and Suspending Agents.Document4 pagesComposition of Suspension and Suspending Agents.hira khanNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines For Distillation ColumnDocument23 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Distillation ColumnCristinaNo ratings yet
- BiosurfactantDocument1 pageBiosurfactantGregorius Budianto100% (1)
- Formulation and Evaluation of MicrospheresDocument45 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of MicrospheresThakkar Dadhichi KiritbhaiNo ratings yet
- Single PotDocument7 pagesSingle Potsky.blueNo ratings yet
- Semi SolidsDocument27 pagesSemi SolidsDrVenu Madhav KNo ratings yet
- Sistem DispersiDocument165 pagesSistem Dispersimuhammad sujarwadNo ratings yet
- Characterization of METHOCEL Cellulose Ethers by Aqueous SEC With Multiple DetectorsDocument11 pagesCharacterization of METHOCEL Cellulose Ethers by Aqueous SEC With Multiple DetectorsCastoriadisNo ratings yet
- SuspensionDocument56 pagesSuspensionHarnil SoniNo ratings yet
- Microsphere MicrocapsulesDocument41 pagesMicrosphere MicrocapsulesaravindnairNo ratings yet
- Dosage - Chapter 14Document57 pagesDosage - Chapter 14kaukau4ever100% (1)
- Rheology of SuspensionsDocument16 pagesRheology of SuspensionsManoj Bansal100% (1)
- Unit 6 AEROSOLSDocument29 pagesUnit 6 AEROSOLSorindiaNo ratings yet
- General Surfactant Intro 190417Document40 pagesGeneral Surfactant Intro 190417bayuNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Emulsions (Formulation & Stabilization)Document27 pagesPharmaceutical Emulsions (Formulation & Stabilization)Nickson DrabeNo ratings yet
- Methocel Coating PolymersDocument36 pagesMethocel Coating PolymersPradeep BhimaneniNo ratings yet
- Propylene Glycol Usp-EpDocument4 pagesPropylene Glycol Usp-Epvanhung68No ratings yet
- C 14 SuspensionDocument119 pagesC 14 SuspensionVinod ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Application of Biosurfactants in Food Industry PDFDocument12 pagesApplication of Biosurfactants in Food Industry PDFRazvan BabanNo ratings yet
- GC and HPLC Chromatography TechniquesDocument10 pagesGC and HPLC Chromatography TechniquesSunday IstifanusNo ratings yet
- Disperse SystemDocument35 pagesDisperse Systemgbshop3No ratings yet
- Microencapsulation 3856535 PowerpointDocument12 pagesMicroencapsulation 3856535 PowerpointShashank UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- How to Name an Inorganic Substance: A Guide to the Use of Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry: Definitive Rules 1970From EverandHow to Name an Inorganic Substance: A Guide to the Use of Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry: Definitive Rules 1970Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Methods of Determining Particle SizeDocument3 pagesMethods of Determining Particle SizejokishNo ratings yet
- Selection of Cleaning Agents and Parameters For CGMPS ProcesDocument11 pagesSelection of Cleaning Agents and Parameters For CGMPS Procesjljimenez1969No ratings yet
- Pressurized Dosage FormsDocument85 pagesPressurized Dosage FormsHuma Hameed Dogar100% (1)
- Ionic Liquids in Lipid Processing and Analysis: Opportunities and ChallengesFrom EverandIonic Liquids in Lipid Processing and Analysis: Opportunities and ChallengesXuebing XuNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Polymer Alloys: Science and Practice : KeywordsDocument15 pagesPolymer Alloys: Science and Practice : KeywordsAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- 235practice Exam 2 AnswerDocument9 pages235practice Exam 2 Answernbobs7No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Survey ReportDocument39 pagesSurvey ReportAdnan MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Uaf 2016Document7 pagesUaf 2016Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- NtroductionDocument3 pagesNtroductionAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Examples of Retrosynthesis AnalysisDocument6 pagesExamples of Retrosynthesis AnalysisAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- RRA Audit Guidelines Final RereviewDocument61 pagesRRA Audit Guidelines Final RereviewRizwan Khan BluchNo ratings yet
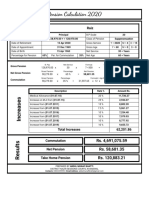
- Pension Calculation 2020 DetailsDocument1 pagePension Calculation 2020 DetailsAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizer For Bioremediation: January 2015Document31 pagesBiofertilizer For Bioremediation: January 2015Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial activity of selected antibiotic classesDocument64 pagesAntibacterial activity of selected antibiotic classesAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Azotobactor on Growth and Yield of Carrot SeedsDocument54 pagesEffect of Azotobactor on Growth and Yield of Carrot SeedsAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Suraface Chem ShankDocument14 pagesSuraface Chem ShankRodhiya ShashankNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5: Instructions & ScoringDocument14 pagesQuiz 5: Instructions & ScoringAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Advances in The Concept and Methods of Seed Priming: October 2019Document32 pagesAdvances in The Concept and Methods of Seed Priming: October 2019P UNo ratings yet
- Assignment MSC ChemistryDocument9 pagesAssignment MSC ChemistryAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- No Enquiry, Audit Para or Demand Certificates for Retired PrincipalDocument3 pagesNo Enquiry, Audit Para or Demand Certificates for Retired PrincipalAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Buffer 0Document27 pagesBuffer 0Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Molecules 21 00573 v2Document17 pagesMolecules 21 00573 v2Marlon Manaya GarriguesNo ratings yet
- No Enquiry, Audit Para or Demand Certificates for Retired PrincipalDocument3 pagesNo Enquiry, Audit Para or Demand Certificates for Retired PrincipalAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Pension Calculation 2020 DetailsDocument1 pagePension Calculation 2020 DetailsAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Scanned by TapscannerDocument3 pagesScanned by TapscannerAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Presented by Nazakat MehmoodDocument7 pagesChromatography: Presented by Nazakat MehmoodAhmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Report 5Document7 pagesTechnical Report 5Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterDocument4 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterMd. Saif Ullah Bari100% (3)
- Sparkler Plate Filter Housing PDFDocument2 pagesSparkler Plate Filter Housing PDFJoshua JohnsonNo ratings yet
- ADDRILL EA (HS) Drilling Fluid ViscosifierDocument1 pageADDRILL EA (HS) Drilling Fluid ViscosifieramistalokNo ratings yet
- Monolayer CoverageDocument1 pageMonolayer CoverageInnocent AchayeNo ratings yet
- Concrete Exposures ClassesDocument4 pagesConcrete Exposures ClasseshamidkarimpourNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sheet Metal & Welder For 12 Jan 23Document2 pagesLesson Plan Sheet Metal & Welder For 12 Jan 23ASHVIN YADAVNo ratings yet
- CC-TM-44 Free Fatty AcidsDocument2 pagesCC-TM-44 Free Fatty AcidsWynona BasilioNo ratings yet
- Amali Kimia 1Document5 pagesAmali Kimia 1Syahmi RifqiNo ratings yet
- Experiment I: Determination of Iron (II) in Mohr Salt Solution Using Potassium DichromateDocument8 pagesExperiment I: Determination of Iron (II) in Mohr Salt Solution Using Potassium DichromateayushmanNo ratings yet
- Sikadur®-330: Product Data SheetDocument4 pagesSikadur®-330: Product Data SheetLeonte AdrianNo ratings yet
- Steel PropertyDocument6 pagesSteel PropertykrishbistNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PHD Thesis FormatDocument5 pagesChemistry PHD Thesis Formatqrikaiiig100% (1)
- Corporate Standard STD 1223: Orientering OrientationDocument4 pagesCorporate Standard STD 1223: Orientering OrientationSERGIO GAUENo ratings yet
- Name: Insong, Osannah Irish B. Section: BSMT 3CDocument1 pageName: Insong, Osannah Irish B. Section: BSMT 3COsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy For Pyrolysis For Several Types of BiomassDocument7 pagesEnthalpy For Pyrolysis For Several Types of BiomassSwiftTGSolutionsNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 Suggested AnswerDocument10 pagesCHP 1 Suggested AnswerRachel Wong74% (31)
- Correction Chapter 6-9Document3 pagesCorrection Chapter 6-9Shweta BagdiNo ratings yet
- TD Istra-40 enDocument2 pagesTD Istra-40 enAsmir SofticNo ratings yet
- A - Lab - Chem EquilibDocument4 pagesA - Lab - Chem EquilibshayneNo ratings yet
- Probing The Fluxional Bonding Nature of Rapid Cope Rearrangements in Bullvalene C10H10 and Its Analogs C8H8, C9H10, and C8BH9Document8 pagesProbing The Fluxional Bonding Nature of Rapid Cope Rearrangements in Bullvalene C10H10 and Its Analogs C8H8, C9H10, and C8BH9PeterNo ratings yet
- BiOBrCISO Crystal Structure and Peak ListDocument4 pagesBiOBrCISO Crystal Structure and Peak Listkẻ khờ khạoNo ratings yet
- Film-Screen Radiography-PhysicsDocument45 pagesFilm-Screen Radiography-PhysicsFouzia NoorNo ratings yet
- 58 CitaDocument6 pages58 CitaKaren Alejandra López CastañosNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of Mass QuizDocument6 pagesLaw of Conservation of Mass QuizLeormhan Jacob Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1784 - Jtvo9242Document4 pagesASTM D1784 - Jtvo9242Nayth Andres GalazNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL LISTINGDocument21 pagesCHEMICAL LISTINGDyeing Dyeing100% (1)
- Water Contents of A Fine-Grained Soil: Its Shrinkage LimitDocument9 pagesWater Contents of A Fine-Grained Soil: Its Shrinkage LimitmaaahiiNo ratings yet
- Solved by Smart Exam Resources: Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesSolved by Smart Exam Resources: Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Custom TrayDocument17 pagesCustom TrayDewo BontangNo ratings yet
- Desmodur MAX-D XL1705Document2 pagesDesmodur MAX-D XL1705French CorvetteNo ratings yet