Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Locomotion: Appendicular Skeleton
Uploaded by
Kristine Mae Pastor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesThe document discusses the skeletal and muscular systems of animals. It describes three types of skeletal systems - endoskeletons, exoskeletons, and hydrostatic skeletons. It also outlines the axial and appendicular parts of the human skeletal system and identifies three main types of muscle: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction is introduced as well.
Original Description:
jjjjj
Original Title
bio-handout
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the skeletal and muscular systems of animals. It describes three types of skeletal systems - endoskeletons, exoskeletons, and hydrostatic skeletons. It also outlines the axial and appendicular parts of the human skeletal system and identifies three main types of muscle: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction is introduced as well.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesAnimal Locomotion: Appendicular Skeleton
Uploaded by
Kristine Mae PastorThe document discusses the skeletal and muscular systems of animals. It describes three types of skeletal systems - endoskeletons, exoskeletons, and hydrostatic skeletons. It also outlines the axial and appendicular parts of the human skeletal system and identifies three main types of muscle: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction is introduced as well.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
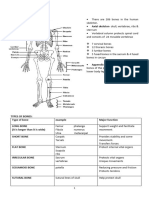
Compare and Contrast in Plants and Animals: • skull and backbone (spiral cord); rib
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms cage
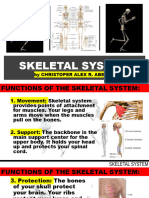
Animal Locomotion APPENDICULAR SKELETON
● any of a variety of methods that animals • includes all bones of the upper and
use to move from one place to another lower limbs, plus the bones that attach
● examples are running, walking, each limb to the axial skeleton
swimming, flying, crawling, hopping • bones of the appendages (arms, legs,
● animals move for a variety of reasons, fins) and bones linking the appendages
to the axial skeleton – the pectoral and
such as
pelvic girdles
○ to find food
○ to find a mate
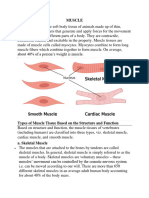
○ to find a suitable habitat 3 Types of Muscle
○ to escape predators SKELETAL MUSCLE
anchored to bone by tendons and is
used to affect skeletal movement such
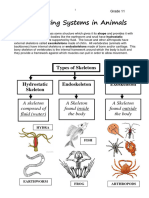
3 Types of Skeletal System as locomotion and maintaining posture
HYDROSTATIC SKELETON
• a skeleton formed by a fluid-filled SMOOTH MUSCLE
compartment within the body, called the found within the walls of organs and
coelom structures and is also an involuntary
• common in aquatic and burrowing muscle
animals
• there is no solid “bone” but the animal CARDIAC MUSCLE
under aquatic pressure can stay upright is involuntary and found only in the heart
and move
EXOSKELETON SLIDING FILAMENT THEORY
• external skeleton that consists of a hard explains the mechanism of muscle
encasement on the surface of an contraction based on muscle proteins
organism that slide past each other to generate
• rigid, armor-like coverings movement
• when arthropods grow, they shed off introduced in 1954 by two research
their old “armor” and grow a new one teams, one consisting of Andrew F.
Huxley and Rolf Niedergerke
ENDOSKELETON the myosin (thick) filaments of muscle
• consists of rigid but flexible support fibers slide past the actin (thin) filaments
made of bones, cartilage surrounded by during muscle contraction, while the two
masses of muscles groups of filaments remain at relatively
• provide support for the body, protect constant length
internal organs, and allow for movement
through contraction of muscles attached
to the skeleton
• human skeleton is an endoskeleton
Human Skeletal Systems
AXIAL SKELETON
• forms the vertical, central axis of the
body and includes all bones of the head, Pastor & Perez (12C)
neck, chest
Compare and Contrast in Plants and Animals: • skull and backbone (spiral cord); rib
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms cage
Animal Locomotion APPENDICULAR SKELETON
● any of a variety of methods that animals • includes all bones of the upper and
use to move from one place to another lower limbs, plus the bones that attach
● examples are running, walking, each limb to the axial skeleton
swimming, flying, crawling, hopping • bones of the appendages (arms, legs,
● animals move for a variety of reasons, fins) and bones linking the appendages
to the axial skeleton – the pectoral and
such as
pelvic girdles
○ to find food
○ to find a mate
○ to find a suitable habitat 3 Types of Muscle
○ to escape predators SKELETAL MUSCLE
anchored to bone by tendons and is
used to affect skeletal movement such
3 Types of Skeletal System as locomotion and maintaining posture
HYDROSTATIC SKELETON
• a skeleton formed by a fluid-filled SMOOTH MUSCLE
compartment within the body, called the found within the walls of organs and
coelom structures and is also an involuntary
• common in aquatic and burrowing muscle
animals
• there is no solid “bone” but the animal CARDIAC MUSCLE
under aquatic pressure can stay upright is involuntary and found only in the heart
and move
EXOSKELETON SLIDING FILAMENT THEORY
• external skeleton that consists of a hard explains the mechanism of muscle
encasement on the surface of an contraction based on muscle proteins
organism that slide past each other to generate
• rigid, armor-like coverings movement
• when arthropods grow, they shed off introduced in 1954 by two research
their old “armor” and grow a new one teams, one consisting of Andrew F.
Huxley and Rolf Niedergerke
ENDOSKELETON the myosin (thick) filaments of muscle
• consists of rigid but flexible support fibers slide past the actin (thin) filaments
made of bones, cartilage surrounded by during muscle contraction, while the two
masses of muscles groups of filaments remain at relatively
• provide support for the body, protect constant length
internal organs, and allow for movement
through contraction of muscles attached
to the skeleton
• human skeleton is an endoskeleton
Human Skeletal Systems
AXIAL SKELETON
• forms the vertical, central axis of the
body and includes all bones of the head, Pastor & Perez (12C)
neck, chest
You might also like
- Anatomy Physiology, 11th Ed. Seeley - SDocument89 pagesAnatomy Physiology, 11th Ed. Seeley - SJames Maverick Chavez100% (2)
- Gimble's Guide to the FeywildDocument84 pagesGimble's Guide to the FeywildYasha515100% (2)
- The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]From EverandThe Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Hematology AutomationDocument117 pagesHematology AutomationRico EdureseNo ratings yet
- Csec Biology Manual of Essential Notes Based Purely On Syllabus RequirementsDocument126 pagesCsec Biology Manual of Essential Notes Based Purely On Syllabus RequirementsNicayne RamnarineNo ratings yet
- Archetypes and SymbolsDocument5 pagesArchetypes and Symbolsapi-282414461No ratings yet
- Ancient Genomic Time Transect From The Central Asian Steppe Unravels The History of The ScythiansDocument15 pagesAncient Genomic Time Transect From The Central Asian Steppe Unravels The History of The ScythiansErwin SchrödringerNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Grade 7: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Cell To BiosphereDocument9 pagesSCIENCE Grade 7: Quarter 2 - Module 3 Cell To Biospheresam patauegNo ratings yet
- CGP Embarking On A Journey of Self Awareness ModuleDocument101 pagesCGP Embarking On A Journey of Self Awareness ModuleKristine Mae Pastor100% (3)
- Introduction to Animal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument141 pagesIntroduction to Animal Anatomy and PhysiologyChristian Paul Palma BasigNo ratings yet
- Genbio Finals Lesson 3 4Document3 pagesGenbio Finals Lesson 3 4Seb LlaveNo ratings yet
- Muskuloskeletal DisordersDocument15 pagesMuskuloskeletal DisordersLienyPerasNo ratings yet
- Locomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLocomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemNathanael MfumbaikaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Tissues and Supporting SystemDocument39 pages2.0 Tissues and Supporting Systemwalterkalu385No ratings yet
- The Muscular System ExplainedDocument5 pagesThe Muscular System ExplainedHannah Mae Supeña CatedrillaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Human BodyDocument19 pagesStructure of Human BodyWimrod CanenciaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocument39 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular SystemsMuhamad IqbalNo ratings yet
- 11LS the Skeleton NOTESDocument28 pages11LS the Skeleton NOTESAdhi PandayNo ratings yet
- Anatomi & Fisiologi IDocument25 pagesAnatomi & Fisiologi ISyasya NanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Muscular and SkeletalDocument19 pages3 Muscular and SkeletalJan Leo QuinioNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument38 pagesSkeletal SystemJOHN ANDREI ZARSADIASNo ratings yet
- 11.7. The Skeleton and LocomotionDocument43 pages11.7. The Skeleton and LocomotionThomas BanksNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System OfficialDocument14 pagesHuman Skeletal System Officialconirv1No ratings yet
- GROSS General Concepts of MusclesDocument28 pagesGROSS General Concepts of MusclesDell E6430No ratings yet
- Support System and MovementDocument38 pagesSupport System and MovementNinamay FajardoNo ratings yet
- Locomotion Handout 2023Document7 pagesLocomotion Handout 2023rheanna0076No ratings yet
- Ansc-20-Anatomy and Physiology Part 3Document20 pagesAnsc-20-Anatomy and Physiology Part 3Jhe ar ButayNo ratings yet
- Bones and muscles that allow movementDocument13 pagesBones and muscles that allow movementmelbert nacuNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue PPT by KanishkaDocument20 pagesAnimal Tissue PPT by KanishkaKanishka SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal System: Structure and Movement in 38 CharactersDocument30 pagesThe Musculoskeletal System: Structure and Movement in 38 CharactersJosee50% (2)
- Grade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Document55 pagesGrade Ix Biology Animal Tissues 2021Purvi Prakash KNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System-Topic 8Document40 pagesMusculoskeletal System-Topic 8Heba TabchNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular System OverviewDocument72 pagesSkeletal and Muscular System OverviewMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- (Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFDocument7 pages(Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Support and MovementDocument8 pagesSkeletal Support and MovementUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementDocument28 pagesSupport and MovementDayangNo ratings yet
- The Four Major Tissue Types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous (less than 40 charsDocument29 pagesThe Four Major Tissue Types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous (less than 40 charsGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: By: Emily Brosten Stephanie ElhardDocument36 pagesMuscular System: By: Emily Brosten Stephanie ElhardPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument36 pagesMuscular SystemDeepak KdNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAlian WilliansNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Report GuideDocument6 pagesMusculoskeletal Report GuideIrish CostalesNo ratings yet
- PDHPE 2020 YR 11 NOTES mmmmDocument30 pagesPDHPE 2020 YR 11 NOTES mmmmicewallowhaNo ratings yet
- Cells-and-Tissues 1Document33 pagesCells-and-Tissues 1Susan Batan BandongNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Sample PDFDocument46 pagesChapter1 Sample PDFakashNo ratings yet
- HSB Week 13Document19 pagesHSB Week 13edhanassarNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE B.Sc-IIDocument13 pagesMUSCLE B.Sc-IIAjinkya BansodeNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahDocument27 pagesEmbryology: Abdulrahman Uday AbdulfatahAbdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2. Skeletal System PowerPointDocument51 pagesGeneral Biology 2. Skeletal System PowerPointMetal ManNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ExplainedDocument36 pagesMuscular System ExplainedAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Casting: Author: Matthew Pitt Senior Orthopaedic PractitionerDocument31 pagesPractical Guide To Casting: Author: Matthew Pitt Senior Orthopaedic PractitionerAmeng GosimNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Systems in VertebratesDocument26 pagesSkeletal Systems in Vertebratesgoldennyeche080No ratings yet
- Skeletal System - 230413 - 185932Document75 pagesSkeletal System - 230413 - 185932Jasmine JuitNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerpointDocument72 pagesSkeletal System PowerpointDiana FrillsNo ratings yet
- HAP Lesson 3 (Muscular System)Document33 pagesHAP Lesson 3 (Muscular System)rodolfogallineroNo ratings yet
- The Four Basic Types of Animal TissueDocument26 pagesThe Four Basic Types of Animal TissueReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Musculoskeletal SystemDocument30 pagesLesson 6 - Musculoskeletal Systemapi-307592530100% (1)
- Skeletal System FinalDocument53 pagesSkeletal System FinalKyle Darren PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Ebook Biology ShazwaniDocument20 pagesEbook Biology ShazwaniNurul shazwaniNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular Systems: A Guide to Bones, Joints, and Muscle TypesDocument2 pagesSkeletal and Muscular Systems: A Guide to Bones, Joints, and Muscle TypesAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Learn About Tissues in BiologyDocument13 pagesLearn About Tissues in BiologyRi DeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Faiz ApaiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Muscular SystemsDocument24 pagesSkeletal and Muscular SystemsMarlyn Laurio-patriarcaNo ratings yet
- 5th Form Biology-Movement - Movement in Man.Document52 pages5th Form Biology-Movement - Movement in Man.Jharell CaravlhoNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Animal TissueDocument43 pagesLesson 4 - Animal TissueFhai SisonNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument5 pagesAnaphyRhona Angela CruzNo ratings yet
- 330Document1 page330Kristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Assign 2Document3 pagesAssign 2Kristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument1 pageInternational TradeKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- I and IIDocument1 pageI and IIKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument2 pagesSwot AnalysisKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- A Turgid Revenge ThrillerDocument3 pagesA Turgid Revenge ThrillerKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Cirilo F. Bautista (July 9, 1941 - May 6, 2018) WasDocument2 pagesCirilo F. Bautista (July 9, 1941 - May 6, 2018) WasKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- PhishingDocument1 pagePhishingKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesNarrative ReportKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Carljoe Javier biographyDocument3 pagesCarljoe Javier biographyKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- STREET AND HIP-HOP DANCE STYLESDocument1 pageSTREET AND HIP-HOP DANCE STYLESKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- National Artist Ildefonso P. Santos Jr landscape architectureDocument3 pagesNational Artist Ildefonso P. Santos Jr landscape architectureKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Architecture "Architecture Must Be True To Itself, Its Land, and Its People" - Francisco Manosa Short BackgroundDocument2 pagesArchitecture "Architecture Must Be True To Itself, Its Land, and Its People" - Francisco Manosa Short BackgroundKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Pe ReviewDocument6 pagesPe ReviewKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Architecture "Architecture Must Be True To Itself, Its Land, and Its People" - Francisco Manosa Short BackgroundDocument2 pagesArchitecture "Architecture Must Be True To Itself, Its Land, and Its People" - Francisco Manosa Short BackgroundKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- This Is A BlankDocument1 pageThis Is A BlankKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Historical Overview of Philippine ArtDocument9 pagesHistorical Overview of Philippine ArtKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- ASSIGN1Document3 pagesASSIGN1Kristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Architecture "Architecture Must Be True To Itself, Its Land, and Its People" - Francisco Manosa Short BackgroundDocument2 pagesArchitecture "Architecture Must Be True To Itself, Its Land, and Its People" - Francisco Manosa Short BackgroundKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument2 pagesSwot AnalysisKristine Mae PastorNo ratings yet
- Diversity With Microorganism (NOTES)Document2 pagesDiversity With Microorganism (NOTES)Clarissa Jane GabiolaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science MCQ Heredity and Evolution 3Document17 pagesClass 10 Science MCQ Heredity and Evolution 3RAKSHANA SELVAMNo ratings yet
- The Selection Process WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Selection Process Worksheetapi-256236481No ratings yet
- Virtual Western Blotting LabDocument4 pagesVirtual Western Blotting Labapi-522349089No ratings yet
- Tissue SectioningDocument21 pagesTissue SectioningGirum TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Diatom Test A Golden Standard Test in Drowning CasesDocument1 pageDiatom Test A Golden Standard Test in Drowning CasesRevathy RNo ratings yet
- Cytiva-Microcarrier cell cultureDocument160 pagesCytiva-Microcarrier cell cultureQuynhMai TrinhNo ratings yet
- PigeoneticsGameTeacherGuideDocument8 pagesPigeoneticsGameTeacherGuideiamtrex1No ratings yet
- Vol 34 No 1 PDFDocument56 pagesVol 34 No 1 PDFrlamtilaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Writing A Literature ReviewDocument72 pagesChapter 3 - Writing A Literature ReviewSerey MardyNo ratings yet
- What Affects The Biocompatibility of PolymersDocument25 pagesWhat Affects The Biocompatibility of PolymersAndreaNo ratings yet
- Lupasol PN 80 On PP Nonwoven - From StevenDocument6 pagesLupasol PN 80 On PP Nonwoven - From StevenSyed Owais Ali NaqviNo ratings yet
- Practice Test A - Reading Question 1-10Document6 pagesPractice Test A - Reading Question 1-10Silence alfa0% (1)
- Mockk 1Document99 pagesMockk 1ADITI NEGINo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIDocument10 pagesLab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIErreneoNo ratings yet
- Plants Emit Informative Airborne Sounds Under Stress: AuthorsDocument23 pagesPlants Emit Informative Airborne Sounds Under Stress: AuthorsArtNo ratings yet
- FRM-321 - Fish Population Dynamics and Stock Assessment - VPA -1Document32 pagesFRM-321 - Fish Population Dynamics and Stock Assessment - VPA -1Dibya Ranjan PatraNo ratings yet
- Redescription of Female Laelaps NuttalliDocument9 pagesRedescription of Female Laelaps Nuttallimelanieruiz09No ratings yet
- Kapita Selekta Modul MKKP PDFDocument74 pagesKapita Selekta Modul MKKP PDFDIKE NOVELLA -No ratings yet
- Facial Expressions and The Regulation of Emotions: Carroll E. IzardDocument12 pagesFacial Expressions and The Regulation of Emotions: Carroll E. IzardMarie-Lou MénétrierNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 ClusteringDocument48 pagesLecture12 ClusteringarjunNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Term Wise Biology Syllabus 2021 22Document6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Term Wise Biology Syllabus 2021 22Krish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project On: Sprindale High SchoolDocument13 pagesProject On: Sprindale High SchoolGoutam MondalNo ratings yet
- CartilagoDocument40 pagesCartilagoIlham DwiNo ratings yet


![The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/238627287/149x198/b1987107b7/1617237212?v=1)