Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Security Tools Using Sensor Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Through Mobile Phone
Uploaded by
Putra DirgatamaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Security Tools Using Sensor Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Through Mobile Phone
Uploaded by
Putra DirgatamaCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/328759421
DESIGN OF SECURITY TOOLS USING SENSOR LIGHT DEPENDENT RESISTOR
(LDR) THROUGH MOBILE PHONE
Article in International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering · November 2018
CITATION READS
1 2,414
2 authors:
Maharani Putri Solly Aryza Lubis
Universitas Pembangunan Panca Budi Universitas Pembangunan Panca Budi
7 PUBLICATIONS 9 CITATIONS 82 PUBLICATIONS 465 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Quality Assurance in Knowledge Data Warehouse View project
Dikti funding indonesia View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Solly Aryza Lubis on 06 November 2018.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN MULTIDISCIPLINARY FIELD ISSN: 2455-0620 Volume - 4, Issue - 10, Oct – 2018
Monthly, Peer-Reviewed, Refereed, Indexed Journal with IC Value: 86.87 Impact Factor: 6.497 Publication Date: 31/10/2018
DESIGN OF SECURITY TOOLS USING SENSOR LIGHT
DEPENDENT RESISTOR (LDR) THROUGH MOBILE PHONE
Maharani Putri1, Solly Aryza2
Lecture Faculty Science and Technology, University Pembangunan Panca Budi Medan, Indonesia.
Email - sollyaryzalubis@gmail.com
Abstract: Many cases of theft due to lack of security systems contained in the house, this is due to limited costs in
the installation of security systems that generally use CCTV cameras or security systems with a microprocessor
using GSM modem. As a settlement of the high cost of installing this system, it is designed and created a security
tool with the priority of forwarded financing and can work to minimize the possibility of theft cases. This tool works
as a detector in the room, where when there is movement within the house it will be notified to the user about the
situation in the room. This tool uses LDR (light dependent resistor) sensors as a detection of movement in the house
and cellular phone as a tool to inform the user of the tool about the condition of the home circumstances. The
results obtained from the use of this tool is obtained information on the mobile phone user tool when there is
movement on the door the secured space, so that the user of the tool can take action in response to the information
transmitted from the tool.
Keywords: LDR sensor, Op-amplifier, Speed dial.
1. INTRODUCTION.
Changes in the current pattern of human life, much due to the rapid development of technology that many
provide all forms of ease in the use of devices or tools that are directly related to human life [1] . This tool is designed
to ensure the safety of the room can be detected by the user of the tool either while indoors or not in the room. This will
also reduce costs when compared to using the services of security guards and improve the security of a room. In
pengoprasiannya, this tool utilizes the LDR sensor whereas this sensor will detect the movement of the door of the room
through the light it receives [2].
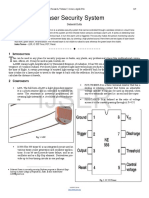
2, LITERATURE REVIEW.
Light
KeySensor
Words:LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) is one type of resistor that can experience changes in resistance
when experiencing changes in light reception. LDR, known by many names: photo-resistor, photo-conductor, photo-
conductive cell, or just photo-cell and which is often used in literature is photo-resistor or photo-cell [3]. The amount of
resistance value on the LDR Light Sensor (Light Dependent Resistor) depends on the size of the light received by the
LDR itself. LDR is often called a device or sensor in the form of resistors that are sensitive to light [4]. Usually LDR is
made of cadmium sulphide which is a semiconductor material whose resistance varies according to the amount of light
(rays) that hit it. Like a conventional resistor, LDR mounting in a circuit is exactly the same as a regular resistor
installation. The LDR symbol can be seen as in the following figure [5].
Figure 1. LDR Sensors and Symbols
2.1 Characteristics
LDR Light Sensor Characteristics (Light Dependent Resistors) The LDR Light Sensor (Light Dependent
Resistor) is a component form that has a change in resistance depending on the amount of light. LDR characteristic
consists of two kinds, namely the Recovery Rate and Spectral Response.
Available online on – WWW.IJIRMF.COM Page 168
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN MULTIDISCIPLINARY FIELD ISSN: 2455-0620 Volume - 4, Issue - 10, Oct – 2018
Monthly, Peer-Reviewed, Refereed, Indexed Journal with IC Value: 86.87 Impact Factor: 6.497 Publication Date: 31/10/2018
2.2. Work principle
The Working Principle of LDR Light Sensor (Light Dependent Resistor) will change with the change of the
intensity of light that surrounds it or the surrounding. In a dark state the LDR resistance is about 10MΩ and in a light
state of 1KΩ or less. LDR is made of semiconductor materials such as cadmium sulphide. With this material the energy
from falling light causes more charge to be released or increased electrical current. This means that the resistance of the
material has decreased [6].
In the dark or dim light, the material from the disk produces free electrons with a relatively small amount. So
there are few electrons to transport the electrical charge. This means that when the light is dim, LDR becomes a bad
conductor, or LDR can also have a great resistance in the dark or dim light. At the bright light, there are more electrons
out of the atom of the semiconductor material. So that will be more electrons to transport the electrical charge. This
means that when the bright light, LDR into a good conductor, or LDR can also have a small resistance during bright
light. When we will set the sensitivity of LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) in a circuit then we need to use potentiometer
[7].
2.3. Photo-Resistor / LDR Mechanism
A Photo-resistor or LDR is a component that uses a photo-conductor between the two pins. When the surface
is exposed to light there will be a change in resistance between them. The mechanism behind the photo-resistor or LDR
is photo-conductivity, that is an event of change in the conductance value of a semiconductor material when the photon
energy from light is absorbed by it. When used as a Photo-resistor or LDR, the semiconductor material is used only as
a resistive element and there is no PN connection. Thus, Photo-resistor or LDR is purely a passive component [8].
2.4. Laser Diodes
In the process of sending light as a source of information for the sensor working system, a laser diode is used
as the light source. The laser diode is one type of diode where the active medium uses a semiconductor with a p-n
junction similar to the LED. Laser diodes are sometimes also abbreviated LD or ILD [2].
Figures 2. Dioda Laser
The laser diode was discovered at the end of this century by Harvard University scientists. The working principle
of this diode is the same as any other diode, that is, through the circuitry of the electronics circuit, which consists of the
terminals p and n. In both terminals are often generated 2 voltages, namely:
charged forward, the current is generated in the direction of the value 0.707 for the division of the peak v, the
waveform above (+).
Back forward biased, this is a reversed voltage that can damage an electronic component.
3. METHODE OF RESEARCH.
Block diagrams are one of the simplest ways to explain how a device works and make it easy to localize errors
from a system. With the block diagram, we can analyze the way the circuit and design the hardware to be made in
general.
A diagram is a sequential relation statement of one or more components that have a separate working entity,
and each component block affects the other components.
Block diagram has a special meaning by providing information in it. For each block is connected to a line
indicating the working direction of each block in question. Here is a block diagram of the room security tool that will
be created.
Available online on – WWW.IJIRMF.COM Page 169
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN MULTIDISCIPLINARY FIELD ISSN: 2455-0620 Volume - 4, Issue - 10, Oct – 2018
Monthly, Peer-Reviewed, Refereed, Indexed Journal with IC Value: 86.87 Impact Factor: 6.497 Publication Date: 31/10/2018
Figure 3. Diagram Block Tools.
In the process of making the tool is done first circuit design using CAD applications, in this case using
eagle.Here is a circuit drawing tool.
Figures 4. The tool circuit scheme.
4. ANALYSIS AND RESULTS.
After designing the circuit and tested on the protoboard board as the first test medium, it can be continued by
designing the PCB board from this tool set. In the design, arranged component layout according to aesthetic elements
and consideration of component functions. In making this PCB path using techniques manually.
Figures 5 . Layout PCB
Available online on – WWW.IJIRMF.COM Page 170
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN MULTIDISCIPLINARY FIELD ISSN: 2455-0620 Volume - 4, Issue - 10, Oct – 2018
Monthly, Peer-Reviewed, Refereed, Indexed Journal with IC Value: 86.87 Impact Factor: 6.497 Publication Date: 31/10/2018
As for the need to be considered in the process of making PCB lines include:
Avoid the formation of the path that menyiku and turn sharp
Try to use the jumper as much as possible
Avoid short links
Make the path as short as possible
The materials and tools used in this PCB manufacturing process are as follows:
Cairan Ferry choloride (Fe2Cl3)
Air (better if there is hot water)
Spidol Permanent
Sand paper
Cutter
Mecin bor
Solder
Tinner
Timah
Cleansing soap
The materials used include:
Resistor (10K,330Ω)
Potensiometer (10K)
Operational Amplifier (IC LM324)
Dioda Laser
LED
Sensor LDR
Handphone seluler
In PCB printing there is often an error in the path, for example the path is disconnected or tangent to other lines.
Therefore, it would be better if the PCB is checked again and corrected if there is an error. The way that can be done in
checking the path is to see the path or by checking with a multimeter. If there is an intersecting path, it can be cut with
a cutter, if one is disconnected, connected by attaching a fine copper with a solder.
Figure 6. Printed PCB
After the inspection and repair process is done, the next step is the installation and soldering of components on
the PCB in accordance with the planned layout.
Available online on – WWW.IJIRMF.COM Page 171
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN MULTIDISCIPLINARY FIELD ISSN: 2455-0620 Volume - 4, Issue - 10, Oct – 2018
Monthly, Peer-Reviewed, Refereed, Indexed Journal with IC Value: 86.87 Impact Factor: 6.497 Publication Date: 31/10/2018
Figure 7.The component installation process
In the process of installation and soldering is done with attention to several things, namely:
Soldering time, done in the not-too-distant future because it is feared to damage paths and heat-sensitive
components.
The use of tin should be kept to a minimum and pay attention to its maturity in the point of connection.
The use of safeguards is made to protect and facilitate the replacement of heat-sensitive components, eg ICs
using socket ICs.
After soldering process, first PCB cleaned from the rest solderan and pasta using tinner. After that, testing the
circuit to test whether the circuit has been running correctly. If the circuit is running, then the next process of assembling
the components into the miniature of the house.
The process carried out in the assembly of the phone is by removing the battery then releasing the front cover
of the button and the next transparent cover over the button.After dismantling the transparent cover over the button, it
will encounter a thin white film in the main terminal. This thin white film is then opened to taste and adjust to the button
that will be used .
Figure 8. Mobile that has been dismantled
The next step is to check the polarity of the button, ie by inserting the battery back into the phone and turning it
on. In this tool, 3 buttons are used for speed dial, therefore simply check the terminals on the button 3. Put the multimeter
on the dc voltage measurement then put the 2 terminal tester on the button and turn the tester position on the terminal
until it is known which one is the positive terminal and which is the negative terminal (in this case, the outer terminal is
the terminal negative and inner terminal is a positive terminal).
Available online on – WWW.IJIRMF.COM Page 172
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN MULTIDISCIPLINARY FIELD ISSN: 2455-0620 Volume - 4, Issue - 10, Oct – 2018
Monthly, Peer-Reviewed, Refereed, Indexed Journal with IC Value: 86.87 Impact Factor: 6.497 Publication Date: 31/10/2018
Figure 9 . Measurement of mobile phone polarity
Next, solder the cable to connect the phone with the sensor driver
.
Figures 10. Mobile phone terminal wiring
5. CONCLUSIONS.
From the process of designing, manufacturing, and testing this tool it can be concluded as follows:
LDR sensor works with working principle of voltage divider circuit.
The intensity of light affects how the LDR sensor works.
IC LM324 op amp in this tool works as comparator difference (comparator).
The phone in this tool acts as the successor of the information from the sensor to the user of the tool.
Do not just secure the front door only in applying the tool, but securing the other doors as well.
REFERENCES.
1. A. P. U. Siahaan, S. Aryza, R. Rahim, and A. H. Lubis, “Comparison Between Dynamic And Static Blocks In
Sequitur Algorithm,” IOSR J. Comput. Eng., vol. 19, no. 04, pp. 39–43, 2017.
2. A. I. Solly Aryza, Hermansyah, Muhammad Irwanto, Zulkarnain Lubis, “a Novelty of Quality Fertilizer Dryer
Based on Solar Cell and Ann,” Scopus, pp. 1–5, 2017.
3. V. Tipsuwanporn, W. Sawaengsinkasikit, and A. Numsomran, “9-Level Inverter for Induction Motor Control,”
Motor Control, pp. 2462–2466, 2010.
4. S. Aryza, M. Irwanto, Z. Lubis, A. Putera, and U. Siahaan, “A Novelty Stability Of Electrical System Single
Machine Based Runge Kutta Orde 4 Method,” IOSR J. Electr. Electron. Eng. Ver. II, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 2278–
1676, 2017.
5. I. Motor, F. E. Methods, B. R. Singla, S. Marwaha, and A. Marwaha, “Design and Transient Analysis of Cage
Induction Motor Using Finite Element Methods,” 2006 Int. Conf. Power Electron. Drives Energy Syst., 2006.
6. S. A. Lubis et al., “APPLICATION HYBRID ECO CAMPUS VEHICLE BASED ON SOLAR POWER,” vol.
3, no. 2, 2015.
7. H. Gain, C. Patch, and A. Filter, “THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE
High Gain Circular Patch Antenna Filter,” vol. 4, no. 11, pp. 50–53, 2016.
8. E. Deptt and J. E. C. Jabalpur, “CONTROL OF STARTING CURRENT IN THREE PHASE Sharda Patwa,”
no. 01, pp. 27–32, 2013.
Available online on – WWW.IJIRMF.COM Page 173
View publication stats
You might also like
- RCA Hobby Circuits Manual 1968Document228 pagesRCA Hobby Circuits Manual 1968algnben1746No ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Data Agglomeration and Intelligent SensingFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Data Agglomeration and Intelligent SensingNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics: Module-1 Semiconductor DiodesDocument39 pagesAnalog Electronics: Module-1 Semiconductor DiodesAyesha HumeraNo ratings yet
- Laser Security SystemDocument18 pagesLaser Security SystemDipin Preet Singh100% (2)
- Automatic Street Light Control Using LDRDocument47 pagesAutomatic Street Light Control Using LDRDivyang Vijay81% (42)
- Electronic EyeDocument14 pagesElectronic EyeHajarath Prasad Abburu100% (1)
- Laser Light Security System - Physics Investigatory Project - Class 12Document15 pagesLaser Light Security System - Physics Investigatory Project - Class 12Devansh Takkar73% (15)
- Design of Security Tools Using Sensor Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Through Mobile PhoneDocument6 pagesDesign of Security Tools Using Sensor Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Through Mobile PhoneMuhammad Alvito FarosNo ratings yet
- Laser Security System: Bachelor of Techonology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument17 pagesLaser Security System: Bachelor of Techonology IN Electronics and Communication Engineering4H9. Aaleem skNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Laser Security Alarm SystemDocument18 pagesPhysics Project Laser Security Alarm SystemMURALI DG67% (3)
- Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics ProjectRavindra SinghNo ratings yet
- L.E.D. (Laser Security System)Document18 pagesL.E.D. (Laser Security System)Vaibhavi MahtoNo ratings yet
- Led-Id S: C F L R T: Ystem Overage and AST INK Ecovery EchniqueDocument13 pagesLed-Id S: C F L R T: Ystem Overage and AST INK Ecovery EchniqueijcsesNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of An Arduino Based Security System Using Laser LightDocument7 pagesDesign and Implementation of An Arduino Based Security System Using Laser LightJoshua DurogaNo ratings yet
- Laser Security SystemDocument18 pagesLaser Security SystemDipin Preet SinghNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Home Security Laser SystemDocument25 pagesProject Report: Home Security Laser Systemyogesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Final Report 2.0Document22 pagesFinal Report 2.0kunalmpatekar10No ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM ISTDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM ISTHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument12 pagesBasic ElectronicsLizM RanzNo ratings yet
- Ieb Microprject (22530)Document10 pagesIeb Microprject (22530)mzaid skNo ratings yet
- Aec Reviw PDFDocument11 pagesAec Reviw PDFBOGGARAPU KUSHALKUMAR 15MIS0446No ratings yet
- Laser Security SystemDocument4 pagesLaser Security SystemVikasNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Automatic Light ControlDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Automatic Light Controlea59j0hq100% (1)
- Ecp Report FinalDocument24 pagesEcp Report FinalMahatva JethavaNo ratings yet
- Laser Alarm Security Planning ReportDocument21 pagesLaser Alarm Security Planning ReportBen TenNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Sensor: Review and Applications: March 2018Document6 pagesOptical Fiber Sensor: Review and Applications: March 2018Hassanein Al-hadadNo ratings yet
- Guru Tegh Bahadur Institute by ManpreetDocument67 pagesGuru Tegh Bahadur Institute by ManpreetmanpreetsinghpannuNo ratings yet
- IOT Based Street Light SystemDocument15 pagesIOT Based Street Light SystemROHIT YADAV100% (1)
- FEE Laser Project I IDocument3 pagesFEE Laser Project I Ipoudelaayush47No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Mankhurd: PHYSICS Investigatory PROJECTDocument23 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Mankhurd: PHYSICS Investigatory PROJECTSHREYA DASNo ratings yet
- Laser Security FinalDocument8 pagesLaser Security FinalHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Laser Security FinalDocument8 pagesLaser Security FinalHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) Based Low Cost Light Intensity Measurement Circuit Design (LUX Meter)Document5 pagesLight Dependent Resistor (LDR) Based Low Cost Light Intensity Measurement Circuit Design (LUX Meter)Nilesh 0059No ratings yet
- Smart Cities Through IoTDocument7 pagesSmart Cities Through IoTIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Different Optical Sources Used in Optical Communication SystemsDocument7 pagesInvestigation On Different Optical Sources Used in Optical Communication SystemsPhan Thê AnhNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesLiterature ReviewStephanie May DancesNo ratings yet
- IR Proximity SensorDocument22 pagesIR Proximity SensorKhushiNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V6I5P12) :Karthikeyan.R.A, Saran Sriram.K, Piyush.DDocument3 pages(IJCST-V6I5P12) :Karthikeyan.R.A, Saran Sriram.K, Piyush.DEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Sensing & Its Applications: July 2018Document10 pagesCapacitive Sensing & Its Applications: July 2018Worku MengstieNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Laser Alarm Circuit: Er - Bhimsen Tudu Er - Ashish SirDocument9 pagesProject Report On Laser Alarm Circuit: Er - Bhimsen Tudu Er - Ashish SirrameshNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Ujjain (M.P)Document13 pagesFaculty of Engineering Ujjain (M.P)Sumit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Automated Color Sensor System Using LDR and RGB Leds Controlled by ArduinoDocument6 pagesAutomated Color Sensor System Using LDR and RGB Leds Controlled by ArduinoNIKHIL ASNo ratings yet
- Certificate: of THAKUR POLYTECHNIC (CODE:0522) Has Completed The Micro Project Satisfactorily inDocument8 pagesCertificate: of THAKUR POLYTECHNIC (CODE:0522) Has Completed The Micro Project Satisfactorily inSaakshi MishraNo ratings yet
- Done - Laser Based Security Alarm System - Neet - MembersDocument13 pagesDone - Laser Based Security Alarm System - Neet - Membersdeepakyadavyadav987No ratings yet
- Workshop ProjectDocument11 pagesWorkshop ProjectF205Rangan SatpathiNo ratings yet
- Bhai Vaibhav AajanaDocument23 pagesBhai Vaibhav AajanaNikhil KushwahNo ratings yet
- Phy Project XIIDocument18 pagesPhy Project XIIEeshani MitraNo ratings yet
- Motion DectectorDocument34 pagesMotion DectectorINDIAN ICONICNo ratings yet
- Street Light Paper 2Document4 pagesStreet Light Paper 2Apoorva v HejjajiNo ratings yet
- Smart Street LightsDocument7 pagesSmart Street LightsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- LDR PrototypeDocument10 pagesLDR PrototypeRomela Grace BenigNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno-Based Water Turbidity Meter Using LDR and LED SensorsDocument6 pagesArduino Uno-Based Water Turbidity Meter Using LDR and LED SensorsLaxusPlayzNo ratings yet
- Study of Simple Spectrophotometer Design Using LDR Sensors Based On Arduino Uno MicrocontrollerDocument7 pagesStudy of Simple Spectrophotometer Design Using LDR Sensors Based On Arduino Uno MicrocontrollerLouis aNo ratings yet
- Nähtava Valguse Kommunikatsiooni Süsteemi Disain Ja RakendamineDocument65 pagesNähtava Valguse Kommunikatsiooni Süsteemi Disain Ja RakendamineConan EdogawaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project For Boards PracticalDocument11 pagesPhysics Project For Boards PracticalShivanshTripathiNo ratings yet
- Density Based Traffic Light Control Using IR Sensors and ArduinoDocument9 pagesDensity Based Traffic Light Control Using IR Sensors and ArduinoIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- IRPA2010Proceedings S12-P12RadiationdetectiontechnologiesandradionuclideanalyticsDocument8 pagesIRPA2010Proceedings S12-P12RadiationdetectiontechnologiesandradionuclideanalyticsVeri TrisnawanNo ratings yet
- FakeDocument17 pagesFakeyogya1109sharmaNo ratings yet
- Density Traffic ControlDocument8 pagesDensity Traffic ControlSai TejaNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument13 pagesProposalj88bmyhbs7No ratings yet
- SSRN Id3918233Document7 pagesSSRN Id3918233M FarhanNo ratings yet
- Power Management System Using PIR SensorDocument4 pagesPower Management System Using PIR SensorDanny SureshNo ratings yet
- Microelectronics and Microsystems - BMEVIEED071: Dr. Zólomy ImreDocument15 pagesMicroelectronics and Microsystems - BMEVIEED071: Dr. Zólomy Imreahmed helalNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of FETDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of FETYogesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SMK Methodist Ayer Tawar Perak Scheme of Work Form 5 Physics YEAR 2020Document22 pagesSMK Methodist Ayer Tawar Perak Scheme of Work Form 5 Physics YEAR 2020khalilNo ratings yet
- .Enthuse Major Test Schedule & Syllabus (Med, F, G, H, I, Q, R)Document1 page.Enthuse Major Test Schedule & Syllabus (Med, F, G, H, I, Q, R)335ynesNo ratings yet
- Bangalore University: Department of Electronic ScienceDocument51 pagesBangalore University: Department of Electronic ScienceBibinNo ratings yet
- Solapur University, Solapur: Syllabus For B.Sc.-I Electronics Semester SystemDocument8 pagesSolapur University, Solapur: Syllabus For B.Sc.-I Electronics Semester SystemJAYASHEEBA.J 19BCC142No ratings yet
- IGBT BasicsDocument20 pagesIGBT Basicsscrewyou2222No ratings yet
- EE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument25 pagesEE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherMirza Azhar HaseebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document136 pagesChapter 6vinothNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document9 pagesQuiz 1Zunaira FavadNo ratings yet
- 9.microcontroller Based Overheat DetectorDocument7 pages9.microcontroller Based Overheat DetectorRAMYA K NNo ratings yet
- Main Lab Report1Document47 pagesMain Lab Report1sonalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MergedDocument65 pagesChapter 1 MergedAdi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Online BitsDocument2 pagesOnline BitsNaresh BopparathiNo ratings yet
- Physics RecordDocument20 pagesPhysics RecordKilluaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Semiconductor Devices: Text BooksDocument2 pagesPhysics of Semiconductor Devices: Text BooksSneha S Revankar100% (1)
- MWD DeconvolutionDocument71 pagesMWD DeconvolutionAndres Felipe Villalba CortesNo ratings yet
- Dang Nguyen - Experiment 9 DiodesDocument5 pagesDang Nguyen - Experiment 9 DiodesNguyễn Hoàng ĐăngNo ratings yet
- ECE313 Quiz 1 Ee 3 eDocument2 pagesECE313 Quiz 1 Ee 3 eIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Basic-Electronics (Rectifier) !Document30 pagesBasic-Electronics (Rectifier) !Rahim AnsariNo ratings yet
- Elex ReviewerDocument3 pagesElex ReviewerJhomel EberoNo ratings yet
- Updated Lab Manual Power ElectronicsDocument43 pagesUpdated Lab Manual Power ElectronicsMuhammad Ali ImranNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument56 pagesTunnel DiodeNaveed Ramzan100% (2)
- Phy 363 ProjectDocument9 pagesPhy 363 ProjectMorongwa MaiselaNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 EE201Document59 pagesBab 2 EE201Noor Hanisah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices EC304 Lab ManualDocument45 pagesElectronics Devices EC304 Lab Manualwwerock786aydNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Optimization Using Arduino Based Maximum Power Point Tracking SystemDocument62 pagesSolar Energy Optimization Using Arduino Based Maximum Power Point Tracking SystemAnkit Kumar BurnwalNo ratings yet