Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Centromere and Mitotic Spindle: Key Structures in Cell Division
Uploaded by
Maria alejandra Penagos CeballosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Centromere and Mitotic Spindle: Key Structures in Cell Division
Uploaded by
Maria alejandra Penagos CeballosCopyright:
Available Formats
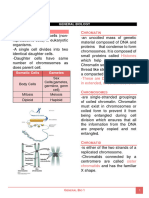
Centromere
, structure in a chromosome that holds together the
two chromatids.
The spindle is the structure that pulls the
chromatids to opposite ends of the cell during the
cell division processes of mitosis.
Chromosomes become even more condesed,making
Astral microtubules them compact.
Microtubules. Spindle Anatomy
Polar microtubules
Kinetochore microtubules directly connect to the
Kinetochores.
kinetochore microtubules
The nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes
are released.
Each chromosome has two chromatids, and each
chromatid has a kinetochore.
Chromosomes The mitotic spindle grow larger and some of the microtubles
begin to capture the chromosomes.
Prohase
the cell grows physically larger, copies G1 Phase
organelles, and makes the molecular building
blocks it will need in later steps All chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate
Metaphase
All this stage, the two kinetochores on each chromosome
Phases Of The must bind to microtubules at opposite poles of the spindle.
the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the Mitosis
DNA in its nucleus. It also duplicates a S Phase Cell Cycle
The sister chromatids separate from each
microtubule-organizing structure called the other.
centrosome. The centrosomes help separate
DNA during M phase.
The chromatids are pulled toward opposite poles of the
cell.
the cell grows more, makes proteins and Anaphase
organelles, and begins to reorganize its
contents in preparation for mitosis.
Mitosis begins
G2 Phase
Microtubules not attached to the chromosomes elongate
and push to separate the poles and make the cell longer.
The mitotic spindle breaks down into its basics components
The new nuclei are formed, one for each set of chromosomes
Nuclear membranes and nuclei reappear.
Mitosis is the part where the DNA of the cell nucleus
Have nucleus and other structures such as splits into two equal sets of chromosomes.
mitochondria divide and produce identical copies of
Telophase The chromosomes begin to descondense and return to
themselves by increasing their cell volume and their stringy shape.
duplicating their DNA.
Eukaryotes
The mechanisms of cell division vary between : Cytokinesis starts during the nuclear division phase
called anaphase and continues through telophase.
Are single celled organisms and have a simple internal Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell is
sturcture with free floating DNA. divided to produce two new cells that are genetically
identical. Performs an essential process to separate the cell in
half and ensure that one nucleus ends up in each
Prokaryotes daughter cell.
Cytokinesis
Use Cell division as a method of asexual
reproduction by binary fission.
The contractile ring shrinks to the point that there are
two separate cells each bound by its own plasma
membrane.
You might also like
- General Biology 1Document65 pagesGeneral Biology 1Anand Wealth JavierNo ratings yet
- 7.3: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument4 pages7.3: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and CytokinesisMartinoKhanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Differences between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument3 pagesDifferences between Mitosis and MeiosisLester VillarminoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument31 pagesCell CycleAlthea Angela BulaclacNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Bio400Document32 pages5.1 Bio400m-5243143No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: BiologyDocument82 pagesThe Cell Cycle: BiologymiraolaguerNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument80 pagesCell CycleBrandon Alforque EsmasNo ratings yet
- Mitosis vs Meiosis Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesMitosis vs Meiosis Cell DivisionfabyunaaaNo ratings yet
- Assingment Bio411Document3 pagesAssingment Bio411NURMIZA SYAZWANI MOHD SANINo ratings yet
- Edit MitosisDocument2 pagesEdit MitosisJemma NocalanNo ratings yet
- Thesoupnazi - Mitosis HihDocument1 pageThesoupnazi - Mitosis Hihkhushi SankhiNo ratings yet
- WS MeiosisDocument4 pagesWS Meiosiszaigham.m.syedNo ratings yet
- Bio Report 2Document2 pagesBio Report 2Fat Asian BoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The Cell CycleDocument57 pagesChapter 12 The Cell CycleMargarette SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document39 pagesGeneral Biology 2Reynail SumayaNo ratings yet
- 07 - Cell CycleDocument65 pages07 - Cell CycleDASHNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 2Document19 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 2AlfielAquino100% (3)
- Cell Cycle Wks ANSWERSDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Wks ANSWERSDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.9 To 3.14: Year: 12 Subject: Biology Unit: 3Document58 pagesTopic 3.9 To 3.14: Year: 12 Subject: Biology Unit: 3reyaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cell DivisionFatima Tul zahraNo ratings yet
- Stages of MitosisDocument2 pagesStages of MitosisWONGNo ratings yet
- 2.chap 3 - Lesson 3 - Growth and Reproduction of Cells - HandoutDocument6 pages2.chap 3 - Lesson 3 - Growth and Reproduction of Cells - HandoutNehal GamalNo ratings yet
- Phases of MitosisDocument11 pagesPhases of MitosiskxtnystromNo ratings yet
- Cell Divisions: Republic of The Philippines Bulacan State University College of ScienceDocument4 pagesCell Divisions: Republic of The Philippines Bulacan State University College of ScienceJosephine FlororitaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument82 pagesCell CyclejxhnrafaelNo ratings yet
- Colegio Concepción Chiguayante®: Particular SubvencionadoDocument6 pagesColegio Concepción Chiguayante®: Particular SubvencionadoAnonymous jBUcTgNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes and Cell Cycle Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison Chromosome InheritanceDocument32 pagesChromosomes and Cell Cycle Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis and Meiosis Comparison Chromosome InheritanceAmandaSherman100% (2)
- 2.1 - ChromosomesDocument42 pages2.1 - ChromosomesdamsaviNo ratings yet
- Genetic 1: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument95 pagesGenetic 1: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Basic Biology of Chromosomes and Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesBasic Biology of Chromosomes and Cell DivisionMr. IconicNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis InfographDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis InfographPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Name - Odango, Clint Xavier F. BSN 1B Score - MCC 1 Seatwork The Cells Date 02/04/2021 A. Draw The Animal Cell and Label The Following PartsDocument3 pagesName - Odango, Clint Xavier F. BSN 1B Score - MCC 1 Seatwork The Cells Date 02/04/2021 A. Draw The Animal Cell and Label The Following Partsclint xavier odangoNo ratings yet
- Week 9 and 10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 9 and 10 WorksheetHope NdwandweNo ratings yet
- Infographic Mitosis 1Document1 pageInfographic Mitosis 1텅텅No ratings yet
- Process of Diffusion, Osmosis, and Plasmolysis in Plant CellsDocument5 pagesProcess of Diffusion, Osmosis, and Plasmolysis in Plant CellsmasorNo ratings yet
- W3 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument38 pagesW3 - Cell Cycle and MitosisNisshokuNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Genral Biology 1Document3 pagesWeek 4 Genral Biology 1Spade ObusaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument11 pagesCell DivisionDr Nicholas AdeNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document17 pagesCH 12ZackNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Document96 pagesMitosis Meiosis 2021 v3Erdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- The Cell: The Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Cytoplasmic Organelles MitochondriaDocument5 pagesThe Cell: The Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Cytoplasmic Organelles Mitochondriavinnie0905No ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetHipster48No ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument16 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Meiosis (1)Document22 pagesMeiosis (1)valerie.bonilla.1282No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument34 pagesMitosisKiruthikasweetyNo ratings yet
- LSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseDocument11 pagesLSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- S4AE BiologyDocument51 pagesS4AE BiologyLeung BibiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlidesDocument19 pagesCell Cycle-Mitosis - Meiosis SlideslkjosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 HWDocument24 pagesChapter 09 HWJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument36 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionHeart VidalNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument46 pages3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument3 pagesMITOSISDaphne Ezra F. OlegarioNo ratings yet
- S402F-Lecture 9 2023 - OLEDocument78 pagesS402F-Lecture 9 2023 - OLECheung Yuk YamNo ratings yet
- NF4SCC5Document21 pagesNF4SCC5Yap Set EnNo ratings yet
- Importance of nuclear division before cell divisionDocument11 pagesImportance of nuclear division before cell divisionLisa Bavaro0No ratings yet
- Bio Notes-Part-4Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-4kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- Interphase Prophase: ChromoDocument12 pagesInterphase Prophase: ChromoNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8 Q4 Module 2 MITOSIS MEIOSISDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 8 Q4 Module 2 MITOSIS MEIOSISDesiree de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Maria Alejandra Penagos VocabularyDocument2 pagesMaria Alejandra Penagos VocabularyMaria alejandra Penagos CeballosNo ratings yet
- Article Maria Alejandra PenagosDocument1 pageArticle Maria Alejandra PenagosMaria alejandra Penagos CeballosNo ratings yet
- Rituals of MemoryDocument1 pageRituals of MemoryMaria alejandra Penagos CeballosNo ratings yet
- Criteria: Criterion A: AnalyzingDocument1 pageCriteria: Criterion A: AnalyzingMaria alejandra Penagos CeballosNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document33 pagesGeneral Biology 2Treshia Jazmin EguinNo ratings yet
- A Descriptive Grammar of SiwaDocument805 pagesA Descriptive Grammar of SiwaAnonymous haKP4qyA9100% (3)
- Immunoserology lectureDocument5 pagesImmunoserology lecturerennel ybarolaNo ratings yet
- DNA EXTRACTION FROM BANANADocument2 pagesDNA EXTRACTION FROM BANANAMaribel MuzadaNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Real-time PCR Detection Kit For Monkeypox VirusDocument2 pagesBrochure-Real-time PCR Detection Kit For Monkeypox VirusMouhamadou Habibi Keys TraoreNo ratings yet
- Life 2e BrE Inter SB U06Document80 pagesLife 2e BrE Inter SB U06Nguyễn Mạnh Thắng100% (1)
- DNA Genetics Unit Test ReviewDocument7 pagesDNA Genetics Unit Test ReviewCorradNo ratings yet
- Lecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesLecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsaditya100% (3)
- Genodermatoses 7 Mark PDFDocument3 pagesGenodermatoses 7 Mark PDFCocoMathewNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 12th Edition Lewis Test BankDocument13 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 12th Edition Lewis Test Bankhubertbak126100% (31)
- Essay On ChildrenDocument6 pagesEssay On Childrenb71bpjha100% (2)
- Data and Observations:: ACTIVITY 2: Relative OrganismsDocument2 pagesData and Observations:: ACTIVITY 2: Relative OrganismsRainyyy100% (1)
- Cell Structure GizmoDocument5 pagesCell Structure GizmoJumana ShahataNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Document17 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells: Shs Stem - Biology 1Dette Dominic BallanoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Variability Studies For Yield and Yield Components in Kodo Millet (Paspalum Scrobiculatum L.)Document4 pagesGenetic Variability Studies For Yield and Yield Components in Kodo Millet (Paspalum Scrobiculatum L.)Guadalupe Fernando Herrera AcostaNo ratings yet
- Taphonomy and Anthropometry The Post Mor PDFDocument1,126 pagesTaphonomy and Anthropometry The Post Mor PDFArlen ElisaNo ratings yet
- Hardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13Document2 pagesHardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13DontsArtNo ratings yet
- The Root-Symbiotic Rhizoscyphus Ericae Aggregate and Hyaloscypha (Leotiomycetes) Are Congeneric: Phylogenetic and Experimental EvidenceDocument31 pagesThe Root-Symbiotic Rhizoscyphus Ericae Aggregate and Hyaloscypha (Leotiomycetes) Are Congeneric: Phylogenetic and Experimental EvidenceOtieres Cirino De CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- WS4 EvolutionDocument2 pagesWS4 Evolutiondelossantosprincejoshua3No ratings yet
- Mitosis divides the chromosomes in a cell nucleusDocument39 pagesMitosis divides the chromosomes in a cell nucleusMuhammad Azhar MagsiNo ratings yet
- Learning Centre Std. Xi Biology Foundation Couse Reproduction in Animals WorksheetDocument3 pagesLearning Centre Std. Xi Biology Foundation Couse Reproduction in Animals Worksheetdnyanada patankarNo ratings yet
- American Heart Association's Life's Simple 7: Lifestyle Recommendations, Polygenic Risk, and Lifetime Risk of Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument11 pagesAmerican Heart Association's Life's Simple 7: Lifestyle Recommendations, Polygenic Risk, and Lifetime Risk of Coronary Heart DiseaseJoban PhulkaNo ratings yet
- 10 - ASD, Lord 2018Document53 pages10 - ASD, Lord 2018Grijisha ChandranNo ratings yet
- BiotechDocument5 pagesBiotechkaiaNo ratings yet
- "We Heal As One": Department of EducationDocument11 pages"We Heal As One": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-TECHNOLOGY AND THE Future of HumanityDocument3 pagesLesson 5-TECHNOLOGY AND THE Future of HumanityRaquelMagtalasNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- Determining Acceptance of The 9:3:3:1 Ratio in Fruit Fly Crosses Using The Chi Squared TestDocument7 pagesDetermining Acceptance of The 9:3:3:1 Ratio in Fruit Fly Crosses Using The Chi Squared TestFUN PHYSICS FOR NEETNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification of Marine Luminescent BacteriaDocument9 pagesIsolation and Identification of Marine Luminescent BacteriaCyriel Jade MendelloreNo ratings yet
- Lect. 12 PL Path 111 - Variability in Plant PathogensDocument25 pagesLect. 12 PL Path 111 - Variability in Plant Pathogensdawit gNo ratings yet