Professional Documents
Culture Documents
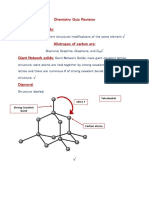
Structure and Bonding Set 2
Structure and Bonding Set 2
Uploaded by
Benjamin Watson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageDiamond is hard because each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbons with strong covalent bonds. Graphite is softer than diamond because each carbon is only bonded to three other carbons, forming layers that are weakly bonded to each other. Graphite can conduct electricity because each carbon has a delocalized electron that can move through the graphite carrying an electric charge. Silicon dioxide is hard with a high melting point because each atom is bonded to many others with strong covalent bonds, requiring a lot of energy to break.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiamond is hard because each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbons with strong covalent bonds. Graphite is softer than diamond because each carbon is only bonded to three other carbons, forming layers that are weakly bonded to each other. Graphite can conduct electricity because each carbon has a delocalized electron that can move through the graphite carrying an electric charge. Silicon dioxide is hard with a high melting point because each atom is bonded to many others with strong covalent bonds, requiring a lot of energy to break.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageStructure and Bonding Set 2
Structure and Bonding Set 2
Uploaded by
Benjamin WatsonDiamond is hard because each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbons with strong covalent bonds. Graphite is softer than diamond because each carbon is only bonded to three other carbons, forming layers that are weakly bonded to each other. Graphite can conduct electricity because each carbon has a delocalized electron that can move through the graphite carrying an electric charge. Silicon dioxide is hard with a high melting point because each atom is bonded to many others with strong covalent bonds, requiring a lot of energy to break.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
C4.
2 Structure and Bonding Set 2
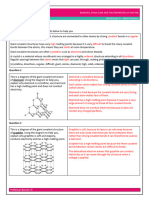
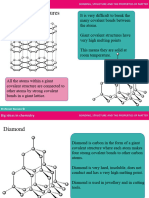
Explain why diamond is hard • Giant covalent structure
• Each carbon bonded to 4 other carbons with
strong covalent bonds
Explain why graphite is softer than diamond • Each carbon only bonded to 3 other carbon atoms
(diamond is bonded to 4) so forms layers
• Weak intermolecular forces between the layers
Explain why graphite can conduct electricity • Each carbon bonded to 3 other carbon atoms
• Each atom has one delocalised electron
• Delocalised electrons move through the graphite
carrying the electric charge
Explain using its structure and bonding why • It is a giant covalent structure
silicon dioxide is hard and has a high melting • Each atom bonded to many atoms with strong
point covalent bonds
• This means it is hard
• Lots of energy needed to break the strong bonds
so it has a high melting point
What is a fullerene? Molecules of carbon atoms with hollow shapes. Fullerenes
are based on hexagonal rings of carbon atoms (or ring
with 5 or 7)
What is Buckminsterfullerene The first fullerene to be discovered. It has 60 carbon atoms
and a spherical shape
What are carbon nanotubes and what are they Cylindrical fullerenes with high length to diameter ratios.
useful for They are useful for nanotechnology, electronics and
materials
What is graphene? A single layer of graphite useful for electronics and
composites
Why is graphene strong? • Each carbon is bonded to 3 other carbon with
strong covalent bonds
• Only one atom layer thick (so no weak
intermolecular forces)
You might also like
- Covalent Bonding Revision QuestionsDocument1 pageCovalent Bonding Revision Questionsrachael.knightNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry Revision PDFjoud amjadNo ratings yet
- MS Worksheet 9Document2 pagesMS Worksheet 9alvaressaschaNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument1 pageAllotropes of Carboninnukhan.sweetNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Compounds NotesDocument21 pagesCarbon and Compounds NotesYash AmbaskarNo ratings yet
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Carbon and Its Compounds: Chapter NotesDocument20 pagesClass X - Science (Chemistry) Carbon and Its Compounds: Chapter NotesAshwani JhaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding GCSE Review and 10QsDocument5 pagesCovalent Bonding GCSE Review and 10QsPuja DhawanNo ratings yet
- Solid LatticesDocument9 pagesSolid LatticesWamia RahmanNo ratings yet
- Molecules and NetworksDocument16 pagesMolecules and NetworksOCRChemistrySaltersNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QuizDocument3 pagesChemistry QuizKarim AL-TijaniNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answers: Topic 2.4Document5 pagesWorkbook Answers: Topic 2.4AbdulRaheem MuhammedNo ratings yet
- O Level Pure Chem SummaryDocument75 pagesO Level Pure Chem SummaryEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- chapter08 (1)Document62 pageschapter08 (1)12defl22No ratings yet
- ChemDocument7 pagesChemsheikh22No ratings yet
- yaren şahinDocument4 pagesyaren şahinyaren.sahin200888No ratings yet
- IB Chemistry - Unit 4 - Bonding Study GuideDocument7 pagesIB Chemistry - Unit 4 - Bonding Study GuideHamzah JoharNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument17 pagesMetallic Bondingaudrey.sengeNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06-Mar-2022 PDFDocument18 pagesAdobe Scan 06-Mar-2022 PDFCerena SinghNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Unit 2 As ChemistryDocument24 pagesEdexcel Unit 2 As ChemistrymukeshNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Bonding and Structure (Answers)Document10 pages4.1 Bonding and Structure (Answers)Deeyana DeenNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument2 pagesAllotropes of Carbonethanli29728No ratings yet
- 2020 Jan. M1W6 Teacher's Notes - Allotropy and Intermolecular Forces - RemovedDocument9 pages2020 Jan. M1W6 Teacher's Notes - Allotropy and Intermolecular Forces - RemovedD SNo ratings yet
- NanotechnologyDocument10 pagesNanotechnologyTanniya Denniz GurureNo ratings yet
- Final PDF For Grade 9 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal PDF For Grade 9 PDFmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- C7b Allotropes of Carbon DCNDocument12 pagesC7b Allotropes of Carbon DCNBaciu Florina GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Molecules and Materials: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument73 pagesMolecules and Materials: Larry Brown Tom Holmemuhammad ali shakeelNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent MoleculesDocument34 pagesGiant Covalent MoleculesaqutiaNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument5 pagesBondingKeith ScarletNo ratings yet
- Unit I-F - Graphite - FullerenesDocument31 pagesUnit I-F - Graphite - Fullerenesjyoti kumariNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument1 pageAllotropes of CarbonarabellaokNo ratings yet
- Graphene and Fullerenes | Shalom Education handsDocument3 pagesGraphene and Fullerenes | Shalom Education handsstaphilokaiNo ratings yet
- L10,11 - Covalent Compounds PropertiesDocument21 pagesL10,11 - Covalent Compounds PropertiesKashifNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 States of Matter (Liquidsolid)Document27 pagesTopic 4 States of Matter (Liquidsolid)Siti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Covalent BondingDocument31 pagesCh8 Covalent BondingSU CHENG LAM, CAREY F4S (36)No ratings yet
- Dr. Anita S. Ethiraj Associate ProfessorDocument12 pagesDr. Anita S. Ethiraj Associate ProfessorGovarthananNo ratings yet
- Giant StructuresDocument11 pagesGiant StructuresSailas Khulumani TshabanguNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint 5Document9 pagesPowerpoint 5alvaressaschaNo ratings yet
- GIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizDocument8 pagesGIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizKoluoch JrNo ratings yet
- Giant Molecule StructureDocument5 pagesGiant Molecule StructureNAURAH AISYAH NAWAWI ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Allotropes%20of%20carbonDocument1 pageAllotropes%20of%20carboninnukhan.sweetNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Allotropes: Class 8Document20 pagesCarbon and Its Allotropes: Class 8Neha ThukralNo ratings yet
- Bonding PDFDocument12 pagesBonding PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Semiconductor MaterialsDocument51 pagesLecture 3 - Semiconductor MaterialsShameer KhanNo ratings yet
- 5c. CrystalsDocument5 pages5c. CrystalsUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Carbon and CompoundsDocument53 pagesCH 4 - Carbon and CompoundsSJ ClassesNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- CHE - SolidDocument8 pagesCHE - SolidChin Ling ChiengNo ratings yet
- Allot RopesDocument6 pagesAllot RopesAmira katkhudaNo ratings yet
- Material Chapter 2 Atomic Structure and BondingDocument19 pagesMaterial Chapter 2 Atomic Structure and BondingÇãłl Mê MęlkãNo ratings yet
- A Non-Metal and A Non-Metal No Ions Electrons Are Shared: Covalent BondsDocument3 pagesA Non-Metal and A Non-Metal No Ions Electrons Are Shared: Covalent BondsThohara RisaliNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry - States of MatterDocument25 pagesAS Chemistry - States of MatterwilsonconcepcionNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding Part 1Document32 pagesCovalent Bonding Part 1TaniNo ratings yet
- 23 Structure and Bonding of CarbonDocument2 pages23 Structure and Bonding of CarbonAradhana SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds One Shot GYAANI KEEDA PDFDocument34 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds One Shot GYAANI KEEDA PDFFakeNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageIonic and Covalent Bonding Cheat Sheet: by ViaAnnaglory NkayalaNo ratings yet
- Carbon & Its CompoundDocument13 pagesCarbon & Its CompoundNeeraj PoddarNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding ReportDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding ReportGun TnNo ratings yet
- Revision Chem Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesRevision Chem Bonding Notesrania samirNo ratings yet
- Bonding (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene and Silicon-Dioxide)Document1 pageBonding (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene and Silicon-Dioxide)Safe GuardNo ratings yet
- Junction Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsFrom EverandJunction Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- PIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkDocument10 pagesPIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- PIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkDocument10 pagesPIANO (2018-2020 Syllabus) : Digital Grades: Technical WorkBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Activity: What Is The Global Positioning System?Document3 pagesActivity: What Is The Global Positioning System?Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 10,000 Reasons (Bless The Lord) : Chorus 1A G D A/C# BM G D A A G BM G A BM G A G/D D G/D DDocument2 pages10,000 Reasons (Bless The Lord) : Chorus 1A G D A/C# BM G D A A G BM G A BM G A G/D D G/D DBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- AQA Gcse Chemistry Unit C10 Revision (Using Resources)Document53 pagesAQA Gcse Chemistry Unit C10 Revision (Using Resources)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Task 1 UR WITH ANSWERSDocument9 pagesTask 1 UR WITH ANSWERSBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Text BookDocument386 pagesText BookBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Worked Solutions Higher Revision Pack 24.04.21Document35 pagesWorked Solutions Higher Revision Pack 24.04.21Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- This Is Where We Used To Live. Mei Daniel KeziahDocument1 pageThis Is Where We Used To Live. Mei Daniel KeziahBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources) : Tasks 2Document6 pagesChapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources) : Tasks 2Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources)Document6 pagesChapter 10: Sustainable Development (Using Resources)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets GCSE 111 (Haber Process)Document1 pageChemsheets GCSE 111 (Haber Process)Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Topic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterDocument8 pagesTopic: Using The Earth's Resources: Water WaterBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.6 Gene Expression and Mutation (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsDocument28 pages13.6 Gene Expression and Mutation (Biology Only) 2020 StudentsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.3 Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages13.3 Exam QuestionsBenjamin Watson100% (1)
- Making Fertiliser Practical SheetDocument3 pagesMaking Fertiliser Practical SheetBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Using Materials Questions For LS Revision Quick Fire QuestionsDocument2 pagesUsing Materials Questions For LS Revision Quick Fire QuestionsBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- 13.4 Why Does The Genome Matter WorksheetDocument3 pages13.4 Why Does The Genome Matter WorksheetBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- NH (Aq) + Hno (Aq) NH No (Aq) Ammonia + Nitric Acid Ammonium NitrateDocument9 pagesNH (Aq) + Hno (Aq) NH No (Aq) Ammonia + Nitric Acid Ammonium NitrateBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Haber Process Task 2Document6 pagesHaber Process Task 2Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonDocument46 pagesLesson Title: B13.4 DNA and The Human Genome Project: Connector: Questions On Prior Learning Linked To Todays LessonBenjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- Go UseDocument2 pagesGo UsensdewNo ratings yet
- Functionalization of GrapheneDocument59 pagesFunctionalization of GrapheneDiego Alejandro Hurtado BalcazarNo ratings yet
- Nanoparticles and Nanotechnology Research: EditorialDocument1 pageNanoparticles and Nanotechnology Research: EditorialhaseebtariqsyedNo ratings yet
- The Nanotechnology Program Projects and NEDO's Project ManagementDocument2 pagesThe Nanotechnology Program Projects and NEDO's Project ManagementMazen SalabNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Selenium Doped Zinc Oxide (Zno-Se) NanoparticlesDocument6 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Selenium Doped Zinc Oxide (Zno-Se) NanoparticlesKrishna DontarajuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document3 pagesUnit 5Yugi YuguNo ratings yet
- Transistor Technology Below 5nm NodeDocument6 pagesTransistor Technology Below 5nm NodeGabriel DonovanNo ratings yet
- RT 201 KrauseDocument45 pagesRT 201 Krausemallik789No ratings yet
- What Makes Technology at The Nanoscale Different From Technology at The Macroscale?Document4 pagesWhat Makes Technology at The Nanoscale Different From Technology at The Macroscale?Jasmin YadavNo ratings yet
- Delhi Technological University: Formerly Delhi College of EngineeringDocument1 pageDelhi Technological University: Formerly Delhi College of Engineeringdoeselephant hNo ratings yet
- Classification of Nanostructured Materials: June 2019Document44 pagesClassification of Nanostructured Materials: June 2019krishnaNo ratings yet
- ANGELICA M.docx REFLECTION 1Document3 pagesANGELICA M.docx REFLECTION 1Angelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 2Hardik SonvaneNo ratings yet
- CW1 PDFDocument1 pageCW1 PDFJerry GZavaletaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Applications in TextilesDocument24 pagesNanotechnology Applications in Textilessathieswaran80% (5)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of NanotechnologyDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of NanotechnologyJuan Tamad100% (1)
- Clay Nano Adsorbent: Structures, Applications and Mechanism For Water TreatmentDocument21 pagesClay Nano Adsorbent: Structures, Applications and Mechanism For Water TreatmentHipolito FamilyNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology in The Defense Industry Advances, Innovation, and Practical Applications by Madhuri Sharon, Angelica Silvestre Lopez Rodriguez, Chetna Sharon, Pio Sifuentes GallardoDocument333 pagesNanotechnology in The Defense Industry Advances, Innovation, and Practical Applications by Madhuri Sharon, Angelica Silvestre Lopez Rodriguez, Chetna Sharon, Pio Sifuentes GallardoKryon68No ratings yet
- Nanomaterials: 1.1 Length Scales and NanotechnologyDocument2 pagesNanomaterials: 1.1 Length Scales and Nanotechnologyimadd9871No ratings yet
- Nuclear Science & Engineering: Presentation On Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor - Prashant Ranjan 2k14/NSE/21Document17 pagesNuclear Science & Engineering: Presentation On Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor - Prashant Ranjan 2k14/NSE/21ranjan_prashant52No ratings yet
- Report Nano - PPTX (Autosaved)Document19 pagesReport Nano - PPTX (Autosaved)Novida Mary GraceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 - Nanotechnology and Its Applications: Grade 9 - Science - Sussex College - WennappuwaDocument10 pagesLesson 15 - Nanotechnology and Its Applications: Grade 9 - Science - Sussex College - WennappuwaSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Fruit Extract of Citrus X Microcarpa CalamansiDocument29 pagesGreen Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Fruit Extract of Citrus X Microcarpa Calamansierrol versoza manaogNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NanofabricationDocument60 pagesIntroduction To NanofabricationLydiaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Benefits and RisksDocument3 pagesNanotechnology Benefits and RisksAhmed BehiryNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology For KidsDocument4 pagesNanotechnology For KidsDek RestyNo ratings yet
- Nanoparticle Based Drug Delivery AssignmentDocument15 pagesNanoparticle Based Drug Delivery Assignmentshowrav100% (1)
- NanotechnologyDocument35 pagesNanotechnologyBenzDave AgsoyNo ratings yet
- Biological Synthesis of Green Nanoparticles Through A Variety of Sources and Their ApplicationsDocument6 pagesBiological Synthesis of Green Nanoparticles Through A Variety of Sources and Their ApplicationsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- A Review of Recent Research On Multifunctional Composite Materials and Structures With Their ApplicationsDocument11 pagesA Review of Recent Research On Multifunctional Composite Materials and Structures With Their ApplicationsberhaneNo ratings yet