Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 2 Cells
Uploaded by
Kandy Anne Castillo AbuanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2 Cells
Uploaded by
Kandy Anne Castillo AbuanCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2: Cells •
-
Cytoskeleton
It is a network of protein fibers extending
throughout the cytosol
a. Microtubule
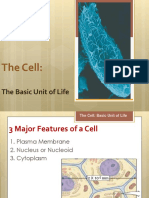
• What is a cell? - Largest of the cytoskeletal components
- Cells are usually referred to as the basic unit of life. - Composed mainly of the protein tubulin
- Why are they considered basic? A singular cell can - Helps determine cell shape
be likened to an organism itself capable of sustaining - Also function in the movement of secretory vesicles,
life on its own. of chromosomes during cell division and of
- Within a cell are organelles, which enable the cell to specialized cell projections <cilia and flagella>
function and contribute to the overall processes b. Microfilament
inside the body. - Thinnest element of the cytoskeleton
• Basic Parts of a Cell: - Composed of the protein actin
1. Nucleus - With respect to movement, they are involved in
- an organelle located near the center of the cell which muscle contraction
contains the cell’s genetic material c. Intermediate Filament
- Since it contains the genetic material, it is said to be - Thicker than microfilaments but thinner than
the control / command center of the cell microtubules
- Within the nucleus is the cell’s genetic material in the - Helps stabilize the position of organelles and helps
form of chromosomes attach cells to one another
(There are 23 pairs of chromosomes, the last pair of • Cell’s Life Cycle
which is the sex chromosomes)
- In the chromosomes are the DNA molecules and G1 Phase
inside the DNA molecules are the genes which Interphase
Growth: the cell grows in size and carry
enable the cell to carry out its basic function out their normal day to day activities.
- The nucleus is enclosed and separated from the rest
of the cytoplasm by the nuclear G2 Phase
membrane/envelope. The cell
S Phase prepares the enzymes and
- The structure of the nuclear membrane is similar to machinery for mitosis.
Prior to mitosis, the cell readies itself
that of the plasma membrane by duplicating its chromosomes and
- The nuclear membrane has tiny openings called other cellular contents. Before DNA
nuclear pores which serves to control the movement synthesis, each of the cell’s
of substances between the nucleus and the chromosomes consist of one
cytoplasm chromatid. After DNA synthesis, each
of the cell’s chromosomes consist of 2
2. Cytoplasm
genetically identical sister chromatids
- Consists of all the cellular contents between the attached at the centromere.
plasma membrane and the nucleus
- Between the nucleus and the plasma membrane is a G2 Phase
space, which is filled up with fluid and organelles. The cell prepares the enzymes and
- It is divided into two parts: machinery for mitosis.
a. Cytosol → fluid portion of the cytoplasm
b. Organelles
3. Cell wall Prophase During early prophase, the
- “cell membrane” chromosomes condense, making them
- “plasma membrane” distinguishable when using a light
- “plasmalemma” microscope.
- Separates the cell’s internal environment from the
external environment During late prophase, the nucleoli
• How are ribosomes manufactured? disappear and the mitotic spindle
apparatus assembles. The mitotic
spindle will consist of microtubules
Proteins in the Once in the The ribosomal that extend from pole to pole.
nucleolus, the subunits will
cytoplasm
proteins will exit the nucleus
move into the into the
nucleus via the bind to rRNA The mitotic spindle has attached to the
cytoplasm Metaphase
nuclear pores which is where they join centromere of each chromosome and
and eventually synthesized with another moves them through the "dance of
reach the inside the ribosomal
nucleolus to subunit to give mitosis".
nucleolus
form ribosomal rise to a
subunits ribosome.
Anaphase During anaphase the mitotic spindle
apparatus pulls the sister chromatids
• 2 types of Ribosomes: of each chromosome apart by
a. Free ribosomes attaching to each centromere and then
- unattached to any structure, free floating pull the chromatids to each pole of the
cell.
- synthesize proteins to be used inside the cell
b. Membrane-bound ribosomes
- attached to nuclear membrane and ER Telophase Chromosomes begin to disperse.
- make protein for export from the cell Spindle fibers disperse. Cytokinesis
begins--formation of daughter cells.
You might also like
- 10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesDocument4 pages10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesWrestling Communication100% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Unit 1 Paper 2 2017 Question 5Document2 pagesCAPE Biology Unit 1 Paper 2 2017 Question 5Kemoy Francis75% (4)
- Clinical Chemistry Review 1 110Document6 pagesClinical Chemistry Review 1 110DELLNo ratings yet
- As Level BiologyDocument18 pagesAs Level BiologyAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 MitosisDocument11 pagesGenbio1 MitosisJessie Katrisha TayagNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument36 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionHeart VidalNo ratings yet
- BIOL-1110 - Unit 3 - Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIOL-1110 - Unit 3 - Study GuideOmarNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translation ReplicationDocument103 pagesTranscription Translation ReplicationFitri FeranandaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceDocument11 pagesMitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Lbybio4 Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesLbybio4 Cell DivisionAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-BDocument6 pagesReflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-Bguirillita acutNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes-Part-4Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-4kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- 10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesDocument4 pages10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesAnanth Dharanidharan100% (1)
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionDocument62 pagesCHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - CellDocument9 pagesWorksheet 1 - CellDiva putri DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Dent 1Document6 pagesGenetics Lab Dent 1FRANCHEZKA ANGELICA TANIEGRANo ratings yet
- Nucleus: (Proteins or Polypeptides Are Biomolecules That Make Up For The Structure of The Cell)Document4 pagesNucleus: (Proteins or Polypeptides Are Biomolecules That Make Up For The Structure of The Cell)Crystal CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleus (Author V.fulga)Document35 pagesNucleus (Author V.fulga)Daniela DucantoniNo ratings yet
- Calamba, Micah Lou C. MD1: Phase, This Is Where The Cells PhysicallyDocument3 pagesCalamba, Micah Lou C. MD1: Phase, This Is Where The Cells PhysicallyKaykie CalambaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- 3 CellsDocument6 pages3 CellsEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- Your Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesYour Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsVisca El BarcaNo ratings yet
- GEN. ZOO (Midterms)Document8 pagesGEN. ZOO (Midterms)mimiNo ratings yet
- Foz Lec M3Document9 pagesFoz Lec M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- BIO 1 The CellDocument54 pagesBIO 1 The CellElyNo ratings yet
- BIODocument7 pagesBIOREYES, Kyla Marie M.No ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell DivisionDocument5 pages1.6 Cell DivisionmariamNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lec Module 3Document6 pagesZoology Lec Module 3Camille AlzolaNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesThe Cell CycleMehrin KabirNo ratings yet
- Basic OrganellesDocument2 pagesBasic OrganellesmaxinejanellaleeNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Cells in Our BodyDocument6 pagesCells in Our BodyKareysha ManceraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 PDFDocument45 pagesUnit 4 PDFSUSHANT SenNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Inventory COMPLETEDocument18 pagesCell Biology Inventory COMPLETEmariam miladNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument81 pagesCytoskeletonMugaboNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between A Plant (Palisade) Cell and An Animal (Liver) CellDocument3 pagesComparison Between A Plant (Palisade) Cell and An Animal (Liver) CellOctaviano SimonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument5 pagesCell Structures and Functions9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cell DivisionFatima Tul zahraNo ratings yet
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Bio EngineeringDocument23 pagesBio EngineeringandasriNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisDocument16 pagesCell Division: Mitosis and MeiosisMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Genetic 1Document64 pagesGenetic 1Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-CellDocument6 pagesChapter 2-CellAlthea BayolaNo ratings yet
- BIO C2 @notastpm04Document35 pagesBIO C2 @notastpm04Aprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- MustakDocument3 pagesMustakMh Mari HereNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- Genetic 1: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument95 pagesGenetic 1: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- 3 - Histology Lecture - Structure of Non Membranous Cell OrganellesDocument42 pages3 - Histology Lecture - Structure of Non Membranous Cell OrganellesAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument8 pagesCells and TissuesA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- Final Synthesis Part 2A: Abraham MaslowDocument2 pagesFinal Synthesis Part 2A: Abraham MaslowKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Finals Part 1: Hildegard PeplauDocument2 pagesFinals Part 1: Hildegard PeplauKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesTopic 4 Integumentary SystemKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesTopic 5 Skeletal SystemKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 TissuesDocument2 pagesTopic 3 TissuesKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 IntroductionDocument3 pagesTopic 1 IntroductionKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Mic 400: Industrial/Research Organization AttachmentDocument61 pagesInternship Report Mic 400: Industrial/Research Organization AttachmentDrexel Faculty Esrat IslamNo ratings yet
- Interferon and Interferon InducersDocument343 pagesInterferon and Interferon InducersSergey LyakhovNo ratings yet
- MCB 253 Final Exam Study GuideDocument1 pageMCB 253 Final Exam Study Guidewakka987No ratings yet
- Autotrophs and Heterotrophs: Photosynthesis & Cellular RespirationDocument7 pagesAutotrophs and Heterotrophs: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respirationapi-319819727No ratings yet
- Biology 12th Edition Mader Windelspecht Test BankDocument29 pagesBiology 12th Edition Mader Windelspecht Test BankEricaPhillipsaszpc100% (32)
- Rubella & FlavivirusDocument53 pagesRubella & Flaviviruskiedd_04No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Review QuizDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Review QuizAlly OcbianNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes 0Document67 pagesGene Regulation in Prokaryotes 0Angel TaylorNo ratings yet
- Exercises KineticsDocument22 pagesExercises KineticsEMERSON JOSE MERCADO CELISNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument32 pagesLecture Noteslira shresthaNo ratings yet
- Department of Molecular Biology: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument1 pageDepartment of Molecular Biology: Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range Methodprabhjyot_uclNo ratings yet
- Salvia Divinorum Is A Highly EfficaciousDocument7 pagesSalvia Divinorum Is A Highly EfficaciousЗлобил ДружелюбовNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology Week 2 Revised Tabrez Specialized Organels-Cytoplasm 1445 HDocument40 pagesCell Physiology Week 2 Revised Tabrez Specialized Organels-Cytoplasm 1445 H6258c7pxkjNo ratings yet
- Rr322304 Bioprocess Engineering IIDocument4 pagesRr322304 Bioprocess Engineering IIgeddam06108825No ratings yet
- KERAGAMAN GENETIK GURITA Octopus Cyanea (LINNAEUS 1758) PAPUADocument9 pagesKERAGAMAN GENETIK GURITA Octopus Cyanea (LINNAEUS 1758) PAPUAJen SajaNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument4 pagesScriptching chongNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Regulation Cancer Webquest 2Document7 pagesCell Cycle Regulation Cancer Webquest 2Camryn HansonNo ratings yet
- CELL101210Document212 pagesCELL101210Ram PrasathNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument34 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisJessa Mae Infante PadillaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDahliza KamatNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q3 Ver4 Mod5Document32 pagesScience10 Q3 Ver4 Mod5Berliese FriasNo ratings yet
- HL Paper 2: (8 Max) If Definition Is MissingDocument55 pagesHL Paper 2: (8 Max) If Definition Is MissingJane ChangNo ratings yet
- BLSDocument35 pagesBLSLucasNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell WallDocument34 pagesBacterial Cell WallParineeta BeraNo ratings yet
- Notes On Micro and Macro EvolutionDocument5 pagesNotes On Micro and Macro EvolutionObaiah JamakalaNo ratings yet
- Nameer Taha Al Hayali - 3622103731Document2 pagesNameer Taha Al Hayali - 3622103731Nameer omarNo ratings yet
- Ferritin Reference Range, Interpretation, Collection and PanelsDocument3 pagesFerritin Reference Range, Interpretation, Collection and Panelson miniNo ratings yet