Professional Documents
Culture Documents
30820-Communication Systems: Amplitude Modulations and Demodulations
Uploaded by
Afzal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views9 pagesThe document discusses various types of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques used in communication systems. It begins with an overview of baseband versus carrier communication and describes double sideband amplitude modulation and its generation using a multiplier modulator. It also discusses amplitude modulation techniques like single sideband, quadrature amplitude modulation and vestigial sideband modulation. The document then covers phase locked loops and their applications as well as superheterodyne AM receivers.
Original Description:
communication system lec
Original Title
Lecture No 18
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various types of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques used in communication systems. It begins with an overview of baseband versus carrier communication and describes double sideband amplitude modulation and its generation using a multiplier modulator. It also discusses amplitude modulation techniques like single sideband, quadrature amplitude modulation and vestigial sideband modulation. The document then covers phase locked loops and their applications as well as superheterodyne AM receivers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views9 pages30820-Communication Systems: Amplitude Modulations and Demodulations
Uploaded by
AfzalThe document discusses various types of amplitude modulation and demodulation techniques used in communication systems. It begins with an overview of baseband versus carrier communication and describes double sideband amplitude modulation and its generation using a multiplier modulator. It also discusses amplitude modulation techniques like single sideband, quadrature amplitude modulation and vestigial sideband modulation. The document then covers phase locked loops and their applications as well as superheterodyne AM receivers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
30820-Communication Systems
Week 6-8 – Lecture 16-21
(Ref: Chapter 4 of text book)
AMPLITUDE MODULATIONS AND
DEMODULATIONS
Contents
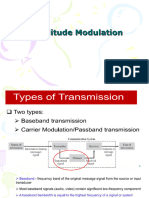
• Baseband versus Carrier Communications
• Double-Sideband Amplitude Modulation
• Amplitude Modulation (AM)
• Bandwidth Efficient Amplitude Modulation
– Amplitude Modulation: Single Sideband (SSB)
– Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM)
• Amplitude Modulation: Vestigial Sideband (VSB)
• Phase Locked Loop and Some Applications
• Superheterodyne AM Receiver
308201- Communication Systems 2
Modulation
• Modulation is a process that causes a shift in the range of frequencies in a
signal.
• Two types of communication systems
– Baseband Communication
– Carrier Modulation
• The baseband is used to designate the band of frequencies of the source
signal i.e., audio signal 4KHz, video 4.3MHz
• In analog modulation the basic parameter such as amplitude, frequency or
phase of a sinusoidal carrier is varied in proportion to the baseband signal
.
• This result in amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM)
or phase modulation (PM).
308201- Communication Systems 3
Modulation
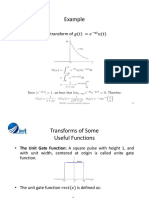
• = Modulating Message Signal
• =Carrier Signal
• =Modulated Signal
308201- Communication Systems 4
Why Modulation?
• To use a range of frequencies more suited to the transmission
medium.
• To allow a number of signals to be transmitted simultaneously
– Frequency division multiplexing (FDM)
• To reduce the size of the antennas in wireless links
308201- Communication Systems 5
Modulation
• Un-modulated Carrier
Such that
• The unmodulated carrier has constant amplitude and
constant instantaneous frequency.
• It carries no information-all components are independent of
the message signal
308201- Communication Systems 6
Modulation
• Carrier: may or may not include a separate carrier term.
If a carrier is presented, has a line spectrum components
at
• Lower Side-Band: Frequency components in for
• Upper Side-Band: Frequency components in for
308201- Communication Systems 7
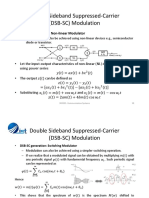
Double Sideband Suppressed-Carrier
(DSB-SC) Modulation
• DSB-SC generation: Multiplier Modulator
• Time Domain Description
Such that
• Information contained in is
embedded in the time varying
amplitude.
308201- Communication Systems 8
Double Sideband Suppressed-Carrier
(DSB-SC) Modulation
• Frequency Domain Description
– Baseband Spectrum of message signal
– 𝑀(𝑓) is shifted to 𝑀(𝑓 − 𝑓 ) and 𝑀(𝑓 + 𝑓 ) after modulation
308201- Communication Systems 9
You might also like
- AM: Modulation Index: 308201-Communication Systems 22Document9 pagesAM: Modulation Index: 308201-Communication Systems 22AfzalNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Modulation Techniques in Wireless Systems - ComtionDocument15 pagesModulation Techniques in Wireless Systems - Comtionjoby josephNo ratings yet
- Properties of Radio Path: 1 © Nokia Bss - Ppt/EgDocument27 pagesProperties of Radio Path: 1 © Nokia Bss - Ppt/EgMakarand DereNo ratings yet
- The Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyFrom EverandThe Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Multi Line Transmission and Filtered-Dealy Multiply and Sum Beamforming in Ultrasound ImagingDocument15 pagesMulti Line Transmission and Filtered-Dealy Multiply and Sum Beamforming in Ultrasound ImagingSwathi SubhaNo ratings yet
- Satellite Television: Analogue and Digital Reception TechniquesFrom EverandSatellite Television: Analogue and Digital Reception TechniquesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Modulation: Presented By-Nidhi Baranwal Mca 6 SemDocument30 pagesModulation: Presented By-Nidhi Baranwal Mca 6 SemDr. M. Karthigai Pandian Asso Prof ICENo ratings yet
- MULTIPLEXINGDocument13 pagesMULTIPLEXINGTofiqe AdamNo ratings yet
- Effects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63Document13 pagesEffects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63AfzalNo ratings yet
- Link Budget Analysis 1Document66 pagesLink Budget Analysis 1Ahmed MilianaNo ratings yet
- Frequency AND Phase Modulation (Angle Modulation)Document66 pagesFrequency AND Phase Modulation (Angle Modulation)Anonymous 1aCZDEbMMNo ratings yet
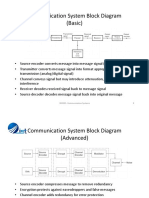
- Communication System Block Diagram (Basic)Document5 pagesCommunication System Block Diagram (Basic)Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Amplitude ModulationDocument73 pagesAmplitude ModulationnitinmgNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Modulation TechniquesDocument30 pagesTopic 4 - Modulation TechniquesmarxxNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Dvb-t2 Utk Dikalt TX Digital 2013Document56 pagesBahan Ajar Dvb-t2 Utk Dikalt TX Digital 2013NabilahNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Basics: 29/01/2003 Property of R. Struza K 1Document38 pagesDigital Modulation Basics: 29/01/2003 Property of R. Struza K 1krishna100% (1)
- Presented By: Se Elex Students PvppcoeDocument30 pagesPresented By: Se Elex Students PvppcoelakkepoguNo ratings yet
- Properties of Radio Path: 1 © Nokia Bss - Ppt/EgDocument22 pagesProperties of Radio Path: 1 © Nokia Bss - Ppt/EgAinul Haque Siddique QadriNo ratings yet
- PSTN LectureDocument38 pagesPSTN LectureZakaria Bashir MoalimNo ratings yet
- EC21B1001 JOssan LAb1Document8 pagesEC21B1001 JOssan LAb1Jossan EleazarEDENNo ratings yet
- 4.digital Modulation Techniques: BY: Kiran Kumar. G Asst - ProfessorDocument28 pages4.digital Modulation Techniques: BY: Kiran Kumar. G Asst - ProfessorKiranKumarNo ratings yet
- CSP Lab1Document8 pagesCSP Lab1Jossan EleazarEDENNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument7 pagesComputer NetworksSandilya MiduthuriNo ratings yet
- Objective of The AssignmentDocument7 pagesObjective of The AssignmentVelvizhi MohanrajNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Document26 pages30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Furqan Ali CheemaNo ratings yet
- Example (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andDocument16 pagesExample (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andAfzalNo ratings yet
- Modulacion-Demodulacion-Medios de Transmision y NormatividadDocument5 pagesModulacion-Demodulacion-Medios de Transmision y NormatividadOziel RivasNo ratings yet
- XB2900 enDocument6 pagesXB2900 enpatopickNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Single Sideband System: ECE121 - Principles of CommunicationsDocument67 pagesLesson 5 - Single Sideband System: ECE121 - Principles of CommunicationsJhezreel JohnNo ratings yet
- 3.reporte de ModulacionDocument5 pages3.reporte de ModulacionFernando OchoaNo ratings yet
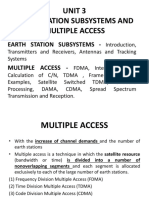
- Unit 3Document55 pagesUnit 3Hema DarshanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2A: - Bernhard (Chapter 2)Document28 pagesLecture 2A: - Bernhard (Chapter 2)meoconhs2612No ratings yet
- Lab Viva SolvedDocument8 pagesLab Viva SolvedMuhammad Umair100% (2)
- GSM OptimizationDocument176 pagesGSM OptimizationAhmed YousryNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Modulation DemodulationDocument88 pagesUnit 2 Modulation Demodulationvaishnavi biradarNo ratings yet
- 3G Radio Planning Essentials - Module 1Document50 pages3G Radio Planning Essentials - Module 1Fouzan Saeed100% (1)
- 003 - Configuration-WEB PDFDocument44 pages003 - Configuration-WEB PDFruben jaramilloNo ratings yet
- Analog Transmission and Bandwidth Utilization: Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Faculty of EngineeringDocument134 pagesAnalog Transmission and Bandwidth Utilization: Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Faculty of Engineeringdips jNo ratings yet
- CN 311 Lect. 06 Analog TransDocument22 pagesCN 311 Lect. 06 Analog Transmohammed almadanyNo ratings yet
- Project PDF FinalDocument21 pagesProject PDF FinalramratanecNo ratings yet
- TeleMetry System (CH 01)Document17 pagesTeleMetry System (CH 01)Moazzam NiaziNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques PDFDocument58 pagesPulse Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques PDFamrutha ammuNo ratings yet
- WDMWDMDocument40 pagesWDMWDMAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document53 pagesUnit 3DJ JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document63 pagesUnit 3CHANDRAKANT TRIPATHI (RA2011053010028)No ratings yet
- A.M. Modulation Lecture 4Document23 pagesA.M. Modulation Lecture 4Gaurav ThakareNo ratings yet
- U6 L2 Multichannel Transmission TechniquesRF Over Fiber1Document4 pagesU6 L2 Multichannel Transmission TechniquesRF Over Fiber1Pratiwi Kusumawardani Ji-WeeNo ratings yet
- 3675Document68 pages3675Adnan ShehzadNo ratings yet
- DCE208Document21 pagesDCE208Hafeex ShuaibuNo ratings yet
- ECT305 Analog and Digital Communication: Module-1, Part-1 Amplitude ModulationDocument52 pagesECT305 Analog and Digital Communication: Module-1, Part-1 Amplitude ModulationanuNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying GMSK: Software Defined Radio EE 194SDR Spring 2006 Brad GaynorDocument8 pagesGaussian Minimum Shift Keying GMSK: Software Defined Radio EE 194SDR Spring 2006 Brad GaynorNazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- 4.materi 4 - Teknik Multiple AksesDocument61 pages4.materi 4 - Teknik Multiple AksesIlham JBNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying GMSK: Software Defined Radio EE 194SDR Spring 2006 Brad GaynorDocument8 pagesGaussian Minimum Shift Keying GMSK: Software Defined Radio EE 194SDR Spring 2006 Brad Gaynorkazem_mirNo ratings yet
- 2 AM - DR SaifulDocument91 pages2 AM - DR SaifulMD. SAKIB HASAN SARKER 1708001No ratings yet
- Satellite Link Models (Satellite Communications)Document14 pagesSatellite Link Models (Satellite Communications)azkasheikh19No ratings yet
- Modulation Types & TechniquesDocument7 pagesModulation Types & TechniquesEric PierceNo ratings yet
- Direct Generation of FM Waves: - The Oscillation Frequency Varies Linearly With The Control VoltageDocument12 pagesDirect Generation of FM Waves: - The Oscillation Frequency Varies Linearly With The Control VoltageAfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 41Document7 pagesLecture No 41Afzal100% (1)
- Lecture No 35Document8 pagesLecture No 35AfzalNo ratings yet
- Effects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63Document13 pagesEffects of Interference: 308201-Communication Systems 63AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power of An Angle Modulated Wave: 308201-Communication Systems 8Document9 pagesPower of An Angle Modulated Wave: 308201-Communication Systems 8AfzalNo ratings yet
- Signal Transmission Over A Linear System: 308201-Communication Systems 28Document6 pagesSignal Transmission Over A Linear System: 308201-Communication Systems 28AfzalNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Distortion: 308201-Communication Systems 43Document5 pagesNonlinear Distortion: 308201-Communication Systems 43AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation: - It Can Take On An Infinite Number of ValuesDocument7 pagesPulse Code Modulation: - It Can Take On An Infinite Number of ValuesAfzalNo ratings yet
- Digital Receivers and Regenerative Repeaters: 308201-Communication Systems 18Document7 pagesDigital Receivers and Regenerative Repeaters: 308201-Communication Systems 18AfzalNo ratings yet
- Double Sideband Suppressed-Carrier (DSB-SC) ModulationDocument7 pagesDouble Sideband Suppressed-Carrier (DSB-SC) ModulationAfzalNo ratings yet
- Example (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andDocument16 pagesExample (1) : - For The Following Modulating Signal For andAfzalNo ratings yet
- Example: - Find The Fourier Transform ofDocument7 pagesExample: - Find The Fourier Transform ofAfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Sampling and Analog To Digital ConversionDocument11 pages30820-Communication Systems: Sampling and Analog To Digital ConversionAfzalNo ratings yet
- Realizability of Reconstruction FiltersDocument8 pagesRealizability of Reconstruction FiltersAfzalNo ratings yet
- Differential Pulse Code Modulation: 308201-Communication Systems 39Document9 pagesDifferential Pulse Code Modulation: 308201-Communication Systems 39AfzalNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation: - Double Sideband and Large CarrierDocument5 pagesAmplitude Modulation: - Double Sideband and Large CarrierAfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 22Document7 pagesLecture No 22AfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 9Document4 pagesLecture No 9AfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Angle Modulation and DemodulationDocument7 pages30820-Communication Systems: Angle Modulation and DemodulationAfzalNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Practical Filters: 308201-Communication Systems 34Document9 pagesIdeal and Practical Filters: 308201-Communication Systems 34AfzalNo ratings yet
- Energy/Power Signals and Energy/Power Spectral DensityDocument8 pagesEnergy/Power Signals and Energy/Power Spectral DensityAfzalNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Analysis and Transmission of SignalsDocument11 pages30820-Communication Systems: Analysis and Transmission of SignalsAfzalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 17Document10 pagesLecture No 17AfzalNo ratings yet
- Wideband FM: - FM Signal Is More Meaningful Only If The Frequency Deviation Is Large EnoughDocument9 pagesWideband FM: - FM Signal Is More Meaningful Only If The Frequency Deviation Is Large EnoughAfzalNo ratings yet
- Indirect Method: ArmstrongDocument9 pagesIndirect Method: ArmstrongAfzalNo ratings yet
- Ele 3203 - Lab4 - Am - DSBFCDocument10 pagesEle 3203 - Lab4 - Am - DSBFCMaitha SaeedNo ratings yet
- Electronic CommunicationDocument117 pagesElectronic CommunicationDivya KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Leader LCG-396 NTSC Pattern Generator - TlabsDocument36 pagesLeader LCG-396 NTSC Pattern Generator - TlabsclaudioNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications Lab ManualDocument88 pagesAnalog Communications Lab Manualvasantha_btech83% (6)
- Secret CB Vol 26 PDFDocument78 pagesSecret CB Vol 26 PDFMoretto, JulianoNo ratings yet
- Course Coordinator:: Dr. Shilpa ShrigiriDocument31 pagesCourse Coordinator:: Dr. Shilpa ShrigiriPaul Tan RegalaNo ratings yet
- RF 4800Document16 pagesRF 4800Edgar LeonNo ratings yet
- Audio Video EnggDocument223 pagesAudio Video Enggविक्रम सिंह राठौड़ खींवसरNo ratings yet
- Module 9 FM THEORY PDFDocument76 pagesModule 9 FM THEORY PDFVince EchaveriaNo ratings yet
- EEB434 Lecture Notes Angle ModulationDocument29 pagesEEB434 Lecture Notes Angle ModulationTebogo Matthew NgwakoNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From RADAR SYSTEMS - Unit-2Document21 pagesExtracted Pages From RADAR SYSTEMS - Unit-2Mahendar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 5G NR - Frequency Domain LocationDocument11 pages5G NR - Frequency Domain LocationMarco AntonioNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemDocument21 pagesMcqs in Broadcasting and Cable TV SystemLovielyn Poquiz De VeraNo ratings yet
- 5 2020 03 11!10 51 12 Am PDFDocument7 pages5 2020 03 11!10 51 12 Am PDFTempaNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual S4100 6175472502 01 00 Man 3 enDocument706 pagesOperating Manual S4100 6175472502 01 00 Man 3 enTeknik Telpen50% (2)
- EEE321 Assignment AM and FM 2 PDFDocument2 pagesEEE321 Assignment AM and FM 2 PDFNafees HasanNo ratings yet
- Galaxy Owners Manual dx99VDocument10 pagesGalaxy Owners Manual dx99Vbellscb100% (2)
- Excel Review Center ECE Refresher/Coaching Course Estth2Document15 pagesExcel Review Center ECE Refresher/Coaching Course Estth2Teena Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- XDocument4 pagesXImmanuel VinothNo ratings yet
- N6QW Homebrewing-For-Qrp-Ssb-Homebrew-Qrp-AndDocument24 pagesN6QW Homebrewing-For-Qrp-Ssb-Homebrew-Qrp-AndEngaf ProcurementNo ratings yet
- 062 Radio NavigationDocument477 pages062 Radio NavigationkgyjuhiNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Communication EngineeringDocument18 pagesEc8395 Communication EngineeringDinesh Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rife S Original FrequenciesDocument21 pagesDr. Rife S Original Frequenciessaso.crxNo ratings yet
- SSB and VSB NotesDocument11 pagesSSB and VSB NotesSamNo ratings yet
- THZ PaperDocument9 pagesTHZ PaperKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Vec 102 KDocument37 pagesVec 102 Kyu3zaNo ratings yet
- Analog Modulation PDFDocument32 pagesAnalog Modulation PDFNazirul HafizNo ratings yet
- A Software-Defined Radio For The Masses, Part 3Document10 pagesA Software-Defined Radio For The Masses, Part 3Leoo cassol100% (2)
- MFJ 8100K ManualDocument40 pagesMFJ 8100K ManualAlonsoRiquelmeNavarreteNo ratings yet
- Elements of Communication System:: Communication: It Is The Process of Conveying orDocument168 pagesElements of Communication System:: Communication: It Is The Process of Conveying orsakthiNo ratings yet