Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pulse Code Modulation: - It Can Take On An Infinite Number of Values
Uploaded by
Afzal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesPulse code modulation (PCM) is used to convert analog signals to digital signals. It involves sampling an analog signal at regular intervals, then quantizing the amplitude of each sample to one of a finite number of values. For a digital telephone signal, the audio bandwidth is sampled at 8000 samples/second, with each sample quantized to one of 256 levels using 8 bits. This results in 64,000 binary pulses needed per second to represent the telephone signal digitally. Quantization introduces error, as the reconstructed signal differs from the original due to approximating each sample value to the nearest of a finite number of levels.
Original Description:
communication system lec
Original Title
Lecture No 37
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPulse code modulation (PCM) is used to convert analog signals to digital signals. It involves sampling an analog signal at regular intervals, then quantizing the amplitude of each sample to one of a finite number of values. For a digital telephone signal, the audio bandwidth is sampled at 8000 samples/second, with each sample quantized to one of 256 levels using 8 bits. This results in 64,000 binary pulses needed per second to represent the telephone signal digitally. Quantization introduces error, as the reconstructed signal differs from the original due to approximating each sample value to the nearest of a finite number of levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views7 pagesPulse Code Modulation: - It Can Take On An Infinite Number of Values
Uploaded by
AfzalPulse code modulation (PCM) is used to convert analog signals to digital signals. It involves sampling an analog signal at regular intervals, then quantizing the amplitude of each sample to one of a finite number of values. For a digital telephone signal, the audio bandwidth is sampled at 8000 samples/second, with each sample quantized to one of 256 levels using 8 bits. This results in 64,000 binary pulses needed per second to represent the telephone signal digitally. Quantization introduces error, as the reconstructed signal differs from the original due to approximating each sample value to the nearest of a finite number of levels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Pulse Code Modulation
• Analog signal is characterised by an amplitude that can take
on any value over a continuous range.
– It can take on an infinite number of values
• Digital signal amplitude can take on only a finite number of
values.
• Pulse code modulation (PCM) is a tool for converting an
analog signal into a digital signal (A/D conversion).
– Sampling and Quantization
308201- Communication Systems 28
Example
(Digital Telephone)
• The audio signal bandwidth is about
• For speech, subjective tests show that signal articulation
(intelligibility) is not affected if all the components above
are suppressed.
• Since the objective in telephone communication is intelligibility
rather than high fidelity, the components above are
eliminated by a low pass filter.
• The resulting bandlimited signal is sampled at a rate of
(8000 samples per second).
– Why higher sampling rate than Nyquist sample rate of ?
• Each sample is then quantized into 256 levels
– 8 bits required to sample each pulse.
• Hence, a telephone signal requires binary pulses
per second ( ).
308201- Communication Systems 29
Quantization
• To transmit analog signals over a digital communication link, we must
discretize both time and values.
• Quantization spacing is ; sampling interval is , not shown in figure.
308201- Communication Systems 30
Quantization
• For quantization, we limit the amplitude of the message signal
to the range .
– Note that is not necessarily the peak amplitude of
– The amplitudes of beyond are simply chopped off.
• is not a parameter of the signal ; rather it is the limit
of the quantizer.
• The amplitude range is divided into uniformly
spaced intervals, each of width .
• A sample value is approximated by the midpoint of the
interval in which it lies.
– Quantization Error!
308201- Communication Systems 31
Quantization Error
• If is the sample of the signal , and if is the
corresponding quantized sample, then from the interpolation formula
and
• Where is the signal reconstructed from the quantized samples.
• The distortion component in the reconstructed signal is
• is the quantization error in the kth sample.
• The signal is the undesired signal and act as noise i.e., quantization
noise.
308201- Communication Systems 32
Quantization Error
• We can calculate the power or mean square value of as
• Since the signal and are
orthogonal i.e.,
• See Prob. 3.7-4 for proof.
308201- Communication Systems 33
Quantization Error
• As we know
• Due to the orthogonality condition, the cross product terms will
vanish and we get
• Since the sampling rate is , the total number of sample over
averaging interval is .
– The above relation is the average or the mean of the square of the
quantization error.
308201- Communication Systems 34
You might also like
- Lecture No 4Document15 pagesLecture No 4Hadia RashidNo ratings yet
- Differential Pulse Code Modulation: 308201-Communication Systems 39Document9 pagesDifferential Pulse Code Modulation: 308201-Communication Systems 39AfzalNo ratings yet
- Noise in CommunicationsDocument14 pagesNoise in CommunicationsSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Sampling and Analog To Digital ConversionDocument11 pages30820-Communication Systems: Sampling and Analog To Digital ConversionAfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 35Document8 pagesLecture No 35AfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Document26 pages30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Tooba SaharNo ratings yet
- Example (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andDocument16 pagesExample (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andAfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Signals and Signal SpaceDocument10 pages30820-Communication Systems: Signals and Signal SpaceSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
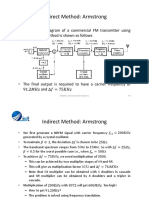
- Indirect Method: ArmstrongDocument9 pagesIndirect Method: ArmstrongAfzalNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Distortion: 308201-Communication Systems 43Document5 pagesNonlinear Distortion: 308201-Communication Systems 43AfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Document26 pages30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Furqan Ali CheemaNo ratings yet
- DC NotesDocument212 pagesDC NotesShaik Khalifa biNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications - MatrialDocument110 pagesDigital Communications - Matrialjubair ul rehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Part 2 - MJ PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 4 - Part 2 - MJ PDFvisionNo ratings yet
- L2 DcomDocument38 pagesL2 DcomYash ShirudeNo ratings yet
- EC - Mod 4 - DigitalcommnDocument33 pagesEC - Mod 4 - DigitalcommnDivya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- DENT 3563: Telecommunication EngineeringDocument27 pagesDENT 3563: Telecommunication EngineeringSanji KarunaNo ratings yet
- Comm. Sys. Lect. 8Document36 pagesComm. Sys. Lect. 8sulllNo ratings yet
- Realizability of Reconstruction FiltersDocument8 pagesRealizability of Reconstruction FiltersAfzalNo ratings yet
- m2 PDFDocument46 pagesm2 PDFlokeshwarihsNo ratings yet
- Analog-To Digital Conversion: Comsats University of Sciences and TechnologyDocument6 pagesAnalog-To Digital Conversion: Comsats University of Sciences and Technology320126512L20 yerramsettibhaskarNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 7Document7 pagesLecture No 7jaweria arshadNo ratings yet
- Communication Systms Chap 2 PresentationDocument43 pagesCommunication Systms Chap 2 PresentationTooba SaharNo ratings yet
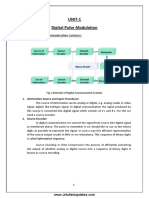
- UNIT-1 Digital Pulse Modulation: Elements of Digital Communication SystemsDocument39 pagesUNIT-1 Digital Pulse Modulation: Elements of Digital Communication SystemsMeghana SusarlaNo ratings yet
- 8thpracticalDocument8 pages8thpracticalShubham RathodNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Lect1Document20 pagesChapter1 Lect1aswardiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document82 pagesChapter 4tadepeace23No ratings yet
- Lec 2 CH 2Document37 pagesLec 2 CH 2Aimen AnwarNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Course Webpage: Lab Assistant: Textbook: GradingDocument20 pagesInstructor: Course Webpage: Lab Assistant: Textbook: GradingteredoxNo ratings yet
- Lec PU March05Document98 pagesLec PU March05Muhammad Awais AshfaqNo ratings yet
- PTM, PWM, PPM, PCMDocument37 pagesPTM, PWM, PPM, PCMTarunNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication and Networks-Encoding Techniques-JasminDocument30 pagesComputer Communication and Networks-Encoding Techniques-Jasminzerihun demereNo ratings yet
- Slide 6Document16 pagesSlide 6Mr RobotNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Lecture-03: Arnisha Akhter Lecturer, Dept. of CSE Jagannath UniversityDocument44 pagesDigital Signal Processing Lecture-03: Arnisha Akhter Lecturer, Dept. of CSE Jagannath UniversityKashfi ShormitaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Final MergedDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Final MergedSwastikNo ratings yet
- 566.digital Communication - April 2017Document124 pages566.digital Communication - April 2017James kaundaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Signal ConditioningDocument33 pagesChapter 4 - Signal ConditioningYab TadNo ratings yet
- Energy/Power Signals and Energy/Power Spectral DensityDocument8 pagesEnergy/Power Signals and Energy/Power Spectral DensityAfzalNo ratings yet
- Direct Generation of FM Waves: - The Oscillation Frequency Varies Linearly With The Control VoltageDocument12 pagesDirect Generation of FM Waves: - The Oscillation Frequency Varies Linearly With The Control VoltageAfzalNo ratings yet
- ADC - Lecture 4b Source Coding - Pusle Code - 2Document35 pagesADC - Lecture 4b Source Coding - Pusle Code - 2nabeel hasanNo ratings yet
- Basic of PCMDocument15 pagesBasic of PCMPablo TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Signal Conversions: Presented By:-Amarjit Kaur (AP)Document21 pagesSignal Conversions: Presented By:-Amarjit Kaur (AP)parasdeep singhNo ratings yet
- PCM Block Diagram: PCM Consists of Three Steps To Digitize An Analog SignalDocument16 pagesPCM Block Diagram: PCM Consists of Three Steps To Digitize An Analog Signaljoo nadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii-1Document142 pagesUnit Iii-1gayathri nathNo ratings yet
- Data Communications: Analog To Digital ConversionDocument14 pagesData Communications: Analog To Digital ConversionAmir fazilNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 17Document10 pagesLecture No 17AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document20 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM)Bishwayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Summer 2018-19: Nafiz Imtiaz Bin Hamid Assistant Prof., EEE DeptDocument16 pagesSummer 2018-19: Nafiz Imtiaz Bin Hamid Assistant Prof., EEE DeptNAZIFA NAWARNo ratings yet
- DC R16 - Unit-1Document39 pagesDC R16 - Unit-1Sivaprasad GanjiNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Transmittal of Digital Signals Between Two or More Points in A Communication SystemDocument28 pagesDigital Transmission Transmittal of Digital Signals Between Two or More Points in A Communication SystemLharie Mae BecinaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63Document13 pagesEffects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lect 5Document34 pagesLect 5Melaku DinkuNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Practical Filters: 308201-Communication Systems 34Document9 pagesIdeal and Practical Filters: 308201-Communication Systems 34AfzalNo ratings yet
- Wideband FM: - FM Signal Is More Meaningful Only If The Frequency Deviation Is Large EnoughDocument9 pagesWideband FM: - FM Signal Is More Meaningful Only If The Frequency Deviation Is Large EnoughAfzalNo ratings yet
- Digital and Analog TransmissionDocument47 pagesDigital and Analog TransmissionRizwanAliNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Chapter 1Document43 pagesDigital Communication Chapter 1aarushibawejajiNo ratings yet
- Cmpe 30094 Logic Circuits and Design Instructional Materials Version 2.02Document183 pagesCmpe 30094 Logic Circuits and Design Instructional Materials Version 2.02cyber4815No ratings yet
- Intro To DigiCom IIDocument81 pagesIntro To DigiCom IIAnonymous FKMfvCbNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringFrom EverandAdaptive Filter: Enhancing Computer Vision Through Adaptive FilteringNo ratings yet
- Direct Generation of FM Waves: - The Oscillation Frequency Varies Linearly With The Control VoltageDocument12 pagesDirect Generation of FM Waves: - The Oscillation Frequency Varies Linearly With The Control VoltageAfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Amplitude Modulations and DemodulationsDocument9 pages30820-Communication Systems: Amplitude Modulations and DemodulationsAfzalNo ratings yet
- Power of An Angle Modulated Wave: 308201-Communication Systems 8Document9 pagesPower of An Angle Modulated Wave: 308201-Communication Systems 8AfzalNo ratings yet
- Effects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63Document13 pagesEffects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 41Document7 pagesLecture No 41Afzal100% (1)
- Nonlinear Distortion: 308201-Communication Systems 43Document5 pagesNonlinear Distortion: 308201-Communication Systems 43AfzalNo ratings yet
- Example: - Find The Fourier Transform ofDocument7 pagesExample: - Find The Fourier Transform ofAfzalNo ratings yet
- Example (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andDocument16 pagesExample (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andAfzalNo ratings yet
- Signal Transmission Over A Linear System: 308201-Communication Systems 28Document6 pagesSignal Transmission Over A Linear System: 308201-Communication Systems 28AfzalNo ratings yet
- Wideband FM: - FM Signal Is More Meaningful Only If The Frequency Deviation Is Large EnoughDocument9 pagesWideband FM: - FM Signal Is More Meaningful Only If The Frequency Deviation Is Large EnoughAfzalNo ratings yet
- Digital Receivers and Regenerative Repeaters: 308201-Communication Systems 18Document7 pagesDigital Receivers and Regenerative Repeaters: 308201-Communication Systems 18AfzalNo ratings yet
- Double Sideband Suppressed-Carrier (DSB-SC) ModulationDocument7 pagesDouble Sideband Suppressed-Carrier (DSB-SC) ModulationAfzalNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Practical Filters: 308201-Communication Systems 34Document9 pagesIdeal and Practical Filters: 308201-Communication Systems 34AfzalNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation: - Double Sideband and Large CarrierDocument5 pagesAmplitude Modulation: - Double Sideband and Large CarrierAfzalNo ratings yet
- Realizability of Reconstruction FiltersDocument8 pagesRealizability of Reconstruction FiltersAfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 22Document7 pagesLecture No 22AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 17Document10 pagesLecture No 17AfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Angle Modulation and DemodulationDocument7 pages30820-Communication Systems: Angle Modulation and DemodulationAfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 9Document4 pagesLecture No 9AfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Analysis and Transmission of SignalsDocument11 pages30820-Communication Systems: Analysis and Transmission of SignalsAfzalNo ratings yet
- Indirect Method: ArmstrongDocument9 pagesIndirect Method: ArmstrongAfzalNo ratings yet
- Energy/Power Signals and Energy/Power Spectral DensityDocument8 pagesEnergy/Power Signals and Energy/Power Spectral DensityAfzalNo ratings yet
- 2 Lathi Chapter 6 PCMDocument57 pages2 Lathi Chapter 6 PCMHanzala RajpootNo ratings yet
- Analog Interfacing Overview: Analog and Digital Signals Analog Interfacing MKL25Z Analog ModulesDocument54 pagesAnalog Interfacing Overview: Analog and Digital Signals Analog Interfacing MKL25Z Analog Modulesjarvis 1011No ratings yet
- BandwidthDocument13 pagesBandwidthAl HasaNo ratings yet
- Classification of SignalsDocument72 pagesClassification of SignalspoomagalNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-unit 2 VTUDocument75 pagesDIGITAL COMMUNICATION-unit 2 VTUraghudathesh100% (12)
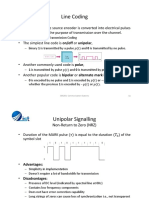
- Line CodingDocument4 pagesLine CodingGermarkNo ratings yet
- STAT343 - Module-I NotesDocument44 pagesSTAT343 - Module-I NotestiwarigulshriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1anushka bhandareNo ratings yet
- Communication Protocols in Process ControlDocument45 pagesCommunication Protocols in Process ControlShivani Palekar100% (2)
- Communications PDFDocument12 pagesCommunications PDFChester Kyles ColitaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio Mec2000Document76 pagesManual de Servicio Mec2000Catalina Fajardo50% (2)
- Delta ModulationDocument2 pagesDelta ModulationPrashant Subramaniam50% (2)
- ECE313 Lesson 1 - 1sem2023-24Document25 pagesECE313 Lesson 1 - 1sem2023-24DelanNo ratings yet
- Coursera - Week 1Document4 pagesCoursera - Week 1Nagulmeera Shaik100% (3)
- Physics Extra QDocument18 pagesPhysics Extra QGadisNovelNo ratings yet
- Video Editing - NotesDocument15 pagesVideo Editing - NotesLavanya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Data Communication (Curtis)Document6 pagesData Communication (Curtis)FLINTYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17-DCCN-2oP PDFDocument39 pagesChapter 17-DCCN-2oP PDFBalkrishan Goswami100% (1)
- AllProblemSets PDFDocument16 pagesAllProblemSets PDFMaxamed CabdiraximNo ratings yet
- ECE 465 Digital Signals Processing: Assoc - Prof. Pham Van TuanDocument45 pagesECE 465 Digital Signals Processing: Assoc - Prof. Pham Van TuanPhan Duy LinhNo ratings yet
- LXM32M Iom1 - enDocument46 pagesLXM32M Iom1 - enMarcus ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To DL DesignDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To DL DesignJontex 254No ratings yet
- REF541 Guide EngDocument68 pagesREF541 Guide Eng021804No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Digital Modulation & Transmission (Sem - 2 - 20152016) - V4Document104 pagesChapter 4 - Digital Modulation & Transmission (Sem - 2 - 20152016) - V4JamesNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture: Web Course Developed For NPTELDocument610 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture: Web Course Developed For NPTELSaransh TewariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Data and SignalsDocument87 pagesChapter 3 Data and Signalsvishnu vardhanNo ratings yet
- Locktronics-An Introductionn To Digital ElectronicsDocument27 pagesLocktronics-An Introductionn To Digital ElectronicsYousif Mousa AdamNo ratings yet
- All Chapters of ComputersDocument32 pagesAll Chapters of ComputersquizzyglobeNo ratings yet
- Library Register Recorded Books-FinalDocument985 pagesLibrary Register Recorded Books-Finalrao159951No ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lab ManualDocument25 pagesDigital Communication Lab Manualyuvaraju ponnadaNo ratings yet