Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Facts at Your Fingertips-200903-Membrane Configurations PDF
Facts at Your Fingertips-200903-Membrane Configurations PDF
Uploaded by
onizuka-t2263Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Facts at Your Fingertips-200903-Membrane Configurations PDF
Facts at Your Fingertips-200903-Membrane Configurations PDF
Uploaded by
onizuka-t2263Copyright:
Available Formats
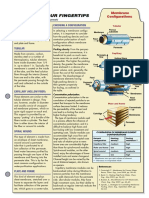
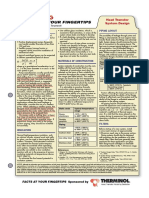
Membrane
Configurations
Department Editor: Kate Torzewski
M
embrane polymers are pack- CHOOSING A CONFIGURATION Tubular
aged into a configuration,
In selecting a membrane configu- Porous
commonly called a device Membrane substrate
or an element. The most-common ration, it is important to consider
element configurations (figure) are how the packing density and con- Concentrate
tubular, capillary fiber, spiral wound, centration polarization of each Feed
and plate and frame. configuration affects membrane
fouling resistance.
Permeate
TUBULAR Packing density. From the perspec-
tive of cost and convenience, it is Capillary
Made from ceramic, carbon,
beneficial to pack as much mem- Permeate
stainless steel or a number of flow
brane area into as small a volume Hollow fibers
thermoplastics, tubular elements
as possible. The higher the packing
have inside diameters from 1/4 Concentrate
density, the greater the membrane Feed
in. up to about 1 in. Typically, the
area enclosed in a device of a
membrane is coated on the inside
given volume, and, generally, the
of the tube, and the feed solution
lower the cost of the membrane
flows through the interior (lumen)
element. The disadvantage of Spiral wound
from one end to the other, with Feed Concentrate
membrane elements having
the permeate passing through the
high packing density is Permeate
wall and collected on the outside
their greater propensity flow Permeate
of the tube. flow
for fouling, as outlined in
CAPILLARY (HOLLOW FIBER) the table.
Concentration polarization. Membranes
These elements are similar to the Concentration polarization is the ac- Feed
tubular element in design. They cumulation of rejected particles to an spacer
are, however, smaller in diameter extent that transport to the membrane Plate and frame
and usually consist of unsupport- surface becomes limited. It reduces Concentrate
ed membrane polymers, which re- the permeability of the solvent and
quire rigid support on each end. can lead to a limiting flux and a
This support is provided by an Cartridge
higher fouling tendency. Membranes
epoxy “potting” of a bundle of the The type of membrane module used
Feed
fibers inside a cylinder. The feed in a process affects the influence of
Permeate
flow is either down the interior of concentration polarization; and it is
the fiber or around its outside. difficult to balance high fluxes and
low fouling with low investment and
SPIRAL WOUND operating costs. Tubular modules can COMPARISON OF MEMBRANE ELEMENT
CONFIGURATIONS
accommodate high cross flow and
This type of element is made from
large particles, but their capital costs Element Packing Fouling
an envelope of sheet membrane, configuration density* resistance**
and ratio of relative price to mem-
wound around a permeate Capillary filter medium high
brane area are considerably higher
tube that is perforated to al-
than those for spiral-wound modules. Plate and frame low high
low collection of the permeate.
Spiral-wound modules, on the other
Feed water becomes purified by Spiral wound medium moderate
hand, enjoy the advantages of lower
passing through one layer of the Tubular low high
installed costs and easier changeout.
membrane and flowing into the * Membrane area per unit volume of element
Channel height can be varied by the
permeate tube. This is by far the ** Tolerance to suspended solids
use of distance keepers, also known
most common configuration in
as spacers.
water-purification applications. References
Capillary membrane modules can be
1. Cartwright, P., Membranes for Process Water
PLATE AND FRAME backwashed inline during filtration to Reuse, Chem. Eng., June 2004, pp. 38–42.
remove particles from the membrane 2. Baird, A., Making High-Purity Water, Chem.
This kind of element employs or to add chemicals from the permeate Eng., May 2005, pp. 36–43.
sheet membrane, stretched over a side. Like tubular modules, they have 3. Buecker, B., Microfiltration for CPI Wastewater,
frame to separate the layers and Chem. Eng., May 2007, pp. 63–65.
high investment costs, but their ability to
4. Lipnizki, J., Strategies for Controlling Membrane
facilitate collection of the perme- backwash at regular intervals reduces the Fouling, Chem. Eng., September 2007, pp.
ate, which goes to a center tube. potential for fouling. 62–64.
You might also like
- Membrane Configurations FactsDocument1 pageMembrane Configurations FactsLisbeth Roos RoosNo ratings yet
- A Membrane Can Essentially Be Defined As A Barrier That Separates Two Phases and Selectively Restricts The Transport ofDocument4 pagesA Membrane Can Essentially Be Defined As A Barrier That Separates Two Phases and Selectively Restricts The Transport ofعبدالله البافاريNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200803-MembranesDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200803-Membranesonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Selecting Systems: Membrane FiltrationDocument4 pagesSelecting Systems: Membrane FiltrationRaul TejedaNo ratings yet
- Membranes: Thickness Effect On CO /N Separation in Double Layer Pebax-1657 /PDMS MembranesDocument13 pagesMembranes: Thickness Effect On CO /N Separation in Double Layer Pebax-1657 /PDMS MembranesMark XANo ratings yet
- Zeolite-Like Performance For Xylene Isomer Purification Using Polymer-Derived Carbon MembranesDocument8 pagesZeolite-Like Performance For Xylene Isomer Purification Using Polymer-Derived Carbon Membranesmissmoh85No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201009-Controlling Membrane FoulingDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201009-Controlling Membrane Foulingonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- PBI (Reverse Osmosis)Document53 pagesPBI (Reverse Osmosis)Muhammad FadillahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Science: Mylène Wang, Sourav Mondal, Ian M. GriffithsDocument8 pagesChemical Engineering Science: Mylène Wang, Sourav Mondal, Ian M. GriffithsRoxana ElenaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Applied Process Design C Hemical Petrochemical Plants1Document1 pagePages From Applied Process Design C Hemical Petrochemical Plants1ashrafNo ratings yet
- Packed Column With Different Type of PackingDocument1 pagePacked Column With Different Type of PackingBhadresh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- CERAMIC MEMBRANE DISTILLATION FOR DESALINATION (Autosaved)Document23 pagesCERAMIC MEMBRANE DISTILLATION FOR DESALINATION (Autosaved)ALAN JOYNo ratings yet
- Membranes FactsDocument1 pageMembranes FactsLisbeth Roos RoosNo ratings yet
- Che 0417 FR3 MPBDocument13 pagesChe 0417 FR3 MPBDario BonillaNo ratings yet
- Processing of FRP CompositesDocument8 pagesProcessing of FRP Compositessamriddhi mukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Membrane ProcessesDocument49 pagesMembrane ProcessesNur AmaninaNo ratings yet
- DESALINATION PROCESS in TAUS PLANTDocument1 pageDESALINATION PROCESS in TAUS PLANTsahar vahdatifarNo ratings yet
- Bituplus EDocument2 pagesBituplus EKHALID NAZKINo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer in Membrane ProcessesDocument16 pagesMass Transfer in Membrane Processestatchanok1525No ratings yet
- Gaztransport & TechnigazDocument4 pagesGaztransport & TechnigaziuliiulianNo ratings yet
- Abdf - Novel ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAbdf - Novel ApplicationsVamsee KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Study of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells With A Novel Compound Flow FieldDocument8 pagesExperimental and Numerical Study of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells With A Novel Compound Flow FieldminliNo ratings yet
- Coffin-Manson Fatigue Model of Underfilled Flip-Chips: Vadim Gektin,, Avram Bar-Cohen,, and Jeremy AmesDocument10 pagesCoffin-Manson Fatigue Model of Underfilled Flip-Chips: Vadim Gektin,, Avram Bar-Cohen,, and Jeremy Amesjulio perezNo ratings yet
- PCO-10techpaper Overview BushingsDocument7 pagesPCO-10techpaper Overview BushingssomeontorrenteNo ratings yet
- Polymer Nanocomposites: A Small Part of The Story : L.S. Schadler, L.C. Brinson, and W.G. SawyerDocument9 pagesPolymer Nanocomposites: A Small Part of The Story : L.S. Schadler, L.C. Brinson, and W.G. SawyergixoNo ratings yet
- Increased Polymer Di Ffusivity in Thin-Film Confinement: James F. Pressly, Robert A. Riggleman, and Karen I. WineyDocument10 pagesIncreased Polymer Di Ffusivity in Thin-Film Confinement: James F. Pressly, Robert A. Riggleman, and Karen I. Winey劉靖騰No ratings yet
- Technip Separations PDFDocument22 pagesTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Es 4013917Document8 pagesEs 4013917이주신No ratings yet
- Paper 1Document19 pagesPaper 1henaldedhia13No ratings yet
- Material Membran 2016Document34 pagesMaterial Membran 2016Ilhãm FahruziNo ratings yet
- PA-CNT FilmDocument10 pagesPA-CNT FilmkrrishNo ratings yet
- A PM 07 Copper PillarsDocument7 pagesA PM 07 Copper PillarsSieww GlenNo ratings yet
- Department Editor: Kate Torzewski: Packed ColumnsDocument1 pageDepartment Editor: Kate Torzewski: Packed ColumnshvananthNo ratings yet
- Esthetic Restorative Materials 4Document1 pageEsthetic Restorative Materials 4Tayyuba AslamNo ratings yet
- Dry Film LaminationDocument9 pagesDry Film LaminationDieselJakeNo ratings yet
- Mechanism For Tensile Strain Hardening in High Performance Cement-Based Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument9 pagesMechanism For Tensile Strain Hardening in High Performance Cement-Based Fiber Reinforced CompositesMark B. BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Syntactic FoamDocument8 pagesMatrix Syntactic FoamxlsysengNo ratings yet
- US3220842Document2 pagesUS3220842Luca BighouseNo ratings yet
- Ultrafiltration Membranes For Macromolecule ProcessingDocument5 pagesUltrafiltration Membranes For Macromolecule ProcessingR YNo ratings yet
- MILLIPORE UltrafiltrationMembranesDocument5 pagesMILLIPORE UltrafiltrationMembranestakwahs12135No ratings yet
- PMA - Materials & CompositesDocument7 pagesPMA - Materials & CompositesreezmanNo ratings yet
- AF 5 FibersDocument3 pagesAF 5 Fibersedilberto.penabrsNo ratings yet
- Role of Capillary Driven Flow in Composite ManufacturingDocument49 pagesRole of Capillary Driven Flow in Composite ManufacturingIAMANDU COSTANo ratings yet
- SpecialChem - Coalescing Agents in Coatings - Definition, Types & PropertiesDocument5 pagesSpecialChem - Coalescing Agents in Coatings - Definition, Types & Propertiesichsan hakimNo ratings yet
- Membranes and ModulesDocument6 pagesMembranes and ModulesmadhujayarajNo ratings yet
- Histo Embedding 1Document3 pagesHisto Embedding 1Karla Mae Tolelis - BurlatNo ratings yet
- SKF Vlaknasti Drsni Ležaji AngDocument8 pagesSKF Vlaknasti Drsni Ležaji Angdivjak70No ratings yet
- A Controlled Sintering Process For More Permeable Ceramic Hollow Fibre MembranesDocument8 pagesA Controlled Sintering Process For More Permeable Ceramic Hollow Fibre Membranesmahesh8760No ratings yet
- Membranes 13 00368 v2Document21 pagesMembranes 13 00368 v2A BNo ratings yet
- lADC/SPE 27503 Recent Advances in Subsea Completion/Workover Blowout PreventersDocument8 pageslADC/SPE 27503 Recent Advances in Subsea Completion/Workover Blowout PreventersWilliam Lim (William Lim)No ratings yet
- Polymers in Separation ProcessesDocument32 pagesPolymers in Separation ProcessesP.A. Gonzales CortesNo ratings yet
- Photoinduced Bending of A Coumarin-Containing Supramolecular PolymerDocument3 pagesPhotoinduced Bending of A Coumarin-Containing Supramolecular PolymerXinshi ChenNo ratings yet
- NatureDocument1 pageNaturearuntnjNo ratings yet
- Compensation To Opening BC BhattacharyaDocument18 pagesCompensation To Opening BC BhattacharyaRADHE GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Origin of Stabilisation of Aqueous Foams in Nanoparticle-Surfactant MixturesDocument10 pagesOrigin of Stabilisation of Aqueous Foams in Nanoparticle-Surfactant MixturessivhongNo ratings yet
- Articulo Membreana TFC-PRO Con Potencial de 25W-m2Document12 pagesArticulo Membreana TFC-PRO Con Potencial de 25W-m2Neymer ReyesNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials 2eFrom EverandPropagation of Sound in Porous Media: Modelling Sound Absorbing Materials 2eRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Optimal Design of Flexural Systems: Beams, Grillages, Slabs, Plates and ShellsFrom EverandOptimal Design of Flexural Systems: Beams, Grillages, Slabs, Plates and ShellsNo ratings yet
- Channels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportFrom EverandChannels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201101-Hansen Solubility Parameters (HSP)Document1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201101-Hansen Solubility Parameters (HSP)onizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201103-Infrared Temperature MeasurementDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201103-Infrared Temperature Measurementonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201104-Hopper Inserts For Improved Solids FlowDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201104-Hopper Inserts For Improved Solids Flowonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201105-Pressure Measurement ConsiderationsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201105-Pressure Measurement Considerationsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201102-Control Valve Position SensorsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201102-Control Valve Position Sensorsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201010-MSMPR Crystallization EquipmentDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201010-MSMPR Crystallization Equipmentonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201009-Controlling Membrane FoulingDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201009-Controlling Membrane Foulingonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201008-Heat Transfer Fluids System FiltrationDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201008-Heat Transfer Fluids System Filtrationonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201011-Viscosity MeasurementDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201011-Viscosity Measurementonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201012-Project Design Decision-Making Option ListsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201012-Project Design Decision-Making Option Listsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201002-Positive Displacement PumpsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201002-Positive Displacement Pumpsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201007-Conservation Economics Carbon Pricing ImpactsDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201007-Conservation Economics Carbon Pricing Impactsonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200812-Fluid FlowDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200812-Fluid Flowonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201003-Steam Tracer Lines and Traps PDFDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201003-Steam Tracer Lines and Traps PDFonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200907-Flowmeter SelectionDocument2 pagesFacts at Your Fingertips-200907-Flowmeter Selectiononizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200809-CrystallizationDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200809-Crystallizationonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-201005-Burner Operating Characteristics PDFDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-201005-Burner Operating Characteristics PDFonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200811-Alternative Fuels (Bio Diesel)Document1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200811-Alternative Fuels (Bio Diesel)onizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-200810-Heat TransferDocument1 pageFacts at Your Fingertips-200810-Heat Transferonizuka-t2263No ratings yet
- MiningGuideFinalVersion 141218Document23 pagesMiningGuideFinalVersion 141218BudKh100% (2)
- Weldability of Tungsten and Its AlloysDocument8 pagesWeldability of Tungsten and Its Alloyss_m_taheriNo ratings yet
- PRT Lecture - 16 17Document30 pagesPRT Lecture - 16 17HimaNo ratings yet
- Umakor Maxwell It ReportDocument46 pagesUmakor Maxwell It ReportChinyereugo OkikeNo ratings yet
- Types of Failure: 1. Alligator Cracking of Flexible PavementsDocument12 pagesTypes of Failure: 1. Alligator Cracking of Flexible PavementsStalan JonathanNo ratings yet
- 9.5 Giant Metallic StructuresDocument2 pages9.5 Giant Metallic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- 7.17.5 Calculation of Short-Term Deflection: I I I I - M / M) (Z / D) (X/D) (B/B) IDocument1 page7.17.5 Calculation of Short-Term Deflection: I I I I - M / M) (Z / D) (X/D) (B/B) IscrNo ratings yet
- Surface Engineering For CorrosionDocument24 pagesSurface Engineering For CorrosionSreedhar Patnaik.MNo ratings yet
- I Imagine A Future Full of Leather Finished in A Qualitative, Compliant and Sustainable WayDocument2 pagesI Imagine A Future Full of Leather Finished in A Qualitative, Compliant and Sustainable Wayzaryab khanNo ratings yet
- Metakom Sarana Pranata PT (Member of Metakom)Document21 pagesMetakom Sarana Pranata PT (Member of Metakom)Recky PahleviNo ratings yet
- Melamine UllmannDocument18 pagesMelamine Ullmannmouse1201100% (1)
- Jaggery Sugar: Material Safety Data SheetDocument3 pagesJaggery Sugar: Material Safety Data SheetIshwari KNo ratings yet
- Biomaterial - HydrogelDocument75 pagesBiomaterial - HydrogelMauhibahYumnaNo ratings yet
- Die Punching Machine PDFDocument1 pageDie Punching Machine PDFAsfakvhora92100% (1)
- Ash Handling by Peter FuDocument102 pagesAsh Handling by Peter FuIrfan AbdullAhNo ratings yet
- Many Theories Have Been Advanced To Account For The Way or Means by Which The Emulsion Is Stabilized by The EmulsifierDocument9 pagesMany Theories Have Been Advanced To Account For The Way or Means by Which The Emulsion Is Stabilized by The EmulsifierShabab BasharNo ratings yet
- 6 Direct Filling GoldDocument100 pages6 Direct Filling GoldShresthaNo ratings yet
- DasdDocument2 pagesDasdAnonymous lApm6PsfNo ratings yet
- Buyers Guide Cleaning&MaintenanceDocument14 pagesBuyers Guide Cleaning&MaintenanceongtatianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Hybrid Machining ProcessesDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Hybrid Machining ProcessesGAURAV KUMAR100% (1)
- Assessing The Quality of Sandstones For Use Aas Aggregate in ConcreteDocument12 pagesAssessing The Quality of Sandstones For Use Aas Aggregate in ConcreteNikolaos ChousidisNo ratings yet
- ASTM E140 - Hardness Conversion Table For Metals RelationshipDocument21 pagesASTM E140 - Hardness Conversion Table For Metals RelationshipKushal PraviraNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Liquid Penetrant Examination Using The Solvent-Removable ProcessDocument6 pagesFluorescent Liquid Penetrant Examination Using The Solvent-Removable ProcessJHONNATAN ORJUELA CORTESNo ratings yet
- 6.730 Physics For Solid State Applications: Lecture 32: Introduction To Boltzmann TransportDocument12 pages6.730 Physics For Solid State Applications: Lecture 32: Introduction To Boltzmann TransportHùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Monarflex Weather ProtectionDocument17 pagesMonarflex Weather ProtectionalokNo ratings yet
- Steel DetailingDocument55 pagesSteel DetailingHarpreet Singh100% (1)
- GridDocument8 pagesGridأنس الجعديNo ratings yet
- Methanol Brine Corrosion InhibitorDocument2 pagesMethanol Brine Corrosion InhibitorsinughoshNo ratings yet
- 19 Ceramics 2nd YrDocument162 pages19 Ceramics 2nd YrLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- PE326Document16 pagesPE326Ramy MaamounNo ratings yet