Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ilustração Metacognição PDF
Uploaded by
taniasakumaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ilustração Metacognição PDF
Uploaded by
taniasakumaCopyright:
Available Formats
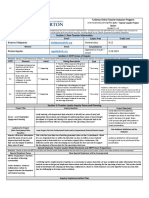
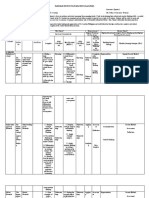
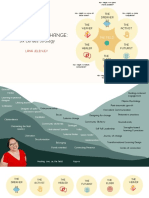
Metacognition When students are metacogni�ve they
understand...
What is Metacogni�on?
• Awareness of one’s own ac�ons and This is my I know my I have ideas of
their effects task steps solu�ons
I can apply my
• Posing internal ques�ons to find
informa�on and meaning knowledge to
various situa�ons I am a learner
• Developing mental maps, pictures,
or plans
• Monitoring plans throughout a process
and revising plans when they do not
work (Nokes & Dole, 2004)
• Self-evalua�ng a completed plan
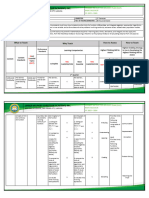
Impact of Metacogni�on
(Costa, 2008)
The Research • Facilitates ac�ve rather than passive
.30 .40 .50 Effect Size: .60 learners
.60
• Gives students a greater awareness of
Typi
.15
Teac ts
.70
their learning
Effe
cal
her
c
De
Eff velop
ect me
s nt ZONE OF
.80
• Promotes “deep learning”
0 al
DESIRED .90 • Makes students aware of their own
REVERSE
EFFECTS thinking
1.0
(Ha�e, 2017) (McElwee, 2009)
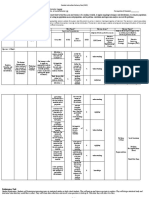
Four Types of Self-Addressed Metacogni�ve Ques�ons
Comprehension Connec�on Strategic Reflec�on
How is this Why is this Does the
What is the problem like strategy the solu�on
Before best to solve
ques�on? one I’ve already make sense?
solved? the problem?
During
&
A�er
Instruc�on
MO EDU-SAIL Effective teaching and learning for ALL students
Educational Systems and Instruction for Learning Missouri Model Districts (MMD)/District Continuous Improvement (DCI)
The contents of this presentation were developed under a grant from the US Department of Education to the Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education (#H323A120018, #H323A170020). However, these contents do not
necessarily represent the policy of the US Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the Federal Government.
You might also like
- A Book of Historic Board Games by Damian Gareth WalkerDocument1 pageA Book of Historic Board Games by Damian Gareth Walkerbah0% (1)
- Jennett Et Al 2008 Measuring ImmersionDocument21 pagesJennett Et Al 2008 Measuring ImmersionAlexandru DumbravaNo ratings yet
- Bleach (Manga)Document16 pagesBleach (Manga)Xavier Smith SchwarzeneggerNo ratings yet
- Mathema 6 Ao 9 AnoDocument55 pagesMathema 6 Ao 9 AnoLeandro Estevam Do NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Accidental Ikigai - Mike Bechtel - Medium PDFDocument8 pagesAccidental Ikigai - Mike Bechtel - Medium PDFRichard PrimeauxNo ratings yet
- Diario de ClasseDocument37 pagesDiario de ClasseRafaella GadelhaNo ratings yet
- Template Exclusivo 30 Slides EditaveisDocument30 pagesTemplate Exclusivo 30 Slides EditaveisRicardo Pereira100% (1)
- Module 1 Critical ThinkingDocument6 pagesModule 1 Critical Thinkingapi-284468263No ratings yet
- Ilp Teacher Leadership ProjectDocument6 pagesIlp Teacher Leadership Projectapi-468894691No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument26 pagesGo To Pageapi-642813219100% (1)
- Flexible Grouping TemplateDocument2 pagesFlexible Grouping Templateapi-402220352No ratings yet
- Fullerton Online Teacher Induction Program: New Teacher Email Subject Area Grade LevelDocument5 pagesFullerton Online Teacher Induction Program: New Teacher Email Subject Area Grade Levelapi-483682821No ratings yet
- Learning in Science - A Comparison of Deep and Surface Approaches - Chin 2000Document30 pagesLearning in Science - A Comparison of Deep and Surface Approaches - Chin 2000Arif Kruyt100% (1)
- Perdev Fidp Sy 2020 2021Document10 pagesPerdev Fidp Sy 2020 2021Mira Rochenie Curan100% (1)
- Subject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofDocument4 pagesSubject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofCedrick Matibag100% (2)
- Teaching & Curriculum DesignDocument12 pagesTeaching & Curriculum DesignDian InezieNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document3 pagesModule 7Karen Marie Dela Pasion100% (1)
- CIDAM Template Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesCIDAM Template Earth ScienceLily RosemaryNo ratings yet
- 1-FIDP TemplateDocument4 pages1-FIDP TemplateMeljoy TenorioNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-INSET 2020Document5 pagesGroup 6 - PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-INSET 2020Tara BautistaNo ratings yet
- Fidp - Tamala, Sharmaine JoyDocument2 pagesFidp - Tamala, Sharmaine JoyJoy TamalaNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Msgr. Lino Gonzaga ST., Jaro, Leyte CidamDocument4 pagesNotre Dame of Jaro, Inc.: Msgr. Lino Gonzaga ST., Jaro, Leyte CidamVia Terrado CañedaNo ratings yet
- Subject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofDocument4 pagesSubject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofMicheal CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Perdev Fidp Sy 2020-2021Document10 pagesPerdev Fidp Sy 2020-2021Tara Bautista100% (2)
- Empowerment Technologies Fidp - GutierrezdocxDocument10 pagesEmpowerment Technologies Fidp - GutierrezdocxCamille Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- COT 2 Lesson Plan - TOQUERODocument6 pagesCOT 2 Lesson Plan - TOQUERODC PortraitsNo ratings yet
- Highest Enabling Strategy To Use in Developing The Highest Thinking Skill To Assess Enabling General Strategy Flexible Learning Strategies (FLS)Document10 pagesHighest Enabling Strategy To Use in Developing The Highest Thinking Skill To Assess Enabling General Strategy Flexible Learning Strategies (FLS)Mikkaella RimandoNo ratings yet
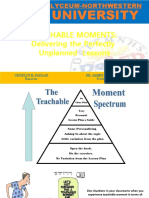
- University: Teachable Moments: Delivering The Perfectly Unplanned LessonsDocument22 pagesUniversity: Teachable Moments: Delivering The Perfectly Unplanned LessonsMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- CIDAM General MathDocument3 pagesCIDAM General MathRuby Ann Rosales67% (3)
- Fidp DissDocument12 pagesFidp DissRexijay PagatpatNo ratings yet
- Fidp PerdevDocument10 pagesFidp PerdevElijah ManuelNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: Senior High SchoolDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: Senior High SchoolRodel MoralesNo ratings yet
- #7E Plan: The BIG PictureDocument2 pages#7E Plan: The BIG Pictureemo mHAYNo ratings yet
- DemonstrationDocument7 pagesDemonstrationKatherine Lapore Llup - PorticosNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Lesson Plan: The Cell: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument13 pages5th Grade Lesson Plan: The Cell: The Building Blocks of LifeCherry Mae B. CorriaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 - GeometryDocument5 pagesGrade 5 - GeometryAnthony RavasNo ratings yet
- Fidp Pre CalDocument5 pagesFidp Pre CalManilyn NahialNo ratings yet
- Cidam 2Document6 pagesCidam 2Nieves JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Students' MetacognitiveDocument11 pagesStudents' MetacognitiveMicheal LezondraNo ratings yet
- Discipline and Ideas in The Social Science - FIDP (De Guia) Hum2Document8 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in The Social Science - FIDP (De Guia) Hum2patrixia73% (11)
- PHILOSOPHYDocument4 pagesPHILOSOPHYGellai GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan EARTH SCIENCEDocument5 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan EARTH SCIENCEREHANA ZAINUDINNo ratings yet
- Grade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionDocument2 pagesGrade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionMicheal CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp) School Year: 2021 - 2022Document21 pagesSenior High School Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp) School Year: 2021 - 2022Jaimie Judelle Alzol100% (1)
- Obtl-Art AppriciationDocument4 pagesObtl-Art AppriciationJustin SanchoNo ratings yet
- Share or Tweet Your Thoughts: How Students LearnDocument8 pagesShare or Tweet Your Thoughts: How Students Learnapi-213863463No ratings yet
- Trends q1 FidpDocument6 pagesTrends q1 FidpAubrae Frances BannawiNo ratings yet
- Why Teach?: How To Assess?Document8 pagesWhy Teach?: How To Assess?Jilmore Caseda CantalNo ratings yet
- Fidp Basic CalculusDocument10 pagesFidp Basic CalculusKaye CabangonNo ratings yet
- Subject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofDocument5 pagesSubject Description: at The End of The Course, The Students Must Be Able To Apply Concepts and Solve Problems Involving Conic Sections, Systems ofMyla Rose AcobaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan TemplateDocument6 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan TemplaterenzpaulorodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fidp - Per-DevDocument3 pagesFidp - Per-DevIn SanityNo ratings yet
- CIDAM 1stDocument4 pagesCIDAM 1stMarife Hermosa - LeymaNo ratings yet
- MathlessonplanDocument3 pagesMathlessonplanapi-357473286No ratings yet
- Self Assessment Education Portfolio-2Document1 pageSelf Assessment Education Portfolio-2api-570743058No ratings yet
- Local Media7448206506575993530Document4 pagesLocal Media7448206506575993530Sai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Reading DisabilitiesDocument33 pagesReading Disabilitiesapi-429757438No ratings yet
- Fidp (Trends)Document5 pagesFidp (Trends)Lea Masilungan100% (4)
- Local Media8442823191121160261Document3 pagesLocal Media8442823191121160261Sai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On The 6 Lenses StrategyDocument15 pagesPresentation On The 6 Lenses StrategyLana JelenjevNo ratings yet
- Ilustração Metacognição PDFDocument1 pageIlustração Metacognição PDFtaniasakumaNo ratings yet
- 5a What Is Visible Learning PDFDocument2 pages5a What Is Visible Learning PDFHande Özkeskin100% (1)
- Creating Learning ObjDocument1 pageCreating Learning ObjtaniasakumaNo ratings yet
- Course Design ProcessDocument1 pageCourse Design ProcesstaniasakumaNo ratings yet
- Database:: Introduction To Database: A. B. C. DDocument4 pagesDatabase:: Introduction To Database: A. B. C. DGagan JosanNo ratings yet
- 0803 InfosatDocument3 pages0803 InfosatAlexander WieseNo ratings yet
- Handout Pragmatics w05Document2 pagesHandout Pragmatics w05Sara EldalyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument14 pagesParts of SpeechSampada SawantNo ratings yet
- Unit II. 2.5DESIGNING LESSON PLANS AND UNIT PLANDocument15 pagesUnit II. 2.5DESIGNING LESSON PLANS AND UNIT PLANSugar Rey Rumart RemotigueNo ratings yet
- Naskah Story Telling - Politeknik Kesejahteraan Sosial Bandung - Alsha Frisma NandyvaDocument3 pagesNaskah Story Telling - Politeknik Kesejahteraan Sosial Bandung - Alsha Frisma NandyvaannisaNo ratings yet
- RHCE EXAM Solution PDFDocument13 pagesRHCE EXAM Solution PDFPravind Kumar100% (1)
- Subjunctive 1 4Document5 pagesSubjunctive 1 4Arizendy Dewi FortunaNo ratings yet
- Happy Birthday: The PIC Chip On A Prototype PC BoardDocument6 pagesHappy Birthday: The PIC Chip On A Prototype PC Boardv1009980No ratings yet
- Needs Analysis and Types of Needs AssessmentDocument19 pagesNeeds Analysis and Types of Needs AssessmentglennNo ratings yet
- Islam Belief and TeachingDocument280 pagesIslam Belief and TeachingIsoimi-dini Ali 210032406No ratings yet
- PID - Compact Error CodesDocument3 pagesPID - Compact Error CodesMokhtar ShamsNo ratings yet
- Avoiding WordinessDocument18 pagesAvoiding WordinesstimurhunNo ratings yet
- 9.digital Signatures CompleteDocument57 pages9.digital Signatures CompleteLalitNo ratings yet
- l193 Study GuideDocument32 pagesl193 Study GuideMarcos González PérezNo ratings yet
- A - Listening: 1. Listen and Circle The Correct OptionDocument4 pagesA - Listening: 1. Listen and Circle The Correct Optionsandramadeira-1No ratings yet
- PDL2 Offline Translator For SGI (Version 5.6x) : RoboticaDocument4 pagesPDL2 Offline Translator For SGI (Version 5.6x) : RoboticaRodrigo Caldeira SilvaNo ratings yet
- Afro-Asian Literature: Practice Test in EnglishDocument3 pagesAfro-Asian Literature: Practice Test in EnglishApple Mae CagapeNo ratings yet
- Basil of Caesarea - S Anti-Eunomian Theory of Names - Christian Theology and Late-Antique Philosophy in The Fourth Century Trinitarian ControversyDocument317 pagesBasil of Caesarea - S Anti-Eunomian Theory of Names - Christian Theology and Late-Antique Philosophy in The Fourth Century Trinitarian ControversyVuk Begovic100% (4)
- Akin ToDocument3 pagesAkin Tomark_torreonNo ratings yet
- 3 Eps 211 2024Document5 pages3 Eps 211 20248knpjk26b7No ratings yet
- Bmo1 2023Document2 pagesBmo1 2023Biswanath BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Cahya Indah R.Document17 pagesCahya Indah R.Naufal SatryaNo ratings yet
- Discrete StructuresDocument317 pagesDiscrete Structureskshitizjain07No ratings yet
- Eegame LogcatDocument11 pagesEegame LogcatRenato ArriagadaNo ratings yet
- 777Document71 pages777Jim Charles III100% (1)
- LinguafolioDocument23 pagesLinguafolioapi-290851941No ratings yet
- Configuration Manual For Scada: Labview 8.2Document14 pagesConfiguration Manual For Scada: Labview 8.2Emir KunalićNo ratings yet
- Ccna Lab ManualDocument109 pagesCcna Lab ManualJoemon Jose100% (8)
- COBOL Hage PDFDocument8 pagesCOBOL Hage PDFykabach87No ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Who Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkFrom EverandWho Tells the Truth?: Collection of Logical Puzzles to Make You ThinkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)