Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells
Uploaded by
AIRENA RAIN TAMPOS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesCells
Uploaded by
AIRENA RAIN TAMPOSCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
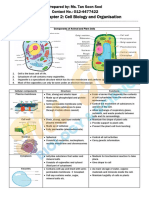
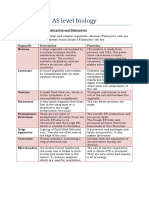
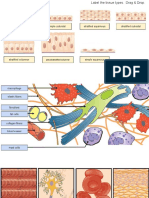
Cells Chromatin
• A loose network of bumpy threads
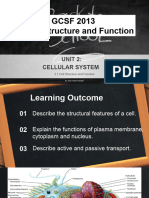
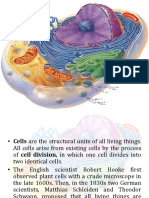
Cells are the building blocks/basic units of composed of DNA and protein
all living things.
Plasma Membrane
ANATOMY OF THE CELL
• Fragile, transparent barrier for cell
Cells are not all the same Contents
• All cells share general structures Hydrophilic (Water- loving) Heads
• Polar heads of phospholipid
Cells are organized into three main molecules
Regions: • Attracted to water
1. Nucleus
2. Cytoplasm Hydrophobic (Water- hating) Tails
3. Plasma membrane
• Nonpolar tails of phospholipid
Nucleus (nucle = kernel) molecules
• Located near the center of the cell • Avoid water
• Headquarter/control center of the cell Role of proteins
• Contains genetic material (DNA) Responsible for specialized
membrane functions:
• Shape conforms to the shape of the cell
• Enzymes
• A round or oval body that is surrounded • Receptors for hormones or other
chemical messengers
by the nuclear envelope • Transport as channels or carriers
Nucleus 3 regions: Role of sugars
1. Nuclear membrane/envelope Glycoproteins are branched sugars
2. Nucleolus attached to proteins that abut the
3. Chromatin extracellular space
Glycocalyx is the fuzzy, sticky,
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
sugar- rich area on the cell’s
The blueprint that contains all the surface
instructions needed for building the whole
body. Plasma Membrane
Nucleoli (little nuclei) Specializations
• Refers to one or more small, dark- Microvilli
staining, essentially round bodies • Finger-like projections that
Nuclear Envelope/Nuclear Membrane increase surface area for absorption
Example: intestine
• Double membrane barrier of the Membrane Junctions
Nucleus Tight Junctions
Are the closely associated areas of
two cells whose membranes join
together forming a virtually • Usually they are rod-shaped, however
impermeable barrier to fluid.
they can be round.
Desmosomes (Macula adherens)
• In living things, they squirm, lengthen,
A cell structure specialized for cell-
to-cell adhesion and change shape almost continuously
Gap Junctions A. Outer membrane – smooth &
They directly connect the featureless
cytoplasm of two cells, which B. Inner membrane – has shelf like
allows various molecules, ions and protrusions called cristae (crests)
electrical impulses to directly pass
through a regulated gate between
cells. Ribosomes
Tiny, bilobed, dark-stained bodies made of
Cytoplasm protein and one variety of RNA (ribosomal
Cellular material outside the RNA)
nucleus and inside the plasma
membrane. Endoplasmic Reticulum
3 major elements: Membranous system of tubules that
1. Cytosol extends throughout the cytoplasm
Fluid that suspends other
Exist in 2 forms:
elements
The fluid in which the Rough ER
organelles of the cytoplasm
are suspended; • Studded with ribosomes
Also called the ground
substance of the cell. • Tubules of rough ER provide an area for
storage and transport of the proteins made
2. Organelles on the ribosomes to other cell areas
Metabolic machinery of the Smooth ER
cell
3. Inclusions • It has no function in protein synthesis
Non-functioning units • It is a site for steroid and lipid synthesis,
Chemical substances that lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification
may or may not be present;
most are stored Golgi Apparatus
nutrients or cell products
Stacks of flattened sacs with bulbous ends
Cytoplasmic Organelles and associated small vsicles
Literally means “little organs.” Lyzosomes
Mitochondria (mitos = thread) Various-sized membranous sacs
containing powerful digestive enzymes.
Singular: mitochondrion
• Tiny threadlike or sausage-shaped
organelles
Peroxisomes Cilia
Small lysozomes- like membranous sacs • moves materials accross cell surface
containing oxidase (oxygen) enzymes that
detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and Flagellum
other harmful chemicals
• propels the cell
Centrioles
Events of Cell Division
Paired cylindrical bodies lie at right angles
Mitosis
to each other close to the nucleus
• The division of the copied DNA of the
Cytoskeleton mother cell to 2 daughter cells
• Provide cellular support by forming an Stages:
internal scaffoldings 1. Prophase
• Function also in intracellular transport 2. Metaphase
• It has 3 different types: 3. Anaphase
1. Microfilament 4. Telophase
2. Intermediate filament
3. Microtubules Interphase
Microfilaments: • Not part of mitosis (no cell division
Ribbon or cordlike elements occurs)- inactive phase
Formed largely of actin (a
Prophase
contractile protein), thus are
important in cell mobility, • First part of cell division
particularlyin muscle cells
• Chromatin condenses, forming bar-like
Intermediate Filament:
Chromosomes
• Proteinaceous cytoskeletal elements that
act as internal guy wires to resist Late Telophase
mechanical (pulling) forces acting on cells
• The nuclear envelope breaks up,
Microtubules allowing the spindle to interact with the
chromosomes
• Slender tubules formed of proteins called
tubulins Metaphase
Cellular Projections • Chromosomes cluster and become
aligned at the metaphase plate (the center
Not found in all cells of the spindle midway between the
centrioles) so that a straight line of is seen
Use for movements
Anaphase
• The shortest phase of mitosis
• It begins abruptly as the centromeres
splits simultaneously
Telophase
• Like prophase in reverse
• Identical chromosomes at opposite ends
of the cell uncoil to become chromatin
Cytokinesis
• Division of the cytoplasm
• Begins when mitosis is near completion
You might also like
- Group 2. Presentation - Cell 1Document57 pagesGroup 2. Presentation - Cell 1Thông LêNo ratings yet
- CGEN - 100 - #2-Parts of A CellDocument2 pagesCGEN - 100 - #2-Parts of A CellEricka MasakayanNo ratings yet
- Cells in Our BodyDocument6 pagesCells in Our BodyKareysha ManceraNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument7 pagesCELLSMaria Theresa BuscasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument56 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Functionazrixone54No ratings yet
- CHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionDocument62 pagesCHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument10 pagesBio Noteschanhongyi16No ratings yet
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure: A Guide to the Organelles and Components of the CellDocument24 pagesCellular Structure: A Guide to the Organelles and Components of the CellTyra Joyce Revadavia100% (1)
- LP1 - Cells - TissuesDocument36 pagesLP1 - Cells - Tissuesstephcruz0726No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-CellDocument6 pagesChapter 2-CellAlthea BayolaNo ratings yet
- 01-The CellDocument25 pages01-The Cellfordgt989No ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure - A 2019Document88 pages2 Cell Structure - A 2019Isworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document40 pagesLecture 3Hà Nguyễn Thị ViệtNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365100% (1)
- Cells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsRenalin ArauneNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesDocument11 pagesCell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Human Cell AnatomyDocument56 pagesHuman Cell Anatomysanthiyasandy100% (3)
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Û CellsDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Û CellsRochelle Dorado BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- Cell and Sub Cellular OrganellesDocument31 pagesCell and Sub Cellular OrganellesDr Asha KumariNo ratings yet
- Cells and tissues: Structures and functionsDocument2 pagesCells and tissues: Structures and functionsMarie SamNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Cell ComponentsDocument37 pagesThe Structure and Function of Cell ComponentsZainab M ZibariNo ratings yet
- As Level BiologyDocument18 pagesAs Level BiologyAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- L2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgDocument65 pagesL2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgNoriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- More Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesMore Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesJaveed KassamNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function MeetingDocument51 pagesCell Structure and Function MeetingenccaNo ratings yet
- Gzoo111 Week 2-13 Olfu ReviewerDocument3 pagesGzoo111 Week 2-13 Olfu ReviewerelynpecsonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Notes Grade 11 IB Biology SLDocument22 pagesCell Structure Notes Grade 11 IB Biology SLathar.m.farhanNo ratings yet
- 3 CellsDocument6 pages3 CellsEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Rev2Document4 pagesAnaphy Rev2antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and TissuesEARLRYAN TUMBALENo ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- 1st QT Bio ReviewerDocument10 pages1st QT Bio ReviewerAliah HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Little Chamber in Plants and AnimalsDocument50 pagesCells: The Little Chamber in Plants and AnimalsPatricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Butuan Doctors' College: Human Anatomy and Physiology HandoutDocument4 pagesButuan Doctors' College: Human Anatomy and Physiology HandoutKlynt BasadreNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument25 pagesThe CellmaryshealshealNo ratings yet
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument25 pagesL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - AnaphyDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - AnaphyCinderilla De AngelNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cell FunctionsDocument24 pagesModule 1 Cell FunctionsLady MeowNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-BDocument6 pagesReflective Journal For Module 2 Unit 1: Name: Yulo, Ires A. Section: BSED-SCI.3-Bguirillita acutNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JNo ratings yet
- Cellular Organization: An SEO-Optimized GuideDocument158 pagesCellular Organization: An SEO-Optimized GuideJeydon LopezNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument8 pagesCells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsLouie May EspinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell 1Document50 pagesChapter 6 Cell 1janardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - First GradingDocument5 pagesGen Bio - First GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesCell Structure and FunctionLili M.No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesLecture 2 Cell Structure and FunctionNIMRAHNo ratings yet
- Scientists That Contribute To The Discovery of The CellDocument6 pagesScientists That Contribute To The Discovery of The Celljerikbenito46No ratings yet
- 2.-The-Cell-Student-copyDocument90 pages2.-The-Cell-Student-copymaricar basilanNo ratings yet
- And Porous Surface Like Honeycomb: AnimalculesDocument5 pagesAnd Porous Surface Like Honeycomb: AnimalculesAngel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bones: Long, Short, Flat & IrregularDocument3 pagesClassification of Bones: Long, Short, Flat & IrregularAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- AIRENA TAMPOS - Body Tissues Labeling 2.5Document4 pagesAIRENA TAMPOS - Body Tissues Labeling 2.5AIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Airena Tampos - Tissues Chart 2.2Document2 pagesAirena Tampos - Tissues Chart 2.2AIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument5 pagesHuman AnatomyAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- AIRENA TAMPOS - (Article) Gene Therapy For The "Butterfly Children" 2.4Document3 pagesAIRENA TAMPOS - (Article) Gene Therapy For The "Butterfly Children" 2.4AIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- AppendicesDocument3 pagesAppendicesAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- 4 MembranesDocument3 pages4 MembranesAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Body Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesBody Cells and TissuesAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- ME2201 Manufacturing Technology IDocument6 pagesME2201 Manufacturing Technology ImsloveindiaNo ratings yet
- Visikol-HISTO - Clarifying Tissue For MicrosDocument30 pagesVisikol-HISTO - Clarifying Tissue For MicrosSathyaSrNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Megadyne V BeltsDocument57 pagesCatalogo Megadyne V BeltsValNo ratings yet
- PHD - Synopsis - in Geography-SVU - Joesph K. JDocument16 pagesPHD - Synopsis - in Geography-SVU - Joesph K. JFr. Joseph Kuzhikandathil0% (1)
- GIS 36-107 Integral Cladding Weld Overlay and Limited LooseDocument17 pagesGIS 36-107 Integral Cladding Weld Overlay and Limited LooseMarkoJovicin100% (5)
- PV 48Document12 pagesPV 48thierrylindoNo ratings yet
- List of major industries in MIDC Chikalthana and Waluj areasDocument33 pagesList of major industries in MIDC Chikalthana and Waluj areasRanadeep Reddy Chezerla100% (1)
- Acids, Bases, & SaltsDocument30 pagesAcids, Bases, & SaltsDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Common UC 1 - Applying Appropriate Sealant - AdhesiveDocument93 pagesCommon UC 1 - Applying Appropriate Sealant - AdhesiveMark Kevin DaitolNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Review CEE With Practice ProblemsDocument148 pagesPharmacokinetics Review CEE With Practice ProblemsBenhur Leithold LapitanNo ratings yet
- Rubber Property-Stiffening at Low Temperatures: Flexible Polymers and Coated FabricsDocument9 pagesRubber Property-Stiffening at Low Temperatures: Flexible Polymers and Coated FabricsPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Production of PhenolDocument65 pagesProduction of Phenolchaitanyavura67% (3)
- CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter Wise Question BankDocument82 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Chapter Wise Question BankVersha Rustagi100% (1)
- LOTHERME Ready Reckoner PDFDocument40 pagesLOTHERME Ready Reckoner PDFAmit DuttaNo ratings yet
- 1-Concrete Mixer SummaryDocument4 pages1-Concrete Mixer SummaryDenise Ann CuencaNo ratings yet
- AAS .PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document53 pagesAAS .PPT (Compatibility Mode)Nadia AdeliaNo ratings yet
- Mformat Arch PDFDocument11 pagesMformat Arch PDFMary Grace ManiponNo ratings yet
- 0653 s16 Ms 32Document5 pages0653 s16 Ms 32yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- GCSE ChemistryDocument22 pagesGCSE ChemistryAmeerul HazeeqNo ratings yet
- Lab Alcohols: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLab Alcohols: ObjectivesNa'im SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Ek Liquid Line Filter Drier and Capacity Table PDFDocument4 pagesEk Liquid Line Filter Drier and Capacity Table PDFDian IchtiarNo ratings yet
- Measuring Control Sensor Technology ProMinent Product Catalogue 2014 Volume 2Document216 pagesMeasuring Control Sensor Technology ProMinent Product Catalogue 2014 Volume 2PUIA DANIELNo ratings yet
- Cutting SpeedsDocument2 pagesCutting SpeedsefrainneneNo ratings yet
- TOEFL - Reading Comprehension - Test 2Document2 pagesTOEFL - Reading Comprehension - Test 2ruswandi_123100% (1)
- PPT-finalDocument21 pagesPPT-finalRamu KetkarNo ratings yet
- Modeling and control of ball mill grindingDocument19 pagesModeling and control of ball mill grindingDarwin HendriNo ratings yet
- ABIR ProfileDocument30 pagesABIR ProfileMohamad NasserNo ratings yet
- Water Quality IndicatorsDocument38 pagesWater Quality IndicatorsLa Ode Muhammad ErifNo ratings yet
- Ashrae-2011-Hvac-Applications-swimming PoolDocument3 pagesAshrae-2011-Hvac-Applications-swimming Poolmhmdjdgmailcom100% (1)
- Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2013: Chemistry Code No. 04Document19 pagesCombined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2013: Chemistry Code No. 04Piyush ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet