Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sepam Series 40 and Its Optional Modules
Uploaded by
WongSemarangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sepam Series 40 and Its Optional Modules
Uploaded by
WongSemarangCopyright:
Available Formats
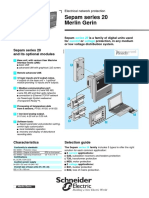
Technical data sheet Electrical network protection
2010 Sepam series 40
Sepam series 40 is a family of current and/or voltage
digital protection relays, for medium voltage public
and industrial distribution networks.
Sepam series 40 and its optional
PE50546a
Standard
modules IEC
61850
1 Base unit, with various types of User 4
3
Machine Interfaces (UMI):
1
b basic UMI
b advanced UMI with graphical LCD
screen.
6
2 Remote advanced UMI.
3 10 logic inputs and 8 output relays,
4 outputs on the base unit + 1 optional
module providing 10 inputs and 4 5
outputs.
1 communication port: 7
4
b connection to 1 or 2 S-LAN and/or
E-LAN networks 2
b Modbus, Modbus TCP/IP,
IEC60870-5-103, DNP3 and IEC 61850
communication protocols
b TCP/IP redundancy
b RS 485 ( 2or 4 wire) or fiber optic
network.
Characteristics
5 Temperature data from 16 sensors,
Conformity to standards
Pt100, Ni100, or Ni120.
IEC 60255 - Protection relays
6 1 analog output, IEC 60529 - Degree of protection IP52 on front panel
IEC 60068 - Operating temperature -25°C to +70°C (-13°F to +158°F)
0-10mA, 4-20mA or 0-20mA. IEC 61850-6, 7-1, 7-2, 7,3, 7-4 and 8-1 Communication networks and system in substation
7 Software tools: Certifications
CE, UL508, CSA C22.2
b Sepam parameter and protection
Auxiliary power supply
setting and control function 24-250 V DC and 110-240 V AC
customization Overall size of base units (H x W x D)
b recovery and display of disturbance 222 X 176 X 130 mm
recording data
b local or remote operation via an
E-LAN.
14 types of Sepam series 40
b S40, S41, S42, S43, S50, S51, S52, S53: substation incomers and feeders protection.
b T40, T42, T50, T52: transformer protection.
b M41: motor protection.
b G40: generator protection.
Protections ANSI code S40 S50 S41 S51 S42 S52 S43 S53 T40 T50 T42 T52 M41 G40
Phase overcurrent 50/51 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Cold load pick-up with phase overcurrent protection CLPU 50/51 4 4 4 4 4 4
Voltage restrained overcurrent 50V/51V 1
Earth fault, sensitive earth fault 50N/51N, 50G/51G 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Cold load pick-up with earth fault protection CLPU 50N/51N 4 4 4 4 4 4
Breaker failure 50BF 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Unbalance/negative sequence 46 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Broken conductor 46BC 1 1 1 1 1 1
Directional phase overcurrent 67 2 2 2 2
Directional earth fault 67N/67NC 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Directional real overpower 32P 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Directional reactive overpower 32Q/40 1 1
Thermal overload 49 RMS 2 2 2 2 2 2
Phase undercurrent 37 1
Locked rotor, excessive starting time 48/51LR/14 1
Starts per hour 66 1
Positive sequence undervoltage 27D 2
Remanent undervoltage 27R 1
Undervoltage (2) 27/27S 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Overvoltage (2) 59 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Neutral voltage displacement 59N 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Negative sequence overvoltage 47 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Overfrequency 81H 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Underfrequency 81L 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Recloser (4 cycles) 79 v v v v v v v v
Temperature monitoring (8 or 16 RTDs, 2 set points per RTD) 38/49T v v v v v v
Thermostat / Buchholz 26/63 v v v v
Metering S40 S41 S42 S43 T40 T42 M41 G40
S50 S51 S52 S53 T50 T52
DE40548
RMS phase current I1,I2,I3, residual current I0 b b b b b b b b
Average current I1, I2, I3 b b b b b b b b
Peak demand current IM1, IM2, IM3
Voltage U21, U32, U13, V1, V2, V3 b b b b b b b b
Residual voltage V0
Positive sequence voltage Vd/rotation direction, b b b b b b b b
Negative sequence voltage Vi
Frequency b b b b b b b b
Active / reactive / apparent power P, Q, S b b b b b b b b
Peak demand power PM, QM, power factor
Calculated active / reactive energy (±W.h, ±var.h) b b b b b b b b
Active/reactive energy impulse counter (±W.h, ±var.h) v v v v v v v v
Temperature v v v v
Network and machine diagnosis
Tripping current TripI1, TripI2, TripI3, TripI0 b b b b b b b b
Tripping context b b b b b b b b
Unbalance ratio/negative sequence current b b b b b b b b
Peak demand negative sequence and positive b b b b b b
sequence current ratio (3)
Phase shift j0, j1, j2, j3 b b b b b b b b
Disturbance recording b b b b b b b b
Fault locator (4) b b b b
Thermal capacity used b b b b
Remaining operating time before overload tripping b b b b
Waiting time after overload tripping b b b b
Running hours counter / operating time b b b b
Starting current and time b
Start inhibit time delay, number of starts before b
inhibition
Switchgear diagnosis
Cumulative breaking current b b b b b b b b
Trip circuit supervision v v v v v v v v
Number of operations, operating time, charging time v v v v v v v v
CT/VT supervision b b b b b b b b
ART.07900 © 2010 - Schneider Electric - All rights reserved
Control and monitoring ANSI code
Circuit breaker / contactor control (1) 94/69 b b b b b b b b
Latching / acknowledgment 86 b b b b b b b b
Logic discrimination 68 v v v v v v v v
Switching of group of settings b b b b b b b b
Annunciation 30 b b b b b b b b
Logical equation editor b b b b b b b b
b standard, v according to parameter setting and MES114/MES114E/
Communication port
MES114F or MET148-2 input/output module options.
(1) For shunt trip unit or undervoltage trip unit. Measurement readout v v v v v v v v
(2) Exclusive choice, phase-to-neutral voltage or phase-to-phase voltage Remote indication and time tagging of event v v v v v v v v
for each of the 2 relays. Remote control orders v v v v v v v v
(3) Only for S50, S51, S52, S53, T50, T52 applications. Remote setting of protections v v v v v v v v
(4) Only for S50, S51, S52, S53 applications. Transfer of disturbance recording data v v v v v v v v
Schneider Electric Industries SAS As standards, specifications and designs change from time to time, please ask for confirmation
35, rue Joseph Monier of the information given in this publication.
CS 30323
F- 92506 Rueil Malmaison Cedex This document has been printed on ecological paper.
RCS Nanterre 954 503 439 Design: Schneider Electric
Capital social 896 313 776 € Photos: Schneider Electric
www.schneider-electric.com Printed:
PCRED301002EN 01/2010
You might also like
- Pcred 301002 enDocument2 pagesPcred 301002 enLimingDengNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 80-Sepd302058enDocument4 pagesSepam Series 80-Sepd302058enDiegoNo ratings yet
- Relay SpecificationDocument3 pagesRelay SpecificationYogi FebriansyahNo ratings yet
- Argus 7SR22Document1 pageArgus 7SR22Arun dasNo ratings yet
- 7sr1206 Relay ModelDocument1 page7sr1206 Relay ModelSudipto MajumderNo ratings yet
- 7SR11 and 7SR12 Argus Catalogue SheetDocument24 pages7SR11 and 7SR12 Argus Catalogue SheetGokul VenugopalNo ratings yet
- 7SR11 and 7SR12 Argus Catalogue SheetDocument24 pages7SR11 and 7SR12 Argus Catalogue SheetJose Gutierrez100% (1)
- 7SR11 and 7SR12 Argus Catalogue SheetDocument24 pages7SR11 and 7SR12 Argus Catalogue SheetmullamoinNo ratings yet
- 2 Page S40 Data SheetDocument2 pages2 Page S40 Data SheetThinh DaoNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesDocument2 pagesSepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesMohamed IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Sepam1000 20 Technical Short DataDocument2 pagesSepam1000 20 Technical Short DataGelu BordeaNo ratings yet
- 5-Reyrolle 7SR10 PresentationDocument18 pages5-Reyrolle 7SR10 PresentationJr FellerNo ratings yet
- P50 Agile P154: Technical ManualDocument286 pagesP50 Agile P154: Technical ManualJanoshNo ratings yet
- P50 Agile: GE Grid SolutionsDocument288 pagesP50 Agile: GE Grid Solutionsnurahmat57No ratings yet
- P34x EN TDS C11Document44 pagesP34x EN TDS C11TSNo ratings yet
- Micom P141, P142, P143, P144, P145: Technical Data SheetDocument80 pagesMicom P141, P142, P143, P144, P145: Technical Data SheetEverton Klinger Sousa Silva100% (1)
- Micom P342, P343, P344: Generator Protection RelaysDocument8 pagesMicom P342, P343, P344: Generator Protection RelaysTSNo ratings yet
- Micom P14X: Feeder Management RelaysDocument8 pagesMicom P14X: Feeder Management RelaysAlejandra E. HernandezNo ratings yet
- 7SRDocument16 pages7SRsurya892100% (1)
- MiCOM P143 feeder relay specificationsDocument3 pagesMiCOM P143 feeder relay specificationsnur azizNo ratings yet
- Easergy P3 Protection Relays - P3U30Document3 pagesEasergy P3 Protection Relays - P3U30pradityo jwuNo ratings yet
- SIP Compact Schutztechnik en 7SK81 Edition2 PDFDocument27 pagesSIP Compact Schutztechnik en 7SK81 Edition2 PDFKartik SamantaNo ratings yet
- Sil-B: Feeder Protection Relay For Primary DistributionDocument6 pagesSil-B: Feeder Protection Relay For Primary DistributionTeban MartinekNo ratings yet
- Feeder Protection (ZIV e-NET Flex Family)Document2 pagesFeeder Protection (ZIV e-NET Flex Family)abbastceNo ratings yet
- P50 Agile: GE Grid SolutionsDocument268 pagesP50 Agile: GE Grid SolutionsPrasenjit MaityNo ratings yet
- Reyrolle 7SR51: Overcurrent ProtectionDocument2 pagesReyrolle 7SR51: Overcurrent ProtectionFelipe FrancoNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric - Easergy-P5-Protection-Relays - REL50331Document5 pagesSchneider Electric - Easergy-P5-Protection-Relays - REL50331Shah Aizat RazaliNo ratings yet
- Hot News GRL150Document2 pagesHot News GRL150Sandy BhaiNo ratings yet
- NT10 BrochureDocument12 pagesNT10 Brochuremaykoll edwards ortiz castilloNo ratings yet
- HCPL 7601 AvagoDocument13 pagesHCPL 7601 AvagoSyed Khawar MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Sepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesDocument2 pagesSepam Series 20 and Its Optional ModulesEphraem KalisNo ratings yet
- First Chapter Engineering TrainingDocument42 pagesFirst Chapter Engineering TrainingHaziq TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Easergy P3 Protection Relays - REL52018Document5 pagesEasergy P3 Protection Relays - REL52018gigiopicheli731No ratings yet
- Siemens Switchgear MCB DB Price ListDocument60 pagesSiemens Switchgear MCB DB Price ListSiDdu KalashettiNo ratings yet
- Reyrolle 5 7SR511 Overcurrent Protection ProfileDocument2 pagesReyrolle 5 7SR511 Overcurrent Protection ProfileDiego Alejandro Cetina MezaNo ratings yet
- Substation 631: Distribution Transformers (Oil Filled Outdoor)Document40 pagesSubstation 631: Distribution Transformers (Oil Filled Outdoor)PrasadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installations From A To Z Price List W e FDocument60 pagesElectrical Installations From A To Z Price List W e FprudduNo ratings yet
- MICOM P64x PDFDocument8 pagesMICOM P64x PDFMujahid Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- 7SR10 Overcurrent Earth Fault Catalogue SheetDocument20 pages7SR10 Overcurrent Earth Fault Catalogue Sheetrahulyadav2121545No ratings yet
- remsdaq-callisto-nxl-lite-system-brochureDocument2 pagesremsdaq-callisto-nxl-lite-system-brochureFarid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installations From A To Z Price List W.E.F. 1st March 2022Document60 pagesElectrical Installations From A To Z Price List W.E.F. 1st March 2022MNSanthoshKumarRajuNo ratings yet
- Powercore Mpc-20: DimensionsDocument2 pagesPowercore Mpc-20: DimensionsspiNo ratings yet
- Description of Option Option E1: E1: Analogue Controller OutputsDocument4 pagesDescription of Option Option E1: E1: Analogue Controller OutputsHeri MunirNo ratings yet
- DC/DC Power Modules 3 7 W PKF 4000 I: Product ProgramDocument22 pagesDC/DC Power Modules 3 7 W PKF 4000 I: Product ProgramJuan SilvaNo ratings yet
- REL50331 product data sheet protection relayDocument3 pagesREL50331 product data sheet protection relayMiguel Huaccha ArmasNo ratings yet
- Ca PR512 (En) C 1VCP000055 PDFDocument44 pagesCa PR512 (En) C 1VCP000055 PDFmohamed karemNo ratings yet
- HD p14x Nrjed111052enDocument8 pagesHD p14x Nrjed111052enganesh_d2k6No ratings yet
- Ingepac Efld Fy48iptt01 CDocument2 pagesIngepac Efld Fy48iptt01 CDavi SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Sectos Product Brochure - EN - 140108Document28 pagesSectos Product Brochure - EN - 140108Mario EliasNo ratings yet
- 74LVC244A/74LVCH244A: Octal Buffer/line Driver With 5-Volt Tolerant Inputs/outputs (3-State) TitleDocument10 pages74LVC244A/74LVCH244A: Octal Buffer/line Driver With 5-Volt Tolerant Inputs/outputs (3-State) TitleDarleiDuarteNo ratings yet
- ON Orks: PLT-22 Power Line Transceiver User's GuideDocument128 pagesON Orks: PLT-22 Power Line Transceiver User's Guidefouad abdNo ratings yet
- Daewoo SP115 Chassis DP42SM Plasma TV SM PDFDocument62 pagesDaewoo SP115 Chassis DP42SM Plasma TV SM PDFdann222No ratings yet
- UC3844B, UC3845B, UC2844B, UC2845B High Performance Current Mode ControllersDocument20 pagesUC3844B, UC3845B, UC2844B, UC2845B High Performance Current Mode Controllers田忠勇No ratings yet
- GRE170 Manual 6F2T0194-2.1Document353 pagesGRE170 Manual 6F2T0194-2.1VanLoveeNo ratings yet
- F PRO 116 Feeder Protection Relay DsDocument6 pagesF PRO 116 Feeder Protection Relay DsbetankourtNo ratings yet
- Dacmcp 4901Document51 pagesDacmcp 4901Ri Cha RdNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Directional Power Relay UpdatedDocument4 pagesThree Phase Directional Power Relay UpdatedDOUGLASNo ratings yet
- PowerLogic™ P5 - REL50334Document4 pagesPowerLogic™ P5 - REL50334RoqsonMarcio SouzaNo ratings yet
- EN FANOX DATA SILG FeederGeneratorProtection ProtectionRelays R016Document13 pagesEN FANOX DATA SILG FeederGeneratorProtection ProtectionRelays R016giauNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase 4 Wire KWH Meter Front View DiagramDocument1 page3 Phase 4 Wire KWH Meter Front View DiagramWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- PC Red 301006 enDocument234 pagesPC Red 301006 enWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- High Flyers / Progress Test F / Unit 3: WritingDocument1 pageHigh Flyers / Progress Test F / Unit 3: WritingWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- Jan 2017Document2 pagesJan 2017WongSemarangNo ratings yet
- Z390 Aorus Ultra: User's ManualDocument60 pagesZ390 Aorus Ultra: User's ManualWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- T3000 Test Set The Substation Equipment Test Set For Testing Relays, CT'S, PT's and Primary InjectionsDocument42 pagesT3000 Test Set The Substation Equipment Test Set For Testing Relays, CT'S, PT's and Primary InjectionsMd Rodi BidinNo ratings yet
- Unindo: Type: LCT Function: Metering Busbar CT & VT W/O Ds WXDXH: 500 X 850 X 1610 MM Weight: 250 KGDocument1 pageUnindo: Type: LCT Function: Metering Busbar CT & VT W/O Ds WXDXH: 500 X 850 X 1610 MM Weight: 250 KGWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- Test & Data Management Software: The Integrated Testing SolutionDocument12 pagesTest & Data Management Software: The Integrated Testing SolutionWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- Transformers PDFDocument5 pagesTransformers PDFWongSemarangNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 GSO5Document40 pagesChapter7 GSO5Lawson SangoNo ratings yet
- For Single Phase: Arr Marn Electric Engineering Group Co-Founder - Wai.N.Htun)Document55 pagesFor Single Phase: Arr Marn Electric Engineering Group Co-Founder - Wai.N.Htun)Aung Thein OoNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Fault Detection Methods AnalysisDocument28 pagesTransmission Line Fault Detection Methods AnalysisAvinash ChimkarNo ratings yet
- 3.5100334-01 - Salwico Cargo Addressable - Service & Maintenance Manual - M - EN - 2013 - GDocument76 pages3.5100334-01 - Salwico Cargo Addressable - Service & Maintenance Manual - M - EN - 2013 - GSerhiiNo ratings yet
- Methods For Coordinating System Protective EquipmentDocument17 pagesMethods For Coordinating System Protective EquipmentMichael Parohinog GregasNo ratings yet
- @airbus: Airbus S.A.SDocument482 pages@airbus: Airbus S.A.Sjoker hotNo ratings yet
- Washington DC Area Low-Voltage Disturbance Event of April 7 2015 FinalDocument27 pagesWashington DC Area Low-Voltage Disturbance Event of April 7 2015 FinalJeans GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Level3 Application Note Neutral Loss Protection RelayDocument2 pagesLevel3 Application Note Neutral Loss Protection RelaynaveedfndNo ratings yet
- Fault Detection ProjectDocument22 pagesFault Detection Projectmayank choukseyNo ratings yet
- EDC17 Chybove KodyDocument222 pagesEDC17 Chybove KodyJan KoutňákNo ratings yet
- JVS Manual JRP 011Document12 pagesJVS Manual JRP 011Tamilventhan_sNo ratings yet
- Service Service Manual Manual: Generator SetDocument54 pagesService Service Manual Manual: Generator Setemildoykov4046100% (1)
- Relays RM4TR32Document9 pagesRelays RM4TR32Anonymous wuB7J6y5g4No ratings yet
- FormulaDocument255 pagesFormulaSEO BDMNo ratings yet
- Pre-Commissioning Testing Procedures of Line Protection SchemeDocument54 pagesPre-Commissioning Testing Procedures of Line Protection SchemeArvindBhadoliya100% (1)
- On-SITE GUIDE BS 7671 2008 IEE Wiring Regulations 17th EditionDocument191 pagesOn-SITE GUIDE BS 7671 2008 IEE Wiring Regulations 17th EditionIraklis Komodromos88% (48)
- Circuit Breakers (CBS) (52) : Handout 10Document8 pagesCircuit Breakers (CBS) (52) : Handout 10Hubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Soft Starter EM GW User ManualDocument25 pagesSoft Starter EM GW User ManualBuddhika MarasinghaNo ratings yet
- Ee Preboard IDocument8 pagesEe Preboard IMAcryan Pacquiao PactolNo ratings yet
- Busbar Protection Using Reverse InterlockingDocument2 pagesBusbar Protection Using Reverse InterlockingsubhashNo ratings yet
- Sc3 Lecture Short CKT Currents BMR Feb.03, 2021Document11 pagesSc3 Lecture Short CKT Currents BMR Feb.03, 2021Khizer AminNo ratings yet
- Acs2000ad Acs2000afeDocument86 pagesAcs2000ad Acs2000afeCristhianLoayzaTacoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Arcing Ground Phenomena in Ungrounded 3-Phase SystemsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Arcing Ground Phenomena in Ungrounded 3-Phase SystemsAbhisht YadavNo ratings yet
- Why speed of protection is importantDocument2 pagesWhy speed of protection is importantAb C100% (3)
- Short Circuit Calc Thesis PDFDocument214 pagesShort Circuit Calc Thesis PDFPGNo ratings yet
- Generator BasicsDocument100 pagesGenerator BasicsTravis Chesna100% (6)
- Transformer Testing PDFDocument42 pagesTransformer Testing PDFBiplab swainNo ratings yet
- ST solutions for 3phase BLDC Motor Control Technology WorkshopDocument45 pagesST solutions for 3phase BLDC Motor Control Technology WorkshopHoussem OuniNo ratings yet
- Megger Shortform-2016smDocument26 pagesMegger Shortform-2016smVictor CruzNo ratings yet
- Relay Coordination Chapter3Document13 pagesRelay Coordination Chapter3Chân Gà NướngNo ratings yet