Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Full Credit, You Must Show How You Got Your Answers or You Will Receive ZERO Score
Uploaded by
Ahmed SabriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Full Credit, You Must Show How You Got Your Answers or You Will Receive ZERO Score
Uploaded by
Ahmed SabriCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 4300/5950 ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS SPRING 12 HW #3
DUE: 02/08/12
NOTE**: There are answers to some of the problems at the end of the textbook. To get
full credit, you must show how you got your answers or you will receive ZERO score.
1. Problem #3.2 pp. 135.
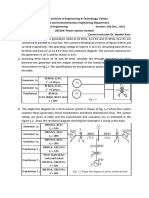
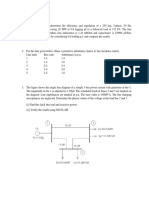
2. A three-phase power system is shown in Fig. P2.1. As a starting point, select a base equal to
2400 V as the base voltage for the generators. The power base is 100 kVA.
(a) Determine the new base voltage for the transmission line system.
(b) Determine the new base voltage for the motor system.
(c) Redraw the on-line diagram of the system, showing the new base voltages for the entire
system.
(d) Determine the per unit impedance of generator G1 converted to the new base values.
(e) Determine the per unit impedance of generator G2 converted to the new base values.
(f) Determine the per unit impedance of transformer T1 converted to the new base values.
(g) Determine the per unit impedance of transformer T2 converted to the new base values.
(h) Determine the per unit impedance of transmission line converted to the base values.
(i) Determine the per unit power of motor M converted to the new base values.
(j) Determine the per unit voltage of motor M converted to the new base values.
(k) Draw an impedance diagram in per unit showing the per unit values.
10 kVA
2400V G1 T1 Transmission Line T2
Z = j0.2 pu M
Z = (50 + j200)
20 kVA 40 kVA 80 kVA 25 kVA
2400V G2 2400/9600 V 10/5 kV 4 kV
Z = j0.2 pu Z = j0.1 pu Z = j0.1 pu
Fig. P2.1
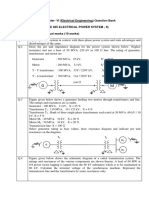
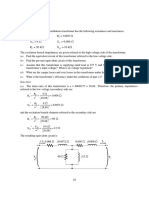
3. One line diagram of a three-phase power system is shown in Fig. P3.1. Three single-phase
transformers, each with an impedance of X1 = 0.24 (on the low-voltage side with negligible
resistance and magnetizing current) and turns ratio N2/ N1 = 10, are connected in a three-phase
bank. The transformer bank is delivering 100 MW at 0.8 PF lagging to a substation bus whose
voltage is 230 kV.
(a) Determine the primary current magnitude, the primary voltage (line-to-line) magnitude,
and the three-phase complex supplied by the generator. Use the line-to-neutral voltage
at the bus, Va’n’, on the secondary side as reference. Account for the phase shift.
(b) Find the phase shift between the primary and secondary voltages
G To rest of the system
Generator
-Y 230-kV substation
Step-up bus
Transformer bank
Fig. P3.1
You might also like
- Sessional Set 17Document1 pageSessional Set 17Vikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Per Unit PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 Per Unit PDFSofia Nadhirah Binti Amluddin100% (1)
- Noida Institute of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida: Section - ADocument3 pagesNoida Institute of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida: Section - AVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Document6 pagesUnit - 1 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Sujit KumarNo ratings yet
- A1Document4 pagesA1hsvskumarNo ratings yet
- Control Loops 2Document22 pagesControl Loops 2Muntadher AbbasNo ratings yet
- 1.per Unit System PDFDocument10 pages1.per Unit System PDFlaxman100% (1)
- Power AnalysisDocument72 pagesPower AnalysisSupawadeeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power System AssinmentDocument3 pagesAdvanced Power System AssinmentJara FeyisaNo ratings yet
- UEE509 Tutorial Sheets and Lab AssignmentsDocument13 pagesUEE509 Tutorial Sheets and Lab AssignmentsAditya AdityaNo ratings yet
- EE8501-Power System AnalysisDocument8 pagesEE8501-Power System AnalysisthiyagusuperNo ratings yet
- !7374656d5f26736f6c7574696f6e73 PDFDocument12 pages!7374656d5f26736f6c7574696f6e73 PDFluckyNo ratings yet
- BE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Document5 pagesBE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Adesh Bhortakke100% (1)
- Question Paper CodeDocument6 pagesQuestion Paper Codeprasad powerNo ratings yet
- Lab QPDocument8 pagesLab QPpmahesh268No ratings yet
- EE4533Tutorial Questions - 2021Document5 pagesEE4533Tutorial Questions - 2021Daniel ChaiNo ratings yet
- Unta BeranakDocument6 pagesUnta Beranakharis kunkunNo ratings yet
- Psas Ut1-QbDocument7 pagesPsas Ut1-QbNaveen RajNo ratings yet
- Pse 1 5 (7 Marks)Document33 pagesPse 1 5 (7 Marks)Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument23 pagesPower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 2Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 2Naasir SheekeyeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Dr.Hesham El-BadawyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1sadNo ratings yet
- EE 3741 Tutorial 2 and Solution - To Student PDFDocument5 pagesEE 3741 Tutorial 2 and Solution - To Student PDFMegan ChaiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFDocument6 pagesTutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFnanangNo ratings yet
- EET301 Tutorial 2-Chapter 2-Session 2017-2018Document4 pagesEET301 Tutorial 2-Chapter 2-Session 2017-2018Nazir AhmedNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument2 pagesTransformerBsal SokoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Preetham ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pse Problems Group AssignmentDocument14 pagesPse Problems Group AssignmentSajid KhanNo ratings yet
- BEEI 2383 TutorialDocument3 pagesBEEI 2383 TutorialAIMAN DANIAL BIN SULONGNo ratings yet
- Important PSA Assignment PDFDocument27 pagesImportant PSA Assignment PDFDevansh PratapNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Document11 pagesEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- Assignment No. 1 PSSA-Fall-2021Document3 pagesAssignment No. 1 PSSA-Fall-2021osama munirNo ratings yet
- Psa I 17ee62Document20 pagesPsa I 17ee62Shreyas KanabaragiNo ratings yet
- Tuto 4 PuDocument3 pagesTuto 4 PuVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- PSA 2018 Tutorials-1Document9 pagesPSA 2018 Tutorials-1vikramNo ratings yet
- Class Test 2 Question PaperDocument1 pageClass Test 2 Question Paperbrahma2deen2chaudharNo ratings yet
- 14 PDFDocument3 pages14 PDFalejanNo ratings yet
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 1Document2 pagesTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 1eh2asham1No ratings yet
- Maquinas ExamenDocument29 pagesMaquinas ExamenJean QuispeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument24 pagesChapter Two: Representation of Power System ComponentsBonsaNo ratings yet
- Pu Assignment 1Document2 pagesPu Assignment 1jasonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Pse - 2012-2013Document23 pagesTutorial Pse - 2012-2013Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Syed Faras HaiderNo ratings yet
- Lab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticaDocument8 pagesLab. Exercise PL1 CC/CC Converters: Electrònica de Potència Grau en Enginyeria Electrònica Industrial I AutomàticageovannyNo ratings yet
- PowerSystem Set1Document9 pagesPowerSystem Set1shivansh gandhiNo ratings yet
- 0.psa - As - Pu System PDFDocument4 pages0.psa - As - Pu System PDFanandNo ratings yet
- Power SystemDocument4 pagesPower Systemj settyNo ratings yet
- Per Unit CalculationsDocument7 pagesPer Unit Calculationsanbuelectrical100% (1)
- Solucionario Cap 2 Máquinas EléctricasDocument48 pagesSolucionario Cap 2 Máquinas EléctricasfernandoNo ratings yet
- One-Line Diagram: Simplified Single-Phase Balanced Three-Phase Single Line Apparatus SymbolsDocument24 pagesOne-Line Diagram: Simplified Single-Phase Balanced Three-Phase Single Line Apparatus SymbolsSyazwan HafidziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: TransformersDocument5 pagesChapter 2: TransformerskhuzaimNo ratings yet
- Q) A Single-Phase Two-Winding Transformer Is Rated 20 kVA, 480/120 Volts, 60 HZDocument8 pagesQ) A Single-Phase Two-Winding Transformer Is Rated 20 kVA, 480/120 Volts, 60 HZMarwan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Test Emc1Document2 pagesTest Emc1Omkar SheteNo ratings yet
- PSA SolutionDocument5 pagesPSA SolutionviswaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1.8 Map of National Grid, Malaysia and South-East AsiaDocument10 pagesFigure 1.8 Map of National Grid, Malaysia and South-East AsiaDa Harlequin GalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PSE 2011-2012Document23 pagesTutorial PSE 2011-2012Mahesh Singh100% (1)
- Power System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Document29 pagesPower System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Jishnuraj KubandrarajNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Fusing Equipment: Elf™ Current-Limiting Dropout FuseDocument12 pagesFusing Equipment: Elf™ Current-Limiting Dropout FuseAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- Transformer ProtectionDocument21 pagesTransformer ProtectionAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Components, Networ Sequence, and FaultsDocument33 pagesSymmetrical Components, Networ Sequence, and FaultsAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- Ece6950 1 - and 3-Phase ReviewDocument14 pagesEce6950 1 - and 3-Phase ReviewAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- All Classroom Class ExamplesDocument51 pagesAll Classroom Class ExamplesAhmed Sabri0% (1)
- CCF04302015 0000Document17 pagesCCF04302015 0000Ahmed SabriNo ratings yet
- Smart Energy Coordination of Autonomous ResidentiaDocument13 pagesSmart Energy Coordination of Autonomous ResidentiaAhmed SabriNo ratings yet
- MA-3600VZ: Macro-Tech SeriesDocument2 pagesMA-3600VZ: Macro-Tech SeriesKevin MaduranNo ratings yet
- Check List For Addressable Fire Alarm Voice Evacuation System Testing CommissioningDocument6 pagesCheck List For Addressable Fire Alarm Voice Evacuation System Testing CommissioningNaing Win TunNo ratings yet
- Interruptor K01 1Document2 pagesInterruptor K01 1nomanNo ratings yet
- Srevice Manual Leica CTR4000-CTR7000 CTR 6 Halogen en V06Document136 pagesSrevice Manual Leica CTR4000-CTR7000 CTR 6 Halogen en V06ricardogsNo ratings yet
- Tec Arc Calibox 6000I Amps and Volts Calibrated Meter BoxDocument1 pageTec Arc Calibox 6000I Amps and Volts Calibrated Meter Boxloren wassoufNo ratings yet
- SUN2000-100KTL-M1 Output Characteristics Curve: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument8 pagesSUN2000-100KTL-M1 Output Characteristics Curve: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDMuhammad Shahrul IzwanNo ratings yet
- PresynopsisDocument26 pagesPresynopsisSav ThaNo ratings yet
- ITP For Non-Fire Resistant CI CableDocument1 pageITP For Non-Fire Resistant CI CableMeng PamplonaNo ratings yet
- AT 17503 AEE Session 27Document18 pagesAT 17503 AEE Session 27pavanraneNo ratings yet
- Gemco: Section 1980SDocument6 pagesGemco: Section 1980SAnu NakiNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 Transistor BiasingDocument19 pagesCh.5 Transistor Biasingdes tosNo ratings yet
- Manual FOR Oc, SC Test On Synchronous AlternatorDocument5 pagesManual FOR Oc, SC Test On Synchronous Alternatorramniwas123No ratings yet
- Experiment 1:: Non-Inverting, Inverting Amplifiers and Voltage FollowerDocument22 pagesExperiment 1:: Non-Inverting, Inverting Amplifiers and Voltage FolloweragNo ratings yet
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial Version: Coron Jet - Utsch - SheetDocument1 pagePDF Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial Version: Coron Jet - Utsch - SheetdNo ratings yet
- Simple Low Power Inverter Circuit (12V DC To 230V or 110V AC) Diagram Using CD4047 and IRFZ44 Power MOSFETDocument4 pagesSimple Low Power Inverter Circuit (12V DC To 230V or 110V AC) Diagram Using CD4047 and IRFZ44 Power MOSFETVikas AdhikariNo ratings yet
- R8D0-MIO-Ex12.FF ManualDocument57 pagesR8D0-MIO-Ex12.FF ManualrifervizNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument3 pagesDatasheetLima LogictelNo ratings yet
- Two-Storey Res - BLDGDocument1 pageTwo-Storey Res - BLDGpeejayNo ratings yet
- Access Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAccess Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsAnanna TithiNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 Common Emitter Fixed Bias Amplifier ConfigurationDocument19 pagesActivity 10 Common Emitter Fixed Bias Amplifier ConfigurationMarvZz VillasisNo ratings yet
- Condenser Bushings 25 KVDocument8 pagesCondenser Bushings 25 KVOktafian PrabandaruNo ratings yet
- The Ship at A Has Just Started To Drill For Oil On...Document2 pagesThe Ship at A Has Just Started To Drill For Oil On...Muhd ZameerNo ratings yet
- Brake - Control - 2 TKEDocument26 pagesBrake - Control - 2 TKETecwyn WebsterNo ratings yet
- Eee 351 - L1 PDFDocument19 pagesEee 351 - L1 PDFprithuNo ratings yet
- AmedaPlatinum Service ManualDocument7 pagesAmedaPlatinum Service ManualPañares NeilNo ratings yet
- Flip FlopsDocument11 pagesFlip FlopsZakaria JubarnNo ratings yet
- Protective Relaying and TestingDocument19 pagesProtective Relaying and Testingsherub wangdiNo ratings yet
- Stp5Nk80Z Stp5Nk80Zfp: N-Channel 800V - 1.9 - 4.3A - To-220/To-220Fp Zener-Protected Supermesh™ Power MosfetDocument15 pagesStp5Nk80Z Stp5Nk80Zfp: N-Channel 800V - 1.9 - 4.3A - To-220/To-220Fp Zener-Protected Supermesh™ Power MosfetMarcilio AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Digital T-Rms Auto-Ranging Multimeter Metrasafe-10: The Quality LeaderDocument5 pagesDigital T-Rms Auto-Ranging Multimeter Metrasafe-10: The Quality LeaderRaja RajaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - 1v2Document43 pagesModule 1 - 1v2Prakash L SNo ratings yet