Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHF Pathophysiology
CHF Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
John Paulo CatacutanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHF Pathophysiology
CHF Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
John Paulo CatacutanCopyright:
Available Formats
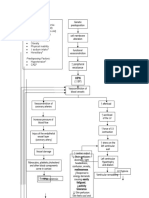
Risk Factors: Genetic
Hytension for 16 years predisposition
Men (64 years old)
Cigarette smoking (32
pack years)
Alcoholic drinker for 32 cell membrane
years alteration
Fond of eating fatty foods
Physical inability
↑ sodium intake functional
Hereditary
\
vasoconstriction
↑ peripheral
resistance
HPN
(↑ BP)
Vasoconstriction of
blood vessels
Vasoconstriction of ↑ afterload
coronary arteries
↑ workload
Increase pressure of of the LV
blood flow
↑ force of LV
contraction
Injury of the endothelial
vessel layer
(coronary artery) Apex beat
↑ stress on the is heard at
left ventricular 6th ICS
wall AAL
Vessel damage
↑ cardiac output
Left ventricular
↑ LV oxygen
Monocytes, platelets,cholesterol Hypertrophy
demand
and other blood components and dilation
come in contact
Ventricular remodeling LV Hypoxia
Scarring
Atherosclerosis
↓ left ventricular
contractility
CAD
↑ residual blood of
the LV at the time of
↓ cardiac tissue diastole
blood flow
↑ LV pressure
↓ cardiac muscle
contraction
↓ Cardiac Output blood backflows
{
from LV to LA
Activation of
baroreceptors in the LV,
aortic arch, carotid sinus ↓ Systemic blood ↑ residual blood
pressure of the LA during
diastole
Stimulation of
vasomotor regulatory
↓ Perfusion of
centers in medulla tissues of the body ↑ LA pressure
Activation of ↓GFR ↓ Renal blood returns to
sympathetic Perfusion pulmonary circulation
nervous system
Renin
Accumulation of
↑ catecolamines blood in the
(epinephrine/ formation of pulmonary capillary
norepineohrine) Angiotensin I bed
(Lungs)
ACE
Angiotensin II
Hypothalamus
Sodium and
ADH Water retention
Pulmonary edema:
dyspnea, easy
fatigability, 2 pillow
↓ urine output ↑osmotic orthopnea
pressure
↑ Venous Return ↑ pulmonary
vascular resistance
Blood pools back to
RV
↑ Work
Load of RV
↑ RV oxygen Left ventricular ↑ stress on the ↑ force of RV
demand Hypertrophy Right ventricular contraction
and dilation wall
↓ Right ventricular
RV Hypoxia Ventricular remodeling
contractility
↑ residual blood
of the RV at the
time of diastole
↑ RV preload
blood backflows
from RV to RA
↑ RA pressure
Peripheral edema
↑ RA preload
↑ fluid moves into blood backflows
the interstitial space from RA to systemic
circulation
You might also like
- Heart McqsDocument33 pagesHeart McqsNaghman Zuberi75% (16)
- Ati Medication Template KetorolacDocument1 pageAti Medication Template KetorolacSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Injection Guidelines: For Needle Length and Gauge SelectionDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection Guidelines: For Needle Length and Gauge SelectionrevinhostingNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Math For Nurses NAME - WorkbookDocument7 pagesIntermediate Math For Nurses NAME - WorkbookRaniela MaeNo ratings yet
- Insulin ChartDocument1 pageInsulin ChartGabriel TaylorNo ratings yet
- RCJ Finals - Non Epithelial Ovarian CaDocument4 pagesRCJ Finals - Non Epithelial Ovarian CaJohn Paulo Catacutan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Diagnosis and InterventionsDocument3 pagesConcept Map Diagnosis and Interventionsmenickel3No ratings yet
- Cardiac 1.01 5 Lead EKG PlacementDocument1 pageCardiac 1.01 5 Lead EKG PlacementEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Week 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument4 pagesPharmacology Week 2 Cheat Sheet: by ViaVijungcoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Abdominal Distensión After GastrectomyDocument1 pageAssessing Abdominal Distensión After GastrectomyEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug ReactionDocument53 pagesAdverse Drug ReactionShruthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 Bariatric Surgery DFM 484 Schneider Shimko BennettDocument6 pagesCase Study 2 Bariatric Surgery DFM 484 Schneider Shimko Bennettapi-298797605No ratings yet
- NRSG 115 CCL CDL Spring 2020 Lab Information SheetDocument7 pagesNRSG 115 CCL CDL Spring 2020 Lab Information SheetSethNo ratings yet
- Mastitis Teaching PlanDocument2 pagesMastitis Teaching Planapi-252910411No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Medrcal-Surgrcal NursingDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Medrcal-Surgrcal NursingGTX123No ratings yet
- C 13Document11 pagesC 13Jo100% (1)
- Poison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFDocument1 pagePoison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFdeeptiNo ratings yet
- Clinical PacketDocument6 pagesClinical PacketE100% (1)
- 106 Prefi Critical Care Nclex ReviewDocument10 pages106 Prefi Critical Care Nclex ReviewraigeneNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionBianca Watanabe - RatillaNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Anjani.S.Kamal 1 Year MSC (N)Document23 pagesPresented By: Anjani.S.Kamal 1 Year MSC (N)shubham vermaNo ratings yet
- Principles For All MedicationDocument6 pagesPrinciples For All MedicationBelle MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Medication Calculations: UNRS 314 Jan Bazner-Chandler CPNP, CNS, MSN, RNDocument47 pagesPediatric Medication Calculations: UNRS 314 Jan Bazner-Chandler CPNP, CNS, MSN, RNHunny BearstenNo ratings yet
- Nurse Sam Nursing School Study Kits, Courses, and Merch! - The Nurse SamDocument6 pagesNurse Sam Nursing School Study Kits, Courses, and Merch! - The Nurse SamRrg0% (1)
- Med Admin Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMed Admin Practice QuestionsArmelle DelvaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Question BankDocument25 pagesPharmacology Question Bankjismi vallachiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25heart Failure and Inflammatory DysfunctionDocument10 pagesChapter 25heart Failure and Inflammatory DysfunctionNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionDocument13 pagesChapter 08: Injectable Medications Mulholland: The Nurse, The Math, The Meds, 3rd EditionadenNo ratings yet
- Clotting Concept Analysis Diagram and ExplanationDocument2 pagesClotting Concept Analysis Diagram and ExplanationJulius Haynes100% (1)
- 3rd SpacingDocument1 page3rd Spacingmidnightdream254589No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Final OutputDocument19 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Final OutputNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabNo ratings yet
- InsulinsDocument1 pageInsulinsReymart Waitforit DulayNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Et Al 11-04-15Document7 pagesConcept Map Et Al 11-04-15api-353656227No ratings yet
- Pharmacology 2 NotesDocument14 pagesPharmacology 2 NotesNikko MabbayadNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template - Enoxaparin SodiumNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Definitions/key Terms Varcarolis Mental Health NursingDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Definitions/key Terms Varcarolis Mental Health Nursingatl_nurse_studentNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Nursing Clinical-Concept Map-2Document3 pagesMedSurg Nursing Clinical-Concept Map-2adaezeNo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.13 Antidepressant Cheat SheetEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Sirs & ModsDocument5 pagesSirs & Modsmarlou agananNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drugs PharmacologyDocument19 pagesAnticancer Drugs PharmacologyZainNo ratings yet
- Med Surg SyllabusDocument16 pagesMed Surg SyllabusCrystal AshleyNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Case Study Heart FailuredocxDocument4 pagesMedsurg Case Study Heart Failuredocxapi-457873289No ratings yet
- Drug BookDocument30 pagesDrug BookLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- Answers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument12 pagesAnswers, Rationales, and Test Taking Strategies: The Client With Peripheral Vascular DiseaseNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- NUR1213L May2013 FinalDocument23 pagesNUR1213L May2013 FinalOzzy Viadnes MalanaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Final 3Document148 pagesPathophysiology Final 3Yeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument6 pagesCardiovascular DisorderClara De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Decrease All Properties of Cardiac Muscle: - H.R - C.O.P Essential For Normal Development of Nervous SystemDocument1 pageDecrease All Properties of Cardiac Muscle: - H.R - C.O.P Essential For Normal Development of Nervous Systemahmed K.Abd el SaterNo ratings yet
- Pharma - Fundamental Concepts of Pharmacology 1Document96 pagesPharma - Fundamental Concepts of Pharmacology 1gelean payodNo ratings yet
- Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Regularity Life Threatening CausesDocument3 pagesRhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Regularity Life Threatening CausesLedio XhezairiNo ratings yet
- Life and DeathDocument23 pagesLife and DeathJea Joel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ch34 PharmDocument8 pagesCh34 PharmShaneka WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Student Name:: Clinical Week #: Clinical InstructorDocument5 pagesStudent Name:: Clinical Week #: Clinical InstructorSusan BensonNo ratings yet
- MedSurgATI1Document97 pagesMedSurgATI1LeelanRamphal100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan #1 Mental HealthDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 Mental HealthNursyNurseNo ratings yet
- 201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pages201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemEidelen Lovani Sembiring100% (1)
- Chapter 45-Antiarrhythmic AgentsDocument13 pagesChapter 45-Antiarrhythmic AgentsMelanie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 5P Handoff SheetDocument1 page5P Handoff SheetBarry SeeboNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Document32 pagesAssessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Maricar RosasNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Emergencies PDFDocument57 pagesCardiac Emergencies PDFJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- DDX, Patho, TXDocument4 pagesDDX, Patho, TXJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Regional IntravenousInhalational Post OperativDocument22 pagesRegional IntravenousInhalational Post OperativJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- A-PULMO - (LEE-TAN-CONSTANTINO) - Prelims (TD) B - Pulmo - (Lee-Tan-Constantino) - PrelimsDocument17 pagesA-PULMO - (LEE-TAN-CONSTANTINO) - Prelims (TD) B - Pulmo - (Lee-Tan-Constantino) - PrelimsJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Anus and RectumDocument140 pagesAnus and RectumJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of TBDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TBJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument7 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- SurgPatho Thyroid 2018Document8 pagesSurgPatho Thyroid 2018John Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition Among Patients With Psychological Disturbances 1Document99 pagesMalnutrition Among Patients With Psychological Disturbances 1John Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Surg Anes OB Anes 2018Document5 pagesSurg Anes OB Anes 2018John Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics AnesthesiaDocument55 pagesObstetrics AnesthesiaJohn Paulo Catacutan100% (2)
- Asthma PEDocument4 pagesAsthma PEJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Asthma DifferentialsDocument1 pageAsthma DifferentialsJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Teaching StrategiesDocument2 pagesTeaching StrategiesJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Mechanical Circulatory SupportDocument8 pagesPediatric Mechanical Circulatory SupportselvakumarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Physiology NotesDocument11 pagesCardiac Physiology Notespunter11100% (1)
- Clinical QDocument52 pagesClinical QamsirakNo ratings yet
- Sono 338 - Echocardiography-Worksheet 2017Document2 pagesSono 338 - Echocardiography-Worksheet 2017api-330589222100% (1)
- JawapanLengkap Modul Biology PDFDocument32 pagesJawapanLengkap Modul Biology PDFT-specialist SNo ratings yet
- National ECG Workshop AIMST MMA 2015Document217 pagesNational ECG Workshop AIMST MMA 2015Sara100% (1)
- Physiology of The HeartDocument27 pagesPhysiology of The HeartNavadeep KalluriNo ratings yet
- Cardiac OutputDocument79 pagesCardiac OutputBrian Adoka OmdangNo ratings yet
- L A Level Biology MS Jan 05Document180 pagesL A Level Biology MS Jan 05annakaranovaNo ratings yet
- File - 20210401 - 231901 - Chapter-7-English 2Document23 pagesFile - 20210401 - 231901 - Chapter-7-English 2Trần Thảo Dân AnhNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Passages Are Sure Shot Scoring QuestionsDocument33 pagesComprehension Passages Are Sure Shot Scoring QuestionssawsanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology: Cardiac Cycle Analysis of Cardiac Activity - PolygramDocument47 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: Cardiac Cycle Analysis of Cardiac Activity - PolygramAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- SP 2.3c - Dissection of A Mammalian HeartDocument4 pagesSP 2.3c - Dissection of A Mammalian HeartPinu CattoNo ratings yet
- Ecg Echo LVHDocument3 pagesEcg Echo LVHSoʋɭ ʜʌcĸɘʀNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CatheterizationDocument9 pagesCardiac CatheterizationAnurag Gupta100% (2)
- Biology Grade 9 - Lesson NoteDocument9 pagesBiology Grade 9 - Lesson NotemicahxNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: By: Loricar Mae SagaDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System: By: Loricar Mae SagaI Need Some SleepNo ratings yet
- Ecg ReviewDocument155 pagesEcg ReviewVimal Nishad100% (5)
- Fuctions of The Parts of The HeartDocument3 pagesFuctions of The Parts of The Heartsonia1519No ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATION 10 Class NotesvvpDocument3 pagesTRANSPORTATION 10 Class NotesvvpSD card 32 gbNo ratings yet
- 5 EkgDocument6 pages5 EkgJessica BNo ratings yet
- 12 Transport of O2 & Co2Document169 pages12 Transport of O2 & Co2Bakhtiar Effendi YahyaNo ratings yet
- King AutopsyDocument6 pagesKing AutopsyJennifer Saylor100% (2)
- Biology JournalDocument21 pagesBiology JournalOM CHAVANNo ratings yet
- Systema-Cardiovasculare-2014-by-OBD (Anat)Document72 pagesSystema-Cardiovasculare-2014-by-OBD (Anat)intan kaniaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Cavity (Chapter 3)Document13 pagesThoracic Cavity (Chapter 3)Alenna BenitezNo ratings yet
- S1 Nov 15Document11 pagesS1 Nov 15Tiago BastoNo ratings yet
- Finalf CLDocument485 pagesFinalf CLToni PacificoNo ratings yet
- SMK Green Road Term 2 Trial Exam 2019 MSDocument4 pagesSMK Green Road Term 2 Trial Exam 2019 MSvoon sjNo ratings yet