Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Carbohydrate Metabolism and Its Regulation
Uploaded by
Angela CastrilloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Understanding Carbohydrate Metabolism and Its Regulation
Uploaded by
Angela CastrilloCopyright:
Available Formats
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM PART 1 ■ Alteration in allosteric
factors
What is metabolism? ● Intercellular Communication
● Totality of chemical reactions in an ○ Between cells
organism ○ Slower response
● Composed of metabolic pathways ○ Types of Signaling:
■ Synaptic - neurotransmitter
Two Types of Metabolic Pathways → target cell
● Anabolism ■ Endocrine - hormones →
○ Synthetic target cell
○ Monomers → Polymers ■ Direct Contact - cell surface
○ Consumes energy (ATP) → target cell surface
○ Reductive ( NADH & NADPH) ● Secondary Messenger
● Catabolism ○ Neurotransmitters and hormones
○ Degradative act on receptors
○ Polymers → Monomers ○ Secondary messenger receptor
○ Releases energy (ATP)
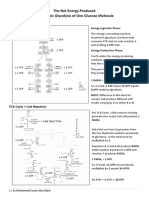
○ Oxidative (NAD+) Glycolysis
● Breaks down glucose
● Occurs in the cytoplasm
● Net Products per 1 Glucose:
○ 2 Pyruvate
○ 2 NADH
○ 2 ATP
● Stages:
○ Energy-investment phase
○ Energy payoff phase
Substrate Product Enzyme and
(Cofactor)
Stages of Catabolism 1. Glucose * G-6-P Hexokinase
(Mg²⁺)
1. Hydrolysis of complex molecules
2. Conversion of building blocks to simple 2. G-6-P F-6-P Phosphohexose
intermediates or Acetyl CoA Isomerase
3. Oxidation of Acetyl CoA which generates
ATP via oxidative phosphorylation 3. F-6-P * F-1,6-BP PFK-1 (Mg²⁺)
4. F-1,6-BP G-3-P Aldolase
Regulation of Metabolism
● Use to meet cellular needs 5. G-3-P DAP TPI
● Intracellular Communication
○ Within the cell 6. G-3-P 1,3-BPG G-3-PD (Mg²⁺)
○ Rapid response
7. 1,3-BPG 3-PG PGK (Mg²⁺)
○ Rate of reaction is influenced by:
■ Availability of substrate 8. 3-PG 2-PG PGM
■ Product inhibition
9. 2-PG PEP Enolase (Mg²⁺)
Electron Transport Chain
10. PEP * Pyruvate PK (Mg²⁺) ● Complex I: NADH Dehydrogenase
○ Rotenone amytal - blocks electron
* = Irreversible transfer from Complex 1 to CoQ
○ Removes H in NADH
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase ● Complex II: Succinate Dehydrogenase
● Transforms pyruvate to Acetyl CoA ○ Removes H from succinate
● 3 enzyme complex ○ Observed in kreb’s cycle
● Five Coenzymes: ● Complex III: Ubiquinone - Cytochrome C
○ Lipoic acid Oxidoreductive
○ Thiamine ○ Coenzyme Q transfers electrons
○ FAD from Complex II to III
○ NAD ○ Antimycin A - blocks electron
○ Coenzyme A transfer with complex III
● Complex IV: Cytochrome Oxidase
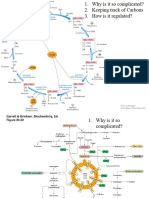
Kreb’s Cycle ○ Chemiosmotic Theory - H+
● Also called TCA or citric acid cycle gradient drives ATP Synthesis
● Amphibolic
● Product per 1 Pyruvate: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM PART 2 AND
○ 3 NADH₂ SPECIAL PRODUCTS OF CARBOHYDRATES
○ 1 FADH
○ 1 GTP Fates of Pyruvate
○ 2 CO₂ ● Kreb’s cycle
● Gluconeogenesis
● Anaerobic respiration
Substrate Product Enzyme ● Fermentation
1. Acetyl CoA Citrate Citrate
& oxaloacetate Synthase Anaerobic Respiration
● Occurs in the lack of O₂
2. Citrate Isocitrate Aconitase ● Converts pyruvate to lactate
● Uses LDH as enzyme
3. Isocitrate * AKG Isocitrate
● Present in anaerobic organisms
Dehydrogenase
● Takes place in poorly vascularized tissues
4. AKG Succinyl AKGD complex and RBC
CoA
Ethanol Fermentation
5. Succinyl Succinate Succinate ● Occurs in yeast and other microorganisms
CoA Thiokinase
● Converts pyruvate to acetaldehyde to
6. Succinate Fumarate Succinate ethanol
Dehydrogenase ● Uses pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol
dehydrogenase as enzyme
7. Fumarate Malate Fumarase
Gluconeogenesis
8. Malate Oxaloaceta Malate
te Dehydrogenase ● Creation of new glucose from
non-carbohydrate sources
* = Irreversible
● Provides constant glucose supply needed
1. Glycogen G-1-P Glycogen
for human life (brain and RBC) Phosphorylase
● Constant but slow, is done when glycogen
is depleted 1.2. G-1-P Reduction of Debranching
● Takes place in the kidney, liver, and Steric Enzyme
intestines Hindrance
● Non-carbohydrate precursors:
2. G-1-P G-6-P Phosphogluco
○ Glycerol mutase
■ Glycerol → G3P → DHAP
→ F-1,6-BP → Glucose 3. G-6-P Glucose G-6-P
○ Lactate (Cori Cycle) Translocase
■ Lactate → Pyruvate → and
Glucose Phosphatase
○ Glucogenic Amino Acid
■ Glucogenic Amino Acid → Lysosomal Degradation
Pyruvate → Glucose ● Lysosomal Acid α(1→4) Glucosidase
○ Only degrades small amounts
Pyruvate Carboxylation ○ Deficiency can lead to disease
● Uses mitochondrial enzymes
○ Pyruvate carboxylase Glycogen Storage Disease
■ Pyruvate → Oxaloacetate
■ Uses ATP and vitamin B7 Type Deficient Symptoms
(biotin) as a cofactor Enzyme
○ PEP Carboxykinase
■ Oxaloacetate → PEP 0 Glycogen - ↓ Blood
■ Uses GTP Synthase Glucose
- Early Death
F 1,6 BP Dephosphorylation Ia - Von G-6- - Enlarged
● Regulation point for gluconeogenesis Gierke Phosphatase Liver
● F-1,6-BP → F-6-P - Kidney Failure
G-6-P Dephosphorylation Ib G-6-P - Enlarged
● Yields 6 ATP and 2 NADH for every Translocase Liver
- Kidney Failure
glucose from 2 pyruvates
● G-6-P → Glucose II - Pompe Lysosomal - Myopathy
Acid
Glycogen Metabolism - occurs in the liver and
muscles III - Cori Debranching - Enlarged
Enzyme Liver
- Myopathy
Glycogenesis
● Breakdown of glycogen to glucose for IV - Branching - Enlarged
energy Andersen Enzyme Liver & Spleen
● Occurs in the liver and muscles - Myoglobinuria
V - McArdle Muscle - Exercise
Substrate Product or Enzyme Glycogen Induced Cramp
Result Phosphorylase - Myoglobinuria
VI - Hers Liver Glycogen - Enlarged Substrate Product Enzyme and
Phosphorylase Liver (Cofactor)
VII - Tarui Muscle PFK-1 - Exercise 1. G-6-P 6- G-6-P
Induced Cramp Phosphogluc Dehydrogenase
- Myoglobinuria onolactone
2. 6 - 6- Gluconolactona
Blood Glucose Control Phosphogluc Phosphogluc se
● Insulin onolactone onate
○ β cells of pancreatic islets of
Langerhans 3. 6 - Ribulose-5- 6-
○ Release: Fed State Phosphogluc Phosphate Phosphoglucon
onate ate
○ Lowers blood glucose level
Dehydrogenase
● Glucagon
○ α cells of pancreatic islets of
Langerhans Glucose-6-Biphosphate Dehydrogenase
○ Release: Fasted State Deficiency
○ Increases blood glucose level ● Most common disease-producing enzyme
abnormality
● Example: Heinz Bodies - oxidative
damage in hemoglobin
Insulin Glucagon
F-6-BP ↓ ↑ Endogenous Heteropolysaccharide
● Glycosaminoglycan
Glycogen Activate Inactivate ○ Mucopolysaccharide
Synthase ○ Long, unbranched, (-) charged
○ Has a gel-like matrix found in:
Glycogen Inactivate Activate
Phosphorylase ■ ECM
■ Synovial Fluid
■ Vitreous Humor
Pentose Phosphate Pathway ● Proteoglycans
● Also known as Hexose Monophosphate ○ Protein + Glycosaminoglycan
Shunt ○ Found in connective tissues
● Has two phases: ● Glycoprotein
○ Oxidative phase ○ Protein + Oligosaccharide
○ Non-oxidative sugar phosphate ○ Associated with:
interconversion ■ Cell Surface Recognition
● Does not consume or produce ATP ■ Cell Surface Antigenicity
● Produces NADPH used for: ■ Extracellular Matrix
○ Glutathione Reduction ■ Mucins
○ FA Synthesis
○ Cholesterol Synthesis LIPID METABOLISM
● Product per 1 G-6-P molecule:
○ 2 NADPH Lipids
○ 1 Ribulose-5-Phosphate ● Heterogenous group
● Functions:
○ Energy
○ Barrier for partition
○ Regulatory
○ Homeostasis
● Water-insoluble organic molecule
● Usually associated with protein
Initial Digestion of Lipids
You might also like
- Jonathan Rauch - Can Frankenfood Save The PlanetDocument8 pagesJonathan Rauch - Can Frankenfood Save The Planettaxidriver32No ratings yet
- BIO121 Chapter 7 Releasing Chemical EnergyDocument45 pagesBIO121 Chapter 7 Releasing Chemical EnergyggttettanNo ratings yet
- 282-002 Syllabus-S2012Document6 pages282-002 Syllabus-S2012Randy Santiago TorresNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and mineralDocument8 pagesVitamin and mineralhobbycontestsNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration (Glycolysis) NotesDocument8 pagesAerobic Respiration (Glycolysis) Noteslaiyinah 09No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Energy Management in PlantsDocument37 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Energy Management in PlantsGilang Satya ArdhanaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument72 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismJeffson BalmoresNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria & Chloroplasts: Structures & FunctionsDocument40 pagesMitochondria & Chloroplasts: Structures & FunctionsrandelNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMICAL PATHWAYSDocument38 pagesBIOCHEMICAL PATHWAYSMarja Shania Galido RañolaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument53 pagesRespirationdhaka20poonamNo ratings yet
- 4 Cell RespirationDocument16 pages4 Cell RespirationbeyonduckNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Biological Oxidation 2: Biochemistry: Shift 1 - Trans 4Document9 pagesBioenergetics and Biological Oxidation 2: Biochemistry: Shift 1 - Trans 4Gemay DanglayNo ratings yet
- ASB0204 Chap 7 - CidDocument42 pagesASB0204 Chap 7 - CidZulhelmiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Week 2Document38 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Week 2shadaalnaas657No ratings yet
- Glycolysis Ch.14Document51 pagesGlycolysis Ch.14Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 How Drugs Act Molecular AspectsDocument82 pagesLecture 3 How Drugs Act Molecular AspectsAuthor Nauman ShadNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument37 pagesGlycolysistalal adlanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 1Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- C12 Energy and Respiration_redactedDocument96 pagesC12 Energy and Respiration_redactedDevRushi VyasNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: The 3 Stages of GlycolysisDocument11 pagesGlycolysis: The 3 Stages of Glycolysismaiang23No ratings yet
- Nucleat Acid MetabolismDocument31 pagesNucleat Acid MetabolismSilvia UsmaniaNo ratings yet
- BIOL10009 Biology Extension ActivitiesDocument17 pagesBIOL10009 Biology Extension Activitieslwekdl wdjlkjNo ratings yet
- 05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and MoreDocument21 pages05 Cell Respiration Fermentation Anaerobic and MoreneelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell & Molecular Biology: Cellular Respiration (II) Photosynthesis (I)Document13 pagesIntroduction To Cell & Molecular Biology: Cellular Respiration (II) Photosynthesis (I)Puron RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Textbook SummaryDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Textbook SummaryshinymaterialsNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and NutritionDocument52 pagesMetabolism and NutritionAlex SaljayNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument41 pagesCellular Respirationrufino delacruzNo ratings yet
- Glucose Energy CalculationDocument2 pagesGlucose Energy CalculationMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDocument40 pagesLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- CHO L5 (Gluconeogenesis) 2020-2021Document20 pagesCHO L5 (Gluconeogenesis) 2020-2021Sara AljadaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Resp Gen Bio Notes Grade 11Document4 pagesCell Resp Gen Bio Notes Grade 11Megan RyanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Pyruvate (3C) Pyruvate (3C)Document4 pagesCellular Respiration: Pyruvate (3C) Pyruvate (3C)rifka fakhiraNo ratings yet
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocument26 pagesHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNo ratings yet
- Botany - RespirationDocument17 pagesBotany - RespirationAira Germaine TanganNo ratings yet
- Botany - RespirationDocument17 pagesBotany - RespirationAira TanganNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Cellular Respiration CompleteDocument31 pagesCH 7 Cellular Respiration CompleteWilly WonkaNo ratings yet
- Cell RespiDocument30 pagesCell Respi11009911No ratings yet
- Metabolism of Nucleotid-$Document74 pagesMetabolism of Nucleotid-$Saad AliNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration (8.2) : Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain or OIL RIGDocument12 pagesCell Respiration (8.2) : Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain or OIL RIGRocio Guadalupe Lopez BlandonNo ratings yet
- Enzymes CC LecDocument4 pagesEnzymes CC LecGian Franco ApesNo ratings yet
- METABOLISMDocument11 pagesMETABOLISMking untalanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Intermediate Exam Short Answers & CasesDocument14 pagesBiochemistry Intermediate Exam Short Answers & CasesMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: By:-Dr - Priyanka Sharma 1 Year MDS Dept. of Public Health DentistryDocument93 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: By:-Dr - Priyanka Sharma 1 Year MDS Dept. of Public Health DentistrySimham Venu0% (1)
- Understanding Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument48 pagesUnderstanding Metabolism of CarbohydratesAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheets - CK and CKMBDocument1 pageLab Sheets - CK and CKMBJilianne SablotNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument12 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismRohan PackiarajNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoADocument30 pagesCell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoAJ15No ratings yet
- 10 Metabolisme MikrobiaDocument51 pages10 Metabolisme MikrobiaHastomo Nur HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Juan de LetranDocument9 pagesColegio de San Juan de Letranking untalanNo ratings yet
- Debanjana Chakraborty 2 Semester MSC BiotechnologyDocument20 pagesDebanjana Chakraborty 2 Semester MSC Biotechnologydebanjana2009No ratings yet
- biochemistryDocument33 pagesbiochemistryochotpremNo ratings yet
- Amphibolic PathwaysDocument29 pagesAmphibolic Pathwayskiran kombeNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument24 pagesCellular RespirationMELISSA MORENONo ratings yet
- Metabolism Week 8 ReviewDocument64 pagesMetabolism Week 8 ReviewZain Hafeez-BaigNo ratings yet
- ADP ATP and Cellular RespirationDocument128 pagesADP ATP and Cellular RespirationLeona Trinity AranasNo ratings yet
- MSB 202: Neurolocomotor: Neurotransmitters - Overview of Metabolism (Anabolism and Catabolism)Document42 pagesMSB 202: Neurolocomotor: Neurotransmitters - Overview of Metabolism (Anabolism and Catabolism)Jacob MasikaNo ratings yet
- 9 Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle-S PDFDocument8 pages9 Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle-S PDFmadhavi goswamiNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument35 pagesGlycolysisAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Viii - Carbohydrates MechanismDocument34 pagesChapter Viii - Carbohydrates MechanismAngelo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument40 pagesCellular RespirationmsmimeeyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Fermentation 1Document29 pagesCellular Respiration Fermentation 1Lorraine LibioNo ratings yet
- Glycoconjugate Research: Proceedings of the Interior Symposium on GlycoconjugatesFrom EverandGlycoconjugate Research: Proceedings of the Interior Symposium on GlycoconjugatesNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lab Learning Module 2 PDFDocument14 pagesMicrobio Lab Learning Module 2 PDFAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- QC Learning Module 1 PDFDocument4 pagesQC Learning Module 1 PDFAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Dispensing Lab 1-4Document2 pagesDispensing Lab 1-4Angela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- QC Learning Module - Neutralization MethodDocument2 pagesQC Learning Module - Neutralization MethodAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Castrillo - Midterms Collaborative Notes - 10202020 PDFDocument2 pagesCastrillo - Midterms Collaborative Notes - 10202020 PDFAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Castrillo - Introduction To Ayurveda - Asynchronous Notes PDFDocument2 pagesCastrillo - Introduction To Ayurveda - Asynchronous Notes PDFAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- PH-PHR-215 - Microbio Lecture Midterm NotesDocument12 pagesPH-PHR-215 - Microbio Lecture Midterm NotesAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Castrillo - Introduction To Ayurveda - Asynchronous Notes PDFDocument2 pagesCastrillo - Introduction To Ayurveda - Asynchronous Notes PDFAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Castrillo - Midterms Collaborative Notes - 10202020 PDFDocument2 pagesCastrillo - Midterms Collaborative Notes - 10202020 PDFAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lab Learning Module 1-2Document14 pagesMicrobio Lab Learning Module 1-2Angela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- PH-PHR-215 - Microbio Lab Module 13-15Document18 pagesPH-PHR-215 - Microbio Lab Module 13-15Angela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lect Module 1-2Document7 pagesMicrobio Lect Module 1-2Angela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Drug Routes of Administration and Dosage FormsDocument5 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Drug Routes of Administration and Dosage FormsAngela CastrilloNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument8 pagesBiology Projectabcd0% (1)
- Pre Final Year and II YearDocument22 pagesPre Final Year and II YearSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Activities (Ecosystem)Document20 pagesActivities (Ecosystem)Rona Carmen LabradorNo ratings yet
- Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of BiosignalingDocument86 pagesMolecular and Cellular Mechanisms of BiosignalingJon QNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Proteins & Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesBiological Molecules: Proteins & Nucleic AcidsKyla Cheyenne BustosNo ratings yet
- Budget-Of-work-gen Bio 1 2nd QTRDocument4 pagesBudget-Of-work-gen Bio 1 2nd QTRAngela Francisca Bajamundi-VelosoNo ratings yet
- Class: Xii Biology Assignment-11 Chapter: 11 Biotechnology: Principles and ProcessesDocument3 pagesClass: Xii Biology Assignment-11 Chapter: 11 Biotechnology: Principles and ProcessesChaithanyaNo ratings yet
- Program 3rd International Symposium Ytrb May 2021Document3 pagesProgram 3rd International Symposium Ytrb May 2021api-376344338No ratings yet
- Veterinary Immunology Principles and Practice, Sec... - (Chapter 2 Antigens and Antibodies)Document12 pagesVeterinary Immunology Principles and Practice, Sec... - (Chapter 2 Antigens and Antibodies)rubydarwin02No ratings yet
- 12 Biotechnology - Applications PPT STUDENTSDocument47 pages12 Biotechnology - Applications PPT STUDENTSPriya Dharshini VNo ratings yet
- Gene TherapyDocument1 pageGene TherapyJenevieve B. CañeteNo ratings yet
- 8 3 PhotosynthesisDocument39 pages8 3 PhotosynthesisKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Effects of Probiotic Metabolites On COVID 19Document11 pagesAntiviral Effects of Probiotic Metabolites On COVID 19Sergio NobreNo ratings yet
- Controlled Drug DeliveryDocument473 pagesControlled Drug DeliveryMET Faculty of PharmacyNo ratings yet
- CMV Cytomegalovirus 04-19-05-EnDocument4 pagesCMV Cytomegalovirus 04-19-05-EnImam Al-DoaibesNo ratings yet
- RNA Extraction: OverviewDocument3 pagesRNA Extraction: OverviewArturo BasantezNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of VirusesDocument24 pagesEconomic Importance of VirusesFakhir Rahmani100% (2)
- VACCINES COVID-19 INVIGORATES A STAGNANT INDUSTRYresDocument22 pagesVACCINES COVID-19 INVIGORATES A STAGNANT INDUSTRYresiyad.alsabiNo ratings yet
- Assesment MultipleDocument4 pagesAssesment MultipleAnn Marjorie GodinNo ratings yet
- Enzymes AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexcelDocument4 pagesEnzymes AS Biology Questions AQA OCR EdexceljanaNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction MethodsDocument22 pagesDNA Extraction MethodsGarshel KellyNo ratings yet
- Bacterial cell wall structures explainedDocument1 pageBacterial cell wall structures explainedamanitaNo ratings yet
- BASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSDocument2 pagesBASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSAnnicoldjohn LariozaNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna DLP 3.0Document8 pagesDna and Rna DLP 3.0HAIDEE VASQUEZNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetics 6Th Edition Snustad Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Genetics 6Th Edition Snustad Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBrettClinewdjc100% (11)
- Lab Manual For Down Stream Process LabDocument31 pagesLab Manual For Down Stream Process LabShaasvath AishvaryaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Snork DNA and TraitsDocument3 pagesAnalyzing Snork DNA and TraitsBrian NguyenNo ratings yet
- Biodata2014 UpdatedDocument34 pagesBiodata2014 UpdatedAwanish MishraNo ratings yet