Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-485
Uploaded by
ahmed shaker0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOriginal Title
W._F._Chen,_Plasticity_for_Structural_Engineers,_1988-485
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-485
Uploaded by
ahmed shakerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
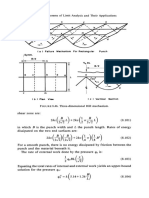
480 8.
General Theorems of Limit Analysis and Their Applications
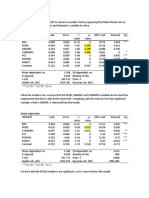
TABLE 8.3. Stress and velocity field parameters a
Upper bound Lower bound
Parameter Plane stress Plane strain Parameter Plane stress Plane strain
1/11 0.750 0.802 PI/Cx 0.976 1.00
1/12 1.209 1.802 P2/ C x 0.685 0.759
1/13 1.466 1.701 ul/C, 0.876 1.092
1/14 1.629 1.505 u 2/Cx 0.670 0.917
eP2
eP3
1.032
1.697
1.385
1.679
°I2
O
0.369
0.707
0.300
0.729
eP4 2.233 2.089
°I
O2
0.000
0.034
0.182
0.369
03 0.179 0.419
04 0.313 0.353
a 1.060 1.019
f3 1.045 1.142
oy 1.127 1.302
a All angles are listed in radians.
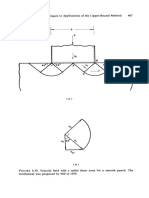
the plane stress case are less than a-:
s , the laterally confined plane stress
(i.e., 3.6Cx ). This implies that ice may fail against very wide structures at
less than the type A plane strain strength.
The upper and lower bounds for indentation pressure are listed in Table
8.2 and are also compared with Michel and Toussaint's (1976) constant
effective strain rate indentation data in Fig. 8.44. The average value for the
pressure is 4.12Cx for the plane strain eas e with a maximum possible error
of ±8%. For the plane stress case, the average value is 3.13 with a possible
error of ±5%. The plane stress bounds agree very weIl with the test data
at the higher aspect ratios. At low aspect ratio, the plane strain bounds are
onlyabout 30% higher than the plane stress bounds and show good
agreement with most of the data obtained with the smaller indenterso This
suggests that the data from tests 13 to 17 may be representative of the proper
material response, and not a consequence of the ice crystal size. Although
the size of these indenters was comparable to the crystal diameter, the size
of the plastic deforming region may have been sufficiently large to obscure
individual crystal effects.
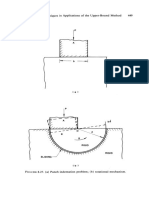
8.6.2. Indentation of a Semi-Infinite Medium by a Square or
Rectangular Punch
Three-dimensional problems of rigid-punch indentation are considered in
this section. The material is assumed to obey Tresca's yield criterion of
constant maximum shearing stress during plastic deformation.
You might also like
- S14 Quantitative Research (Rstudio Video)Document14 pagesS14 Quantitative Research (Rstudio Video)Andrés Espinoza100% (1)
- Spec. No. 7311-DE-041Document1 pageSpec. No. 7311-DE-041HEMANTNo ratings yet
- Gempa Sni 2011 Kota YogyaDocument74 pagesGempa Sni 2011 Kota YogyaMersiantyNo ratings yet
- 2022 ECMF - Log Pearson - Parcial v2Document2 pages2022 ECMF - Log Pearson - Parcial v2wadeb83585No ratings yet
- Asset-V1 CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+Type@Asset+Block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2Document26 pagesAsset-V1 CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+Type@Asset+Block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2salehmashrur 98No ratings yet
- 8950P229 SampleDocument5 pages8950P229 SamplecarlosNo ratings yet
- Lab Task 02Document6 pagesLab Task 02hammad javedNo ratings yet
- Master CalculationsDocument37 pagesMaster Calculationsb89502164No ratings yet
- HC PoissonProcessesDocument14 pagesHC PoissonProcessesKELVIN JORDAN CASTILLO CASASOLANo ratings yet
- asset-v1-CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+type@asset+block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2Document42 pagesasset-v1-CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+type@asset+block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2Axel DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Kurva Kalibrasi Larutan Standar C-Organik: 1. Penentuan LinieritasDocument4 pagesKurva Kalibrasi Larutan Standar C-Organik: 1. Penentuan Linieritasaprilia kurnia putriNo ratings yet
- MS21254Document5 pagesMS21254Bogdan RusuNo ratings yet
- Bi C012 E-Side FullDocument9 pagesBi C012 E-Side FullChe Amar Shafiq Che BaharumNo ratings yet
- CuucuDocument2 pagesCuucuA.zhalzhabilla azzahrah AzzahrahNo ratings yet
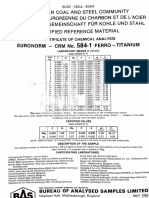
- 584-1 Ferro TitaniumDocument2 pages584-1 Ferro Titaniummayur khalatkarNo ratings yet
- Steel Design: Aisc-Lrfd93 Steel Section CheckDocument1 pageSteel Design: Aisc-Lrfd93 Steel Section Checkmang juhaiNo ratings yet
- BBD Test at BBSR For RKDDocument2 pagesBBD Test at BBSR For RKDPrashant GaradNo ratings yet
- Spec. No. 7311-DE-042Document1 pageSpec. No. 7311-DE-042HEMANTNo ratings yet
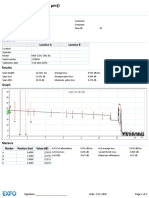
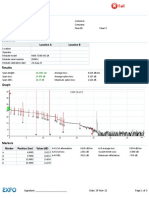
- General Information: Location A Location BDocument3 pagesGeneral Information: Location A Location BAsrafur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Fiber 38Document6 pagesFiber 38Nityanand GuptaNo ratings yet
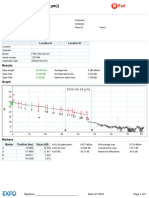
- Result Analysis Report: Um D (0.9) : 5.787 14.694 D (0.1) : Um Um 1.131 D (0.5)Document1 pageResult Analysis Report: Um D (0.9) : 5.787 14.694 D (0.1) : Um Um 1.131 D (0.5)Baghiu TeodorNo ratings yet
- Human CortisolDocument4 pagesHuman CortisolFaiz Kamal HasanNo ratings yet
- HEA200 COLUMN - ٠٦١٧٢٥Document1 pageHEA200 COLUMN - ٠٦١٧٢٥Mahmoud MatarNo ratings yet
- Table - 8 Conductor PropertiesDocument1 pageTable - 8 Conductor PropertiesMichael DarmstaedterNo ratings yet
- Fiber 27Document6 pagesFiber 27Nityanand GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fastenal 01 05 2018Document1 pageFastenal 01 05 2018Marcel BaqueNo ratings yet
- HBBVDocument5 pagesHBBVA.zhalzhabilla azzahrah AzzahrahNo ratings yet
- Project Job Number EngineerDocument1 pageProject Job Number EngineerRichard FelipNo ratings yet
- Bromatologia CurvasDocument9 pagesBromatologia CurvasMarco Antonio Cabana MezaNo ratings yet
- Area of Steel Calculation: (Limit State)Document16 pagesArea of Steel Calculation: (Limit State)RAVI PRAKASH SAININo ratings yet
- Tatt Agrotek BDocument17 pagesTatt Agrotek BJun AdityaNo ratings yet
- Validasi H2SDocument18 pagesValidasi H2Sseptian_bbyNo ratings yet
- Abs 0114Document11 pagesAbs 0114kevin seine100% (2)
- Data Priyanto Tekknik ListrikDocument1 pageData Priyanto Tekknik Listrikkarya nabilaNo ratings yet
- Stress 3Document10 pagesStress 3ardi yansaNo ratings yet
- Visible Spectroscopy of FeDocument1 pageVisible Spectroscopy of FeAnnaReyesNo ratings yet
- Log Interpretation Well BZ-04: INKA PRATIWI 071.16.058 OWEN 071.16.089 BELLA HARYADI 071.15.027Document24 pagesLog Interpretation Well BZ-04: INKA PRATIWI 071.16.058 OWEN 071.16.089 BELLA HARYADI 071.15.027Inka PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Surface DrainageDocument8 pagesCalculation of Surface Drainagekingsuk1980No ratings yet
- Section 2 - Thread - BasicsDocument27 pagesSection 2 - Thread - BasicsChris MedeirosNo ratings yet
- PN. Khoza (21541575) - Exp3.1Document7 pagesPN. Khoza (21541575) - Exp3.1Nkosazana MakaringueNo ratings yet
- Gpp-I Train 2 Feed Gas Composition, Rev-02Document2 pagesGpp-I Train 2 Feed Gas Composition, Rev-02sanjayNo ratings yet
- Bs 916 StandardDocument1 pageBs 916 Standardatif iqbalNo ratings yet
- NASM21314Document1 pageNASM21314Bogdan RusuNo ratings yet
- NAS1303 CoastFabricationDocument2 pagesNAS1303 CoastFabricationsje productionNo ratings yet
- Herc-Alloy 800 ChainDocument17 pagesHerc-Alloy 800 Chainjoche2005No ratings yet
- InsulinDocument4 pagesInsulinfitri wulandariNo ratings yet
- MPPWD 2014 SOR CH 1 To 5 in ExcelDocument66 pagesMPPWD 2014 SOR CH 1 To 5 in ExcelElvis GrayNo ratings yet
- Grid FDocument144 pagesGrid FJohn Dell TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Examen Titulo BRMDocument3 pagesExamen Titulo BRMMario JosafatNo ratings yet
- Report of Resistance, Self Propulsion Tests With Stock Propeller, Three-Dimensional Wake Field Including Trial Speed-Power PredictionDocument4 pagesReport of Resistance, Self Propulsion Tests With Stock Propeller, Three-Dimensional Wake Field Including Trial Speed-Power PredictionTudor ChirilaNo ratings yet
- Cold-Formed Steel Design CheckDocument2 pagesCold-Formed Steel Design CheckLuís OliveiraNo ratings yet
- CVV 4Document22 pagesCVV 4Nemanja PapricaNo ratings yet
- Beams of Relatively Great WidthDocument3 pagesBeams of Relatively Great WidthMarshall MarsNo ratings yet
- Kurva Tinggi 19 March 2019Document8 pagesKurva Tinggi 19 March 2019Iskandar Isyda QuincyNo ratings yet
- Project BEM 92303Document12 pagesProject BEM 92303Jair BoulosNo ratings yet
- Metric Dowel PinsDocument1 pageMetric Dowel PinszainudinNo ratings yet
- Additive AravinthDocument15 pagesAdditive AravinthAravinth subramanianNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document3 pagesTest 3ROBERTO ANDRES GOMEZ MERCADONo ratings yet
- Fiber 25Document6 pagesFiber 25Nityanand GuptaNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-350Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-350ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-441Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-441ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers 1988-120 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers 1988-120 PDFahmedNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-356Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-356ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- ,KK, V PDFDocument1 page,KK, V PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-441Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-441ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-325 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-325 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-562Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-562ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-59 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-59 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 588 9. Limit Analysis of Engineering Struetures: - Size - PrismDocument1 page588 9. Limit Analysis of Engineering Struetures: - Size - Prismahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-35 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-35 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 394 7. Implementation in Concretes: Stress and Strain IncrementsDocument1 page394 7. Implementation in Concretes: Stress and Strain Incrementsahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 482 8. General Theorems of Limit Analysis and Their ApplicationsDocument1 page482 8. General Theorems of Limit Analysis and Their Applicationsahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 9.5. Limit Analysis of Plates 527: 4 y !4 XY !4 YxDocument1 page9.5. Limit Analysis of Plates 527: 4 y !4 XY !4 Yxahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-46 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-46 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-260Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-260ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-384Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-384ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-472Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-472ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-454Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-454ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 8.6. Example Problems in Plane Stress, Plane Strain, and 3-D 475Document1 page8.6. Example Problems in Plane Stress, Plane Strain, and 3-D 475ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 156 3. Elastic Stress-Strain Relations: T (KenDocument1 page156 3. Elastic Stress-Strain Relations: T (Kenahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 394 7. Implementation in Concretes: Stress and Strain IncrementsDocument1 page394 7. Implementation in Concretes: Stress and Strain Incrementsahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-531Document1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-531ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 8.6. Example Problems in Plane Stress, Plane Strain, and 3-D 475Document1 page8.6. Example Problems in Plane Stress, Plane Strain, and 3-D 475ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers 1988-119 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers 1988-119 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- 7.4. Plasticity Modeling: Softening Behavior 383Document1 page7.4. Plasticity Modeling: Softening Behavior 383ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- (V) - (1 - 0) (JL) J: 6.6. Bounding Surface Theory 325Document1 page(V) - (1 - 0) (JL) J: 6.6. Bounding Surface Theory 325ahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-364 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-364 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- W. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-364 PDFDocument1 pageW. F. Chen, Plasticity For Structural Engineers, 1988-364 PDFahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Analysis User's ManualDocument82 pagesAbaqus Analysis User's ManualAbhishek ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Structures: M A M N e FDocument25 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Structures: M A M N e FhoneybNo ratings yet
- MAT FemInglesDocument29 pagesMAT FemIngleshoneybNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ME 106Document1 pageCourse Outline ME 106pauljustine091No ratings yet
- Problems: 7.1 Through 7.4Document4 pagesProblems: 7.1 Through 7.4GertaNo ratings yet
- The Plane Stress ProblemDocument14 pagesThe Plane Stress ProblemSaif RahmanNo ratings yet
- 07 04ChapGereDocument31 pages07 04ChapGereZero Yip100% (1)
- Hill Criterion and Von MisesDocument10 pagesHill Criterion and Von MisesSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 3Document78 pagesTDS Lec 3YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Design of Pressure Vessels Under ASME Section VIIIDocument122 pagesDesign of Pressure Vessels Under ASME Section VIIIAnonymous d23gWCRQNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Plane Stress Bracket)Document3 pagesTutorial (Plane Stress Bracket)allen.20.79308No ratings yet
- FEM BitsDocument3 pagesFEM BitsDarbhalaPavanKumarNo ratings yet
- Ansys Tutorial 3Document4 pagesAnsys Tutorial 3deathesNo ratings yet
- CE 322 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Kristine May Maturan, CE Cor Jesu College, IncDocument5 pagesCE 322 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Kristine May Maturan, CE Cor Jesu College, IncKristine May MaturanNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document28 pagesModule 5MARYVELLE AIZEN SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Stress StateDocument4 pagesExercises On Stress StatecusanhNo ratings yet
- ME6603-Finite Element AnalysisDocument20 pagesME6603-Finite Element AnalysisPRAKASHNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Plane Stress and Strain PDFDocument14 pagesTransformation of Plane Stress and Strain PDFFitsum OmituNo ratings yet
- Ugural 재료역학과 탄성론 6판Document1,232 pagesUgural 재료역학과 탄성론 6판김민혁No ratings yet
- Machine Design (ME - 316) : Assignment # 1 (PLO-2, CLO-2)Document3 pagesMachine Design (ME - 316) : Assignment # 1 (PLO-2, CLO-2)Sayam AliNo ratings yet
- Multi Axial Loading - ResourceDocument29 pagesMulti Axial Loading - ResourceEirickTrejozuñigaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Equation For Stepped Bar Problems Case: 1 Four Elements ProblemsDocument13 pagesFinite Element Equation For Stepped Bar Problems Case: 1 Four Elements ProblemsVasundaraNo ratings yet
- Mohr Circle ADocument3 pagesMohr Circle AMikhaelrams RamsNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Shigley SlidesDocument139 pagesCH 3 Shigley Slidesengineer60638100% (2)
- Applications of Theory of Elasticity in Rock MechanicsDocument25 pagesApplications of Theory of Elasticity in Rock MechanicsRMolina65No ratings yet
- Composite Design and TheoryDocument203 pagesComposite Design and Theoryapi-3700351100% (6)
- Chapter 4 - ModellingDocument25 pagesChapter 4 - ModellingRickNo ratings yet
- Design of Perforated PlatesDocument13 pagesDesign of Perforated PlatesScribdUserBest100% (1)
- UB Mae 311Document4 pagesUB Mae 311Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument50 pagesChapter1 PDFShueibNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (65)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraFrom EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (593)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeFrom EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderFrom EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (283)