Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asexual Repro
Uploaded by
Kurt Gabriel LopezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asexual Repro
Uploaded by
Kurt Gabriel LopezCopyright:
Available Formats
REPRODUCTION: b.
Layering
THE CONTINUITY OF LIFE - In layering a shoot of a parent plant is bent
until it can be covered by soil. The tip of the
Two Modes of Reproduction
shoot remains above ground. New roots and
Asexual
Sexual Reproduction eventually a new plant will grow. These plants
Reproduction
can then be separated.
- A new individual is - Is a mode of
produced from a reproduction that
2. Budding
single parent. involves two parents.
It is a process wherein a new individual is
formed through formation of a bud, in which in
ASEXUAL Reproduction
time splits off from the parent and develops
Asexual Reproduction is the formation
into anew individual.
of new individuals from a single parent.
Example: Hydra sp.
The new individual formed is identical
to its parent.
3. Fragmentation
Parents passes the precise copy of its In this form of asexual reproduction, the body
own genetic make up to the offspring. of the parent breaks into distinct pieces, each of
Most common in Plants, Fungi, Bacteria which develops into a new individual.
and Microbes, and lower forms of Example: Planaria
animals. Regeneration
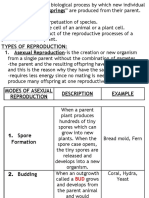
Types of Asexual Reproduction? In this form of asexual reproduction, if a
1. Vegetative Propagation piece of a parent becomes detached, it
2. Budding can grow and develop into a completely
3. Fragmentation new individual
4. Fission Example: Starfish
5. Spore Formation
1. Vegetative Propagation 4. Fission
• It is a common asexual method of It is a process wherein the body divides into two
reproduction in plants. (binary fission) or into many fragments
• The roots, stem & leaves of a plant are (multiple fission) and which are the exact clones
“special vegetative structures” that of the parent.
naturally give rise to a new plant. Example: Bacteria like Chlamydia and
Examples: Rickettsia
Stem: Strawberries 5. Spore Formation
Roots: Sweet Potato Common among fungi and simple plants like
Leaves: Katakataka mosses and ferns. A spore contains haploid cells
enclosed in a thick case and held together by a
Artificial Vegetative Propagation structure called sporangium. Spores are light
a. Grafting and can easily be dispersed by wind from one
- In grafting 2 plants are used to develop a new place to another. Upon maturation, the
plant with combined traits from the 2 parent sporangium burst and releases the spores. The
plants. In grafting the scion is the above ground spores germinate into new individuals as they
part of one plant. The scion is attached to land on an environment with favorable
the stock which is the rooted part of the second conditions.
plant. Example: Fungi, Mosses
You might also like
- All Orisha & Palo HerbsDocument17 pagesAll Orisha & Palo HerbsMuurish Dawn100% (2)
- Biology Handbook Class 12Document235 pagesBiology Handbook Class 12Michael John100% (3)
- Bonsai Tips PDFDocument53 pagesBonsai Tips PDFtop20% (1)
- Asexual ReproductionDocument20 pagesAsexual ReproductionAxestetikriey HalesNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.5 - Types of ReproductionDocument25 pagesTopic 2.5 - Types of Reproductionbienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- Types of ReproductionDocument18 pagesTypes of ReproductionCharm VergaraNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesGeneral Biology 2 (4 Quarter) : Animal and Plant Reproductionamethyst grande100% (1)
- Native Invasives Worksheet With AnswersDocument5 pagesNative Invasives Worksheet With Answersapi-508447935No ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson: ReproductionDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Lesson: ReproductionJoedelyn Wagas100% (1)
- General Biology 2Document33 pagesGeneral Biology 2Treshia Jazmin EguinNo ratings yet
- Science Module 4A-CDocument10 pagesScience Module 4A-CRachelle Garobo BisaNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesLesson 7 - Asexual ReproductionAbegail HernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - SCIENCEDocument18 pagesModule 3 - SCIENCEGian HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Y10 Reproduction TeacherDocument143 pagesY10 Reproduction Teachervijayp22No ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 12Document16 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 12megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesREPRODUCTIONElisa EstebanNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument16 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproducePetrichorNo ratings yet
- Bio Plant ReproDocument3 pagesBio Plant ReproPriya MalpaniNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument35 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduceanmolchandravanshi15No ratings yet
- How Do Organism ReproduceDocument40 pagesHow Do Organism ReproduceNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- OneShot - How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument84 pagesOneShot - How Do Organisms ReproduceMuskan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science: ReproductionDocument9 pagesGrade 7 Science: ReproductionJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction Presentation by Arnav Raj X-CDocument14 pagesAsexual Reproduction Presentation by Arnav Raj X-CArnav RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1reilyshawnNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument10 pagesAsexual Reproduction1445800No ratings yet
- How Do Organism Reproduce (PW)Document42 pagesHow Do Organism Reproduce (PW)Rahul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Notes of ReproductionDocument17 pagesNotes of ReproductionShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Reproduction in OrganismDocument11 pagesCh-1 Reproduction in OrganismNEERU JINDALNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesTypes of Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual ReproductionMarievic DavidNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction - GR 8Document23 pagesAsexual Reproduction - GR 8AmmuNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction - GR 8Document23 pagesAsexual Reproduction - GR 8AmmuNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument28 pagesAsexual ReproductionAntonio BulaonNo ratings yet
- 11 HUMSS ELS PERPETUATION OF LIFE 5as LPDocument9 pages11 HUMSS ELS PERPETUATION OF LIFE 5as LPNOVIE JOY HONTIVEROSNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductioniancyrillvillamer10No ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce X-1 PDFDocument97 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce X-1 PDFPooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesDocument11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce NotesPlayer dude65No ratings yet
- Science G7 Q2 W5 MODDocument8 pagesScience G7 Q2 W5 MODAveCorpuz BioCornerNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 ReproductionDocument19 pagesWEEK 4 Reproductionbalikanalovemissnakita23No ratings yet
- Asex UAL Repr Oduc Tion Revie W Shee T: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesAsex UAL Repr Oduc Tion Revie W Shee T: ObjectivesjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesDocument8 pages8 How Do Organisms Reproduce NotesBurhaan MalikNo ratings yet
- Week 6 (A) BiologyDocument5 pagesWeek 6 (A) BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Gen. BIO 2 Module 1Document8 pagesGen. BIO 2 Module 1faithmartin616No ratings yet
- Multiple Assessmen T-2: Topic - Asexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesMultiple Assessmen T-2: Topic - Asexual ReproductionManogya JainNo ratings yet
- Asexually ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexually ReproductionKhor KiNo ratings yet
- Bab 38Document4 pagesBab 38Manoj ParidaNo ratings yet
- General Biology II: Compare and Contrast: Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology II: Compare and Contrast: Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsJoanna LapuzNo ratings yet
- Fission: 1. The Splitting of An Unstable Atomic Nucleus Into Two or More NucleiDocument6 pagesFission: 1. The Splitting of An Unstable Atomic Nucleus Into Two or More NucleiSelwyn Moya MadronaNo ratings yet
- Puc II Biology Notes (Ncert) SiddagangaDocument179 pagesPuc II Biology Notes (Ncert) Siddagangasumangalabavannavar67No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 AEXUAL REPRODUCTION UpdatedDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 8 AEXUAL REPRODUCTION UpdatedElite PaladinNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesReproduction in PlantsArvind KotagiriNo ratings yet
- Biology PDFDocument344 pagesBiology PDFUrmilaAnantNo ratings yet
- CH 8 - Asexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesCH 8 - Asexual ReproductionDivyansh JhaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument5 pagesReproduction in OrganismsRenuNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Perpetuation of Life (Autosaved)Document38 pagesWeek 3 Perpetuation of Life (Autosaved)SANTIAGO, David Joshua B.No ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument56 pagesAsexual Reproduction in Plantsamulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument1 pageHow Do Organisms ReproduceRK KreedaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500 Basic Education Unit Iso CertifiedDocument34 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500 Basic Education Unit Iso CertifiedElliah Joy AcioNo ratings yet
- Reproduction - Docx 4Document1 pageReproduction - Docx 4Peter Gabriel EdrosolanoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument23 pagesREPRODUCTIONEA CatalanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction, A Characeristic of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesReproduction, A Characeristic of Living ThingspilarmdNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Document11 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Varshini PeraNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- English Language Year 2 Paper 013 (Pemahaman) 2016Document10 pagesEnglish Language Year 2 Paper 013 (Pemahaman) 2016Patrick TawieNo ratings yet
- Where and How Ranunculus Grow Best: R. AsiaticusDocument1 pageWhere and How Ranunculus Grow Best: R. AsiaticusLivia BârsanNo ratings yet
- Tomatoes: (Lycopersicon Esculentum)Document13 pagesTomatoes: (Lycopersicon Esculentum)hainy09No ratings yet
- Rajat Seminaar FinalDocument58 pagesRajat Seminaar Finalrajat sharmaNo ratings yet
- ST Joseph's Institution (Senior School) IBDP1 HL Biology PracticalDocument5 pagesST Joseph's Institution (Senior School) IBDP1 HL Biology PracticalSean NgNo ratings yet
- 0610 w09 Ms 6Document6 pages0610 w09 Ms 6Fayeed Ali RassulNo ratings yet
- Double Fertilization - WikipediaDocument27 pagesDouble Fertilization - WikipediaNaniNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Notes Class 10Document4 pagesTranspiration Notes Class 10proodootNo ratings yet
- Sample PDF of STD 7th General Science Notes English Medium Maharashtra BoardDocument20 pagesSample PDF of STD 7th General Science Notes English Medium Maharashtra BoardVarsha. ShirkeNo ratings yet
- Steamy Jungle SexDocument5 pagesSteamy Jungle SexEmil KolomparNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Macroeconomics in Modules 3rd Edition Krugman Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument32 pagesInstant Download Macroeconomics in Modules 3rd Edition Krugman Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterJoseOrrksey100% (8)
- Mesta 1.0Document5 pagesMesta 1.0Sharath.H sharuNo ratings yet
- Cycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisDocument9 pagesCycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisTers MedinaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Propagation by InarchingDocument8 pagesAsexual Propagation by Inarchingdelbert sonsonaNo ratings yet
- Plants of The Okefenokee SwampDocument2 pagesPlants of The Okefenokee SwampKay StephensonNo ratings yet
- Biomex Starter Horticulture Single Page PDFDocument2 pagesBiomex Starter Horticulture Single Page PDFAl- ImanuddinNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual - Crop DiseasesDocument82 pagesPractical Manual - Crop DiseasesPrakash Kumar Kumar86% (7)
- Plant KingdomDocument7 pagesPlant Kingdomchannel of dhyanaNo ratings yet
- Classical Review On MundiDocument12 pagesClassical Review On MundiPavel PeresypkinNo ratings yet
- Bio 133 Exercises 5-6Document14 pagesBio 133 Exercises 5-6Vhey CasisonNo ratings yet
- Seed Propagation of Arisaema Sikokianum AraceaeDocument5 pagesSeed Propagation of Arisaema Sikokianum AraceaeMick TalbotNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Class 10Document15 pagesTranspiration Class 10shreya morajkarNo ratings yet
- Weed Book - 060824Document32 pagesWeed Book - 060824cliffordmsndNo ratings yet
- Telipogon UribeveleziiDocument7 pagesTelipogon UribeveleziirpsauledaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Edexcel 5 2 Reproduction in Flower PDFDocument27 pagesIGCSE Edexcel 5 2 Reproduction in Flower PDFwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Grade.8 Ch.6 L.4 Review: BY Moshera SowarDocument7 pagesGrade.8 Ch.6 L.4 Review: BY Moshera SowarHano MohdNo ratings yet
- Awesome Plants For Dry Times: Featured by Suncrest Nurseries, IncDocument26 pagesAwesome Plants For Dry Times: Featured by Suncrest Nurseries, Incapi-291931154No ratings yet