Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MELCS Unpacking
Uploaded by
Tawagin Mo Akong Merts0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
298 views2 pagesOriginal Title
MELCS Unpacking.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
298 views2 pagesMELCS Unpacking
Uploaded by
Tawagin Mo Akong MertsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
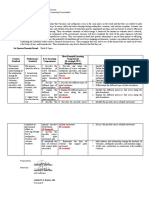
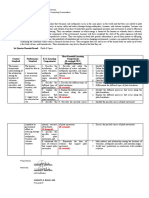
MODULE 2: Most Essential Learning Competencies
Required/Expected Output: Sample MELCs Unpacking Presentation
Subject: Science 10
Week/Quarter: 1
1st Quarter Standard
At the end of Grade 10, learners realize that volcanoes and earthquakes occur in the same places in the world and that these are related to plate
boundaries. They can demonstrate ways to ensure safety and reduce damage during earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. Learners can
explain the factors affecting the balance and stability of an object to help them practice appropriate positions and movements to achieve efficiency
and safety such as in sports and dancing. They can analyze situations in which energy is harnessed for human use whereby heat is released,
affecting the physical and biological components of the environment. Learners will have completed the study of the entire organism with their
deeper study of the excretory and reproductive systems. They can explain in detail how genetic information is passed from parents to offspring,
and how diversity of species increases the probability of adaptation and survival in changing environments. Learners can explain the importance of
controlling the conditions under which a chemical reaction occurs. They recognize that cells and tissues of the human body are made up of water,
a few kinds of ions, and biomolecules. These biomolecules may also be found in the food they eat.
1st Quarter Domain/Strand: Earth & Space
Most Essential Learning
Content Performance K-12 Learning Competencies
Learning objectives
Standard Standard Competencies (R-retained; M/C-
Merged/Clustered)
The learners The learners 1. Describe the 1. Describe and relate the 1. Identify the active volcanoes in the Philippines
demonstrate should be able to: distribution of distribution of active volcanoes, 2. Define fault, earthquake, and epicenter
understanding of active volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and major 3. Learn location of major faults in the Philippines
the relationship 1. demonstrate earthquake mountain belts to Plate Tectonic 4. Describe the seismic activities in the country.
among the ways to ensure epicenters, and Theory 5. Describe the distribution of active volcanoes,
locations of disaster major mountain (R-retained) earthquake epicenters, and major mountain belts.
volcanoes, preparedness belts; 6. State the Plate Tectonic Theory.
earthquake during 2. describe the 2. Describe the different types of 1. Identify the different types of plate boundaries.
epicenters, and earthquakes, different types of plate boundaries 2. Differentiate the different types of plate boundaries.
mountain ranges tsunamis, and plate boundaries; (R-retained)
volcanic 3. explain the 3. Explain the different processes 1. Identify the different processes that occur along the
eruptions different that occur along the plate plate boundaries.
processes that boundaries 2. Explain the different processes that occur along the
2. suggest ways occur along the (R-retained) plate boundaries.
by which he/she plate boundaries;
can 4. describe the 4. Describe the possible causes 1. Identify the possible causes of plate movement.
contribute to internal structure of plate movement 2. Discuss the possible causes of plate movement.
government of the Earth; (R-retained)
efforts in (D-dropped)
reducing damage 5. describe the
due to possible causes
earthquakes, of plate
tsunamis, and movement; and
volcanic 6. enumerate the 5. Enumerate the lines of 1. Infer patterns and relationship among the locations of
eruptions lines of evidence evidence that support plate volcanoes, earthquake epicenters, and mountain ranges.
that support plate movement 2. Justify one’s predictions or conclusions with available
movement (R-retained) evidence.
Prepared by:
CHESTER F. MERTOLA
Noted by:
CHESTER F. MERTOLA
LAC Facilitator
ANGELITA E. BARAL, EdD
Principal IV
You might also like
- Contacts Modeling in AnsysDocument74 pagesContacts Modeling in Ansyssudhirm16100% (2)
- Social Studies Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesSocial Studies Lesson Plan 3api-260708940No ratings yet
- FAME - Teachers' Material TDocument6 pagesFAME - Teachers' Material TBenny PalmieriNo ratings yet
- Filcro - LabrevDocument19 pagesFilcro - LabrevKim ArniñoNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Grade 8 Week 1Document2 pagesDLL Science Grade 8 Week 1Aika Unica Gabriel100% (1)
- CBC Events Management NC IIIDocument105 pagesCBC Events Management NC IIIJM Llaban Ramos86% (14)
- Pink Certificate of RecognitionDocument3 pagesPink Certificate of RecognitionTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 BOLDocument7 pagesGrade 10 BOLJesselyn Dacdac Llantada-Bautista100% (3)
- Reading Selection in ScienceDocument4 pagesReading Selection in ScienceBenes Salamanca BolascoNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal:: Repair & Extension of Tle LabDocument3 pagesProject Proposal:: Repair & Extension of Tle LabTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Voting BehaviorDocument23 pagesVoting BehaviorWela Paing FallitangNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W9 - D3Document2 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - W9 - D3zenaida a academiaNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries WorksheetDocument2 pagesPlate Boundaries WorksheetTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Value For Money Analysis.5.10.12Document60 pagesValue For Money Analysis.5.10.12Jason SanchezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Bow ScienceDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Bow ScienceValir JanNo ratings yet
- Science 10 First QuarterDocument52 pagesScience 10 First QuarterLani Bernardo Cuadra50% (2)
- Grade 10 Exam 19-20 JuneDocument11 pagesGrade 10 Exam 19-20 Junefe janduganNo ratings yet
- 7es New DLL Grade 9 ScienceDocument4 pages7es New DLL Grade 9 ScienceAna Ats YviNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior DLLDocument2 pagesEarth's Interior DLLGivby Dollente100% (1)
- Advance Strategic Marketing: Project Report of Nayatel.Document46 pagesAdvance Strategic Marketing: Project Report of Nayatel.Omer Abbasi60% (15)
- Science 9 DLL Session 1Document5 pagesScience 9 DLL Session 1NikkieIrisAlbañoNovesNo ratings yet
- CBLM LO3-BREAD - AND - PASTRY - PRODUCTION - NC - II - NDocument26 pagesCBLM LO3-BREAD - AND - PASTRY - PRODUCTION - NC - II - NRodolfo CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 5 Sci 10Document4 pagesDLL Week 5 Sci 10Matet GenerosaNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Should Be Able To: The Learners Should Be Able ToDocument21 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of: The Learners Should Be Able To: The Learners Should Be Able ToBik Bok50% (2)
- Aug 25 Major and Minor PlatesDocument4 pagesAug 25 Major and Minor PlatesHelen Grace CabalagNo ratings yet
- Least Learned Competencies (Science7-Q4)Document3 pagesLeast Learned Competencies (Science7-Q4)marissa quijanoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics 7-3: Modified True/FalseDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonics 7-3: Modified True/Falsemichelle100% (1)
- DLL Sept 2-6, 2019yDocument3 pagesDLL Sept 2-6, 2019yAq Nga ToNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: S10ES - Ia-J-36.1 S10ES - Ia-J-36.2 S10ES - Ia-J-36.3Document6 pagesI. Objectives: S10ES - Ia-J-36.1 S10ES - Ia-J-36.2 S10ES - Ia-J-36.3Arquero NosjayNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Science 9 (3rd Quarter)Document7 pagesCurriculum Map - Science 9 (3rd Quarter)Welbert AmarNo ratings yet
- Unit Standards and Competencies Diagram in Science 8: Perforamce StandardDocument1 pageUnit Standards and Competencies Diagram in Science 8: Perforamce StandardDixie AgregadoNo ratings yet
- TOS Gen Physics 1 Second Quarter RAWDocument4 pagesTOS Gen Physics 1 Second Quarter RAWGenesis NgNo ratings yet
- Tos - Science 10 Final ExamDocument1 pageTos - Science 10 Final Examcristito inovalNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map G11 Earth and Life ScienceDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map G11 Earth and Life ScienceReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science 10 (Week 5)Document5 pagesDLL in Science 10 (Week 5)Lhester D. AntolinNo ratings yet
- Teaching-Guide-Catchup-Science Values Grade 7Document6 pagesTeaching-Guide-Catchup-Science Values Grade 7Cristina Sarmiento JulioNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 7 Week 4Document4 pagesDLL Science 7 Week 4Imneil Jeanne Melendres-PerezNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map SCIENCE 10Document5 pagesCurriculum Map SCIENCE 10Teacher MelNo ratings yet
- DLL 7es Seafloor SpreadingDocument3 pagesDLL 7es Seafloor SpreadingJonathan Tabbun100% (1)
- Grade 9, Quarter 3 DLLDocument59 pagesGrade 9, Quarter 3 DLLKathelyn Ruiz-SumandoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 First QuarterDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First QuarterAnjhiene CambaNo ratings yet
- Q4, Peformance Task #2 - Ener-Vention!Document2 pagesQ4, Peformance Task #2 - Ener-Vention!Ericha Solomon100% (1)
- Biodiversity and Evolution-WorkbookDocument9 pagesBiodiversity and Evolution-WorkbookJenny Rose BatalonNo ratings yet
- DLL Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesDLL Plane MirrorLea Juadiong100% (1)
- DLL Oceanic OceanicDocument2 pagesDLL Oceanic OceanicHelen Grace Llemos Cabalag50% (2)
- Formative Test in ScienceDocument8 pagesFormative Test in ScienceFredjayEdillonSalocotNo ratings yet
- Co-Heat Engine-Grade-9-FinalDocument8 pagesCo-Heat Engine-Grade-9-FinalApolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- Science 10 Performance TaskDocument6 pagesScience 10 Performance TaskBrandz Dojenias RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - SCIENCE: Learning Activity Sheet No.4 Quarter 4 Week 7-8Document2 pagesGrade 10 - SCIENCE: Learning Activity Sheet No.4 Quarter 4 Week 7-8Dominic PalapuzNo ratings yet
- DLPDocument2 pagesDLPEldie Ocariza100% (1)
- Unpacked Melc Science 9Document1 pageUnpacked Melc Science 9Marjorie Brondo100% (1)
- Science 10 Quarter 1 Performance Task No. 1: Differentiated Performance TaskDocument3 pagesScience 10 Quarter 1 Performance Task No. 1: Differentiated Performance TaskJunard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 1Document13 pagesScience 8 Module 1FATE OREDIMONo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q3 Week 6Document13 pagesScience 9 Q3 Week 6Mervin LudiaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 9-3rd WeekDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Grade 9-3rd WeekJohnRenzoMolinar100% (1)
- Gutad HS Lesson Exemplar G7-8-9-10Document20 pagesGutad HS Lesson Exemplar G7-8-9-10HajjieCortezNo ratings yet
- DLP Q3 Demo - Gen Bio2 Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument3 pagesDLP Q3 Demo - Gen Bio2 Mechanisms of EvolutionErlyn Joy Agum VerdeNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter DLP in Science 10Document28 pages1st Quarter DLP in Science 10yamikoNo ratings yet
- Activities For Grade 9Document6 pagesActivities For Grade 9Richelle100% (1)
- Learning Plan in Science Grade Level: 9 Quarter: 1Document14 pagesLearning Plan in Science Grade Level: 9 Quarter: 1Chin CustodioNo ratings yet
- Most and Least Learned Skills/Competencies: Potrero High SchoolDocument1 pageMost and Least Learned Skills/Competencies: Potrero High SchoolRosita CayananNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For Grade 8 Quarter 2, SCIENCEDocument2 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan For Grade 8 Quarter 2, SCIENCEQueenindira MolinyaweNo ratings yet
- DLL July 15-19, 2019Document4 pagesDLL July 15-19, 2019ROdney BArbaNo ratings yet
- TOS-G8 FORCE MOTION AND ENERGY (1st Grading) .Docx Version 1Document6 pagesTOS-G8 FORCE MOTION AND ENERGY (1st Grading) .Docx Version 1Kimberly Sumbillo MonticalboNo ratings yet
- Sen. Gil Puyat National High School: Email AddDocument5 pagesSen. Gil Puyat National High School: Email AddRaymond BugagaoNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 9Document3 pagesDLL Science 9Belinda LapsitNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionapi-511024079No ratings yet
- DLL Oersted's DiscoveryDocument27 pagesDLL Oersted's DiscoveryHelen Grace Llemos CabalagNo ratings yet
- Science ReflectionDocument2 pagesScience Reflectionapi-280789569No ratings yet
- MELCS UnpackingDocument2 pagesMELCS UnpackingTawagin Mo Akong Merts100% (5)
- MELCS Unpacking2Document2 pagesMELCS Unpacking2Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- RDT RESULTS IN Science 9Document3 pagesRDT RESULTS IN Science 9Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Feeding ProgramDocument1 pageFeeding ProgramTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Certification: Department of Education Schools Division of Zambales Sto. Rosario Integrated SchoolDocument1 pageCertification: Department of Education Schools Division of Zambales Sto. Rosario Integrated SchoolTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- PST - Module 8 - Career Stage 2 JEL OutputDocument3 pagesPST - Module 8 - Career Stage 2 JEL OutputTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Proposal Community-PantryDocument2 pagesProposal Community-PantryTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- eDITABLE tEMPLATEDocument1 pageeDITABLE tEMPLATETawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- DM No. 233 S. 2022 Web Content Management Using WordPress Training Program 7Document12 pagesDM No. 233 S. 2022 Web Content Management Using WordPress Training Program 7Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- ET Module 1aDocument32 pagesET Module 1aTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- LESSON-PLANDocument15 pagesLESSON-PLANTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- New AwardDocument1 pageNew AwardTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- School History (SRIS)Document6 pagesSchool History (SRIS)Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Kaunlaran High School K-12 T.L.E. Exploratory Course (Electricity) Project Plan - (Making An Extension Cord)Document2 pagesKaunlaran High School K-12 T.L.E. Exploratory Course (Electricity) Project Plan - (Making An Extension Cord)Tawagin Mo Akong Merts100% (1)
- Masinloc District ICT Infra PPA 2021 2022Document2 pagesMasinloc District ICT Infra PPA 2021 2022Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles and Inventories Teacher Resource: 1. Perceptual Modality DescriptionsDocument4 pagesLearning Styles and Inventories Teacher Resource: 1. Perceptual Modality DescriptionsTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Home - School Agreement 2014Document2 pagesHome - School Agreement 2014Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Letter of IntroductionDocument1 pageLetter of IntroductionTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Some Myths & Misconceptions About (College) Education: 1) Education Credit Hours/DiplomaDocument3 pagesSome Myths & Misconceptions About (College) Education: 1) Education Credit Hours/DiplomaTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Home - School Agreement 2014Document2 pagesHome - School Agreement 2014Tawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Pink Certificate of RecognitionDocument3 pagesPink Certificate of RecognitionTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Core Skills For DepEd StaffDocument4 pagesCore Skills For DepEd StaffTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Sample TemplateDocument3 pagesSample TemplateTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Content Standard: Most Essential Learning CompetencyDocument6 pagesContent Standard: Most Essential Learning CompetencyTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of Submission of FormsDocument1 pageEfficiency of Submission of FormsTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- Sample LNGDocument1 pageSample LNGTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- School HistoryDocument1 pageSchool HistoryTawagin Mo Akong MertsNo ratings yet
- PNAPDocument79 pagesPNAPYu chung yinNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Factors in LearningDocument3 pagesCognitive Factors in LearningNad DeYnNo ratings yet
- Pashchimanchal Campus: Set ADocument1 pagePashchimanchal Campus: Set AAnonymous uTC8baNo ratings yet
- Kompilasi Soal Paket BDocument10 pagesKompilasi Soal Paket Babdul wahidNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6Document6 pagesCase Study 6Shaikh BilalNo ratings yet
- Scenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Document7 pagesScenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Tyson RuvengoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For MDocument22 pagesQuestion Bank For MchinnnababuNo ratings yet
- H-Beam Catalogue JindalDocument4 pagesH-Beam Catalogue JindalVikram DalalNo ratings yet
- What Is System and Subsystem? What Is Its Relationship?Document6 pagesWhat Is System and Subsystem? What Is Its Relationship?Mulugeta kinde100% (1)
- Bba-Mq Tias 2023-24Document2 pagesBba-Mq Tias 2023-24Chris PresleyNo ratings yet
- Pink & Green Colorful Vintage Aesthetic Minimalist Manhwa Interior Decor Illustration Work From Home Basic PresentationDocument221 pagesPink & Green Colorful Vintage Aesthetic Minimalist Manhwa Interior Decor Illustration Work From Home Basic PresentationHứa Nguyệt VânNo ratings yet
- Deguzman Vs ComelecDocument3 pagesDeguzman Vs ComelecEsnani MaiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Int Unit 3aDocument2 pagesPre-Int Unit 3aKarla Chong Bejarano0% (1)
- Questão 13: Technology Anticipates Fast-Food Customers' OrdersDocument3 pagesQuestão 13: Technology Anticipates Fast-Food Customers' OrdersOziel LeiteNo ratings yet
- Avila-Flores Etal 2017 - The Use of The DPSIR Framework To Estimate Impacts of Urbanization On Mangroves of La Paz BCSDocument13 pagesAvila-Flores Etal 2017 - The Use of The DPSIR Framework To Estimate Impacts of Urbanization On Mangroves of La Paz BCSKriistian Rene QuintanaNo ratings yet
- H2S Personal Gas MonitorDocument14 pagesH2S Personal Gas Monitormaher mansiNo ratings yet
- Name and Logo Design Contest For Public Wi-Fi Network Services Terms & ConditionsDocument2 pagesName and Logo Design Contest For Public Wi-Fi Network Services Terms & ConditionsAc RaviNo ratings yet
- 1 MergedDocument81 pages1 MergedCHEN XIAN YANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Magellan 8300Document540 pagesMagellan 8300Fleming AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Autodesk 2016 Product Keys 1Document3 pagesAutodesk 2016 Product Keys 1EfrEn QuingAtuñaNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Tree Vegetation of Rajasthan, India: Tropical Ecology September 2014Document9 pagesDiversity of Tree Vegetation of Rajasthan, India: Tropical Ecology September 2014Abdul WajidNo ratings yet
- Sokkia MagnetDocument9 pagesSokkia Magnetbbutros_317684077No ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Teaching Learning 1Document4 pagesQuestionnaire On Teaching Learning 1Sonia Agustin100% (1)