Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Education and Health: Fitness
Uploaded by
Khie MonidaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Education and Health: Fitness
Uploaded by
Khie MonidaCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH: FITNESS
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
1
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
MODULE 2 PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH: FITNESS
COURSE SUBJECT DESCRIPTION
Physical Education and Health offers experiential learning for the learners to adopt an active
life for fitness and lifelong health. The knowledge, skills and understanding in which include the
Physical and Health literacy competencies support them in accessing, synthesizing and evaluating
information, making informed decision, enhancing and advocating their own as well as the other
fitness and health. This course on exercise for fitness enables the learner to set goals, monitor one’s
participation in aerobic and muscle bone strengthening activities and constantly evaluate how well
one has integrated this into one’s personal lifestyle. It consists of an array of offering which learners
can choose from.
MODULE CONTENT
Health and optimizing P.E. (HOPE 1) Exercise for Fitness
a. Eating Habits
b. Sleep
c. Stress Management
d. Hobbies
LEARNING COMPETENCIES
1. Relates health behavior (eating habits, sleep and stress management) to health risk factors
and physical activity assessment performance.
2. Differentiate types of eating (fueling for performance, emotional eating, social eating, eating
while watching TV or sports events.)
Reminder:
Before you flip into the next page of this module always ask the guidance of
our God to give us the knowledge and understanding in answering and
exploring this module.
Dear Lord and Father of All
Thank you for ways in which you provide for all of us. For your
protection and love we thank you.
Help us focus our hearts and minds now on what we are about to learn.
Inspire us by your Holy Spirit as we listen and write.
Guide us by your eternal light as we discover more about the world
around us.
We ask all thus in the name of Jesus
Amen
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
2
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
DISCUSSION: HEALTH AND RISK IN OUR LIFESTYLE
LESSON 1: GETTING GOOD EATING HABITS
EATING HABITS
Healthy eating means making choices about what you eat for the purpose of providing our
body with nutrients that improve or maintain good health. It essentially involves eating the right kind of
food in the right amount in accordance with expert’s recommendation. Both the quality and the
quantity of foods are central not only to the prevention of disease, but proper nutrition also forms the
foundation for physical activity.
Nutrition provides the fuel for physical activity and the essential elements that repair existing
cells. It promotes the growth of the new tissues and provides the material for our bones and muscle.
Adequate water intake keeps you hydrated before, during, and after a physical activity. Avoiding
dehydration can prevent heat disorder and heart illness because water and fluids are essential to
maintaining body temperature.
Expending energy through physical activity helps you manage your weight for healthy body
composition. As your physical activity levels increase, you will need a greater amount of energy. It
now becomes important for you to follow the serving recommendations for carbohydrates, proteins,
and water or fluids. In order to achieve and maintain healthy body weight, focus on regular physical
activity and nutritious diet. These two major components will help you avoid the effects of creeping
obesity or the negative consequences of a cycle of weight gain and loss. For a fat loss program,
physical activity is the best predictor for maintaining weight loss.
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
3
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
HEALTH TIPS:
DR. DAVID GOFF (Heart Disease and Public Expert)
According to analysis, nearly half (45%) of deaths in 2012 from this three disease was
associated with too much or too little of this dietary factors.
The study establishes the number of cardio metabolic death can be linked to eating habits.
TECHNIQUES FOR A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE ARE:
Eat smart
Move more
Be well
Healthy eating starts with healthy food choices. You don’t need to be a
chef to create nutritious, heart and healthy meals your family will love.
EAT SMART Learn what to look for at the grocery store, restaurants, your workplace
and any eating occasion.
Make healthy, delicious choices whenever and whenever you eat.
A good starting goal is at least 150 minutes, but if you don’t want to
sweat the numbers, just moves more. Find forms of exercise you like
MOVE MORE and will stick with and build more opportunities to be active into your
routines.
Infuse more movements in your life for optimal health.
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
4
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
How do you want to live? Along with eating right and being active, real
health includes getting enough sleep, practicing mindfulness, managing
stress, keeping mind and body fit, connecting socially and more.
Create balance, vitality and well being through self care.
BE WELL
ACTIVITY 1
1. Enumerate at least 3 possible diseases that we can get in poor eating habit.
2. List down the three techniques of a healthy lifestyle.
LESSON 1.1 GETTING GOOD SLEEPING HABIT
SLEEPING HABITS
Getting average of seven to nine hours of sleep in night is important to our health. Both the
quantity and the quality of your sleep contribute to how you feel and function during the day. A restful
sleep impacts on your energy level during the day and keeps you alert, while habitual sleep deficit
negatively impact on your mental functioning, mood, and inevitably your health. Sleep deprivation
decrease you reaction time, increase irritability, and cause hormonal and metabolic changes that
parallel the aging process.
Inadequate sleep impairs your immunity and increases your risk for obesity, hypertension and
depression. Sleep deficits also directly relate to fatigue which in turn can result in injuries. Significant
sleepiness during the day suggests that your body need more and better sleep. Regular sleep
participation in the physical activity as well as moderately intense aerobic activity three hours before
the bedtime is associated with improved sleep.
WHY LACK OF SLEEP IS BAD IN OUR HEALTH
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
5
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
Effect of lack of sleep, such as feeling grumpy and not working t your best.
But did you know that sleep deprivation can also have profound consequences on your
physical health.
If you don’t sleep you will experience the fatigue, short temper, lack of focus that often follows
a poor night’s sleep. In occasional night without sleep makes you feel tired and irritable the
next day.
After continuous sleepless nights, the mental effects become more serious. Your brain will fog,
making you difficult to concentrate and make decisions. You’ll start to feel down, and may fall
asleep during the day. Your risk of injury and accidents at home and on the road also
increases.
Figure 1: Good Sleeping and Bad Sleeping effects
WHY OVERSLEEPING IS BAD FOR YOUR HELATH?
Sleep plays an important role in our brain, as the brain clears our waste byproducts, balance
neurotransmitters and process memories at rest. But too much may have effect on mood and
mental health. Cognition, degenerative disease and depression.
More time in bed linked with more frequent waking after sleep and reduces sleep efficiency.
Fatigue causes longer sleep and sleeping more can make people feel more lethargic.
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
6
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
THE MOST IMPORTANT THINGS WE CAN DO TO PROMOTE GOOD SLEEP
LESSON 1.2 STRESS MANAGEMENT
WHAT IS STESS?
Mental or emotional tension or strain resulting from adverse or very demanding
circumstances.
FACTS ON STRESS
Stress helps the body to prepare to face danger
Symptoms can be both physical and psychological
Short term stress can be helpful, but long term stress is linked to various health
conditions.
We can prepare for stress by learning some self management tips.
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO MANAGE STRESS?
If you are living with the high level of stress, you’re putting your entire well being at risk. Stress
wreaks havoc on your emotional equilibrium as well as your physical health. It narrows your
ability to think clearly, function effectively and enjoy life.
Effective stress management, on the other hand, helps you break the hold stress has on your
life, so you can be happier, healthier and more productive. The ultimate goal is balanced life,
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
7
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
with time for work, relationship, relaxation and fun and the resilience to hold up under pressure
and meet challenges head on. But stress management is not one size fits all. That’s why it is
important to experiment and find out what work best for us. The following stress management
tips can help you do that.
TOP 10 EMERGENCY STRESS STOPPERS
1. Count to 10 before you speak or react
2. Take a few slow, deep breaths until you feel your body unclench a bit.
3. Go for a walk, even if it’s just to the restroom and back. It can help break the tension
and give you a chance think things through.
4. Try a quick meditation or prayer to get some perspectives.
5. If it’s not urgent, sleep on it, and respond tomorrow. This works especially well for
stressful emails and social media trolls.
6. Walk away from the situation for a while, and handle it later once things have calmed
down.
7. Break down big problems into smaller parts. Take one step at a time, instead of trying to
tackle everything at once.
8. Turn on some chill music or an inspirational podcast to help you deal with road range.
9. Take a break to pet the dog, hug and loved one or do something to help someone else.
10. Work out or do something active. Exercise is the great antidote for stress.
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
8
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
STRESS BUSTING ACTIVITIES
MAKE AN ART Draw, color, paint or play a musical instrument
WORK ON SCRAPBOOK Making scrapbook and photo album to focus on good memories
READ A BOOK Reading short story, novels, or magazine
MEET A FRIEND Meet your friend for a coffee or meal
PLAY SPORTS Play your favorite sports like chess, badminton and etc.
Do your hobby Like sewing, knitting or making jewelry
Play Play with kids or pet or outside if possible
Listen to music or watch inspiring performance
Take walk in nature
Take a relaxing bath and feel the stress wash away
Meditate or practice yoga
Work in the garden or do home improvement project
Go for run or bike ride to clear your head.
Regular participation in exercise can be therapeutic when it comes to managing stress. First , it
reduce the body’s stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol which remain elevated when the
body experiences a stressor. By expending these through exercise, these biochemicals are flushed
out of the body.
Second, exercise stimulates the production of endorphins, which are the body’s natural pain
killers and mood elevators. They are the responsible for the runner’s high or feelings of euphoria and
for the feelings of relaxation as they diminish the perception of pain. Endorphins and
neurotransmitters that transmit electrical signals within the nervous system.
Third, exercise engages the different body system, cardiovascular, renal, muscular, central,
and sympathetic nervous system much more closely than usual. These are the same body system
which are involved in dealing with stress, thus exercise parallels the body’s response to a stressor. In
this way, exercise not only strengthens the body but enhances its ability to respond to stress
management.
ACTIVITY 1. HEALTHY LIFESTYLE ASSESSMENT
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
9
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
Direction: Assess your habits in sleeping, eating and physical activity. Along with how you manage
your stress, these factors influence your health, which in turn affect your capacity as a student to
think, remember, process information, and learn. Rate yourself using the following scale by checking
the corresponding box.
1 – Rarely if ever 2 – sometimes 3 – most of the time 4 – always
SLEEP HABITS 1 2 3 4
I sleep between 7 to 9 hours on most nights
I wake up feeling rested
I have trouble staying awake in class or when reading
I often feel tired during the day
EATING HABITS 1 2 3 4
I drink 6 -8 glasses of water each day
I eat a variety of fruits and vegetables each day
I eat 3 servings of fruits and vegetables each day
I et 6 -8 serving of whole grain products (bread, rice, corn or root crops)
I eat 2 -3 serving of protein rich foods (meat, poultry eggs, fish) each day
STRESS MANAGEMENT 1 2 3 4
I fell stress when I am in school
I feel stress when I am not in school
When I feel stress, I worry all the time
When I feel stress, I have difficulty in sleeping (stay asleep/can’t sleep)
When I feel stress, I have difficulty in concentrating
When I feel stress, my appetite is affected (tend to eat more)
I’d rather be alone when I feel stress
I have someone I can talk to about my private feelings
I have faith in greater power or being (God)
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY 1 2 3 4
I perform active household chores(mopping or scrubbing floors, cleaning
the car, fetching water in a pail) daily
I walk, bike or take to the public transport when going to school
I perform at least 40 minutes Aerobic activities (sports and dance) on
most day of the week
I engage in at least 20 minutes of sustained vigorous activities that
results in rapid breathing on most day of the week
I perform muscle and bone strengthening (weights) 2 -3 times a week
I don’t have time for exercise, sports and dance
I am too tired to exercise, play sports and dance
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL LEARNING MODULE S/Y 2020 – 2021
10
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND HEALTH G11 - FITNESS
You might also like
- Health and Fitness Articles 2Document4 pagesHealth and Fitness Articles 2ᴅꜱʀ ɪꜱ ʙᴀᴄᴋNo ratings yet
- Holistic Health: A Comprehensive Guide to WellnessFrom EverandHolistic Health: A Comprehensive Guide to WellnessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physical FitnessDocument17 pagesPhysical FitnessmickyNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document14 pagesModule 1charlesdarwingarcia28No ratings yet
- Great Health Is Wealth: Strategies to Healthy Living: Strategies To Healthy LivingFrom EverandGreat Health Is Wealth: Strategies to Healthy Living: Strategies To Healthy LivingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Health and FitnessDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Health and FitnessJellane SeletariaNo ratings yet
- PEDocument2 pagesPEJJNo ratings yet
- Health Risk in Our Lifestyle: Full Name: Grade 12Document7 pagesHealth Risk in Our Lifestyle: Full Name: Grade 12Julliene Sanchez DamianNo ratings yet
- Act Of, How It's Linked To Health: Module 2: WELLNESSDocument10 pagesAct Of, How It's Linked To Health: Module 2: WELLNESSHyacenth Claire TumbaliNo ratings yet
- HOPE-1 Grade 11-Quarter IIIDocument10 pagesHOPE-1 Grade 11-Quarter IIIDevonNo ratings yet
- Esquero, Maecy Anne Victoria D. Bs Architecture 2ADocument3 pagesEsquero, Maecy Anne Victoria D. Bs Architecture 2AluffyNo ratings yet
- Bped 2 - Mapeh 7-Wps OfficeDocument3 pagesBped 2 - Mapeh 7-Wps OfficeSamson J. EsmeraldaNo ratings yet
- NSTP U Ba PsychDocument25 pagesNSTP U Ba PsychJeorge Justine SorianoNo ratings yet
- How to Become More Healthy: Your Path to a Healthier You! Hidden Treasures of Health, Energy, and Long LifeFrom EverandHow to Become More Healthy: Your Path to a Healthier You! Hidden Treasures of Health, Energy, and Long LifeNo ratings yet
- Wellness and FitnessDocument2 pagesWellness and Fitnesstenten desarapenNo ratings yet
- Hope Lp12dnjDocument7 pagesHope Lp12dnjEnnik SomiNo ratings yet
- Healthy Home, Happy Family - A Comprehensive Guide To Family WellnessFrom EverandHealthy Home, Happy Family - A Comprehensive Guide To Family WellnessNo ratings yet
- Notes SsssDocument6 pagesNotes SsssJoey Nalla ValdezNo ratings yet
- Personal DevDocument8 pagesPersonal DevDAVE NARDONo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document3 pagesLesson 12cristylynopfloresNo ratings yet
- Pe109q7w1 4M1Document2 pagesPe109q7w1 4M1Julien AlabadoNo ratings yet
- The Importance of A Healthy LifestyleDocument3 pagesThe Importance of A Healthy LifestylePamelaNo ratings yet
- Module For Health and WellnessDocument3 pagesModule For Health and WellnessMary Ann Andes CaruruanNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION Health Education Year 2Document44 pagesINTRODUCTION Health Education Year 2DxmplesNo ratings yet
- Self-Care Strategies : Prioritizing Your Health and HappinessFrom EverandSelf-Care Strategies : Prioritizing Your Health and HappinessNo ratings yet
- Simple yet Critical Ways to Health, The Joy of LifeFrom EverandSimple yet Critical Ways to Health, The Joy of LifeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Week 1: Introduction To Physical Education What Is Physical Fitness?Document28 pagesWeek 1: Introduction To Physical Education What Is Physical Fitness?Gotto InamoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Fitness and HealthDocument25 pagesLESSON 1 Fitness and Healthjon.aguirre.1022No ratings yet
- Facts On Fitness and HealthDocument17 pagesFacts On Fitness and HealthMary Ann F. MendezNo ratings yet
- PE ReviewerDocument5 pagesPE ReviewereukiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and WellnessDocument24 pagesNutrition and WellnessArianne Rose FangonNo ratings yet
- The Path to Wellness: Nurturing Body, Mind, and Relationships: Healthy Lifestyle, #2From EverandThe Path to Wellness: Nurturing Body, Mind, and Relationships: Healthy Lifestyle, #2No ratings yet
- LUYỆN VIẾT ĐOẠN VĂN TIẾNG ANH - ON HEALTH & FITNESSDocument3 pagesLUYỆN VIẾT ĐOẠN VĂN TIẾNG ANH - ON HEALTH & FITNESSVũ TuấnNo ratings yet
- Being Healthy and Fit in Simple Terms Means Taking Good Care of The Body PDFDocument3 pagesBeing Healthy and Fit in Simple Terms Means Taking Good Care of The Body PDFolympianbestNo ratings yet
- PeDocument11 pagesPeAndrea B.No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Physical Education 11Document5 pagesReviewer in Physical Education 11tolentinodrei94No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Peh1 Week 5 6Document17 pagesGrade 11 Peh1 Week 5 6Erickson FernNo ratings yet
- Paper Living A Healthy Lifestyle-1Document9 pagesPaper Living A Healthy Lifestyle-1LaylaNo ratings yet
- NOTESSSSSDocument13 pagesNOTESSSSSJoey Nalla ValdezNo ratings yet
- H O P E-3-2nd-QuarterDocument24 pagesH O P E-3-2nd-QuarterDanna GomezNo ratings yet
- 100 Ways to stay fit: The Easy Way to Get in Shape and Stay in Shape for the Rest of your LifeFrom Everand100 Ways to stay fit: The Easy Way to Get in Shape and Stay in Shape for the Rest of your LifeNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Business School: Name: Matrix No: Contact No: EmailDocument23 pagesFaculty of Business School: Name: Matrix No: Contact No: EmailNOOR AIN WAHIDA BINTI MAT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Lesson 1 Health Enhancing Physical ActivityDocument53 pagesPe 1 Lesson 1 Health Enhancing Physical Activitydario serranoNo ratings yet
- The Path to Happiness: Nurturing Your Mind, Body, and Spirit: Healthy Lifestyle, #3From EverandThe Path to Happiness: Nurturing Your Mind, Body, and Spirit: Healthy Lifestyle, #3No ratings yet
- The Mind-Body Connection: A Holistic Approach to Achieving Optimal Health and WellnessFrom EverandThe Mind-Body Connection: A Holistic Approach to Achieving Optimal Health and WellnessNo ratings yet
- Mpu3313 V2Document11 pagesMpu3313 V2Kaipro98 HiiNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Good Health & It's Balance For Positive MindsetDocument12 pagesModule-1 Good Health & It's Balance For Positive Mindsetaman.kekkarNo ratings yet
- Health and Wellness Module 1Document14 pagesHealth and Wellness Module 1Albert Fabros GapasinNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health: Dance: Senior High School Learning ModuleDocument8 pagesPhysical Education and Health: Dance: Senior High School Learning ModuleKhie MonidaNo ratings yet
- Sample Weekly Home Learning Plan Source: Appendix D. MEMORANDUM DM-CI-2020-00162, From DIOSDADO M. SAN ANTONIO UndersecretaryDocument10 pagesSample Weekly Home Learning Plan Source: Appendix D. MEMORANDUM DM-CI-2020-00162, From DIOSDADO M. SAN ANTONIO UndersecretaryKhie MonidaNo ratings yet
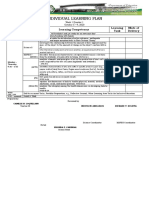
- Individual Learning Plan: Day and Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Task Mode of DeliveryDocument2 pagesIndividual Learning Plan: Day and Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Task Mode of DeliveryKhie MonidaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Learning Module: Colegio Dela Virgen Del Pilar Inc. Colacling Lupi, Camarines Sur S/Y 2020 - 2021Document12 pagesSenior High School Learning Module: Colegio Dela Virgen Del Pilar Inc. Colacling Lupi, Camarines Sur S/Y 2020 - 2021Khie MonidaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Traditional To New MediaDocument10 pagesThe Evolution of Traditional To New MediaKhie MonidaNo ratings yet
- 4life Distributor New Prices-1Document3 pages4life Distributor New Prices-1Hermosa BellisimaNo ratings yet
- 2019 NCP P2 Desarrollando y Usando La Terminologã A JANDDocument16 pages2019 NCP P2 Desarrollando y Usando La Terminologã A JANDSofia GersenowiesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 4 NotesHeisel Hernandez LopezNo ratings yet
- Perspectives in Nutrition 7th EditionDocument1,037 pagesPerspectives in Nutrition 7th EditionAlizoo MalikNo ratings yet
- Twitter Trends - Indonesia - ReportDocument30 pagesTwitter Trends - Indonesia - ReportasrielrusdyawanNo ratings yet
- 5.theories and Models of MidwiferyDocument29 pages5.theories and Models of MidwiferyRatna KumariNo ratings yet
- A Nam Upper-LowerDocument330 pagesA Nam Upper-Lowerhieu nguyenNo ratings yet
- The Warm UpDocument6 pagesThe Warm Upgustavoperezcattani6253100% (1)
- Shannon Billows Fitness Calculator With WaistDocument3 pagesShannon Billows Fitness Calculator With WaistprincessmosmanNo ratings yet
- Bill Starr - CFJ - Building A Strong Shoulder GirdleDocument9 pagesBill Starr - CFJ - Building A Strong Shoulder GirdleTomSusNo ratings yet
- Physique Zero WorkoutDocument18 pagesPhysique Zero WorkoutJB JB100% (1)
- Abs: Tips To Develop A Six Pack: Ab TrainingDocument20 pagesAbs: Tips To Develop A Six Pack: Ab TrainingJordan NobleNo ratings yet
- Column Marking For G+4 Hostel Building: Column Size 0.3 X 0.4 No of Column'S 30Document1 pageColumn Marking For G+4 Hostel Building: Column Size 0.3 X 0.4 No of Column'S 30gowtham gowdaNo ratings yet
- Farming Foodsteps To Health PresentationDocument26 pagesFarming Foodsteps To Health Presentationlj;kbhvgjNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Training PrinciplesDocument24 pagesLesson 3: Training PrinciplesChen BalNo ratings yet
- Biomems As A Tool To Decifer The Shortcomings of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Importance in Patient Self CareDocument2 pagesBiomems As A Tool To Decifer The Shortcomings of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Importance in Patient Self CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- AnSCI LAB 2Document2 pagesAnSCI LAB 2Chirs Nicole CaguitlaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Self ExplorationDocument39 pagesModule 1 Self ExplorationBrylle Espares Lumberio0% (1)
- Sample Size in Qualitative Interview Studies: Guided by Information PowerDocument8 pagesSample Size in Qualitative Interview Studies: Guided by Information PowermohammedNo ratings yet
- PE and Health 12 - Module 3Document21 pagesPE and Health 12 - Module 3Stephen Lorenzo A. DoriaNo ratings yet
- Pe4 Quarter1Document27 pagesPe4 Quarter1Sheena Claire dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- D218 - Task 1 - Brianna KnoxDocument3 pagesD218 - Task 1 - Brianna KnoxbriannakaraNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Active RecreationDocument2 pagesQuiz in Active RecreationRemedios Encarnacion CabrerosNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan CHFDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan CHFInah Floresta Besas100% (1)
- The 90 Day Push Challenge PDFDocument10 pagesThe 90 Day Push Challenge PDFСавелий СмирновNo ratings yet
- QuestionaireDocument3 pagesQuestionairebashirkinza679No ratings yet
- S09.s1 - Ejercicios 1 (Worksheet) DocxDocument3 pagesS09.s1 - Ejercicios 1 (Worksheet) DocxPierinaMendozaCamposNo ratings yet
- Zac Efron WorkoutDocument12 pagesZac Efron WorkoutSzvami ItarabNo ratings yet
- 2021 Life Skills ATP Grade 5Document10 pages2021 Life Skills ATP Grade 5Koketso SekwenyaneNo ratings yet
- TFN PrelimDocument9 pagesTFN PrelimElla ArnocoNo ratings yet