Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name: Citra Puspita Sari NIM:18301083
Uploaded by
Citra Puspita SariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Citra Puspita Sari NIM:18301083
Uploaded by
Citra Puspita SariCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Citra Puspita Sari
NIM:18301083
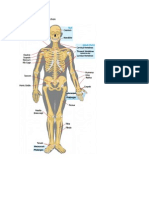
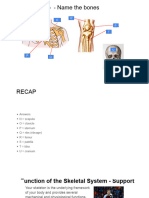
Pelvic Bones
1. As a bone that functions to protect and support lower organs such as the bladder and
others.
2. As a bone that functions to support body weight together with the vertebrae.
3. As a bone that serves to support the fat or meat that is or sticks to the hip
Femur
1. As the strongest bone to support the body
2. Place of attachment and stickiness of muscles and pigments
3. As a place for the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow
4. Play an important role as a lower body exercise tool
5. As the largest and strongest bone in the body
6. The thighbone can create the condylar joint with the knee
7. The knee cap is attached
8. As a liaison for the hips and knees
Knee bones
1. Forming the knee joint
2. Helping the knee to bend and move
3. Help and balance the movement of the knee joint
4. Protect the knee joint
5. Connect the thigh muscles and shins
6. Increase thigh muscle strength
7. Maintain the tendons in the thigh
Shinbone
1. Support your body weight
2. Connect the knees and ankles
3. Maintain body balance
4. Support various leg muscles
5. Producing red blood cells
Ankle
1. Serves to allow for up and down movement of the leg, because there is a hinge joint.
2. Make it easy for people to step and walk in a way that is as comfortable and efficient
as possible.
3. Serves as a link between the lower leg bones of the forearm to the soles of the feet.
4. In this ankle there is a swivel joint that can help the movement of the foot so that it
can be used more flexibly.
Toes bones
1. As a passive system of locomotion.
2. As a place of attachment to muscle tissue.
3. As a support for the body.
4. As an enforcer or body support.
5. As a place for the production of blood cells in the bone marrow.
6. As a storage area for mineral substances in the form of calcium and phosphate.
7. As a protector of body organs.
You might also like
- Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesSkeletal SystemCrii XiaNo ratings yet
- CSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesDocument4 pagesCSEC - Form 4 Human and Social Biology NotesLeon Abel80% (5)
- Bones and Muscles and Organs, Oh My! | Anatomy and PhysiologyFrom EverandBones and Muscles and Organs, Oh My! | Anatomy and PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument62 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemAnjanette Lopez PorlucasNo ratings yet
- The Science of Bones 3rd Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Science of Bones 3rd Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Body MovementsDocument54 pagesBody MovementsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionFrom EverandBones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Science4 - Q2 - Mod1 - Major Organs of The Human Body-ABRIDGEDDocument8 pagesScience4 - Q2 - Mod1 - Major Organs of The Human Body-ABRIDGEDRonie PadlanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesSkeletal Systemariolajose5No ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument29 pagesSkeletalROMNICK NILMAO100% (1)
- Grade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14Document26 pagesGrade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14John Benedict CruzNo ratings yet
- 10 Important Bones With Special FunctionDocument3 pages10 Important Bones With Special FunctionCindy Darmawan EffendyNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Science Chapter 3Document18 pagesClass 5 - Science Chapter 3deviNo ratings yet
- Fidarlin Hulu - Lower Part of The BodyDocument3 pagesFidarlin Hulu - Lower Part of The BodyHikmah KosmetikNo ratings yet
- Bones Worksheet2Document3 pagesBones Worksheet2Cindy Darmawan EffendyNo ratings yet
- 1.parts and Function of Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages1.parts and Function of Skeletal SystemLailaniNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SYatemDocument188 pagesSkeletal SYatemJasmine GañganNo ratings yet
- Locomotion and Support: (Chapter 2 Biology Form 5)Document26 pagesLocomotion and Support: (Chapter 2 Biology Form 5)Max WardNo ratings yet
- Skeleton: What Are Bones?Document6 pagesSkeleton: What Are Bones?Tik TokNo ratings yet
- St. Xavier's High School: Sector 49, GurgaonDocument4 pagesSt. Xavier's High School: Sector 49, GurgaonJsjn NNo ratings yet
- Ll3yt0etw - Lesson 3.1-The Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLl3yt0etw - Lesson 3.1-The Skeletal SystemPrecious RoxasNo ratings yet
- Track EventDocument21 pagesTrack Eventbosshage2No ratings yet
- Q2 SCI - W1 Main Function of The Major OrgansDocument35 pagesQ2 SCI - W1 Main Function of The Major OrgansMaimona TotongNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument2 pagesBonesAngie Espinoza UribeNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Skelital SystemDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of The Skelital SystemLucshaan GaneshadasanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument23 pagesModule 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Body System: Name: Akanksh Grade: 10KC Lesson: Skeletal System & Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Body System: Name: Akanksh Grade: 10KC Lesson: Skeletal System & Muscular SystemAkanksh SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Are Bones Bendy? Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandAre Bones Bendy? Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Science Year 7 Cambridge Presentation Powerpoint Unit 1 Part 2Document9 pagesScience Year 7 Cambridge Presentation Powerpoint Unit 1 Part 2ahmad sabryNo ratings yet
- The Body in Sport - LearnerDocument31 pagesThe Body in Sport - Learnerplumbs23No ratings yet
- Functions of The SkeletonDocument10 pagesFunctions of The SkeletonsammyshepleyNo ratings yet
- What Organ of The Chicken Do We Call MeatDocument1 pageWhat Organ of The Chicken Do We Call Meatkathciri teroNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Bones Muscles and JointsDocument5 pages9.3 Bones Muscles and JointsDerick NKANDU KALUBANo ratings yet
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument7 pagesPathfit ReviewerbantayalagaNo ratings yet
- Aisyah Tasha Putri 3B AssignmentDocument4 pagesAisyah Tasha Putri 3B AssignmentLiaNo ratings yet
- XI Unit 7 Phy. Edu. Fundamentals of Anatomy Physiology in SportsDocument17 pagesXI Unit 7 Phy. Edu. Fundamentals of Anatomy Physiology in Sportsranike4842No ratings yet
- Skeletal System - mp4 - Google DriveDocument7 pagesSkeletal System - mp4 - Google Drivefaresalesa2005No ratings yet
- Subjective Type Questions and Answers Chapter - 5: Class VDocument17 pagesSubjective Type Questions and Answers Chapter - 5: Class VabhinavNo ratings yet
- 3 Muscles and JointsDocument17 pages3 Muscles and Jointsbertha tandiNo ratings yet
- Skele TA L Syste M: Prepared By: Shiela Mae EslumDocument16 pagesSkele TA L Syste M: Prepared By: Shiela Mae EslumShiela Mae EslumNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Biology 2024Document51 pagesCuadernillo Biology 2024Fiorella Panizza (Miss Fiore)No ratings yet
- Bones, Muscles, and Joints: What Are Bones and What Do They Do?Document4 pagesBones, Muscles, and Joints: What Are Bones and What Do They Do?Rolavilla BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lower Part of The BodyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lower Part of The BodyHikmah khanza PutriNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesHandouts in Skeletal SystemShiela Mae EslumNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument15 pagesSkeletal SystemKarla OñasNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Parts and Functions of The Body Systems IDocument3 pagesUnit 3 - Parts and Functions of The Body Systems IAlfaNo ratings yet
- Assignment#2: The Human BodyDocument2 pagesAssignment#2: The Human BodyTeryy HerreraNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document14 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)NorhalizaIsmailNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Reading 2Document2 pagesSkeletal System Reading 2musunuru.nikhilNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 2ND QUARTERScience 6 EDITDocument8 pagesMODULE 1 2ND QUARTERScience 6 EDITEmie PonceNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PresentaionDocument7 pagesSkeletal System PresentaionNdaeja PetersNo ratings yet
- Bones Muscles and Joints Info SheetDocument3 pagesBones Muscles and Joints Info SheetAlena ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Bones and Muscles Day 1Document26 pagesBones and Muscles Day 1rosemarie molenillaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument52 pagesParts and Function of Musculo-Skeletal SystemJane Ilagan VizcoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJo BesandeNo ratings yet
- S1 2022 Premid Quick RevisionDocument12 pagesS1 2022 Premid Quick RevisionYee shinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Ortho)Document13 pagesAnatomy (Ortho)Jo BesandeNo ratings yet
- Science q2 Week 1Document30 pagesScience q2 Week 1BerMat100% (1)
- Biology Minor AssignmentDocument7 pagesBiology Minor AssignmentBessy MulayaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System-2Document13 pagesSkeletal System-2CHARLES HARYONO TEGUH HS STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Name: Citra Puspita Sari Nim:18301083 Class: 3C Nursing IntervensionDocument2 pagesName: Citra Puspita Sari Nim:18301083 Class: 3C Nursing IntervensionCitra Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Home Health Solutions Group Home Companion Services: Nursing Assessment Form - RecertificationDocument5 pagesHome Health Solutions Group Home Companion Services: Nursing Assessment Form - RecertificationCitra Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Citra Puspita Sari - Assignment 3 (Medical Record)Document2 pagesCitra Puspita Sari - Assignment 3 (Medical Record)Citra Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Sim Dalam Asuhan KeperawatanDocument14 pagesAplikasi Sim Dalam Asuhan KeperawatanCitra Puspita SariNo ratings yet