Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Introduction To Railways, Its Component Parts and Its Functions (16 Hours) PDF
Uploaded by
Pangerwati Ozukum0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views14 pagesOriginal Title
1.1 Introduction to railways , its component parts and its functions ( 16 hours ).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views14 pages1.1 Introduction To Railways, Its Component Parts and Its Functions (16 Hours) PDF
Uploaded by
Pangerwati OzukumCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
INTRODUCTION TO RAILWAYS , ITS
COMPONENT PARTS AND ITS
FUNCTIONS
• Introduction with various aspects of railway engineering .( 2 )
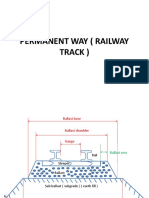
• Permanent way component parts and its functions .( 2 )
• Various types of rails , its functions , creep in rails , creep movement ,
coning of wheels , rail fixation.( 6 )
• Sleepers – various types , merits , demerits ( 2 )
• Ballast – various types
• Subgrade preparation .
One degree of freedom :
Those modes in which vehicles are free to move only along a line i.e vehicles
are vertically and laterally restrained . eg : railways , pipelines , conveyor
systems , cableways etc .
Two degree of freedom :
Those modes in which vehicles can move along a line as well as laterally i.e
vehicles are restrained only vertically . eg : highway vehicles , ships , boats etc.
Three degree of freedom :
Those modes in which vehicles are free to move in any plane i.e vehicles are
neither laterally or vertically restrained .eg : aeroplanes , underwater vehicles
i.e submarine.
Railway is a means of land transport .
The railways have their greatest utilization in the transport of large
volumes of heavy and bulk commodities over long distances and in very
long journeys of passengers with safety , comfort , and convenience .
The first railway opened for the public in the history of the world on 27th
September , 1825 in UK ( England ) between Stockton and Darlington in
the county of Durham .
The first proposal for the construction of railway in India was submitted to
the East India Company by Mr . George Stephenson .( Lord Dalhousie (
Doctrine Of Lapse ) was the Governor General from 1848 – 1856 . A salute
of 21 guns was given to the train )
The first railway line opened in India for the public on 16th April 1853
between Bombay and Thane , ( 32 km stretch = 21 miles which was
covered in 1 hr 15 mins ) which had 14 coaches and was driven by 3
engines .
Engine = locomotion no.1 = 6.6 t = 66 kN.
Indian railway has been divided into 9 zones after independence and
further extra 7 zones ( 6 + 1 ) have been develeoped .
SL . no Name of zones ( old ) Headquarters
1 NR ( northern railway ) delhi
2 NER ( north eastern railway ) Gorakhpur ( U.P )
3 ER ( Eastern Railway ) Kolkata ( Howrah )
4 SER ( South Eastern Railway ) Kolkata ( Howrah )
5 CR ( Central Railway ) Mumbai
6 WR ( Western Railway ) Mumbai
7 SR ( Southern Railway ) Chennai
8 SCR ( South Central Railway ) Secunderabad
9 NEFR ( North Eastern Frontier Railway ) Maligaon ( Guwahati )
SL . no Name of zones ( NEW ) Headquarters
1 ECR ( East Central Railway ) Hajipur ( Bihar )
2 E.Co.R ( East Coast Railway ) Bhubaneshwar
3 SWR ( South Western Railway ) Bangalore ( Hoogly )
4 NCR ( North Central Railway ) Allahabad
5 NWR ( North Western Railway ) Jaipur ( Rajasthan )
6 WCR ( West Central Railway ) Jabalpur
7 SECR ( Southern East Central Railway ) Bilaspur ( Chattisgarh )
Besides zonal railways , there are 6 production units of Indian Railways as
given below :
SL . Manufacturing units Headquarters Functions
no
1 Chittaranjan Locomotive Chittaranjan ( West Manufacture of
Works ( CLW ) Bengal ) electric locomotives
2 Diesel Locomotive Works Varanasi ( U.P) Manufacture of diesel
( DLW ) locomotives
3 Integral Coach Factory ( Chennai Manufacture of
ICF ) coaches
4 Diesel Components Patiala ( Punjab ) Manufacture of diesel
Works ( DCW ) components
5 Rail Coach Factory ( RCF ) Kapurthala ( Punjab ) Manufacture of coach
6 Wheel and Axle Plant ( W Bangalore ( Karnataka ) Manufacture of wheels
& AP ) and axle
Gauge :
The gauge of a railway track is defined as the clear distance between the
inner or running faces of two track rails . The distance between the inner
faces of a pair of wheels is called the “ wheel gauge “ .
Types of gauge in India :
1. Broad Gauge ( BG ) : Gauge width G = 1.676 m
2. Meter Gauge ( MG ) : Gauge width G = 1.000 m ; Local train
3. Narrow Gauge ( NG ) : Gauge width G = 0.762 m ; Hilly Zone ( 0.762 m to
0.61 m )
4. Light Gauge ( LG ) : Gauge width G = 0.61 m ; Feeder Gauge
5. Standard Gauge , G = 1.435 m ( UK , USA , China 0
6. Cap Gauge , G = 1.006 m ( Japan )
Characteristics of railways :
1) The railways are the cheapest in preference to other modes of transport .
2) The railways require the least amount of power as compared to their
weight .
3) The direction of movement is controlled and practically no steering is
required as the vehicles are not at the liberty to deviate from the rails.
4) The railways alone can carry lot of people quickly and safely through big
towns full of crowded streets .
5) As compared to a car or a truck or an aeroplane , it is better to travel in a
train for making long journeys , carrying a lot of heavy things .
Locomotive :
• It is a machine which transfers chemical energy of fuel into mechanical
energy of motion . Fuel may be water and coal or diesel or electricity .
• Steam locomotives are designated by the type and number of wheels such
as
• => 4 – 6 – 2 type locomotive shows
a) 4 – Four wheels or bogie carriers
b) 6 – Six central or driving or coupled wheels . More the number of driving
wheels , better will be the performance of the locomotive .
c) 2 – Two rear or trailing wheels .
Bogie wheels Driving wheels Trailing wheels
Figure : 4 – 6 – 2 Type of Steam Locomotives
Questions :
1. Railways have _____ degree of freedom .
2. Highway vehicles have _____ degrees of freedom .
3. Aeroplanes have ____ degrees of freedom .
4. Indian railway is divided into _______ zones .
5. The clear distance between the inner or running faces of two track rails
is ______ .
6. The distance between the inner faces of a pair of wheels is called the
_______ .
7. _________ is a machine which transfers chemical energy of fuel into
mechanical energy of motion .
8. Railways require the ______ amount of power as compared to their
weight .
9) Which of the following options correctly describes the numerical values in 4 – 6 –
2 type of steam locomotive :
a) Option a
4 – Four wheels or bogie carriers
6 – Six central or driving or coupled wheels .
2 – Two rear or trailing wheels
b) Option b
4 – Four rear or trailing wheels
6 – Six central or driving or coupled wheels .
2 – Two wheels or bogie carriers
b) Option c
4 – Four central or driving or coupled wheels .
6 – Six wheels or bogie carriers
2 – Two rear or trailing wheels
b) Option d
4 – Four wheels or bogie carriers
6 – Six rear or trailing wheels.
2 – Two central or driving or coupled wheels
You might also like
- IndianRailways History and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesIndianRailways History and Developmentpriyanka joshiNo ratings yet
- Railway Zones Head QuartersDocument9 pagesRailway Zones Head QuartersRanjib kumarNo ratings yet
- RDSO Training Report Wagon PDFDocument55 pagesRDSO Training Report Wagon PDFVikas RajpootNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Electric Loco ShedDocument38 pagesProject Report On Electric Loco Shedjohn power100% (1)
- Railway EnggDocument145 pagesRailway EnggPooja AnnamreddyNo ratings yet
- Railway Report on Inplant TrainingDocument18 pagesRailway Report on Inplant TrainingRAKESHKANNANNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Overview of OrganisationDocument61 pages1.1 Overview of Organisationashwin royNo ratings yet
- Intro RailwayDocument11 pagesIntro RailwayRajendra Kumar100% (1)
- Seminar Report On Inidan RailwaysDocument35 pagesSeminar Report On Inidan RailwaysMohd DanishNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Electric Loco, TuglakabaadDocument39 pagesProject Report On Electric Loco, TuglakabaadSaurabh Madeel88% (8)
- Izzatnagar Railway Workshop, BareillyDocument84 pagesIzzatnagar Railway Workshop, BareillyAreeb SirajNo ratings yet
- Railway Disal ShedDocument84 pagesRailway Disal ShedAreeb Siraj100% (1)
- INDIAN RAILWAYS SWOT ANALYSIS REVEALS MAJOR STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSESDocument5 pagesINDIAN RAILWAYS SWOT ANALYSIS REVEALS MAJOR STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSESHarish BishtNo ratings yet
- Railway Workshop Training ReportDocument37 pagesRailway Workshop Training ReportChandan Kumar40% (5)
- Electric Locomotive Workshop.Document38 pagesElectric Locomotive Workshop.Apurwa Patil100% (1)
- BR - Phase I 1.1 Organization of Indian RailwaysDocument60 pagesBR - Phase I 1.1 Organization of Indian RailwaysBhaskar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Railway Training Report at Ajmer Group of WorkshopsDocument39 pagesRailway Training Report at Ajmer Group of Workshopsayush093No ratings yet
- Coach Rehab Workshop BhopalDocument8 pagesCoach Rehab Workshop Bhopalochrerocker100% (1)
- Railnet Pdf35Document35 pagesRailnet Pdf35Ravi Prakash YadavNo ratings yet
- HISTORY-OF-INDIAN-RAILWAY - DFCCIL-2023-02-10-10-43-32 - RemovedDocument73 pagesHISTORY-OF-INDIAN-RAILWAY - DFCCIL-2023-02-10-10-43-32 - RemovedDharnidhar kumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1. History and General Features of Indian RailwaysDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 1. History and General Features of Indian RailwaysaranavNo ratings yet
- RDSO Training Report WagonDocument55 pagesRDSO Training Report WagonGaurav Pathak0% (1)
- Signalling, Telecommunication and Digital Systems in Indian RailwaysDocument55 pagesSignalling, Telecommunication and Digital Systems in Indian RailwaysJwala Prakash100% (1)
- Railway Engineering-2Document40 pagesRailway Engineering-2sivaraman assocaiatesNo ratings yet
- Railway Zones: Sl. No Name Abbr. Date Established Headquarters DivisionsDocument4 pagesRailway Zones: Sl. No Name Abbr. Date Established Headquarters Divisionssathish_51100% (1)
- Project Based On Working of The Wheel Shop in Kharagpur WorkshopDocument9 pagesProject Based On Working of The Wheel Shop in Kharagpur WorkshopArup SheeNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument45 pagesIndustrial Training ReportSahil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Railway Traning ReportDocument45 pagesRailway Traning Reportbharat_90100% (1)
- Indian Railways ProjectDocument15 pagesIndian Railways ProjectGaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Railway Training Project Repot PDFDocument42 pagesRailway Training Project Repot PDFMd Dilshad AlamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian RailwaysDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Indian RailwaysShashank Rai100% (2)
- Rail Coach Corrosion RepairDocument36 pagesRail Coach Corrosion RepairNithin GowdaNo ratings yet
- Railway History of PakistanDocument79 pagesRailway History of Pakistanرضا خټکNo ratings yet
- Railway Engineering NotesDocument15 pagesRailway Engineering NotesUdayram PatilNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways 1234Document15 pagesIndian Railways 1234abhi0006100% (1)
- Indian Railways - WikipediaDocument29 pagesIndian Railways - WikipediaAbhinav PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- TriangDocument73 pagesTriangNikhil SinglaNo ratings yet
- Coach Rehabilitation WorkshopDocument8 pagesCoach Rehabilitation WorkshopAbhishek PauranikNo ratings yet
- GagandeeprailDocument145 pagesGagandeeprailKhan AmanNo ratings yet
- Ankur Singh: Shree Ganpati Institute of Technology, GhaziabadDocument49 pagesAnkur Singh: Shree Ganpati Institute of Technology, GhaziabadAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - History + Rail GaugesDocument25 pagesLecture 8 - History + Rail GaugesUmer NaveedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Railway OrganisationDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Railway OrganisationVinay KushawahaNo ratings yet
- Indian Railway SystemDocument12 pagesIndian Railway SystemHimanshu JainNo ratings yet
- Fib Various Types of Structures For Namma MetroDocument34 pagesFib Various Types of Structures For Namma MetroRohitNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways (.) Is An IndianDocument10 pagesIndian Railways (.) Is An Indianmukulkanojiya100% (1)
- Maintenance Book1Document200 pagesMaintenance Book1rakesh ranjanNo ratings yet
- 1622175199606-4general Introduction To Indian RailwaysDocument7 pages1622175199606-4general Introduction To Indian RailwaysMd Nawed AzadNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument33 pagesFinal ReportLalit PrakashNo ratings yet
- Study on Turbo Super Charger Maintenance and Failure AnalysisDocument19 pagesStudy on Turbo Super Charger Maintenance and Failure AnalysisDrSumedha SarmaNo ratings yet
- Railway Diary 2016: Important Signalling Parameters & SafetyDocument434 pagesRailway Diary 2016: Important Signalling Parameters & Safetysignalcontrolspj100% (1)
- Training ReportDocument49 pagesTraining ReportAjay kumarNo ratings yet
- Indian RailwaysDocument20 pagesIndian RailwaysNirmalNo ratings yet
- The Southern Region (B R) Class 73 and 74 Locomotives: A Pictorial OverviewFrom EverandThe Southern Region (B R) Class 73 and 74 Locomotives: A Pictorial OverviewNo ratings yet
- Theory and Technology for Improving High-Speed Railway Transportation CapacityFrom EverandTheory and Technology for Improving High-Speed Railway Transportation CapacityNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument19 pagesFluid MechanicsPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Alignment, Superelevation, Negative Superelevation, Cant Deficiency, Example ProblemsDocument21 pagesAlignment, Superelevation, Negative Superelevation, Cant Deficiency, Example ProblemsPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Alignment, Superelevation, Negative Superelevation, Cant Deficiency, Example ProblemsDocument21 pagesAlignment, Superelevation, Negative Superelevation, Cant Deficiency, Example ProblemsPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training Report On: Slope Protection, Construction of RCC Bridge, Pavement Milling and FootpathDocument33 pagesA Summer Training Report On: Slope Protection, Construction of RCC Bridge, Pavement Milling and FootpathPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument19 pagesFluid MechanicsPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training Report On: Slope Protection, Construction of RCC Bridge, Pavement Milling and FootpathDocument33 pagesA Summer Training Report On: Slope Protection, Construction of RCC Bridge, Pavement Milling and FootpathPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design of Industrial Building in Mcdonald Steel Building Products LTD (MSBPL)Document70 pagesStructural Analysis and Design of Industrial Building in Mcdonald Steel Building Products LTD (MSBPL)Koti Veera BhadramNo ratings yet
- STAAD Analysis and Design of Residential BuildingDocument60 pagesSTAAD Analysis and Design of Residential BuildingMd Mufazzel Hossain Chowdhury100% (1)
- REPORT ON Fluid MechanicsDocument20 pagesREPORT ON Fluid MechanicsPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Summer Training On STAAD Pro V8iDocument24 pagesSummer Training On STAAD Pro V8iParwin Mards80% (5)
- STAAD Analysis and Design of Residential BuildingDocument60 pagesSTAAD Analysis and Design of Residential BuildingMd Mufazzel Hossain Chowdhury100% (1)
- REPORT ON Fluid MechanicsDocument20 pagesREPORT ON Fluid MechanicsPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- A Report On Staad ProDocument35 pagesA Report On Staad ProPangerwati Ozukum100% (1)
- STAAD - Pro: Department of Civil Engineering, Iit RoorkeeDocument21 pagesSTAAD - Pro: Department of Civil Engineering, Iit RoorkeeNayan FataniaNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro ReportDocument35 pagesStaad Pro ReportPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Creep of Rail, Coning of Wheels PDFDocument9 pagesCreep of Rail, Coning of Wheels PDFPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDocument70 pagesIndustrial Wastewater TreatmentAudrius100% (3)
- Final Report On Staad ProDocument36 pagesFinal Report On Staad ProPangerwati Ozukum90% (10)
- Summer Training On STAAD Pro V8iDocument24 pagesSummer Training On STAAD Pro V8iParwin Mards80% (5)
- Soil Damping and Its Use in Dynamic AnalysesDocument8 pagesSoil Damping and Its Use in Dynamic AnalysesPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Permanent Way in RailwayDocument19 pagesPermanent Way in RailwayPangerwati Ozukum100% (1)
- Inverted Siphon Design PDFDocument12 pagesInverted Siphon Design PDFPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- Machine FoundationDocument42 pagesMachine FoundationRakesh SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Design of Septic TankDocument5 pagesDesign of Septic TankPangerwati OzukumNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of RocksDocument35 pages3 Types of RocksJulieta Bias100% (4)
- Machine FoundationDocument42 pagesMachine FoundationRakesh SapkotaNo ratings yet
- 16 Balance TestDocument15 pages16 Balance Testelga saniNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: Quarter 3 - 8: Imaging and Design Fo R The Online Environment IDocument14 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: Quarter 3 - 8: Imaging and Design Fo R The Online Environment IShaira Jane Estrella UcolNo ratings yet
- BARACARBDocument2 pagesBARACARBYudha Satria50% (2)
- Solar Collectors Final WordDocument14 pagesSolar Collectors Final WordVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- Assignment 12Document7 pagesAssignment 12Anonymous mqIqN5zNo ratings yet
- Training ManualDocument41 pagesTraining Manualemiliow_1100% (3)
- Transcript Ken Robinson 2010 NewDocument34 pagesTranscript Ken Robinson 2010 NewCarmen Maria FluturaşNo ratings yet
- Airway Management in The Critically Ill: ReviewDocument9 pagesAirway Management in The Critically Ill: ReviewQuarmina HesseNo ratings yet
- Factors to Consider in Reactor Design for Industrial ProcessesDocument3 pagesFactors to Consider in Reactor Design for Industrial Processesuma villashini100% (2)
- Algebra 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2Document2 pagesAlgebra 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2Makala DarwoodNo ratings yet
- MIND - BODY RelationshipDocument18 pagesMIND - BODY RelationshipvishwabhashaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Plated HoleDocument5 pagesAnatomy of A Plated Holepbs0707No ratings yet
- Tutorial - DGA AnalysisDocument17 pagesTutorial - DGA Analysisw automationNo ratings yet
- Regulation 1 Regulation 2 Regulation 3 Regulation 4 Regulation 5 Regulation 6 Regulation 7 Regulation 8 Regulation 9 AppendixDocument10 pagesRegulation 1 Regulation 2 Regulation 3 Regulation 4 Regulation 5 Regulation 6 Regulation 7 Regulation 8 Regulation 9 AppendixAnonymous 7gJ9alpNo ratings yet
- Instapdf - in Bangalore Tourist Places List 674Document31 pagesInstapdf - in Bangalore Tourist Places List 674R K PathamNo ratings yet
- Booklet English 2016Document17 pagesBooklet English 2016Noranita ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Crops - FlaxDocument33 pagesFiber Crops - Flaxmalath bashNo ratings yet
- Ic M802 UDocument79 pagesIc M802 Uharis_fikriNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Structures of The UniverseDocument228 pagesMathematical Structures of The UniverseMaki MajomNo ratings yet
- Beneficiation of Cassiterite From Primary Tin OresDocument11 pagesBeneficiation of Cassiterite From Primary Tin OresSULMAGNo ratings yet
- Rotating Sharp Shooting Multi Target Mechanism Improves Military AimDocument13 pagesRotating Sharp Shooting Multi Target Mechanism Improves Military AimVishal GNo ratings yet
- Marketing 5 0Document23 pagesMarketing 5 0gmusicestudioNo ratings yet
- Monthly Fire Extinguisher Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesMonthly Fire Extinguisher Inspection ChecklistisaacbombayNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Development of The Brooks-Corey CapillDocument7 pagesTheoretical Development of The Brooks-Corey CapillDiana Vanessa PedrazaNo ratings yet
- Aam April 2023Document198 pagesAam April 2023Adhitya DewantaraNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument8 pagesSampleAntônioNo ratings yet
- Rate Analysis-Norms 1Document10 pagesRate Analysis-Norms 1yamanta_rajNo ratings yet
- Figure of SpeechDocument27 pagesFigure of SpeechSabel Ross CaliliwNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Fabric Opacity by ScannerDocument7 pagesEstimation of Fabric Opacity by ScannerJatiKrismanadiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Services for Abadan Petrochemical Plant VCM Unloading Station Piping DesignDocument28 pagesEngineering Services for Abadan Petrochemical Plant VCM Unloading Station Piping DesignMehdi NouriNo ratings yet