Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TM2 TVET Respond Tesda
Uploaded by
Aljubir MarrackOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TM2 TVET Respond Tesda
Uploaded by
Aljubir MarrackCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPETENCY BASED LEARNING MATERIAL
Sector : TVET
Qualification Title : TRAINING METHODOLOGY I
Unit of Competency : Facilitate Learning Session
Module Title : Facilitating Learning Session
Technical Education & Skills Development Authority
NATIONAL TVET TRAINERS ACADEMY
Marikina City
TABLE OF CONTENTS
HOW TO USE THIS COMPETENCY BASED LEARNING MATERIAL ....................... v
LIST OF COMPETENCIES: ...................................................................................vi
Competency Summary ........................................................................................vii
Learning Outcomes : .......................................................................................... viii
LEARNING OUTCOME #1
Learning Experiences.................................................................................. 3
Information Sheet 2.1-1 .............................................................................. 4
Training Facilities/Resources ............................................................ 4
Training Activity Matrix ..................................................................... 4
Guidelines in making the Training Activity Matrix .................... 5
Job Sheet 2.1-1 .......................................................................................... 6
Performance Criteria Checklist .......................................................... 7
LEARNING OUTCOME #2
CONDUCT PRE-ASSESSMENT ................................................................... 8
Learning Experiences................................................................................ 10
Information Sheet 2.2-1 ............................................................................ 11
Pre-assessment ............................................................................... 11
Pre-assessment Activities ................................................................ 11
Test Administration ......................................................................... 13
Job Sheet 2.2-1 ........................................................................................ 14
Performance Criteria Checklist ........................................................ 15
LEARNING OUTCOME #3
Facilitate Training Session ........................................................................ 16
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page i of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
Learning Experiences................................................................................ 18
Information Sheet 2.3-1 ............................................................................ 19
Competency Based Training Delivery ............................................... 19
Role of the CBT Trainer ................................................................... 21
SELF-CHECK .................................................................................. 24
Answer Key ............................................................................ 25
Information Sheet 2.3-2 ............................................................................ 27
The Competency Based Training Procedures ............................................. 27
Delivery and Evaluation Activities ............................................................. 27
Job Sheet 2.3-2 ........................................................................................ 32
Performance Criteria Checklist ........................................................ 33
Facilitate Training Session ........................................................................ 33
Conduct Competency Assessment............................................................. 35
Learning Experiences................................................................................ 37
Learning Outcome 4
Conduct Institutional Competency Assessment ......................................... 37
Information Sheet 2.4-1 ............................................................................ 38
Conduct Learning Evaluation .......................................................... 38
Job Sheet 2.4-1 ........................................................................................ 41
Performance Checklist ..................................................................... 42
Information Sheet 2.4-2 ............................................................................ 44
Feedback Mechanism ...................................................................... 44
Feedback Strategies ........................................................................ 46
Tools use in providing Feedback ...................................................... 48
THE PROGRESS CHART ................................................................. 48
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page ii of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
The Sample Progress Chart for TM1 ................................................ 49
Guidelines in Making the Progress Chart ......................................... 49
Job Sheet 2.4-2 ........................................................................................ 52
Performance Criteria ....................................................................... 53
Job Sheet 2.4-3 ........................................................................................ 54
Performance Criteria ....................................................................... 55
LEARNING OUTCOME #5
Review Delivery of Training Session .......................................................... 56
Learning Experiences................................................................................ 57
Information Sheet 2.5-1 ............................................................................ 58
CBT Review and Evaluation ............................................................. 58
CBT Evaluation Tools ...................................................................... 60
Rating Sheets .................................................................................. 60
Focus Group Discussion ................................................................. 61
Document review............................................................................. 61
Areas for Evaluation ........................................................................ 61
Self Evaluation ................................................................................ 62
JOB SHEET 2.5-1 ..................................................................................... 63
Performance Criteria Checklist ........................................................ 64
Evaluation Instruments ............................................................................ 65
TRAINING SESSION EVALUATION FORM ................................................. 65
Self Evaluation Instrument ....................................................................... 70
PRE-TEST POST-TEST .............................................................................. 70
Self-Check ................................................................................................ 71
Answer key...................................................................................... 72
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page iii of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
Information Sheet 2.5 -2 ........................................................................... 73
Interpretation and Analysis of Evaluation Results............................ 73
Analysis and Interpretation of Data ................................................. 75
PRETEST and POSTTEST ............................................................... 76
Graph of the Pretest and Post Test Scores .............................. 77
Sample analysis ........................................................... 77
Using Excel to analyze data.................................................... 79
t-Test: Paired Two Sample for Means ...................................... 81
Sample Analysis ........................................................... 81
Job Sheet 2.5-2.......................................................................................... 82
Hypothetical Data ........................................................................... 83
Answer Key ..................................................................................... 87
SUMMARY TABLE.................................................................. 89
Information Sheet 2.5-3 ..................................................................... 90
Training Session Adjustment................................................ 90
Self-Check .......................................................................... 91
Answer Key ......................................................... 92
Job Sheet 2.5-3......................................................................................... 93
Answer Key ........................................................... 95
Job Sheet 2.5-4......................................................................................... 97
Performance Criteria Checklist ............................................. 98
Job Sheet 2.5-5 ........................................................................................ 99
Performance Criteria Checklist ...................................................... 100
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page iv of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
HOW TO USE THIS COMPETENCY BASED LEARNING MATERIAL
Welcome to the module in Facilitating Learning Session. This module
contains training materials and activities for you to complete.
The unit of competency "Facilitating Learning Session" contains knowledge,
skills and attitudes required for TRAINING METHODOLOGY (TM) 1.
You are required to go through a series of learning activities in order to
complete each learning outcome of the module. In each learning outcome are
Information Sheets, Self-Checks, Operation Sheets and Job Sheets. Follow these
activities on your own. If you have questions, don‟t hesitate to ask your facilitator
for assistance.
The goal of this course is the development of practical skills. To gain these
skills, you must learn basic concepts and terminology. For the most part, you'll get
this information from the Information Sheets and TESDA Website,
www.tesda.gov.ph
This module was prepared to help you achieve the required competency, in
"Facilitating Learning Session".
This will be the source of information for you to acquire knowledge and
skills in this particular competency independently and at your own pace, with
minimum supervision or help from your instructor.
Remember to:
Work through all the information and complete the activities in each section.
Read information sheets and complete the self-check. Suggested references
are included to supplement the materials provided in this module.
Most probably your trainer will also be your supervisor or manager. He/she
is there to support you and show you the correct way to do things.
You will be given plenty of opportunity to ask questions and practice on the
job. Make sure you practice your new skills during regular work shifts. This way
you will improve both your speed and memory and also your confidence.
Use the Self-checks, Operation Sheets or Job Sheets at the end of each
section to test your own progress.
When you feel confident that you have had sufficient practice, ask your
Trainer to evaluate you. The results of your assessment will be recorded in your
Progress Chart and Accomplishment Chart.
You need to complete this module before you can perform the next module,
Supervise Work-Based Learning.
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page v of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
TRAINING METHODOLOGY 1
COMPETENCY-BASED LEARNING MATERIALS
List of Competencies
No. Unit of Competency Module Title Code
1. Plan Training Session Planning Training Session
2. Facilitate Learning Facilitating Learning Session
Session
3. Supervise Work-Based Supervising Work-Based
Learning Learning
4. Conduct Institutional Conducting Institutional
Assessment Assessment
5. Maintain Training Maintain Training Facilities
Facilities
6. Utilize Electronic Utilizing Electronic Media in
Media in Facilitating Facilitating Training
Training
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page vi of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
MODULE CONTENT
UNIT OF COMPETENCY: Facilitate Learning Session
MODULE TITLE : Facilitating Learning Session
MODULE DESCRIPTOR:
This module covers the knowledge, skills and attitude in Facilitating
Competency Based Learning Session. It includes preparing training
facilities/resources, conducting pre-assessment, facilitating training session,
conducting competency assessment and reviewing delivery of training session.
This module covers materials to use such as the CBLM information sheets, self-
checks, job sheets, operation sheets and performance criteria checklists.
NOMINAL DURATION:
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
At the end of this module you MUST be able to:
1. Prepare Training facilities/resources;
2. Conduct pre-assessment;
3. Facilitate training session;
4. Conduct competency assessment; and
5. Review delivery of training session.
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page vii of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
Competency Summary
Qualification Title : Training Methodology I
Unit of Competency : Facilitate Learning Session
Module Title : Facilitating Learning Session
Introduction
This unit covers the knowledge, skills and attitude required in facilitating
learning session in training methodology I. This module includes facilitating
learning session in the delivery of TM I, such as preparing the workshop venue
and resources needed in facilitating learning session. This also include the
learning on how to conduct effective learning session.
Learning Outcomes :
Upon completion of this module , you must be able to:
1. Prepare training facilities/resources
2. Conduct pre-assessment
3. Facilitate learning sessions
4. Conduct competency assessment
5. Review training delivery
Assessment Criteria:
6. Prepares venue, supplies and materials
7. Prepares attendance sheets
8. Reproduces hand-outs and other training materials.
9. Orients trainees regarding training delivery .
10. Identifies unit/s of competency included in each learning outcomes
11. Conducts pre-assessment
12. Facilitates learning session
13. Conducts competency assessment
14. Reviews/evaluates training delivery
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page viii of ix
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # ___
LEARNING OUTCOME #1 PREPARE TRAINING
FACILITIES/RESOURCES
CONTENTS:
Training Facilities/Resources preparation
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA:
1. Appropriate training facilities/resources are prepared based on the
session requirement
2. Learning stations are prepared &set-up according to learning activities
3. Tools and equipment are prepared and set-up according to learning
activities
CONDITION:
Students/Trainees must be provided with the following:
1. WORKPLACE LOCATION
EQUIPMENT
Computer
LCD
2. TOOLS, ACCESSORIES AND SUPPLIES
White board
CD
Tapes
3. TRAINING MATERIALS
Learning Packages
Bond Paper
Ball pens
Manuals
Competency Standards
Training Regulations
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page 1 of 103
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # 00
ASSESSMENT METHOD:
Demonstration & Oral Questioning
Portfolio
Written Test
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page 2 of 103
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # 00
Learning Experiences
Learning Outcome 1
Prepare Training Facilities/Resources
Learning Activities Special Instructions
Read information sheet LO2.1-1 Read and understand the information
sheet
Perform Job Sheet LO2.1-1 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording
If you have questions about the use of
the matrix please ask your trainer.
After doing all activities of this LO, you
are ready to proceed to the next LO on
preparing session plans
Date Developed: Document No.
NTTA-
Training July 2010 Issued by:
TESDA
Methodology I
QA Page 3 of 103
Facilitate Training Developed by:
SYSTEM Session
Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.1-1
Training Facilities/Resources
In LO 5 of the Module on Planning Training Session you learned how to
make inventory of your training resources and how to layout your workshop and
your training facilities. You also learned how to organize these resources for easy
access and maintenance. In this module you will learn how to prepare training
facilities and resources based on session requirements.
In this section we will discuss how you will prepare the training facilities
and resources for your sessions for ease of access and use.
Your shop layout specified locations for your CBT areas and the learning
stations for each competency. Resources were also specified in your Job Sheets.
These are your reference materials in preparing them for your training sessions.
Since your trainees are working with different competencies at the same time, you
should design a way such that materials needed by trainees for their learning
activities can easily be accessed. This is the reason why each instructional sheet
should have a list of training Facilities and Resources. This will be the main basis
for the preparation of training materials for the day or the session.
Proper scheduling and management is the answer for the use of limited
equipment. The trainer should therefore schedule training activities based on
both current competencies of trainees and the availability of training resources
making sure that no trainee is idle.
The following Training Activity Matrix is recommended to schedule and
monitor the use of the facilities and resources.
Training Activity Matrix
Venue Date
Training Facilities/Tools
Trainee (Workstation/ & Remarks
Activity and Equipment
Area) Time
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 4 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Guidelines in making the Training Activity Matrix
1. Write the training activities for the session based on training needs and
on trainee‟s chosen competency.
2. Based on the instructional sheet needed in the activity (Job Sheet, Task
Sheet, and Information Sheet) list down the facilities/Tools and
Equipment needed for the activity.
3. Instructional Sheet number should be specific.
4. Total number of facilities listed should not exceed the number of the
specific tool, materials or facilities in the inventory.
5. Trainees should not be crowding in a workstation/area.
6. Ensure full utilization of equipment/work area.
7. Date and time of use should be specified.
8. Remarks should be made on the activity.
It is recommended that this training matrix be accomplished as guide in
scheduling trainees every training session. This is an additional tool in monitoring
trainee‟s activities and the use of facilities, tools, supplies and materials.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 5 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.1-1
Title: Prepare Training Matrix
Performance Objective:
Given the session plan and the inventory of
materials per competency, you should be able to prepare a training matrix
for a training session.
Supplies/Materials : bond paper(coupon bond,) a template
for Training Matrix
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Secure a session plan of your qualification.
2. Secure the inventory of facilities and resources you made in the
previous activities.
3. Determine the list of trainee‟s current competencies
4. Assign the trainees in the different work areas/workstations.
5. Prepare a training Matrix using the template above.
6. Present your work to your trainer.
Assessment Method:
Portfolio Assessment, Questioning, Performance Criteria Checklist
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 6 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Criteria Checklist
CRITERIA YES NO
Training activities are based on CBLM information sheets
Instructional sheets needed for the activity have specific
number
All equipment, facilities, supplies and materials listed in the
instruction sheets are reflected in the specified column
Not more than 5 trainees are in a station/area at one time
Total number of facilities listed should not exceed the number of
the specific tool, materials or facilities in the inventory
Date and time of use is specified
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 7 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
LEARNING OUTCOME #2 CONDUCT PRE-ASSESSMENT
CONTENTS:
Pre-assessment
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA:
1. Pre-assessment instruments are prepared in accordance with the
number of applicants
2. Context and procedures of pre-training assessment are well
explained according to guidelines.
3. Evidence is gathered using the assessment tools specified in the
evidence plan.
4. Evidences are evaluated and feedbacks are discussed based on the
results of the pre-training assessment.
5. Current competencies and prior learning are determined and
credited.
6. Characteristics and profile of learners are evaluated
CONDITION:
Students/Trainees must be provided with the following:
1. WORKPLACE LOCATION
EQUIPMENT
Computer
LCD
2. TOOLS, ACCESSORIES AND SUPPLIES
White board
CD
Tapes
3. TRAINING MATERIALS
Learning Packages
Bond Paper
Ball pens
Manuals
Competency Standards
Training Regulations
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 8 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
ASSESSMENT METHOD:
1. Demonstration & Oral Questioning
2. Portfolio
3. Written Test
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 9 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Learning Experiences
Learning Outcome 2
Conduct Pre-assessment
Learning Activities Special Instructions
Read information sheet LO2.2-1 Familiarize yourself with specific
pre-assessment activities and each
allotted time.
Perform Job Sheet LO2.2-1 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording
This activity may need a group of
observers who will evaluate the
performance based on the given
performance criteria.
A focus group discussion may follow to
point out strengths and weaknesses in
the performance of the trainer.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 10 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.2-1
Pre-assessment
In LO 1 of the module for Planning Training Sessions you were able to
prepare the gathering tools to determine trainee‟s characteristics and their
training needs.
In this module you will use the said tools along with the pre-assessment
instrument you prepared.
The purpose of pre-assessment is to establish baseline knowledge of trainees
about the qualification they are going to learn. It will also validate the results of
the self-assessment instrument in gathering training needs.
Pre-assessment Activities
1. Determine the time for each student to accomplish all forms. Write them
down on the board before the pre-assessment starts.
Nitko(2001, p.117) provides some estimates of time to complete various
types of questions for junior and senior high school students. Oosterhof(2001, p.
117), gives similar estimates but indicates poor readers might need more time.
Type of Test Time to finish a question
True-False 15-30 seconds
Multiple Choice(recall questions that 30-60 seconds
are brief)
More complex multiple choice 60-90 seconds
Multiple choice problems with 2-5 minutes
calculations
Short answer(one word) 30-60 seconds
Short answer(longer than one word) 1-4 minutes
Matching(5 premises, 6 responses) 2-4 minutes
Short essays 15-20 minutes
Data analyses/graphing 15-25 minutes
Drawing models/labeling 20-30 minutes
Extended essays 35-50 minutes
2. Explain the purpose of the pre-assessment which are the following:
a. To determine the learner‟s characteristics
b. To determine current competencies
c. To recognize prior learning
d. To determine training needs
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 11 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
e. The data gathered will be used to adjust learning methods,
facilities/resources to fit individual training needs
f. Plan adjustments for trainees special needs such as the following:
i. Providing written instructions for students with hearing
problems
ii. Using large print, reading or recording the questions on
audiotape (The student could record the answers on tape.)
iii. Having an aide or assistant write/mark the answers for the
student who has coordination problems, or having the student
record the answers on audiotape or type answers
iv. Using written assessments for students with speech problems
g. Administering the test in sections if the entire test is too long.
h. Asking the students to repeat the directions to make sure they
understand what to do
i. Starting each sentence on a new line helps students identify it as a
new sentence Including an example with each type of question,
showing how to mark answers
j. Check to see that directions for marking or scoring (point values, etc.)
are included with each type of item.
k. Decide if students are to mark answers on the test, use a separate
answer sheet, or use a blank sheet of paper.
l. Make an answer key. (This is easy to do as you write the questions.)
m. Check the answer key for response pattern. If necessary, re arrange
the order of questions within a question so the correct answers appear
to be in random order.
3. Prepare the following forms for the pre-assessment for each student:
Form 4.1
Form 4.2
Form 4.3
Questionnaire for determining learning style
Written Pre-assessment Instrument
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 12 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Test Administration
Before the test
A trainer‟s test administration procedures can have great impact on trainee‟s
test performance. As you will see in the guidelines below, test administration
involves more than simply handling out and collecting the test.
1. Avoid instilling anxiety
2. Give as many of the necessary oral directions as possible before
distributing the tests, but keep them to a minimum.
3. Explain the purpose of the test.
4. Give test-taking hints about guessing, skipping and coming back, etc.
5. Tell students the amount of time allowed for the test. You may want to
put the length of time remaining for the test on the board. This can be
changed periodically to help students monitor their progress. If a clock is
prominently available, an alternative would be to write the time at which
they must be finished.
6. Tell the students how to signal you if they have a question.
7. Tell the students what to do with their papers when they are finished
(how papers are to be collected).
8. Tell the students what they are to do when they are finished, particularly
if they are to go on to another activity (also write these directions on the
chalkboard so they can refer back to them).
9. Rotate the method of distributing papers so you don't always start from
the left or the front row.
10. Make sure the room is well lighted and has a comfortable
temperature.
11. If a student is absent, write his/her name on a blank copy of the test
as a reminder that it needs to be made up.
After the Test
1. Collect the test paper and answer sheets immediately after a trainee
finishes.
2. Check the papers as soon as possible.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 13 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.2-1
Title: Conduct Pre-assessment
Performance Objective: Given the TNA instrument, you must be able
to conduct pre-training assessment and
produce the following:
1. Pre-assessment result (ready for item analysis purposes)
2. Database of trainee‟s characteristics
3. Database of trainees current competencies
Supplies/Materials : TR and CBC
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Get copies of the pre-assessment instrument of the
qualification assigned to you, Forms 1-4 you developed in LO1
of Plan Training and the Gathering Instrument of Trainees‟
Characteristics.
2. Prepare copies enough for every trainee.
3. Following the guidelines above in conducting the pre-training
assessment.
4. Conduct pre-assessment.
5. Check the answers for pre-assessment.
6. Score each paper.
7. Prepare the data base of answers and set them aside for item
analysis.
8. Prepare the data base of trainees‟ characteristics.
9. Based on the Self-assessment Form (Form 4.1) and the
Validation of Competency Evidences(Form 4.2) make the
summary of Current Competencies versus required
competencies(Form 4.3) and the Training Needs Form(4.4)
10. Present your work to your trainer.
Assessment Method:
Portfolio Assessment, Questioning
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 14 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Criteria Checklist
CRITERIA YES NO
Were the trainees oriented about the following:
Purposes of the pre-assessment?
Type of test?
Time allotted for the test?
Scoring?
Was an answer key prepared before the assessment?
Were the test papers immediately checked and scored?
Was the database for answers of the pre-assessment tools
prepared?
Was the database for trainees characteristics complete for each
trainee?
Are training needs identified using the pre-training forms?
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 15 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
LEARNING OUTCOME #3 Facilitate Training Session
CONTENTS:
Competency Based Training Delivery
Competency Based Training Procedures
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA:
1. Learners are properly oriented on the CBT delivery system
2. Appropriate training methods are used based on the level and
characteristics of the learners.
3. Learners are assisted to achieve session outcomes.
4. Work and learning activities are monitored based on training plan.
5. Feedback are provided to improve learners competence.
CONDITION:
Students/Trainees must be provided with the following:
1. WORKPLACE LOCATION
EQUIPMENT
Computer
LCD
2. TOOLS, ACCESSORIES AND SUPPLIES
White board
CD
Tapes
3. TRAINING MATERIALS
Learning Packages
Bond Paper
Ball pens
Manuals
Competency Standards
Training Regulations
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 16 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
ASSESSMENT METHOD:
Demonstration & Oral Questioning
Portfolio
Written Test
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 17 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Learning Experiences
Learning Outcome 3
Facilitate Training Session
Learning Activities Special Instructions
Read information sheet LO2.3-1 Understand information sheet.
Answer Self-Check Compare answers with the answer key
Perform Job Sheet LO2.3-1 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording
This activity may need a group of observers
who will evaluate the performance based on
the performance criteria checklist.
A focus group discussion may follow to
point out strengths and weaknesses in the
performance of the trainee.
Perform Job Sheet LO2.3-2 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording
This activity may need a group of observers
who will evaluate the performance based on
the performance criteria checklist.
A focus group discussion may follow to
point out strengths and weaknesses in the
performance of the trainee.
This is the most critical part of the Training
because everything learned in Plan Training
Session competency will be implemented in
this section. Although this competency
focuses on the execution of the plan,
performance will greatly depend on the
plan.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 18 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.3-1
Competency Based Training Delivery
Learning Object: After reading this INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST be able to:
1. Illustrate the sequence of activities in a CBT workshop;
2. Enumerate the roles of the trainer;
3. Enumerate the roles of a trainee; and
The Module on Planning Training Session presents your session plan which
is a documentation of how you will be undergoing the training. In this module,
Facilitating Learning Session you will be implementing your plan. However, before
the sessions, different learning management tools should be prepared to help you
manage your learning session.
In CBT approach the students are given opportunities to learn in their own
pace but the instructor, like in any teaching-learning approach, is still an integral
part in the success of the learners. All learners may require guidance and support
to actively participate in the learning process. It is, therefore, very important for
the learner to know exactly what you expect them to do. The learner should then
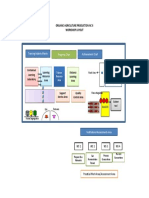
be provided all the learning management tools that the trainer can prepare.
Student enters YES
Review learning
program
package
Satisfactorily
Orientation
performed
Role of trainer/trainee View multi-media Competency
Administer RPL/TNA materials
Instructor Instructor
Identify training Needs observes rates
Organize learning Strategy performance performance
Use manuals
NO
Observe Student Student rates
Student selects demonstration
Competency and attempts task own Have
receive instructions performance enough
competency
Practice skills in been
Administer Learning Agreement workshop achieved?
Provide Materials
Introduce CBLM materials Receive assistance
Use of Achievement/ Progress and feedback EXIT PROGRAM YES
Report
Competency Based Training Delivery
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 19 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
The Competency Based Training Delivery approach should be explained so
that the learner will know exactly what activities he needs to undergo to acquire
the required competencies. The diagram above shows the CBT process.
Managing CBT versus Traditional Programs
There is always a tendency for the trainer to go back to the traditional
approach of teaching because of the Law or Primacy in learning. That is, the
things that are learned first are very difficult to re-learn but if the trainer is aware
of the advantages of CBT he would be more conscious about this tendency.
The following table differentiates Traditional Approach and CBT Approach.
Traditional Approach CBT Approach
Instructors focus on managing Trainers focus on managing learning
instruction
Most students enter at about the Trainees enter various times throughout
same time the year
Students all cover the same Different trainees may be training for
material different occupations within the same
program
Students all proceed from one Each trainee moves on to next task only
topic to the next at the same time after mastering the task he she is
currently working on.
The instructor controls the Each trainee progresses at his or her own
learning pace pace
All students are usually tested Each trainee is tested when ready to
once demonstrate mastery
Very little continuous feedback is Immediate feedback is given to each
given trainee at critical points in the learning
process.
The instructor is involved in The trainer must be able to answer
teaching only one topic at a time questions on many different tasks each
day.
Retesting is discouraged or not Retesting is encouraged for mastery
allowed at all
Materials, tools and supplies for The trainer must see that all materials
only one topic are needed at a needed for many tasks are readily
time. available.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 20 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Traditional Approach CBT Approach
The number of students enrolled As vacancies are filled, trainees
is maximum capacity at the enrollment remains at maximum capacity
beginning of the year or term and all year long.
declines to half or less toward the
end
Most instruction is delivered by or The trainer must manage the use of a
dependent upon the instructor wide variety of instructional media and
materials each day
The program is usually closed The program usually operates year round
down or shortened during the
summer months.
The instructor controls the If possible, trainees determine the
sequence in which topics will be sequence of tasks.
covered.
The evening program is usually Day and evening programs both have
separate and distinct from day access to all learning guides and
program. resources.
Role of the CBT Trainer
The major role of the trainer is one of “coordinating learning activities” other
than traditional “dispensing of information”. Trainer in a CBT system spend the
major portion of training time giving demonstrations, assigning tasks to students,
providing individual and small group assistance, evaluating trainee‟s progress and
providing individual consultation. The following functions outline the role of the
trainer in learner-centered instructional situations.
1. Serves as a team member to determine what is to be learned
2. Stimulates trainees‟ motivation.
3. Manages learning: a consultation rather than a provider of information; a
facilitator of the of the facilitator of the learning
4. Diagnose and solves learning problems
5. Evaluates student achievement
6. Assist learners to obtain individualized rewards
7. Assist each trainee in designing a personalized plan of study.
8. Installs confidence in the learner by providing experiences where learners
may succeed
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 21 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
9. Serves as a model for desirable work habits, attitudes and tasks
performance in the occupational field
10. Spends more time interacting with students on a 1:1 or small group
basis
11. Helps those students who really need help
12. Accepts responsibility along with the student for the tasks learned or
not learned.
Role of the CBT Trainee
Competency Based Training is individualized and “Learner-centered”.
Trainees, therefore, pursue instructions for their personal goals and objectives.
The trainee spends most of his time in directed self-study and practice, supervised
by the trainer who can provide immediate assistance and feedback.
In CBT, Trainees have the following roles:
1. Trainees may select what they want to learn and when they want to learn
it, within reason.
2. Trainees learn at their own rate within program guidelines. They may
speed up, slow down, stop or even repeat a task.
3. Trainees may request to receive credit for what they already know. This
is done either through pre-testing or through a review o a task list
completed at another training site.
4. Trainees may choose how they want to learn-individually, on a one-to-
one basis, in small group, in large groups or with audio-visuals.
5. Trainees are responsible for what they learn and when they learn it.
6. Trainees decide when they are ready to perform each task or demonstrate
mastery of learning to a job-like level of proficiency before receiving credit
for the task.
7. Trainees help develop personalized prescription for learning worked out
cooperatively and based upon what the students already knows, his
preference for learning, learning style and other needs.
8. Trainees compete against pres job standards and not against other
students and are graded on achievement of the standards or criteria of
each task.
9. Trainees know “up front”, before instruction begins what they are
expected to know and do to complete the program.
10. Trainees evaluate their own progress to see how well they are doing.
11. Trainees move freely in the workshop, laboratory and or training
center.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 22 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
12. Trainees know they will be rated mainly on performance, while paper
and pencil tests will be used mainly to check their knowledge of the task.
13. Trainees learn according to their interest, needs and abilities – not
14. according to teacher timelines and expediency.
The diagram on the Competency Based Training Delivery would show how
learning in a CBT approach is undergone. After discussing the Trainer‟s and the
Trainee‟s Role in the acquisition of learning, the trainee should be oriented on his
training environment which include the workshop, the facilities and the training
resources available.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 23 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
SELF-CHECK
Identification: Identify which of the following statement is a characteristic of a
CBT approach. On your answer sheet, write down the number of the item which
characterizes CBT.
1. Trainers focus on managing learning
2. Very little continuous feedback is given.
3. As vacancies are filled, trainees‟ enrollment remains at maximum
capacity all year long.
4. Retesting is discouraged or not allowed at all
5. The trainer must be able to answer questions on many different tasks
each day.
6. All students are usually tested once
7. Each trainee progresses at his or her own pace
8. Trainees enter various times throughout the year
9. If possible, trainees determine the sequence of tasks.
10. Students all proceed from one topic to the next at the same time
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 24 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Answer Key
1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 25 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.3-1
Title: Prepare a Demonstration-Performance Method Training Session
Performance Objective: Given a skill in the qualification assigned to
you, prepare a session for demonstration performance training session.
Supplies/Materials : TR and CBC
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Select a skill for demonstration from the skills of the qualification
assigned to you.
2. Using the following steps, prepare the plan:
4. Prepare the equipment, facilities, supplies and materials needed
for the demonstration.
5. Demonstrate the skill.
6. Select a trainee or a pair of trainees to perform the same skills.
Assessment Method:
Portfolio Assessment, Questioning, Demonstration
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 26 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.3-2
The Competency Based Training Procedures
Learning Objectives: After reading this INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST be able
to use the teaching/learning methods and approaches to manage your CBT
training.
In the previous discussions, you gathered information about the
characteristics of trainees, their current competencies and their training needs.
You were also presented with different modes and methods of teaching in the first
competency of the Teaching Methodology course.
Our main concern now is how to make use of this information in actual
training. How do we handle trainees with varied characteristics and different
training needs considering the Principles of Competency Based Training?
Delivery and Evaluation Activities
To effectively carry out the delivery of learning the following steps are hereby
recommended:
1. Pre-training activities
2. Construct pre-assessment instruments
3. Prepare TNA instruments
4. Prepare session plan
5. Develop CBLM for your qualification
6. Layout your workshop by workstation following the CBT Principles
7. Organize training resources
8. Monitoring of attendance
Although attendance is not a basis in evaluating trainees in CBT, the trainer
should still monitor the attendance of his trainees. This serves as a basis for the
planning of the activities for the day specially if there are limited training
resources. Monitoring attendance need not use the traditional way of checking
attendance but the trainer can devise a way in which attendance (time-in and
time-out) are recorded. Log books, biometric system or Bundy clock are some
ways of recording.
Conduct TNA and pre-assessment
Training Need Analysis (TNA) reveals important data such as the current
competencies and trainees‟ characteristics. These are basis for the planning and
scheduling of training sessions.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 27 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Schedule training sessions
Training schedule is based on trainees‟ characteristics and current
competencies. Trainer should be creative enough to maximize use of available
resources to facilitate learning. Training methodologies may vary trainee by
trainee. Small group maybe formed for some competencies wherein fast learners
may serve as leaders. In some cases a trainee may opt to learn alone.
Trainees choose competency
For TM, Plan Training Session is a prerequisite to all other competencies
except the competency Utilize Multi-Media Materials in Facilitating Session. It is,
therefore, the first competency that trainees should learn. You have to design your
first training sessions for the attainment of the learning outcomes of Plan Training
Sessions.
Prepare training facilities and resources
Assign Trainees in their workstations
Assign trainees depending on Trainees current competencies and the
availability of training resources
Orient Trainees
Orientation of Trainees to Competency Based Training
To acquaint trainees of the environment in Competency Based Training, an
orientation program is very important. It is during orientation that trainers
motivate students about the program and its benefits to trainees. This is the time
when you get trainees excited about the prospects of getting real occupational
training and confident that they can succeed in the training program.
There are two levels of the orientation program, the orientation about the
institution and the orientation about your particular qualification.
Orientation about the institution
Usually, training institutions that start qualifications at the same time
orient students about the institution during the Trainees‟ Induction Program. It
is during this time that trainees get acquainted with the school faculty and staff,
facilities, programs and services. If arrangements warrants, this orientation is a
responsibility of an orientation committee preferably headed by the guidance
counselor. But if schedules do not allow for a mass orientation, it is your
responsibility as the assessor to orient them about the institution.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 28 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Orientation about the qualification or training program
Aside from orienting the trainees about the Competency Based Training
System, the following elements of CBT needs to be discussed before the start of
any training program:
1. The role of the trainee
2. The role of the trainer
3. Basic operations in which the training operates
4. The competencies that has to be covered based on TR
5. The use of the CBLM
6. The CBLM basically has instructions in itself but trainees need to be
acquainted with its parts to ensure that every part will not be neglected.
Orient trainees on the importance of each part in the training.
7. Instructional Facilities and Resources
8. A tour of the workshop during the orientation maybe needed to
familiarize the students about facilities existing in the workshop and how
they will be accessed and returned. Their role in the maintenance of the
tools is reiterated during this time
9. The workshop and its stations
10. The evaluation system
11. The trainees will always be interested on how they will be rated. They
should know what to be and how they will be evaluated, how
achievements will be recorded and what credits to get after the training.
Guide Trainees in doing the activities of the session
The trainee is guided by the CBLM about the activities to be undertaken
through the learning activities page. All instruction sheets are also provided with
necessary sections which will serve as a guide in undertaking the activities such
as the Occupational Health and Safety practices, tools and materials needed,
standards to be met and speed.
Provide feedback on the on-going activities
Self-Checks, Task/Job Sheet, Operation Sheets, and assignment sheets are
provided with Performance Criteria Checklist or Procedural Checklist to serve as a
guide for trainees in checking their own work but it is also important that trainers
check the performance of each trainee. Always remember that immediate feedback
is critical in training.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 29 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Provide remedial activities such as lecture/discussions for knowledge or
additional Task/Job Sheets for practice as the need arises.
Since learning is self-paced, trainees are expected to finish at different times
and maybe doing different things at a time. Slow learners would need more
guidance than the others. The trainer should be very sensitive about the needs of
trainees with special needs such that of the slow learners. In some cases, several
task sheets to practice would be needed before they are ready for more complex
activities such that in the Job Sheet. The trainer should use his judgment and
ingenuity in providing these to his trainees. This would eventually increase the
materials in the CBLM and improve the efficiency of the training program.
Record achievement of trainees on the Progress Chart and
Accomplishment Chart
A Progress Chart and an Accomplishment Chart is a record of all the
accomplished activities and acquired Learning Outcomes of the trainee. They are
essentially references for both the trainer and the trainee about the on-going
training. The progress chart and the Accomplishment chart reflect important
feedback which may be bases for the adjustments in the teaching learning
process. If the progress chart shows that a trainee is too slow, for example, the
trainee would be motivated to catch up with the others. The trainer, on the other
hand, could be alarmed and find ways in guiding the trainee to achieve better.
(The Progress Chart and the Accomplishment Charts are further discussed in the
next LO.)
Evaluate trainees’ performance
The performance of the task and job sheets are venues for practicing a task
or a skill based on the criteria in the Performance Criteria Checklist. The
Performance checklist for the particular Job/Task Sheet is likewise the basis for
formative evaluation of the trainee‟s performance. A well prepared Competency
Assessment (Institutional) for each competency is however, encouraged for
summative evaluation.
Provide Feedback on the result of the evaluation
Results of evaluation should be immediately communicated to the trainees.
Decide whether the trainee advances to the next competency or to do
more practice activities
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 30 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
In doing the activities above, take note of the following principles:
Effective facilitation involves acquiring relevant knowledge about students
and using that knowledge to develop our course design and training session.
Effective facilitation involves aligning the three major components of
instruction: learning objectives, assessments and instructional activities.
The CBLM as the primary learning material is provided with the following to
allow self-paced learning:
Information sheet – learning objectives are stipulated at the start of
each information sheet.
Job/task/operation Sheets - provides opportunity for trainees to
practice skills related to the learning objective.
Performance Criteria/Procedural Checklist – provides feedback on the
performance of the activities in the Instructional Sheets. It is a
benchmark of performance criteria for the trainee for self-assessment
and for the trainer to assess trainee‟s performance.
Effective facilitation involves articulating explicit expectations regarding
learning objectives and policies.
Being clear about the objectives of learning and communicating them
explicitly to the trainees learn more and perform better. It gives trainees a clear
target to aim and to monitor.
Effective facilitation involves prioritizing the knowledge and skills we choose
to focus on.
Too many topics work against learning so you have to decide what you will
not include in the course. This involves (a) recognizing the parameters of the
course (b) setting priorities (c) determining course content that will be useful in
attaining objectives set by the Competency Standards.
Effective facilitation involves recognizing and overcoming our expert blind
spots.
We are not our trainees. Experts tend to perform acquired skills
unconsciously that they tend to become inherent in the trainer so we tend to skip
or combine critical steps when we teach. The trainer should be keen enough to
break skills into smaller tasks so that trainees can practice them well before they
can combine them with other tasks.
Effective facilitation involves adopting appropriate teaching roles to support
our learning goals.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 31 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.3-2
Title: Facilitate Training Session
Performance Objective: Given the following:
1. Results of TNA
2. Session Plan and CBLM for all competencies of TM 1
3. A TM1 workshop with computers
4. Progress Chart and Accomplishment Chart
YOU MUST be able to facilitate one training session.
Supplies/Materials : TR, CBC, CBLM, Bond papers,
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Prepare training facilities and resources
2. Monitor the attendance of trainees
3. Orient Trainees on a condition that this is the first time you meet
a group of trainees and TNA has been previously conducted.
4. Assign trainees in their workstations
5. Guide trainees in undergoing the activities
6. Provide feedback as the training is going on
7. Evaluate performance of trainees based on Performance Criteria
Checklist
8. Record trainees‟ achievement on Progress Chart and
Accomplishment Chart.
Assessment Method:
Demonstration, Portfolio Assessment, Questioning
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 32 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Criteria Checklist
Facilitate Training Session
Criteria YES NO
Did the Trainer prepare
Workstations?
Facilities/resources?
Was attendance monitored?
Was there a full utilization of work areas/resources?
Did the trainer orient the trainees on
CBT?
The role of the trainer?
The role of the trainee?
The competencies that has to be covered based on
TR
The use of the CBLM
Instructional Facilities and Resources
Workshop and its stations
The evaluation system
Did the trainer conduct pre-assessment (RPL)?
Did the trainer schedule individual and small-group
activities as appropriate?
Did the trainer use a variety of teaching techniques,
designed to match learner capabilities with the
requirements of the task?
Did the trainer monitor the activities?
Did the trainer allow students to assume individual
responsibility for learning?
Did the trainer evaluate the performance of the trainees
based on Performance Criteria Checklist?
Did the trainer record the achievements of the trainees
in the
Progress chart?
Accomplishment chart?
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 33 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Criteria YES NO
Did the trainer personally provide continual feedback to
trainees.
Were slow learners assisted in their activities?
Did the trainer evaluate the learning session?
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 34 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
LEARNING OUTCOME #4 Conduct Competency Assessment
CONTENTS:
Conduct Learning Evaluation
Feedback Mechanism
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA:
1. Learners are oriented on the evidence requirements relevant to the
evidence plan.
2. Competency assessment tools, materials and equipment are provided to
learners.
3. Evidences are gathered and documented using relevant assessment
tools.
4. Assessment results and recorded in accordance with the approved
rating system
5. Appropriate feedback mechanism is used to inform learner of his/her
progress.
CONDITION:
Students/Trainees must be provided with the following:
1. WORKPLACE LOCATION
2. EQUIPMENT
Computer
LCD
3. TOOLS, ACCESSORIES AND SUPPLIES
White board
CD
Tapes
4. TRAINING MATERIALS
Learning Packages
Bond Paper
Ball pens
Manuals
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 35 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Competency Standards
Training Regulations
ASSESSMENT METHOD:
1. Demonstration & Oral Questioning
2. Portfolio
3. Written Test
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 36 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Learning Experiences
Learning Outcome 4
Conduct Institutional Competency Assessment
Learning Activities Special Instructions
Read information sheet LO2.4-1
Perform Job Sheet LO2.4-1 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording
This activity will need a group of
observers who will evaluate the
performance based on the performance
criteria checklist.
A focus group discussion may follow to
point out strengths and weaknesses in
the performance of the trainee.
Perform Job Sheet 2.4-2 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording.
Perform Job Sheet 2.4-3 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 37 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.4-1
Conduct Learning Evaluation
After reading this INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST be
Learning Objective: able conduct learning evaluation.
Learning evaluation‟s primary goal is to assess trainee‟s performance with
the purpose of adjusting the training process so that it meets the trainees‟ training
needs. Learning evaluation may take place anytime during the training. Self-
evaluation is done by the trainee based on the performance criteria for each
activity, formative evaluation is done by the trainers to check the
accomplishments and to evaluate the level of competencies for purposes of
adjustments in the training and a summative evaluation is done at the end of the
training to assess trainees‟ performance and knowledge of trainees.
In competency based training, learning evaluation essentially measures the
sufficiency of trainees‟ performance, knowledge and attitudes compared to a set
competency standard. Institutional Competency Evaluation is done to check
whether the competencies set in the Training Regulations and the Competency
Based Curriculum is met by the trainee. It is one of the bases for giving the
training certificate of the trainee.
Since training is self-paced, institutional assessment may be done anytime
towards the end of a training when a trainee is ready for institutional competency
assessment. The trainer should encourage trainees to schedule their institutional
competency assessment by signing in a logbook. The number of trainees to be
evaluated at a certain day should be set by the trainer depending on the available
facilities and resources considering that other trainees are still undergoing
training.
Preparations for Institutional Competency Assessment
Prior to institutional assessment, the trainer should prepare the following:
Competency Assessment tool for every trainee
Answer sheet for written test
Marking sheets
Test package
Tools, materials and equipment needed for assessment
A well lighted and well-ventilated assessment area within the
workshop
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 38 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Monitor attendance
Trainees undergoing assessment should sign in an attendance sheet for
documentation.
Before the test
1. Give a short description of the assessment
2. Orient the trainees about:
the evidence requirements that has to be observed during the
assessment process
what type of tests will be given
how the evidences of competencies will be gathered
time allotted for each activity
3. Give specific instruction as slowly and as clearly
4. Specify the do‟s and don‟ts specially on concerns of safety
5. Issue tools and materials in orderly manner.
6. Assign each trainee to work stations systematically
During the test
1. Make all necessary announcements just before the test
2. Help trainees overcome their nervousness, distractions and irritation
3. Translate a test written in English to the local dialect, if necessary
4. Ensure that trainees are in appropriate working attire during the
performance test
5. Be present at the test area during the entire test
6. Observe carefully the specified time limits
7. Stop the trainee if they destroy equipment or work in hazardous manner
8. Give follow up questions in case a performance criteria is not
demonstrated.
9. Closely watch the demonstration of critical aspects of competency
10. Tick on the performance criteria on the rating sheets observed as
demonstrated as the performance test is going on
After the test
1. Ensure that all test packages are returned
2. Check answers of the written test.
3. Provide immediate feedbacks starting with positive feedback to the
performance that needs improvement.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 39 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
4. In case, the trainee is not yet competent on an area, advice him to go
back to the workstation designated for the competency for more practice.
5. Re-assess the candidate on the competency that he did not perform well.
6. Record the result of the evaluation, Competent (C) or not yet competent
(NC), on the progress chart.
Note After the learning evaluation, a successful trainee should be advised to
do the following:
1. Fill-up Program evaluation form
2. Come back for the orientation for Supervised Industry training or
On-the-Job Training.
3. Apply for National Competency Assessment
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 40 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.4-1
Title: Conduct Institutional Competency Assessment
Performance Objective: Given an assessment package and the materials
needed for assessment, you should be able to conduct institutional
assessment to at least 1 trainee
Supplies/Materials : CBLM, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Secure assessment package.
2. Prepare the supplies and materials.
3. Orient the trainees based on the given guidelines above.
4. Conduct the assessment
5. Analyze/evaluate assessment result
6. Provide feedback to the trainees
7. Record the result of the assessment on the observation checklist
and progress chart.
Assessment Method:
demonstration and questioning
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 41 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Checklist
Conduct Institutional Competency Assessment
CRITERIA YES NO
Did the trainer…
monitor the attendance?
prepare enough supplies and materials for each candidate?
orient the trainees being assessed on the following:
the evidence requirements that has to be observed
during the assessment process
what type of tests will be given
how the evidences of competencies will be gathered
time allotted for each activity
specify safety precautions during the assessment?
observe trainee in his activity?
record observations on the rating sheets?
check the written test?
ask follow-up questions?
give immediate feedback?
notify the trainee about the result of the assessment?
record the result of the assessment on the progress chart?
notify the trainee about the other requirements of the course
such as the National Competency Assessment and the
SIT/OJT?
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 42 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Other Observations:
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Comments/suggestions about the performance of the trainer:
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 43 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.4-2
Feedback Mechanism
Learning Objective: After reading this INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST be able
to determine the importance of feedback in effective learning process.
What is Feedback?
Feedback is a dialogue between people which reflects back how another
person sees someone else behavior or performance. As people we get feedback
from the way people react to us. As managers, coaches, trainers and peers we may
have more formal conversations about performance, or how someone could carry
out an aspect of their job role more effectively.
Types of Feedback
Positive Feedback – serves to sustain behavior that is appropriate and
effective.
Negative or coercive Feedback – serves to change behavior that is
inappropriate or ineffective.
Principles in Giving Effective Feedback
Give feedback only when asked to do so or when your offer is
accepted.
Give feedback as soon after the event as possible.
Focus on the positive.
Feedback needs to be given privately wherever possible, especially
more negative feedback.
Feedback needs to be part of the overall communication process and
„developmental dialogue‟. Use skills such as rapport or mirroring,
developing respect and trust with the learner.
Stay in the „here and now‟ don‟t bring up old concerns or previous
mistakes, unless this is to highlight a pattern of behaviors.
Focus on behaviors that can be changed, not personality traits.
Talk about and describe specific behaviors, giving examples where
possible and do not evaluate or assume motives.
Use „I‟ and give your experience of the behavior („when you said…, I
thought that you were…‟).
When giving negative feedback, suggest alternative behaviors.
Feedback is for the recipient, not the giver – be sensitive to the impact
of your message.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 44 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Consider the content of the message, the process of giving feedback
and the congruence between your verbal and non-verbal messages.
Encourage reflection. This will involve posing open questions such as:
(a) Did it go as planned? If not why not?
(b) If you were doing it again what would you do the same next time and
what would you do differently? Why?
(c) How did you feel during the session? How would you feel about doing it
again?
(d) How do you think the patient felt? What makes you think that?
(e) What did you learn from this session?
Be clear about what you are giving feedback on and link this to the learner‟s
overall professional development and/or intended programme outcomes.
Do not overload – identify two or three key messages that you
summarize at the end.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 45 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Feedback Strategies
Characteristics Purpose
Timing For students to get feedback while they are still mindful
of the learning target.
For student to get feedback while there is still time for
them to act on it.
Amount For students to get enough feedback so that they
understand what to do but not so much that the work
has been done for them (differs case by case).
For students to get feedback on “teachable moment”
points but not an overwhelming number.
Mode To communicate the feedback message in the most
appropriate way.
The following tools provides written feedback about a
trainee‟s performance:
Progress chart
Trainees record book
Scores in written tests
Audience To reach the appropriate students with specific
feedback.
To communicate, through feedback, that student
learning is valued.
Focus To describe specific qualities of the work in relation to
the learning targets.
To make observation about students‟ learning processes
and strategies that will help them figure out how to
improve.
To foster student-efficacy by drawing connections
between students‟ work and their mindful, intentional
efforts.
To avoid personal comments.
Comparison Usually, to compare student work with established
criteria.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 46 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Characteristics Purpose
Sometimes, to compare a student‟s work with his or her
own past performance.
Rarely, to compare a student‟s work with the work of
other students.
Function To describe student work.
To avoid evaluating or “judging” student work in a way
that would stop students from trying to improve.
Valence To use positive comments that describe what is well
done.
To make suggestions about what could be done for
improvement.
Barriers in Giving Feedback
A fear of upsetting the trainee or damaging the trainee–trainer
relationship
A fear of doing more harm than good
The trainee being resistant or defensive when receiving criticism. Poor
handling of a reaction to negative feedback can result in feedback
being disregarded thereafter
Feedback being too generalized and not related to specific facts or
observations
Feedback not giving guidance on how to rectify behavior
Inconsistent feedback from multiple sources
A lack of respect for the source of feedback.
The Role of Feedback in Learning
Learning involves the interaction of new information provided by instruction
with existing information already in the learner‟s memory. Feedback‟s role in the
learning process is not simply information processing, but a more complex milieu
with feedback having an influence on the learner‟s affective and motivational
processes, along with cues, participation, and reinforcement as one of his four
elements to determine the quality of instruction. It is an important construct for
improving instruction and performance.
Feedback is an essential part of education and training programmes. It
helps learners to maximize their potential at different stages of training, raise their
awareness of strengths and areas for improvement, and identify actions to be
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 47 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
taken to improve performance. It is part of the overall dialogue or interaction
between trainer and learner and not a one-way communication. Feedback can be
seen as informal (e.g. day to day encounters between trainer and trainee, between
peers or colleagues) or formal (for example as part of written or clinical
assessment). It is very important to ensure that the feedback given to the learner
is aligned with the overall learning outcomes of the programme/teaching session
in which the learner is engaged.
Feedback in Competency-Based Learning
Feedback is vital to success of competency-based training, we all
know that this is self-paced approach, continuous and instantaneous. The
learning materials provide the means for continuous progress checks. Results are
known quickly, correction and reinforcement are immediate. It is giving specific
information about a trainee‟s current behaviour in order to help him/her either
continue the behaviour or modify the behavior.
Providing regular feedback to the trainee regarding his/her work with you is
the most powerful teaching tool a trainers has. It is also the area most commonly
cited as lacking when trainees evaluate trainers. Quite simply, feedback is the
sharing of information about the trainee‟s performance. The feedback should be
specific enough that the trainee understands which behaviours are appropriate
and which ones need to be changed. It is most meaningful when it is based on
solid data obtained while observing or interacting with the trainee. An experienced
trainer who has worked on developing this skill can incorporate feedback
comfortably and quickly into regular interactions with a trainee.
Tools use in providing Feedback
Progress Chart
Evaluative Feedback
Trainees record Book
THE PROGRESS CHART
In Competency Based Training, this is a Chart that shows learning
outcomes where the trainees show the required degree of competence. It is a
record of trainee‟s progress and a form of giving information for the trainees which
learning outcomes are accomplished and what LOs are yet to be learned.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 48 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
The Sample Progress Chart for TM1
Guidelines in Making the Progress Chart
1. It should be written on a board preferably 4 feet by 6 feet in dimension so
that it can be glanced at by the trainee from any corner of the workshop
2. The Qualification Title should be written on top
3. It should contain all the Learning Outcomes as reflected in the Training
Regulation.
4. The names of the trainees are reflected on the second column in
alphabetical order.
5. The training duration reflects the nominal duration of the qualification.
6. All trainers involved in the training are reflected in space provided.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 49 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
THE ACCOMPLISHMENT CHART
The accomplishment chart is a record of the required activities for every
trainee. Compared to the progress chart, it is a more detailed record of the self-
checks, Job sheets, operation sheets, competency assessments and other related
projects accomplished by each trainee.
EVALUATIVE FEEDBACK
Feedback about the result of competency assessment such as scores and
acquired competency are very important information which the trainee should be
notified of as soon as possible. Immediate feedback is very critical in learning.
The trainee should, therefore, be informed about his performance, his mistakes
and the gaps in his performance just after the assessment.
Characteristics of Effective Feedback
• It is specific and performance based.
• It is descriptive, not labeling.
• It focuses on the behavior, not the trainee.
• It is based on observations, repeated if possible.
• It begins with "I" statements.
• It balances negative and positive comments.
• It is well timed.
• It is anchored to common goals (for example, the trainee‟s learning or
performance).
• It provides for two-way communication, soliciting, and considering the
receiver‟s input.
• It is brief. (Be alert to signs of resistance).
• It is based on trust, honesty, and concern.
• It is private, particularly if it is negative.
• It is part of your regular teaching process, not an exception to the
norm.
• It provides for follow-up.
Guidelines for Providing Constructive Feedback
• All comments should be based upon observable behavior and not
assumed motives or intents.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 50 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
• Positive comments should be made first in order to give the trainee
confidence and gain his/her attention.
• Language should be descriptive of specific behaviors rather than
general comments indicating value judgments.
• Feedback should emphasize the sharing of information. There should
be opportunities for both parties to contribute.
• Feedback should not be so detailed and broad. It should not
"overload" the trainee.
• Feedback should deal with the behaviors the trainee can control and
change.
• Feedback requires the ability to tolerate a feeling of discomfort.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 51 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.4-2
Title: Prepare Progress Chart
Performance Objective: Given the TR of the qualification assigned to
you, you should be able to prepare the progress chart.
Supplies/Materials : TR, CBC, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Acquire the TR or CBC of the qualification assigned to you.
2. Prepare the Progress Chart of the qualification including the LOs
of the Basic and Common Competencies using the recommended
format.
3. Present your work to your trainer.
Assessment Method:
Portfolio
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 52 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Criteria
CRITERIA YES NO
Competencies are lifted from the TR or the CBC
Basic competencies are included
Common competencies are included
Core competencies are in the Progress Chart
All LOs are reflected
A legend for recording achievement is present
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 53 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.4-3
Title: Prepare Accomplishment Chart
Performance Objective: Given the CBLM of the qualification assigned to
you, you should be able to prepare the progress chart.
Supplies/Materials : TR, CBC, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Acquire the TR or CBC of the qualification assigned to you.
2. Prepare the Accomplishment Chart of the qualification using the
recommended format.
3. Present your work to your trainer.
Assessment Method:
Portfolio
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 54 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Criteria
CRITERIA YES NO
Competencies are lifted from the TR or the CBC
Required Job Sheets are included
Job Sheets are lifted from the CBLM
Job Sheet numbers are specific
Self-Checks are listed per competencies
There is a specific legend
Learning evaluations are specified
There is a column for pre-test and post-test scores
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 55 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
LEARNING OUTCOME #5 Review Delivery of Training Session
CONTENTS:
1. Competency Based Training Review and Evaluation
2. Interpretation and Analysis of Evaluation Results
3. Training Session Adjustments
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA:
1. Appropriate Training session evaluation instrument is used.
2. Interpretations are made on the results of training session evaluation.
3. Adjustments on training are made on the results of evaluation.
CONDITION:
Students/Trainees must be provided with the following:
1. WORKPLACE LOCATION
2. EQUIPMENT
Computer, LCD
3. TOOLS, ACCESSORIES AND SUPPLIES
White board
CD
Tapes
4. TRAINING MATERIALS
Learning Packages
Bond Paper
Ball pens
Manuals
Competency Standards
Training Regulations
ASSESSMENT METHOD:
1. Demonstration & Oral Questioning
2. Portfolio
3. Written Test
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 56 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Learning Experiences
Learning Outcome 5
Review Delivery of Training Session
Learning Activities Special Instructions
Read information sheet 2.5-1
Perform Job Sheet 2.5-1 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording
Answer Self-Check Compare answers with the answer key
Read Information Sheet 2.5-2
Perform Job Sheet 2.5-2 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording.
Read Information Sheet 2.5.3 If you need the assistance of your
trainer in installing the needed software,
please ask assistance.
Perform Job Sheet 2.5-3 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording.
Perform Job Sheet 2.5-4 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording.
Perform Job Sheet 2.5-5 Evaluate your own work using the
Performance Criteria
Present your work to your trainer for
evaluation and recording.
After doing all the activities in this
competency you may ask your trainer
for a Institutional Competency
Assessment and proceed to the next
competency
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 57 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.5-1
CBT Review and Evaluation
Learning Objectives: After reading this INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST
be able to enumerate and describe ways of reviewing and evaluating training
sessions
Competency based Training, like any training, should evolve dynamically.
The drive for continuous improvement will only be possible if training is reviewed,
measured and evaluated. Adjustments can be made based on the results of the
evaluation.
The evaluation of training refers to any attempt to obtain information or
feedback on the effects of a training program and to assess the value of the
training in the light of that information. The primary purpose evaluation is to
improve training by determining which training processes achieved their
objectives.
It is important after you deliver a training session that you review your
delivery and look at what went well and what might be improved.
In your review, look at the achievement of training objectives, the content of
the session, how trainees developed their skills and knowledge and training skills.
In order to review your training you will need to gather feedback. It is useful
to gather this feedback at the end of each session so that you can think about
whether you need to make any changes to your next session. For reporting
Feedback can be obtained from participants, other people like other trainers
or supervisor and yourself.
Sometimes you need to report feedback in order to help management make
decisions about whether to continue the program as it was, change it or stop it.
Feedback can be gathered in a number of ways. The table lists the most
commonly used methods, their advantages and disadvantages.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 58 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Method Advantages Disadvantages
Evaluation sheets Cheap and easy to use Cannot identify skills
Identifies areas for acquired
improvement Gives limited
information
Interviews with trainees Provides useful Time consuming
or supervisor information Effectiveness depends
Explores problems in on the skills of the
depth interviewer
Supervisor‟s Can use checklist May influence
observation Provides expert opinion performance
Time consuming
Evaluation workshops Provides useful in-depth Time consuming,
information costly
Provides opportunity for Results difficult to
open discussion report
Need an experienced
facilitator
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 59 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
CBT Evaluation Tools
The table below shows some information gathering tools:
Information Required Evaluation Tool
1. seek expression of satisfaction Rating scale
with the training process from the Written comments
trainees
2. examine his/her own perceptions Rating scale (self-evaluation)
of the success of the training Written comments from trainees
process
3. examine success of the training Focus group discussion on specific
program in the light of the criteria
subject criteria
4. examine success of the training Passing rates in assessments
program in light of the area of the Average training time to achieve
objective criteria satisfactory level performance
5. review success of training Rating scale on applicability of
program in meeting enterprise competencies acquired
goals Written comments
Impact of evaluation
6. examine own performance Evaluation of preparation,
timeliness, thoroughness, attitude
towards trainees, closing training
session.
Rating Sheets
In preparing a rating sheet to evaluate competency based training, a trainer
must recall the characteristics of an ideal competency based training (CBT).
Group the characteristics into the following aspects, preparation, delivery, support
system and facilities. For ease of analysis a recommended rating scale should be
used such as the Likert scale.
A sample evaluation tool and an analysis follow in the succeeding pages.
The rating sheet will however depend on what the trainer need to know or verify
about his performance as a trainer or the appropriateness of the methodologies
that are used.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 60 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Focus Group Discussion
To use a focus group discussion as a form of evaluation, you will have to list
down discussion questions, which focuses on the areas you want to evaluate.
Examples or questions for discussion are the following:
1. What are the competencies you have acquired from the training that are
very useful?
2. Do you think the training prepared you with the competencies required
in the workplace?
3. What do you think are the weaknesses and strength of the CBT program?
4. What improvements can you suggest for the program?
Once questions are prepared you can organize a meeting where all
respondents will be present to give their opinions and come up with a concession.
Document review
This is done to gather information relating to the average training time of
learners to acquire the desired level of competency, to identify the success rates in
national and institutional assessment, and to summarize the written comments of
participants, supervisor and other stakeholders. Available data such as the
individual records of trainees, national assessment results as in RWAC and results
of focus group discussion or satisfaction surveys and other related researches that
covers a certain period of time.
Areas for Evaluation
Depending on the purpose and objectives of the review and evaluation of
CBT session, the following areas must be given ample considerations.
Overall Preparation - this should give a clear picture on how prepared you
are in delivering the CBT session
Program Design – evaluating this area would tell you whether the learners
are able to follow the CBT framework.
Support Staff – this area would give you an idea whether you are
maintaining the right staff to help you deliver CBT session effectively
Training Facilities – this must be evaluated if you want to have an idea if
you conform with TESDA training requirements whether the learners are satisfied
with them.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 61 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Self Evaluation
An important part of the evaluation process is if self evaluation. Self
evaluation can take place during your training session as you reflect on how
things are going. This will help you make any instant changes to your plan in
response to the situation.
Self evaluation can also take place after training session when you ask
yourself in-depth questions about whether there are things to be changed or
problems to be solve.
The following strategies can be used for evaluating your own training and
help you improve:
1. Take a video of the CBT and look for ways to improve yourself
2. Ask for feedback from colleagues and other trainers
3. Compare your training methods and techniques with other trainers.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 62 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
JOB SHEET 2.5-1
Title : Gather statistical data using the necessary evaluation instruments
Performance Objective :
Given the evaluation instruments gather the statistical data from the
respondents( trainees and trainer)
Supplies and Materials:
CBC Training regulation, bond paper. Evaluation instruments, Computer
Steps and Procedures:
1. Acquire evaluation instruments.
2. Training session evaluation instruments
Trainers/instructors
Training preparation
Program design and delivery
Training facilities and resources
Support staff
3. Distribute the evaluation instruments to the respondents-trainees.
4. Collect the filled-up evaluation instruments.
5. Sort out and prepare the gathered data for analysis.
Assessment Method:
Portfolio, oral questioning
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 63 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Performance Criteria Checklist
Criteria YES NO
1. Appropriate Training session evaluation instruments are
used.
2. Interpretations were made on the results of training
session‟s evaluation.
3. Recommendations are properly communicated.
4. Adjustments on trainings were made on the results of
evaluations.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 64 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Evaluation Instruments
TRAINING SESSION EVALUATION FORM
INSTRUCTIONS:
This post-training evaluation instrument is intended to measure how
satisfactorily your trainer has done his job during the whole duration of your
training. Please give your honest rating by checking on the corresponding. Your
answers will be treated with utmost confidentiality.
TRAINERS/INSTRUCTORS Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Good/ Outstan-
Unsatis- Satis- Adequate Very ding
factory factory Satisfactory
Name of Trainer:
1 2 3 4 5
_______________________
Orients trainees about
CBT, the use of CBLM
and the evaluation
system
Discusses clearly the
unit of competencies
and outcomes to be
attained at the start of
every module
Exhibits mastery of the
course he/she is
teaching
Motivates and elicits
active participation from
the students or trainees
Keeps records of
evidence/s of
competency attained by
each student/trainees
Instill the value of safety
and orderliness. in the
classrooms and
workshops
Instills the value of
teamwork and positive
work values
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 65 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
TRAINERS/INSTRUCTORS Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Good/ Outstan-
Unsatis- Satis- Adequate Very ding
factory factory Satisfactory
Name of Trainer:
1 2 3 4 5
_______________________
Instills good grooming
and hygiene
Instills value of time
Clarity of voice while
teaching
Use appropriate
language or dialect
Provides extra attention
to trainees with
specific learning needs
Attends classes regularly
and promptly
Shows energy and
enthusiasm while
teaching
Maximizes use of
training supplies and
materials
This post-training evaluation instrument is intended to measure how
satisfactorily your trainer prepared and facilitated your training. Please give your
honest rating by ticking on the corresponding responses. Your answers will be
treated with utmost confidentiality.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 66 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
PREPARATION Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Good/ Outstanding
Unsatisfactory Satisfactory Adequate Very
Satisfactory
1 2 3 4
5
Workshop layout
conforms with the
components of a
CBT workshop
Number of CBLM
is sufficient
Orientation given
is clear and
comprehensive
Objectives of every
training sessions
are well explained
Expected
activities/outputs
are clarified
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 67 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
PROGRAM DESIGN AND Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Outstan-
DELIVERY Unsatis- Satis- Adequate Good/ ding
factory factory Very
Satisfac-
tory
1 2 3 5
4
Course contents are
sufficient to attain
objectives
CBLM are logically
organized and presented
Information Sheet are
comprehensive in
providing the required
knowledge
Provide relevant examples,
illustrations and
demonstrations.
Sufficiency exercises, like
Task/Job Sheets are
sufficient to learn required
skills
Appropriate knowledge
are learned through the
contents of the course
Training Methodologies
are effective
Assessment Methods and
evaluation system are
suitable for the trainees
and the subject matter
Recording of achievements
and competencies
acquired is prompt and
comprehensive
Feedback about the
performance of learners
are given immediately
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 68 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
TRAINING FACIITIES/ Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Outstan-
RESOURCES Unsatis- Satis- Adequate Good/ ding
factory factory Very
Satisfac-
tory
1 2 3 5
4
Training Resources
are adequate
Training Venue is
conducive for
learning
Equipment,
Supplies, and
Materials are
Sufficient
Equipment,
Supplies and
Materials were
suitable and
appropriate
Promptness in
providing Supplies
and Materials
SUPPORT STAFF Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Outstan-
Unsatis- Satis- Adequate Good/ ding
factory factory Very
Satisfac-
tory
1 2 3 5
4
Support Staff are
accommodating
Support Staff are
knowledgeable on
the tools and
equipment in their
respective stations
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 69 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Self Evaluation Instrument
A template below is used as instruments for self evaluation
During the session did I YES NO
Establish an atmosphere of trust?
Encourage all trainees to speak and contribute ideas?
Assist the less articulate to express their ideas?
Consider all contributions to be worthwhile?
Remain aware of non verbal communication?
Praise/appreciate effort?
Summarize key points?
Used varied activities and task
Provide opportunities for practice?
Achieve the stated learning objectives?
Questions to answer
1. Were there any parts of the session which did not run as expected? Why?
2. Did any unexpected problem arise?
3. Were the session outcomes achieved? If not why?
4. Should anything be changed for the next session?
PRE-TEST POST-TEST
The end result of the teaching learning process is the reflected in the scores
of trainees in written examinations. That‟s why the pretest-post test method of
evaluation is a very important tool in evaluating training. A properly constructed
pretest, preferably standardized through item analysis, should therefore be
produced for every training program. Statistical interpretation of test scores using
paired t-test is recommended to test the significant differences between pretest
and posttest scores.
In the interpretation, the null hypothesis that “there are no significant
differences between pretest and posttest scores” is being tested. The t-test
statistical function of Microsoft excel can be used to test the null hypothesis.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 70 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Self-Check
Direction:
Identify which item is true to CBT training review and evaluation.
Encircle the number of the correct answers.
1. Feedback is necessary in order to make management make decisions
whether to continue, changed or stop the program.
2. If possible the trainees determine the sequence of task.
3. A review of the training session is necessary to know what went well and
what to improve.
4. Necessary adjustments can be made on the basis of the results of the
review and evaluation.
5. Positive feedback serves to sustain behavior that is appropriate and
effective.
6. Feedback is a dialogue between two people which reflects back how
another person sees someone else‟s behavior and performance.
7. The primary purpose of evaluation is to improve training by determining
if the training process achieved the objectives.
8. The trainer must manage the use of wide variety of instructional
materials.
9. Evaluating program design is necessary to know that training is
anchored to CBT framework.
10. Feed back is not effective for program evaluation.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 71 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Answer key
Correct answers
1
3
4
6
7
9
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 72 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.5 -2
Interpretation and Analysis of Evaluation Results
Learning Objectives: After reading this INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST be
able to interpret and analyze evaluation results from: a) pretest-posttest and b)
rating sheets
The above sample of rating sheet for the evaluation of training session uses
the 5 point Likert Scale
Adjectival Ratings corresponding to the numeric ratings were described as
follows:
5 – Outstanding
4 – Very Good/ Very Satisfactory
3 – Good/Adequate
2 – Fair/ Satisfactory
1 – Poor/Unsatisfactory
For purposes of analysis, the following ratings will be used
4.5 - 5.00 - Outstanding
3.5 - 4.49 - Very Good/ Very Satisfactory
2.5 - 3.49 - Good/ Adequate
1.5 - 2.49 - Fair/Satisfactory
0.0 - 1.49 - Poor/ Unsatisfactory
Note that we chose a 5 point Likert scale to allow the evaluator to have a
neutral stand about the items being rated. Below is a sample data for the purpose
of illustrating the result.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 73 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Number of Respondents: 25
PREPARATION Poor/ Fair/ Good/ Very Outstan
Unsa- Satis- Ade- Good/ -ding
tisfac- factory quate Very INTER-
tory Satis- AVE. PRE-
factory TATION
1 2 3 4 5
Workshop layout
conforms with the Good/
5 8 15 2 2.96
components of a Adequate
CBT workshop
Number of CBLM is Good/
3 2 15 5 2.88
sufficient Adequate
Orientation given is
Fair/Sati
clear and 2 17 3 3 2.28 sfactory
comprehensive
Objectives of every
Good/
training session is 2 10 14 4 3.2 Adequate
well explained
Expected
Fair/Sati
activities/outputs 10 12 3 1.72 sfactory
are clarified
OVERALL AVE. 2.61
Good/
Adequate
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 74 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Analysis and Interpretation of Data
The hypothetical data shown above is analyzed and interpreted as follows:
The table above shows the average ratings of 25 trainees who rated the
preparation of the training sessions. The data reveals that the clarity and
comprehensiveness of orientation activities is rated with an average of 2.28 which
is “fair”, the workshop layout (2.88), sufficiency of CBLM (2.96) and how well
objectives are explained is rated with an average of 3.2 are rated as “good”.
Overall average rating, which is 2.61, means that preparation is generally
“GOOD/ADEQUATE”.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 75 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
PRETEST and POSTTEST
Presented below is a hypothetical data of the pretest and posttest scores
which will be the basis of our discussions and example for analyzing the results of
a pretest and post test.
Student pretest score posttest score
1 23 27
2 23 28
3 15 20
4 24 30
5 26 32
6 22 24
7 20 25
8 28 26
9 30 35
10 27 27
11 25 30
12 28 33
13 32 32
14 30 35
15 33 33
16 27 27
17 25 25
18 20 30
19 30 35
20 31 27
21 22 40
22 34 40
23 26 30
24 31 34
25 29 34
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 76 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Graph of the Pretest and Post Test Scores
pre-post test
45
40
35
30
Test Scores
25
pretest score
20
posttest score
15
10
5
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Sample analysis
From the pretest and post test scores above, the graph is generated. The
blue line represents the pretest scores of the trainees and the red line represents
posttest scores. Generally, the red line is higher that the blue line which means
that post test scores are generally higher than the pretest scores although some
students did not show an increase in score like in the case of trainee 15, 16 and
17.
To establish that there is an increase in scores statistically, we test the null
hypothesis “there are no significant differences between the pre and post test
scores” using paired t-test.
Note: An average, say 25 and 26 may obviously be different but may not differ
statistically. There is a need to statistically analyze data, to test whether
test scores are statistically different.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 77 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Microsoft Excel provides statistical tools to do this
Steps in Statistical Analysis
1. Install Excel Analysis Pak add-in in Excel
How?
a. Click the Microsoft Office Button , and
b. then click Excel Options.
c. Click Add-ins, and then in the Manage box, select Excel Add-ins.
d. Click Go.
e. In the Add-Ins available box, select the Analysis ToolPak check
box, and then click OK.
f. Tip If Analysis ToolPak is not listed in the Add-Ins available box,
click Browse to locate it.
g. If you are prompted that the Analysis ToolPak is not currently
installed on your computer, click Yes to install it.
After installing Analysis Toolpak you will see the data analysis icon on your
Data Toolbar
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 78 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Using Excel to analyze data
2. Type your data in excel
To perform paired t-test, select Data
1. Click on the icon Data Analysis (the dialog box on Analysis Tools will
appear)
2. Click t-Test: paired Two sample for means
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 79 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Then click OK
3. Click on the red arrow beside the blank area for Variable 1 Range, select
the range of scores for posttest, then click on the arrow again.
4. Click on the red arrow beside the blank area for Variable 2 Range, select
the range for pretest scores, then click on the red arrow to go back to the
dialog box.
5. On the blank area for Hypothesized Mean Difference type 0.
6. Select the output range( or the range where the table will appear)
7. Then click OK
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 80 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
t-Test: Paired Two Sample for Means
posttest score pretest score
Mean 30.36 26.44
Variance 23.823 21.257
Observations 25 25
Pearson Correlation 0.596279298
Hypothesized
Mean Difference 0
df 24
t Stat 4.588851193
P(T<=t) one-tail 5.90706E-05
t Critical one-tail 1.710882067
P(T<=t) two-tail 0.000118141
t Critical two-tail 2.063898547
Sample Analysis
The table shows the mean difference between pretest and posttest scores. It
also shows if the scores are statistically different. The mean difference of pretest
and posttest scores is 4.59 and the p-value is 0.0001 which means that pretest
and posttest are significantly different, that is posttest scores are higher than
pretest scores. This means that the training increased the knowledge and skills of
the trainees.
Note: t Stat is the mean difference of scores while p is the probability that the
test scores are significantly the same. If the p-value is below 0.05, the test
scores are significantly different at 95% degree of significance. If p-value is
greater than 0.05 there are no significant differences between the pretest
and posttest.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 81 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.5-2
Title: Analysis of Ratings based on Filled-up rating sheets
Performance Objective: Given a set of hypothetical ratings you must
be able to interpret and analyze the data.
Supplies/Materials : CBLM, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Acquire a hypothetical data from your trainer.
2. Compute for the average ratings of each item.
3. Make a table of averages for each item.
4. In the last column, write the corresponding adjectival ratings
based on the suggested table above.
5. Make generalizations about the following areas of evaluation:
a. Trainers overall performance
b. Preparation
c. Design and Delivery
d. Training resources/facilities
e. Support staff
6. Make recommendations based on the conclusions made.
Assessment Method:
Answers will be compared to a prepared answer key
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 82 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Hypothetical Data
Trainer
1. Orients trainees
about CBT, the use
23 3 2 2 1 33 2 2 3 3 2 2 1 3 3 2
of CBLM and the
evaluation system
2. Discusses clearly
the unit of
competencies and
outcomes to be 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
attained at the
start of every
module
3. Exhibits mastery
of the
22 2 2 2 2 22 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
subject/course
he/she is teaching
4. Motivates and
elicits active
participation from 3 2 2 3 2 3 22 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 2 2 3
the students or
trainees
5. Keeps records of
evidence/s of
competency 11 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
attainment of each
student/trainees
6. Instill value of
safety and
orderliness in the 2 3 3 2 2 2 33 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 2
classrooms and
workshops
7. Instills the value of
teamwork and
23 2 2 3 2 32 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 2 2
positive work
values
8. Instills good
grooming and 2 2 2 2 3 3 22 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2
hygiene
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 83 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Trainer
9. Instills value of
11 1 2 2 2 11 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 2
time
10. Quality of voice
22 2 3 2 2 22 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3
while teaching
11.Clarity of
language/dialect 11 3 3 2 2 13 3 1 1 3 3 2 2 1 3 3
used in teaching
12. Provides extra
attention to
trainees and
33 3 3 2 2 33 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 3 3 3
students with
specific learning
needs
13. Attends classes
regularly and 2 3 2 3 2 2 32 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 3 2 3
promptly
14. Shows energy and
enthusiasm while 2 1 2 1 3 2 12 1 2 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 1
teaching
15. Maximizes use of
training supplies 2 3 2 3 3 2 32 3 2 3 2 3 3 2 3 2 3
and materials
PREPARATION
1. Workshop layout
conforms with the
32 2 3 2 2 22 3 3 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3
components of a
CBT workshop
2. Number of CBLM
22 3 3 2 2 23 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 3
is sufficient
3. Orientation given
is clear and 3 3 2 2 2 2 32 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 3 2 2
comprehensive
4. Objectives of every
training session is 2 2 3 2 2 2 23 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3 2
well explained
5. Expected
activities/outputs 22 2 1 1 1 22 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 1
are clarified
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 84 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
DESIGN AND DELIVERY
1. Course contents are sufficient to
2 3 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3 2 2
attain objectives
2. CBLM are logically organized
2 3 2 3 2 3 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 3 2 3
and presented
3. Information Sheet are
comprehensive in providing the 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 2 2
required knowledge
4. Examples, illustrations and
2 2 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 3 2 1 2
demonstrations help you learn
5. Practice exercises like
Task/Job Sheets are sufficient 3 2 2 2 1 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 1 3 2 2 2
to learn required skills
6. Valuable knowledge are
learned through the contents of 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2
the course
7. Training Methodologies are
2 1 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 2 2
effective
8. Assessment Methods and
evaluation system are suitable
2 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 3 2
for the trainees and the subject
matter
9. Recording of achievements and
competencies acquired is 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2
prompt and comprehensive
10. Feedback about the
performance of learners are 3 3 2 2 2 1 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 1 3 2 2
given immediately
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 85 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
TRAINING
FACILITIES/RESOUR
CES
1. Training
Resources are 3 3 2 2 2 3 32 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2
adequate
2. Training Venue is
conducive and 2 2 2 1 1 1 22 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 1
appropriate
3. Equipment,
Supplies, and
33 2 2 2 3 32 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2
Materials are
Sufficient
4. Equipment,
Supplies and
33 2 2 3 3 32 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 2 2
Materials suitable
and appropriate
5. Promptness in
providing Supplies 2 2 3 3 2 2 23 3 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 3
and Materials
SUPPORT STAFF
1. Support Staff are
44 4 4 4 4 44 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
accommodating
2. Support Staff are
knowledgeable on
the tools and
equipment in their
respective stations
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 86 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Answer Key
TRAINERS Average
Adjectival Rating
Rating
1. Orients trainees about CBT, the use of
CBLM and the evaluation system 2.33 Fair/Satisfactory
2. Discusses clearly the unit of
competencies and outcomes to be
attained at the start of every module 2.00 Fair/Satisfactory
3. Exhibits mastery of the subject/course
he/she is teaching 2.00 Fair/Satisfactory
4. Motivates and elicits active
participation from the students or
trainees 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
5. Keeps records of evidence/s of
competency attainment of each Poor/
student/trainees 1.00 Unsatisfactory
6. Instill value of safety and orderliness in
the classrooms and workshops 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
7. Instills the value of teamwork and
positive work values 2.33 Fair/Satisfactory
8. Instills good grooming and hygiene 2.22 Fair/Satisfactory
9. Instills value of time Poor/
1.44 Unsatisfactory
10. Quality of voice while teaching 2.22 Fair/Satisfactory
11. Clarity of language/dialect used in
teaching 2.11 Fair/Satisfactory
12. Provides extra attention to trainees
and students with specific learning
needs 2.78 Good/ Adequate
13. Attends classes regularly and promptly 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
14. Shows energy and enthusiasm while
teaching 1.67 Fair/Satisfactory
15. Maximizes use of training supplies and
materials 2.56 Good/ Adequate
General Average 2.13 Fair/Satisfactory
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 87 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
PREPARATION Average
Adjectival Rating
Rating
1. Workshop layout conforms with the
components of a CBT workshop 2.33 Fair/Satisfactory
2. Number of CBLM is sufficient 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
3. Orientation given is clear and comprehensive 2.33 Fair/Satisfactory
4. Objectives of every training session is well
2.22 Fair/Satisfactory
explained
5. Expected activities/outputs are clarified 1.56 Fair/Satisfactory
General Average 2.18 Fair/Satisfactory
DESIGN AND DELIVERY Average
Adjectival Rating
Rating
1. Course contents are sufficient to attain
objectives 2.22 Fair/Satisfactory
2. CBLM are logically organized and presented
2.56 Good/ Adequate
3. Information Sheet are comprehensive in
providing the required knowledge 2.56 Good/ Adequate
4. Examples, illustrations and demonstrations
help you learn 1.78 Fair/Satisfactory
5. Practice exercises like Task/Job Sheets are
sufficient to learn required skills 2.11 Fair/Satisfactory
6. Valuable knowledge are learned through the
contents of the course 2.22 Fair/Satisfactory
7. Training Methodologies are effective 1.78 Fair/Satisfactory
8. Assessment Methods and evaluation system
are suitable for the trainees and the subject
matter 2.33 Fair/Satisfactory
9. Recording of achievements and competencies
acquired is prompt and comprehensive 2.33 Fair/Satisfactory
10.Feedback about the performance of learners
are given immediately 2.22 Fair/Satisfactory
General Average 2.21 Fair/Satisfactory
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 88 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
TRAINING FACILITIES/RESOURCES Average Rating Adjectival Rating
1. Training Resources are adequate 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
2. Training Venue is conducive and
appropriate 1.56 Fair/Satisfactory
3. Equipment, Supplies, and Materials are
Sufficient 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
4. Equipment, Supplies and Materials
suitable and appropriate 2.56 Good/ Adequate
5. Promptness in providing Supplies and
Materials 2.44 Fair/Satisfactory
General Average 2.29 Fair/Satisfactory
SUPPORT STAFF Average Rating Adjectival Rating
1. Support Staff are
accommodating 4.00 Very Good/ Very Satisfactory
2. Support Staff are knowledgeable
on the tools and equipment in
their respective stations
SUMMARY TABLE
Areas Average
Adjectival Rating
Rating
Trainer 2.13 Fair/Satisfactory
Preparation 2.18 Fair/Satisfactory
Design & Delivery 2.21 Fair/Satisfactory
Training Facilities/Resources 2.29 Fair/Satisfactory
Support Staff 4.00 Very Good/
Very Satisfactory
OVERALL AVERAGE 2.56 Good/ Adequate
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 89 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Information Sheet 2.5-3
Training Session Adjustment
Learning Objectives: After reading the INFORMATION SHEET, YOU MUST be
able to recommend adjustments to the training sessions.
In the previous lessons, you learned to evaluate training sessions through
different methods such as the self evaluation, focus group discussions, rating
sheets and pretest posttest.
The results from these methodologies are legitimate sources of information
and basis for adjusting training sessions. Self assessment and self reflections, if
properly recorded, in the provided space in the session plan would give the trainer
an idea what to adjust to improve the attainment of knowledge and skills.
Trainee‟s satisfaction on the training session, activities that are
unsuccessful, feedback from trainees among others are sources of important
information which will lead to a successful adjustment in the training sessions.
Proper documentation and analysis of these important data should be done
to serve as a basis for more scientific modifications in training.
Documentations should be submitted to proper authorities to serve as a
basis for decision making about training methodologies and curriculum. These
documents maybe very useful to the following:
1. Other instructors
2. The research team
3. The Vocational Instruction Supervisor
4. The administrators
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 90 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Self-Check
Enumerate at least 5 sources of information which could be a basis for
adjusting training session.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 91 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Answer Key
1. Analysis of Pretest and Posttest scores
2. Data analysis of Program Evaluation
3. Trainee‟s Feedback on Training Session
4. Instructors‟ Self Evaluation of the training
5. Trainees‟ Satisfaction Survey results
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 92 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.5-3
Title: Analysis of Pretest and Posttest
Performance Objective: Given a hypothetical pretest and posttest scores,
you should be able to statistically analyze the test scores and produce the
following:
1. Line graph of the test scores with analysis
2. t Stat and the p-value
3. Conclusion whether the training intervention has an effect to the test
scores.
Supplies/Materials : CBLM, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Acquire a hypothetical data of test scores from your trainer.
2. In excel type the test scores based on the format of the example above.
3. Make a line graph showing the pretest and posttest scores in one
plane.
4. Write a written analysis of the graph
5. Using paired t-test as a statistical tool, analyze the test scores.
6. Make a written analysis of the statistical table of values.
7. Make a conclusion whether the posttest score is higher than the
pretest scores.
8. Give a recommendation based on the result of your analysis.
Assessment Method:
Answers will be compared to a prepared answer key
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 93 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Sample Hypothetical data
(trainer may prepare different sets of hypothetical data)
Pre- Post-
test test
student score scores
1 23 20
2 23 34
3 15 28
4 24 30
5 26 40
6 22 38
7 20 29
8 28 33
9 30 31
10 27 32
11 25 26
12 28 36
13 32 34
14 30 33
15 33 36
16 27 30
17 25 29
18 20 25
19 30 32
20 31 20
21 22 30
22 34 30
23 26 24
24 31 34
25 29 31
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 94 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Answer Key
Line Graph should be more or less like this.
45
40
Graph of Pretest and Posttest scores
35
30
SCORES
25
pretest score
20
posttest scores
15
10
5
0
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25
Analysis
Posttest scores, in red line, is generally higher than the posttest
scores, in blue line although three students did not show an increase in test
scores.
t-Test: Paired Two Sample for Means
posttest scores pretest score
Mean 30.6 26.44
Variance 24.41666667 21.25666667
Observations 25 25
Pearson
Correlation 0.229348301
Hypothesized
Mean Difference 0
df 24
t Stat 3.504677889
P(T<=t) one-tail 0.000910583
t Critical one-tail 1.710882067
P(T<=t) two-tail 0.001821166
t Critical two-tail 2.063898547
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 95 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Analysis
The table reveals that the t Stat is equal to 3.50. This is the mean difference
between the posttest and pretest scores. The p-value is 0.0018 which is less than
.05 which means that the test scores are significantly different. Mean posttest
scores are therefore higher than pretest scores.
Conclusion: Training intervention increased the scores of the trainees.
NTTA- Date Developed: Document No.
Training
TESDA Methodology I July 2010 Issued by:
QA
SYSTEM Facilitate Training Developed by: Page 96 of 101
Session Redilyn C. Agub Revision # 00
Job Sheet 2.5-4
Title: Focus Group Discussion about the Conduct Institutional Competency
Assessment
Performance Objective: After observing the Job Sheet LO2.4-1 (Conduct
of Competency Institutional Assessment Center), you should be able to undergo
a focus group discussion with a group of trainees and list down observations
about the activity
Supplies/Materials : CBLM, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. Closely observe the Conduct of Institutional Competency Assessment
(Job Sheet LO2.4-1)
2. Each trainee should fill-up the Performance Criteria Checklist and list
down observations about the demonstration.
3. After the demonstration, assign a leader and a secretary from among
the trainees to facilitate the discussion.
4. Use the Performance Criteria Checklists as a guide during the
discussion.
5. The secretary should list down common observations and
recommendations that arise during the group discussion.
6. Write the names of the members of the group on the result of the
discussions.
7. Submit the list to the trainer.
Assessment Method:
Performance criteria checklist, questioning
Date Developed: Document No.
July 2010
NTTA-TESDA Issued by:
QA Training Methodology
I Page 97 of 204
SYSTEM Developed by:
Planning Training
Session
Revision # __
Performance Criteria Checklist
CRITERIA YES NO
Were all the members of the group present during the discussion?
Did each member have the performance criteria checklist filled-up?
Is there a maximum participation of all members?
Are the members encouraged and motivated in giving their
observations?
Is the observation summary signed by all members?
Are suggestions and recommendations included in the summary?
Date Developed: Document No.
July 2010
NTTA-TESDA Issued by:
QA Training Methodology
I Page 98 of 204
SYSTEM Developed by:
Planning Training
Session
Revision # __
Job Sheet 2.5-5
Title: Focus Group Discussion on Facilitate Training Session
Performance Objective: After observing the Job Sheet LO2.3-1 (Facilitate
Training Session), you should be able to undergo a focus group discussion with
a group of trainees and list down observations about the activity
Supplies/Materials : CBLM, Bond papers
Equipment : PC, printer with ink
Steps/Procedure:
1. observe the Conduct of Institutional Competency Assessment
(Job Sheet LO2.4-2)
2. Each trainee should fill-up the Performance Criteria Checklist and list
down observations about the demonstration.
3. After the demonstration, assign a leader and a secretary from among
the trainees to facilitate the discussion.
4. Use the Performance Criteria Checklists as a guide during the
discussion.
5. The secretary should list down common observations and
recommendations that arise during the group discussion.
6. Write the names of the members of the group on the result of the
discussions.
7. Submit the list to the trainer.
Assessment Method:
Questioning
Date Developed: Document No.
July 2010
NTTA-TESDA Issued by:
QA Training Methodology
I Page 99 of 204
SYSTEM Developed by:
Planning Training
Session
Revision # __
Performance Criteria Checklist
CRITERIA YES NO
Were all the members of the group present during the
discussion?
Did each member have the performance criteria checklist
filled-up?
Is there a maximum participation of all members?
Are the members encouraged and motivated in giving their
observations?
Is the observation summary signed by all members?
Are suggestions and recommendations included in the
summary?
Date Developed: Document No.
July 2010
NTTA-TESDA Issued by:
QA Training Methodology
I Page 100 of 204
SYSTEM Developed by:
Planning Training
Session
Revision # __
You might also like
- Stranger Things Episode Script 2 05 Chapter Five Dig DugDocument67 pagesStranger Things Episode Script 2 05 Chapter Five Dig Dugyonas123No ratings yet
- Trust Law: Common Law Property Settlor Trustees Beneficiary FiduciaryDocument8 pagesTrust Law: Common Law Property Settlor Trustees Beneficiary FiduciaryDekweriz100% (1)
- Module 1: Caregiver Self CareDocument54 pagesModule 1: Caregiver Self Carerey yuyNo ratings yet
- Philippine Constitution - Civil Service Exam ReviewerDocument41 pagesPhilippine Constitution - Civil Service Exam ReviewerYzza Veah Esquivel50% (2)
- TULIP ChartDocument1 pageTULIP ChartMiguel DavillaNo ratings yet
- 5000 TOEFL Words PDFDocument36 pages5000 TOEFL Words PDFPrudhveeraj Chegu100% (2)
- 5000 TOEFL Words PDFDocument36 pages5000 TOEFL Words PDFPrudhveeraj Chegu100% (2)
- TM 1 COC 2Document5 pagesTM 1 COC 2Marife CulabaNo ratings yet
- Regulatory, Warning and Informative Traffic SignsDocument14 pagesRegulatory, Warning and Informative Traffic SignsOrbe JeromeNo ratings yet
- Animal Production Ruminants NCII Forage MaintenanceDocument23 pagesAnimal Production Ruminants NCII Forage MaintenanceMeynard Baptista100% (1)
- 2018 Nissan Qashqai 111809Document512 pages2018 Nissan Qashqai 111809hectorNo ratings yet
- Jim Beam Case Study Identify Roles and Organizational IssuesDocument4 pagesJim Beam Case Study Identify Roles and Organizational IssuesoluNo ratings yet
- Cbc-Agricultural Crops Production Ncii (Gad)Document43 pagesCbc-Agricultural Crops Production Ncii (Gad)Danica Joy PaasaNo ratings yet
- Organic Cbc1Document52 pagesOrganic Cbc1Elonah Jean ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Assessor's Guide for Organic Agriculture Production AssessmentDocument5 pagesAssessor's Guide for Organic Agriculture Production AssessmentAngelyn TansiongcoNo ratings yet
- Firebird Developer Guide Beta Delphi FiredacDocument162 pagesFirebird Developer Guide Beta Delphi FiredacDanilo CristianoNo ratings yet
- Final Script On Facilatate LearningDocument7 pagesFinal Script On Facilatate LearningAngelyn Tansiongco100% (1)
- CBLM Basic Work in A Team EnvironmentDocument21 pagesCBLM Basic Work in A Team Environmenternest macalaladNo ratings yet
- COMPETENCY-BASED LEARNING MATERIALS ON PRODUCING ORGANIC FERTILIZERDocument19 pagesCOMPETENCY-BASED LEARNING MATERIALS ON PRODUCING ORGANIC FERTILIZERDanny R. Salvador100% (1)
- CBC Blended Oap MoiDocument86 pagesCBC Blended Oap MoiConcepcion ObcenaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance To Become Arice Competitivenes Enhancement Fund-Learning Site For Agriculture FormDocument1 pageAcceptance To Become Arice Competitivenes Enhancement Fund-Learning Site For Agriculture FormDennis SarmientoNo ratings yet
- CBC-Artificial Insemination (Large Ruminants) NC IIDocument51 pagesCBC-Artificial Insemination (Large Ruminants) NC IICei mendozaNo ratings yet
- Juarez Cca Evidence PlanDocument10 pagesJuarez Cca Evidence PlanClaireSobredilla-JuarezNo ratings yet
- Quality Management and Control in ConstructionDocument22 pagesQuality Management and Control in ConstructionjennyNo ratings yet
- Plan Training Session on Planting CropsDocument82 pagesPlan Training Session on Planting CropsRose CasugaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Training Calendar ACP NC IIIDocument11 pages6 - Training Calendar ACP NC IIIrcsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Icai Oap Ncii Uc 4Document4 pagesIcai Oap Ncii Uc 4Rico Bandal EsponillaNo ratings yet
- Cca Script in Eim Ncii GreetingDocument5 pagesCca Script in Eim Ncii GreetingShairrah Claire Bañares Batangue100% (1)
- CBC Organic Agricultural NC II New NormalDocument96 pagesCBC Organic Agricultural NC II New Normaljazzy mallariNo ratings yet
- Icai Oap Ncii Uc 3Document4 pagesIcai Oap Ncii Uc 3Rico Esponilla0% (1)
- Training Activity Matrix Achievement Chart Progress Chart: Organic Agriculture Production NC Ii Workshop LayoutDocument1 pageTraining Activity Matrix Achievement Chart Progress Chart: Organic Agriculture Production NC Ii Workshop Layoutaaronjules100% (1)
- Data Gathering Instrument For TraineeDocument16 pagesData Gathering Instrument For TraineeMianne Grace SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Trainers Methodology (TM) Level I Study GuideDocument11 pagesTrainers Methodology (TM) Level I Study GuideKen Ferrolino100% (1)
- Cca SequenceDocument3 pagesCca Sequencefernando_drdNo ratings yet
- 3 Training Activity Matrix Oap Ncii Day 1 & 2Document2 pages3 Training Activity Matrix Oap Ncii Day 1 & 2Ronnie NaagNo ratings yet
- Tm1 Portfolio.3Document29 pagesTm1 Portfolio.3Paul Omar PastranoNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering Instrument for Trainee CharacteristicsDocument137 pagesData Gathering Instrument for Trainee CharacteristicsZOOMTECHVOC TRAINING&ASSESSMENTNo ratings yet
- New Normal CBC Acp Ncii 2021 Gold FarmDocument75 pagesNew Normal CBC Acp Ncii 2021 Gold FarmGold Farm100% (1)
- COMPETENCY-BASED CURRICULUM FOR LIGHT VEHICLE DRIVINGDocument68 pagesCOMPETENCY-BASED CURRICULUM FOR LIGHT VEHICLE DRIVINGSSVTC LRCNo ratings yet
- 21st-Century-Skills-HILOT (Wellness Massage) MOI Basic Competencies 9Document3 pages21st-Century-Skills-HILOT (Wellness Massage) MOI Basic Competencies 9Victor De Jesus0% (1)
- CCA Script Scene 2Document3 pagesCCA Script Scene 2Cjrylai CrystamaidNo ratings yet
- Session Plan Oap NciiDocument5 pagesSession Plan Oap NciiRonnie NaagNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Scope of Curriculumdevelopment: (Philippine Context)Document161 pagesThe Nature and Scope of Curriculumdevelopment: (Philippine Context)Aljubir Marrack100% (1)
- Procedures Manual On Utpras Unified TVET Program Registration and Accreditation System Program Registration (Land-Based)Document27 pagesProcedures Manual On Utpras Unified TVET Program Registration and Accreditation System Program Registration (Land-Based)Valcy MadzNo ratings yet
- Core Modules of Instruction Agriculture NC IIDocument32 pagesCore Modules of Instruction Agriculture NC IIMEAMALLORCANo ratings yet
- Competency Based Learning Material: S: A F Q: O A P Ncii U C: P O V M T: P O VDocument38 pagesCompetency Based Learning Material: S: A F Q: O A P Ncii U C: P O V M T: P O VDanny R. Salvador100% (1)
- Aquaculture NCII Training: Geronimo R. RosarioDocument58 pagesAquaculture NCII Training: Geronimo R. RosarioBryanNo ratings yet
- TG - Science 10 - Q1 PDFDocument78 pagesTG - Science 10 - Q1 PDFCarlos Miguel De Torres100% (3)
- Factors Affecting Child DevelopmentDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting Child DevelopmentAljubir Marrack100% (1)
- Agricrops Ncii Training PlanDocument20 pagesAgricrops Ncii Training PlanRonnie Naag100% (1)
- Basic and Common Session PlanDocument4 pagesBasic and Common Session PlanGlandale Sentasas67% (3)
- JOHN MARK B. BAUTISTADocument4 pagesJOHN MARK B. BAUTISTAHannah PayasNo ratings yet
- Institutional Assessment ToolsDocument11 pagesInstitutional Assessment ToolsJomar Ababa DenilaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Hydrogen Fuel CellDocument57 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Hydrogen Fuel CellSayem BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Basic Competencies Course StructureDocument14 pagesBasic Competencies Course StructureMichael IbarraNo ratings yet
- (I) QuestionnaireDocument4 pages(I) Questionnaireganesh1433No ratings yet
- CBC Agroentrep NCII (AutoRecovered)Document32 pagesCBC Agroentrep NCII (AutoRecovered)Archelyn Gagula GuialelNo ratings yet
- Dressmaking NC II: Preparing and Cutting MaterialsDocument96 pagesDressmaking NC II: Preparing and Cutting MaterialsAljubir Marrack100% (1)
- TESDA Registration FormDocument2 pagesTESDA Registration FormJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Organic Fertilizer Production Self-CheckDocument68 pagesOrganic Fertilizer Production Self-CheckSumbungan Ng Brgy TaraNo ratings yet
- 10.my Facilitate Learning SessionDocument9 pages10.my Facilitate Learning SessionNeri ErinNo ratings yet
- Women in PoliticsDocument13 pagesWomen in PoliticsMusa M. KamaraNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern Shipping Vs CADocument2 pagesFar Eastern Shipping Vs CAAnonymous 5MiN6I78I0No ratings yet
- CBC Organic NC IiDocument17 pagesCBC Organic NC IiElonah Jean ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Procedures Manual On Utpras Unified TVET Program Registration and Accreditation System Program Registration (Land-Based)Document2 pagesProcedures Manual On Utpras Unified TVET Program Registration and Accreditation System Program Registration (Land-Based)Eric SongcalNo ratings yet
- Trainers Methodology Level 1 Portfolio SubmissionDocument170 pagesTrainers Methodology Level 1 Portfolio Submissionlemuel sardualNo ratings yet
- Forms 1.1.14 Assesment Check-1Document14 pagesForms 1.1.14 Assesment Check-1baitan dadiganNo ratings yet
- Animal Production CLMDocument42 pagesAnimal Production CLMzNo ratings yet
- Trainees Progress Sheet OAP NCIIDocument2 pagesTrainees Progress Sheet OAP NCIIRonnie NaagNo ratings yet
- As A Trainer 1 Day OrientationDocument1 pageAs A Trainer 1 Day OrientationVincentnhoj L ChattoNo ratings yet
- Facilitate Learning Session ModuleDocument1 pageFacilitate Learning Session ModuleMelissa Agarrado ReputanaNo ratings yet
- MTF - Acp IiiDocument26 pagesMTF - Acp IiiBergo AgustinNo ratings yet
- 3 Session PlanDocument5 pages3 Session PlanFabie BarcenalNo ratings yet
- Updated Training Plan Smaw NC IDocument43 pagesUpdated Training Plan Smaw NC IEdward LyleNo ratings yet
- TESDA-SOP-CO-01-f07 - Competency Based Curriculum OrganicDocument39 pagesTESDA-SOP-CO-01-f07 - Competency Based Curriculum OrganicMae D. Saliring0% (1)
- 1 Task Operation Job Sheet TemplateDocument6 pages1 Task Operation Job Sheet TemplateWAGAYEN , MarvenNo ratings yet
- Session Plan 2 1Document9 pagesSession Plan 2 1vayaNo ratings yet
- Juarez Cca Evidence PlanDocument10 pagesJuarez Cca Evidence PlanClaireSobredilla-JuarezNo ratings yet
- Facilitate Learning Session PDFDocument119 pagesFacilitate Learning Session PDFRobiNo ratings yet
- Sexuality in the Philippines: From Ancient Tribes to Modern TimesDocument5 pagesSexuality in the Philippines: From Ancient Tribes to Modern TimesAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Object PermanenceDocument28 pagesObject PermanenceAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Index of DiscriminationDocument1 pageIndex of DiscriminationAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Determining Appropriate Evaluation InstrumentsDocument9 pagesDetermining Appropriate Evaluation InstrumentsAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Bronfenbrenner'sDocument333 pagesBronfenbrenner'sAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Item IndexDocument2 pagesItem IndexAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Related Kidshealth LinksDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Related Kidshealth LinksAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Related Kidshealth LinksDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Related Kidshealth LinksAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument28 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For Lemon Production in CaliforniaDocument84 pagesBusiness Plan For Lemon Production in CaliforniaAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Genie SusanDocument5 pagesGenie SusanAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Examples of Psychoanalytic Theory. ... Psychoanalytic Theory Is A Method of Investigating and TreatingDocument1 pageExamples of Psychoanalytic Theory. ... Psychoanalytic Theory Is A Method of Investigating and TreatingAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Defense Mechanism and Acute Stress Disorder StudyDocument16 pagesDefense Mechanism and Acute Stress Disorder StudyAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- Linking VerbsDocument2 pagesLinking VerbsAljubir MarrackNo ratings yet
- CPSC5125 - Assignment 3 - Fall 2014 Drawing Polygons: DescriptionDocument2 pagesCPSC5125 - Assignment 3 - Fall 2014 Drawing Polygons: DescriptionJo KingNo ratings yet
- CIMA Financial Accounting Fundamentals Past PapersDocument107 pagesCIMA Financial Accounting Fundamentals Past PapersAnonymous pwAkPZNo ratings yet
- Name of Student: Ayush Soni Sap Id: 1000012241Document2 pagesName of Student: Ayush Soni Sap Id: 1000012241Ayush SoniNo ratings yet
- Indexed Journals of Pakistan - Medline and EmbaseDocument48 pagesIndexed Journals of Pakistan - Medline and EmbaseFaisal RoohiNo ratings yet
- Philips NTRX505Document28 pagesPhilips NTRX505EulerMartinsDeMelloNo ratings yet
- FTI-Forming SuiteDocument2 pagesFTI-Forming SuiteMithun RajuNo ratings yet
- Integrated BMSDocument14 pagesIntegrated BMSjim.walton100% (5)
- General Learning Outcomes: Lesson Title/Foc Us Math Grade 1 Ordering Vegetables/Addition Sign Teache R: DateDocument5 pagesGeneral Learning Outcomes: Lesson Title/Foc Us Math Grade 1 Ordering Vegetables/Addition Sign Teache R: Dateapi-296438662No ratings yet
- Form of Bid SecurityDocument3 pagesForm of Bid SecurityKrishna EelaNo ratings yet
- HG532s V100R001C01B016 version notesDocument3 pagesHG532s V100R001C01B016 version notesKhaled AounallahNo ratings yet
- Arijit Singh Lyrics: "Saawali Si Raat"Document1 pageArijit Singh Lyrics: "Saawali Si Raat"123No ratings yet
- Pre Test in Pe 12Document3 pagesPre Test in Pe 12HERMINIA PANCITONo ratings yet
- Lemuria (Continent) - WikipediaDocument3 pagesLemuria (Continent) - WikipediaAdam McNo ratings yet
- God Hates Us All AlbumDocument3 pagesGod Hates Us All AlbumDannyNo ratings yet
- Muster Roll 24Document2 pagesMuster Roll 24Admirable AntoNo ratings yet
- Question 1 - Adjusting EntriesDocument10 pagesQuestion 1 - Adjusting EntriesVyish VyishuNo ratings yet
- TQM Implementation in ToyotaDocument15 pagesTQM Implementation in ToyotaSaikat GhoshNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Evaluation of Feeds pH and AcidityDocument5 pagesLinear Programming Evaluation of Feeds pH and AcidityAugust Ridlof RiwuNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument30 pagesConsumer BehaviourManoj BaghelNo ratings yet
- Seam 3 - Lesson 8 & 9 - Week 9Document12 pagesSeam 3 - Lesson 8 & 9 - Week 9Jeffrey SacramentoNo ratings yet