Professional Documents
Culture Documents
hw03 Ans
Uploaded by
Kim Hân100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
67 views1 pageOriginal Title
hw03-ans
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
67 views1 pagehw03 Ans
Uploaded by
Kim HânCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
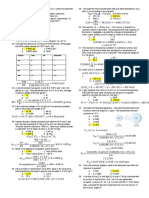
Q20/ Consider the following system in a 1.
00 L container: A(g) + B(g) 2C(g)
o
The equilibrium concentrations at 200 C were determined to be:
[A] = 0.200 M [B] = 3.00 M [C] = 0.500 M
How many moles of A must be added to increase the concentration of C to 0.700 M at
200oC?
(a) 0.225 mol
(b) 0.305 mol
(c) 0.417 mol
(d) 0.610 mol
(e) 0.700 mol
Solution:
A(g) + B(g) 2C(g)
K c =¿ ¿
x: moles of A are added to increase the concentration of C to 0.700.
According to reaction:
[A] = x (M)
[B] = x (M)
[C] = 0.700 – 0.500 = 0.200 (M)
x∗x
K c= =0.417 → x=√ 0.417∗0.200=0.309 moles
0.200
2. The lattice energy* of NaI is 686 kJ/mol, and the enthalpy of hydration is _694 kJ/mol.
Calculate the enthalpy of solution per mole of solid NaI.
NaI(s) NaI (aq)
,
Δ H solute=− Δ H lattice = 686 kJ/mol (This term must be positive because we need
energy to break down NaI)
∆ H hydration of ions=−694 kJ /mol
Solution energy = 686 – 694 = - 8 kJ/mol
You might also like
- Problem SolvingDocument9 pagesProblem SolvingJenny LlanesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chemical Energetics Part I SolutionsDocument20 pagesTutorial Chemical Energetics Part I SolutionsDarren LimNo ratings yet
- CH302 General Chemistry II Homework 4Document6 pagesCH302 General Chemistry II Homework 4Edward Spelling100% (1)
- (Chapter 2) (Solutions) : Intext QuestionsDocument11 pages(Chapter 2) (Solutions) : Intext QuestionsMo RafeeusshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument44 pagesChapter 2 SolutionsPanchi palNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Part 1 Chapter 2Document44 pagesNCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Part 1 Chapter 2Rajput PratikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Form ADocument5 pagesChemistry 1 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Form AKyle LoughranNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document43 pagesCH 2TechView TeamTamilNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document43 pagesCH 2Tamanna GaurNo ratings yet
- Soln Conc Molarity Molality Chemistry ProblemsDocument11 pagesSoln Conc Molarity Molality Chemistry ProblemsSusi KeerthiNo ratings yet
- Useful Information on Gas Laws, Equilibria, and ThermochemistryDocument11 pagesUseful Information on Gas Laws, Equilibria, and ThermochemistryAhmadAlabadiNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument51 pagesSolutionsSaad MazharNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Part 1 Chapter 2Document44 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Part 1 Chapter 2Kdot PNo ratings yet
- MebcDocument3 pagesMebcJainam JoshiNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constant - Practice Problems For Assignment 5Document4 pagesEquilibrium Constant - Practice Problems For Assignment 5Catrina RiveraNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 204 Final Test Solutions CalculationsDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY 204 Final Test Solutions Calculationsbeo_bi_1No ratings yet
- Assignment 5 SolutionsDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 SolutionscarolNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Thermochemistry (Answers) : 5.2 Define Exothermic and Endothermic Reaction and Solve Related ProblemsDocument5 pagesUnit 5. Thermochemistry (Answers) : 5.2 Define Exothermic and Endothermic Reaction and Solve Related ProblemsbillingsleyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Mass Percentages, Mole Fractions, Molalities, and Molarities from Chemistry ProblemsDocument40 pagesCalculation of Mass Percentages, Mole Fractions, Molalities, and Molarities from Chemistry ProblemsTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics TutorialDocument20 pagesChemical Energetics TutorialTimNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistryZERO TO VARIABLENo ratings yet
- KIM20E Homework.15.04.2021Document1 pageKIM20E Homework.15.04.2021Beyza SuvernNo ratings yet
- 2 - Heat of Solution and Mixing PDFDocument33 pages2 - Heat of Solution and Mixing PDFshifa veronicaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry SolutionsDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Solutionsnagendra_rdNo ratings yet
- Ag + C H ODocument9 pagesAg + C H OMuhammadNo ratings yet
- CH 2 NCERTDocument44 pagesCH 2 NCERTsPaRkLiNg wAtErNo ratings yet
- CH150 Practiceexam 2Document4 pagesCH150 Practiceexam 2johnNo ratings yet
- CHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-AnsDocument2 pagesCHM3010 Module Thermodynamic-Ansnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- STEM-Dawgs Workshops – Practice Exam 3 KEY CHEM 142ADocument3 pagesSTEM-Dawgs Workshops – Practice Exam 3 KEY CHEM 142AAlana Yudha-WrightNo ratings yet
- Soluitons Ncert SolutionsDocument33 pagesSoluitons Ncert SolutionsADWAITH LALUNo ratings yet
- UP ALCHEMES Chem 17 LE 1 ReviewDocument6 pagesUP ALCHEMES Chem 17 LE 1 Reviewkennethleo69100% (1)
- Ice EgDocument7 pagesIce EgAidah Amir0% (1)
- SolutionsDocument21 pagesSolutionsbansallove2008No ratings yet
- 2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesDocument12 pages2223 Grade 10 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesZa Evolution ClanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem II Exam 2 Practice Problems f08Document8 pagesGen Chem II Exam 2 Practice Problems f08Nikka LopezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Tutorial with Examples on Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument3 pagesChemical Equilibrium Tutorial with Examples on Le Chatelier's PrincipleYting Tan100% (1)
- Chemistry 31 Exam 2 Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesChemistry 31 Exam 2 Key ConceptsAbdelfattah oufNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry ProblemsDocument7 pagesStoichiometry ProblemsFitri AnnisakNo ratings yet
- TUGAS ATK KELOMPOK 8 Anggota: Anton, Dian, HendriadiDocument4 pagesTUGAS ATK KELOMPOK 8 Anggota: Anton, Dian, Hendriadisongjihyo16111994No ratings yet
- Energetics Worksheet 3 AnswersDocument5 pagesEnergetics Worksheet 3 Answersreyhanehfaraji.2007No ratings yet
- Presentation of Solution 1 and 2Document30 pagesPresentation of Solution 1 and 2Joshua meinfadeNo ratings yet
- Answers For Tuto 3 and 4 (Chem)Document8 pagesAnswers For Tuto 3 and 4 (Chem)Aina AqilahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria ICE SolutionsDocument15 pagesChemical Equilibria ICE SolutionsAmirah Alhabshi0% (1)
- DAHILOG Chemistry Quiz PART 2Document5 pagesDAHILOG Chemistry Quiz PART 2Ybur Clieve Olsen DahilogNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Heat of Precipitation 10-37Document10 pages4.2 Heat of Precipitation 10-37yokekeannNo ratings yet
- 2020-General Chemistry 1 Review WorksheetDocument4 pages2020-General Chemistry 1 Review WorksheetNgọc Thảo Vy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- AP Equilibrium Review Free ResponseDocument8 pagesAP Equilibrium Review Free ResponseRichSevillaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ProblemDocument2 pagesThermodynamics ProblemRajveer Fandan100% (1)
- Project in ChemistryDocument24 pagesProject in ChemistryKarlaNo ratings yet
- CHEM1070B - Assignment 4 KeyDocument7 pagesCHEM1070B - Assignment 4 Keymakabigail7No ratings yet
- Test Moles and EquilibriaDocument2 pagesTest Moles and Equilibrianaeem mushtaqNo ratings yet
- lecture-4 (1)Document18 pageslecture-4 (1)natiyirgu552No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument49 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 SolutionsNirvan JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Assignment Equilibrium Calculations and CompositionsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Assignment Equilibrium Calculations and CompositionsAftab57.No ratings yet
- Equilibrium Practice Problems SolutionsDocument6 pagesEquilibrium Practice Problems SolutionsJuniorGarciaNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Moles Equations and MolarityDocument18 pagesMole Concept Moles Equations and MolarityNageya paulNo ratings yet
- Exam For GEDocument2 pagesExam For GEcamille lei CalderonNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem QuizDocument18 pagesGen Chem QuizNoime Labayog AgravanteNo ratings yet
- Final AssessmentDocument10 pagesFinal AssessmentDiogo Tavares de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Problem 1:: MATLAB CodeDocument2 pagesProblem 1:: MATLAB CodeKim HânNo ratings yet
- PracticesDocument4 pagesPracticesKim HânNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: (20 Points)Document6 pagesProblem 1: (20 Points)Kim HânNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument1 pageQuizKim HânNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document1 pageQuiz 1Kim HânNo ratings yet
- International University Chemistry Homework 3Document8 pagesInternational University Chemistry Homework 3Kim HânNo ratings yet
- Homework 04 - Sem 1 - 2020-2021Document5 pagesHomework 04 - Sem 1 - 2020-2021Kim HânNo ratings yet