Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Deformation & Hooke'S Law: Revision Session
Uploaded by
Usman AmeenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Deformation & Hooke'S Law: Revision Session
Uploaded by
Usman AmeenCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Session [DEFORMATION & HOOKE’S LAW]
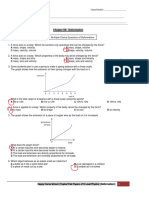
1. The graph shows the extension of a piece of copper wire 4. A steel spring is stretched by a load. The load is
as the load on it is increased. increased. At first the extension is proportional to the
load. The spring reaches its limit of proportionality at L.
Which is the correct graph of the extension against load
for the spring?
What does the graph show?
A. At certain load the wire becomes easier to extend.
B. At certain load the wire becomes harder to extend.
C. The load and extension are directly proportional
D. The load and extension are inversely proportional
2. An extension-load graph for a wire is shown.
5. A metal wire, initially 1.000 m long, extends by 4 mm
when a load of 2 N is added to it. What will the length of
the wire be if a further 3 N is added, assuming it does
not extend beyond its limit of proportionality?
A 1.060 m B 1.080 m C 1.010 m D 1.012 m
6. Which part of the graph shows the limit of proportionality
for an elastic solid?
What is the load at the limit of proportionality?
A. 4 N B 15 N C 60 N D 70 N
3. A single spring is loaded with a 1 N weight. The load is
then increased to 2 N and the extension increases by
1.0 cm, as shown.
A O B OP CP D PQ
7. The table shows how the extension of a spring varies
with load.
Two springs that are identical to the first one is put side by
side. They are connected at both ends, and a 1 N weight is
hung on them. The load is then increased to 2 N.
Between which two loads would you find the limit of
proportionality?
A 0 N and 2 N B 8 N and 10 N
C 10 N and 12 N D 14 N and 16 N
8. A spring extends by 4cm when 10 N is suspended from
it. Two of these springs are used as shown to carry a 30
What is the new increase ‘x’ in the extension? N load.
A 0.5 cm B 1.0 cm C 2.0 cm D 3.0 cm
Revision Session [DEFORMATION & HOOKE’S LAW]
(ii) The gravitational field strength is 10N/kg. Calculate the
size of each of the two forces acting on the mass.
first force = ...........................
second force............................ [2]
What is the extension of each spring?
A 4 cm B 6 cm C 8 cm D 12 cm
(c) The mass is pulled downwards. State and explain what
happen to the upward force.
9. An extension-load graph is plotted to show the result of
increasing the load on a spring. Which point marks the
...............................................................................................
limit of proportionality for this spring?
...............................................................................................
.......................................................................................... [2]
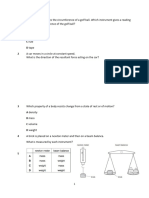
Q3: The apparatus shown in Fig. 3.1 is used to measure
the extension of a spring.
10. Load L is suspended from two springs that are in
parallel. The extension of each spring is ‘X’
(a) Explain how the mass causes a force on the
The springs are then arranged to hang vertically, one spring.
below the other. ..............................................................................................
..............................................................................................
........................................................................................ [1]
(b) The force on the spring is a vector quantity. State what
is meant by a vector quantity.
In this new arrangement, what is the total extension of ..............................................................................................
the two springs? ..............................................................................................
A 1/2X B X C 2X D 4X ........................................................................................ [1]
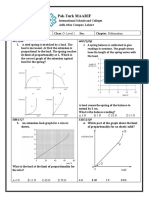
(c) Fig. 3.2 shows a graph of the length of the spring
Q2: Fig.2.1. shows a 0.4kg mass hanging at rest from a plotted against the force on the spring, for forces
spring. between 0 and 10 N.
(a) State what is meant by the mass of an object.
...............................................................................................
............ ………………………………………………………. [1]
(b) (i) On Fig.2.1, draw an arrow showing the direction
and the line of action for each of the two forces that
act on the mass. Write the name of the force next
to each arrow. [2]
Revision Session [DEFORMATION & HOOKE’S LAW]
(i) State a formula that relates the unstretched length lo of
the spring, the stretched length l of the spring and the
extension e of the spring.
...............................................................................................
......................................................................................... [1]
(ii) A mass produces a force of 9.0 N on the spring. Deter
mine the extension of the spring caused by this mass.
extension = ...................[1]
(iii) The limit of proportionality of the spring is reached
when the force is 10 N. The spring is easier to stretch
after the limit of proportionality. On Fig. 3.2, continue
the line to suggest how the length changes when the
force is greater than 10 N. [1]
You might also like
- DeformationDocument14 pagesDeformationlohanamehakkumari0No ratings yet
- 6 Deformation OrigDocument36 pages6 Deformation Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Elastic DeformationDocument36 pages3.2 Elastic DeformationHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Rashid - W.sheet 1 DeformationDocument4 pagesMohammad Rashid - W.sheet 1 DeformationM IqtadarNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument37 pagesPDF DocumentJamillea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- DeformationDocument37 pagesDeformationShnia RodneyNo ratings yet
- Combined Science - Physics - Deformation - 1 - 7Document9 pagesCombined Science - Physics - Deformation - 1 - 7orangejasmineNo ratings yet
- G11 - Assignment As Chapter Wise TestDocument5 pagesG11 - Assignment As Chapter Wise TestccNo ratings yet
- Pak-Turk MAARIF: A 3 N B 5 N C 10 N D 15 NDocument4 pagesPak-Turk MAARIF: A 3 N B 5 N C 10 N D 15 NIqra ArshadNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics P1 (1st Term - Premock)Document11 pagesPhysics P1 (1st Term - Premock)Haleema GulNo ratings yet
- 9702 Physics P2 QP Mock 2020 PDFDocument12 pages9702 Physics P2 QP Mock 2020 PDFTasneemNo ratings yet
- p1 DeformationDocument4 pagesp1 DeformationCreative BaratNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForceDocument4 pagesTurning Effect of ForceIbrahim Khurram100% (1)
- 8 Worksheet (AS) Deformation: 2dd 2d 2lDocument3 pages8 Worksheet (AS) Deformation: 2dd 2d 2lMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- HW3-Forces and motion-5 (学生版) - 022532Document16 pagesHW3-Forces and motion-5 (学生版) - 022532Jun WuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document9 pagesChapter 7Darren ChristoffNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Worksheet 0625Document6 pagesPhysics Practice Worksheet 0625emmanuelNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sec 4 Pure Physics SA2 Fuhua SecondaryDocument30 pages2020 Sec 4 Pure Physics SA2 Fuhua SecondaryTaneltyNo ratings yet
- Block Prept1 g112324-1Document7 pagesBlock Prept1 g112324-1Alexxander Govinda KhevinNo ratings yet
- Moment of Force4Document2 pagesMoment of Force4Cake RuskNo ratings yet
- 7 Hookes Law - New Aug 2022Document26 pages7 Hookes Law - New Aug 2022WaleedNo ratings yet
- 1575286840Document12 pages1575286840Rloofy namiNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law (Multiple Choice) QPDocument8 pagesHooke's Law (Multiple Choice) QPdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- SHM and Waves Problem SetDocument5 pagesSHM and Waves Problem SetbananacrunchNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 - FrocesDocument15 pagesPaper 1 - Frocesnadine yzakiNo ratings yet
- A11ADocument9 pagesA11ADanisha mathurNo ratings yet
- DeformationDocument21 pagesDeformationoshane rodneyNo ratings yet
- Effect of Motion - Mass and WeightDocument23 pagesEffect of Motion - Mass and WeightkhalidNo ratings yet
- Физика 11- 2021-2022Document14 pagesФизика 11- 2021-2022Nameless RFGNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2.1 Bulk Properties of SolidsDocument94 pages3.4.2.1 Bulk Properties of Solidssara patwardhanNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123Document176 pagesKoleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123shahidaNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123Document180 pagesKoleksi Trial 2017 Paper 123Yuska ZaitieNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis: Part 1 - Brass CylinderDocument8 pagesData Analysis: Part 1 - Brass Cylindersam man0% (1)
- Phy116 5Document9 pagesPhy116 5Fahim HoqueNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 IB DP Physics Mock Exam - Chapters 1.1 - 4.1 QuestionsDocument29 pagesGrade 11 IB DP Physics Mock Exam - Chapters 1.1 - 4.1 QuestionsRahul RajagopalNo ratings yet
- A2 Fields Part IIDocument38 pagesA2 Fields Part IIjohnNo ratings yet
- As G481 MechanicsDocument69 pagesAs G481 MechanicsCyn Syjuco0% (1)
- Forces B : The Reading On The Scales Is 500 N. He Lifts One Foot Off The Scales and Keeps It LiftedDocument5 pagesForces B : The Reading On The Scales Is 500 N. He Lifts One Foot Off The Scales and Keeps It Lifted许某No ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument4 pagesName: - Class: - DateFrancis Ho HoNo ratings yet
- The Matters and Materials ExaminationDocument8 pagesThe Matters and Materials ExaminationHartono Wijaksono SantosaNo ratings yet
- BPhO Round 1 2017-2018 S2 PDFDocument12 pagesBPhO Round 1 2017-2018 S2 PDFWWTNo ratings yet
- 2022 WA3 Science (Physics) 3E ModifiedDocument11 pages2022 WA3 Science (Physics) 3E ModifiedfinNo ratings yet
- 1 General Physics - 1.5 Forces (Part 2) - Worksheet - Paper 2Document7 pages1 General Physics - 1.5 Forces (Part 2) - Worksheet - Paper 2Katrine Jaya AndrewNo ratings yet
- Beam ExperimentDocument14 pagesBeam ExperimentRussell DomingoNo ratings yet
- Torque+ Rotational Motion Problems: AnnouncementsDocument23 pagesTorque+ Rotational Motion Problems: AnnouncementsFatehNo ratings yet
- Physics 2.4 Name:: Worksheet Nine SpringsDocument2 pagesPhysics 2.4 Name:: Worksheet Nine SpringsAnevay RolonNo ratings yet
- 2021 WA1 Science (Physics) 3E ModifiedDocument11 pages2021 WA1 Science (Physics) 3E ModifiedfinNo ratings yet
- A2 Fields Part IVDocument38 pagesA2 Fields Part IVmata4cholNo ratings yet
- Materials 1Document10 pagesMaterials 1DhanBahadurNo ratings yet
- Y10 C4 Spring ConstantDocument2 pagesY10 C4 Spring ConstantshafiqaNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2.1 Bulk Properties of SolidsDocument96 pages3.4.2.1 Bulk Properties of SolidsAnh TranNo ratings yet
- Topics 1,2,6 Summative SLDocument14 pagesTopics 1,2,6 Summative SLAhmad OmarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test For Midterm 3 Chapters 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 in Preparation For The Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesPractice Test For Midterm 3 Chapters 13, 15, 16, 17, 18 in Preparation For The Midterm ExamRAIZZNo ratings yet
- Forces in ActionDocument23 pagesForces in Actionapi-422428700100% (1)
- © Ucles 2019 9702/12/o/n/19Document5 pages© Ucles 2019 9702/12/o/n/19Zohair AghaNo ratings yet
- P 1Document16 pagesP 1Chaos GamingNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge Ordinary Leveljean jeanNo ratings yet
- Mettalic BondingDocument2 pagesMettalic BondingUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- 1123 s18 QP 22 PDFDocument8 pages1123 s18 QP 22 PDFArsalan QadirNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Assignment Topic: Linear Inequality Marks: 10 Q1Document3 pagesMathematics Assignment Topic: Linear Inequality Marks: 10 Q1Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System Johar Town Boys: Assignment # 02 Topic: Graph of Linear InequalityDocument4 pagesBeaconhouse School System Johar Town Boys: Assignment # 02 Topic: Graph of Linear InequalityUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of Covalent CompoundsDocument3 pagesMolecular Structure of Covalent CompoundsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Covelent BondingDocument6 pagesCovelent BondingUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- 1123 s18 Ms 22 PDFDocument14 pages1123 s18 Ms 22 PDFSyed AsharNo ratings yet
- Directed WritingDocument1 pageDirected WritingUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Sensors PDFDocument1 pageSensors PDFUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Nizam PassageDocument2 pagesNizam PassageUsman Ameen50% (2)
- Sensors 2Document11 pagesSensors 2Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- These Are Direct Questions For Which The Answers Are Stated Clearly in The Text. These Are Normally What, Where, When and How QuestionsDocument1 pageThese Are Direct Questions For Which The Answers Are Stated Clearly in The Text. These Are Normally What, Where, When and How QuestionsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TopicalDocument12 pagesChapter 4 TopicalUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument2 pagesOperating SystemsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Sensors 2Document11 pagesSensors 2Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Operating Systems and Computer Architecture: Syllabus ContentDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Operating Systems and Computer Architecture: Syllabus ContentUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument2 pagesOperating SystemsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Nutrition in Humans: O' Level Biology / 5090Document2 pagesChapter: Nutrition in Humans: O' Level Biology / 5090Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Marking SchemeUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Operating Systems and Computer Architecture: Syllabus ContentDocument24 pagesChapter 4 - Operating Systems and Computer Architecture: Syllabus ContentUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Fetch Decode Execute: Fetch Execute Cycle: Von Neumann Architecture: Processor Can Directly Access Memory!Document4 pagesFetch Decode Execute: Fetch Execute Cycle: Von Neumann Architecture: Processor Can Directly Access Memory!Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- The Beaconhouse School System: PhysicsDocument2 pagesThe Beaconhouse School System: PhysicsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
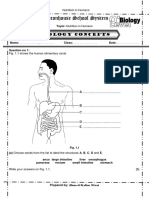
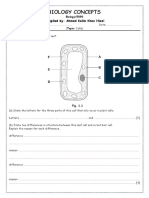
- Beaconhouse School System: Biology ConceptsDocument3 pagesBeaconhouse School System: Biology ConceptsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Biology Concepts: Compiled By: Ahmed Kalim Khan NiaziDocument2 pagesBiology Concepts: Compiled By: Ahmed Kalim Khan NiaziUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Nuitration in Human 3Document2 pagesNuitration in Human 3Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Nuitration in Human 2Document2 pagesNuitration in Human 2Usman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System: Biology ConceptsDocument2 pagesBeaconhouse School System: Biology ConceptsUsman AmeenNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of Forces (Worksheet)Document3 pagesTurning Effect of Forces (Worksheet)Usman Ameen100% (1)
- Dynamics Unit Test 2010 - DMCIDocument5 pagesDynamics Unit Test 2010 - DMCIeric_vincentNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two D.C. Motors: Fleming's Left Hand RuleDocument20 pagesChapter Two D.C. Motors: Fleming's Left Hand Rulenoor aliNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Bi-Directional Converter For Flywheel Energy Storage ApplicationsDocument10 pagesHigh Efficiency Bi-Directional Converter For Flywheel Energy Storage Applicationsmridul mpNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis Test StandDocument10 pagesFinite Element Analysis Test StandDan EhlkeNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of Closed Loop BLDC Motor ControlDocument30 pagesModelling and Simulation of Closed Loop BLDC Motor Controlaarya5No ratings yet
- Quest - Potential Energy and Energy ConservationDocument9 pagesQuest - Potential Energy and Energy ConservationEric HuangNo ratings yet
- Topological Insulators BasicsDocument10 pagesTopological Insulators BasicsSushilNo ratings yet
- G107A Student Project 2Document14 pagesG107A Student Project 2Charlotte WilkinsonNo ratings yet
- Er 2Document11 pagesEr 2Parveen Sahni ErNo ratings yet
- HiZ Auxiliary Units Catalogue SheetDocument12 pagesHiZ Auxiliary Units Catalogue SheetKasenNo ratings yet
- Belenky, Vadim Sevastianov, Nikita B. Stability and Safety of Ships - Risk of Capsizing 2007Document455 pagesBelenky, Vadim Sevastianov, Nikita B. Stability and Safety of Ships - Risk of Capsizing 2007Mai Kawayapanik100% (1)
- BA SR 2.1 For Slide HV - LV Panel Testing - Bus-BarDocument9 pagesBA SR 2.1 For Slide HV - LV Panel Testing - Bus-BarNameer Parammal PNo ratings yet
- SdarticleDocument14 pagesSdarticleConstantinescu MateiNo ratings yet
- Transformers - Voltage and Current - Rosy - CT 0106 - R01Document1 pageTransformers - Voltage and Current - Rosy - CT 0106 - R01Jainish GhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Shipboard High VoltageDocument64 pagesShipboard High VoltageHarendra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document10 pagesPhy 1Garlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Speed, Distance & Time Worksheet Watermarked 17-5Document3 pagesSpeed, Distance & Time Worksheet Watermarked 17-5purple crocNo ratings yet
- Sun2000 5 6KTL M1Document2 pagesSun2000 5 6KTL M1ATS d.o.o. SarajevoNo ratings yet
- Robo Analyzer User ManualDocument20 pagesRobo Analyzer User ManualaustinvishalNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Original Equations: December 2011Document15 pagesMaxwell's Original Equations: December 2011ALEX sponsoredNo ratings yet
- A Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformer Representation For Electromagnetic Transient StudiesDocument6 pagesA Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformer Representation For Electromagnetic Transient StudiesPutu Wegadiputra WirathaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Newtons Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesLecture 4 Newtons Laws of MotionDonnette Commissiong JamesNo ratings yet
- Power-Synchronization Control of Grid-Connected PDFDocument12 pagesPower-Synchronization Control of Grid-Connected PDFMona ValikhaniNo ratings yet
- Iit/Aiims Screening Test: 22A Section-I - : Straight Objective Type (4, - 1) Physics + Chemistry + MathematicsDocument8 pagesIit/Aiims Screening Test: 22A Section-I - : Straight Objective Type (4, - 1) Physics + Chemistry + Mathematicsb productiveNo ratings yet
- Mve 500 - 3Document2 pagesMve 500 - 3Amol SarinNo ratings yet
- Maxwell Stress TensorDocument8 pagesMaxwell Stress Tensorkushaldave227No ratings yet
- BS en Iso 13783 - 1998Document12 pagesBS en Iso 13783 - 1998Kim WongNo ratings yet
- Design of EMI Filters For DC-DC ConverterDocument6 pagesDesign of EMI Filters For DC-DC ConverterPABLO MAURONo ratings yet
- DC Power SystemDocument24 pagesDC Power SystemboltgingerkoppyNo ratings yet
- Seg V 3001 Electronic PrinciplesDocument71 pagesSeg V 3001 Electronic PrinciplesJonathan segovia100% (1)