Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet: O or H
Uploaded by
Lara GreyjoyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet: O or H
Uploaded by
Lara GreyjoyCopyright:
Available Formats
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet
1. Predict which compound in each pair will have the higher melting point and explain (use MW or
intermolecular forces)
(a) CS2 or CCl4
(b) HI or KI
(c) Cl2 or F2
(d) Na2O or H2O
(e) SiO2 or CO2
(f) CH4 or NH3
(g) CHCl3 or CF4
(h) CaF2 or HF
(i) BF3 or P4
2. Rank the following by from lowest to highest anticipated boiling point: C2H4, CH4, Ne, H3COCH3.
Ne<CH4<C2H4<H3COCH3
3.Label the following:A: Covalant Non-Polar B: Covalant Polar C: Network Covalant D.Metallic E:
Ionic Lattice F: Ion-Dipole G: Hydrogen Bonding H: Dipole-Dipole I: London
- Quartz C
- HCl H
-As D
- KF E
4. Classify the following solids at room temperature as molecular, ionic, network, or metallic.
a) K mp=74 C metallic b)KCl mp=770C ionic lattice
c)P mp=590C network d)BI3 mp=50C molecular
5.Arrange the following in order of increasing melting point CH3OH, SiO2, C2H6, NaCl.
C2H6 ,CH3OH, NaCl, SiO2
6. Which of the following contains no dipole-dipole forces
a) AsH3 b) CO2 c) H2O d)SeCl2
7.Which is most likely to be a gas at room temperature?
a) NaCl b)C2H2 c) Na metal d) CH3F
For each of the following compounds, determine the main intermolecular force. You may find it
useful to draw Lewis structures for some of these molecules:
1) nitrogen LONDON DISPERSION
2) carbon tetrachloride LONDON DISPERSION
3) H2S DIPOLE DIPOLE
4) sulfur monoxide DIPOLE DIPOLE
5) N2H2 HYDROGEN BONDING
6) boron trihydride LONDON DISPERSION
7) CH4O HYDROGEN BONDING
8) SiH2O DIPOLE DIPOLE
You might also like
- 11U CHEMISTRY EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS June 2010Document9 pages11U CHEMISTRY EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS June 2010Maden betoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Chemistry MCQ PracticeDocument6 pagesQuantitative Chemistry MCQ PracticeAnupa MedhekarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 126 Test AnswersDocument7 pagesChemistry 126 Test AnswersEzequiel OrellanaNo ratings yet
- SNC1D Exam Review CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesSNC1D Exam Review CHEMISTRYSwae LeeNo ratings yet
- SNC2D Chemistry Practice TestDocument8 pagesSNC2D Chemistry Practice TestSteve M Hall0% (1)
- Equilibrium Practice TestDocument11 pagesEquilibrium Practice TestAbeer MajdiNo ratings yet
- 08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetDocument33 pages08a. Chemical Kinetics SheetVIKRANTH KUMAR JAKKOJUNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations Ws AnsDocument4 pagesChemical Equations Ws AnsRia AlbertNo ratings yet
- 12 3+Review+Questions+KeyDocument4 pages12 3+Review+Questions+KeySaira ManzoorNo ratings yet
- SPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionDocument14 pagesSPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionMatthew GreesonNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Practice ProblemsDocument9 pagesKinetics Practice ProblemsnairdanipsoNo ratings yet
- Workbk 10Document177 pagesWorkbk 10Manushree NayakNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument13 pagesEnergy ChangesLok Jun HaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Questions 1.: (Total 1 Mark)Document22 pagesTopic 2 Questions 1.: (Total 1 Mark)Arda RahmainiNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument4 pagesConcentration of SolutionsPRANAV BANSAL100% (1)
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDocument10 pagesPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 7Document6 pagesTopic 7Bert ManNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry 12Document5 pagesWorksheet Chemistry 12mohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Chem Quiz BeeDocument4 pagesChem Quiz BeeAdrimar AdrianoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Che 101: Prof. Moavin Islam PHD Ficorr Mim Ceng (Mvi)Document77 pagesGeneral Chemistry Che 101: Prof. Moavin Islam PHD Ficorr Mim Ceng (Mvi)Irfanul HoqueNo ratings yet
- SCH4U Equilibrium Questions With SolutionsDocument28 pagesSCH4U Equilibrium Questions With SolutionsS P100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics SolDocument40 pagesChemical Kinetics SolVIKRANTH KUMAR JAKKOJUNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds WorksheetDocument5 pagesNaming Compounds Worksheet吴蔓华No ratings yet
- Chap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRADocument129 pagesChap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRA黄麒安No ratings yet
- INTERMOLECULAR FORCESDocument2 pagesINTERMOLECULAR FORCESada wangNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Worksheet - 3Document6 pagesThermodynamics Worksheet - 3Louis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- Trig Identities QsDocument5 pagesTrig Identities QsboostoberoiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Final Exam Review KEYDocument7 pagesChemistry Final Exam Review KEYZetrix JensenNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Note - Empirical & Molecular FormulasDocument5 pages3.3 Note - Empirical & Molecular FormulasRoddyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NomenclatureDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry NomenclatureAYON GANGULYNo ratings yet
- CH.8 Energy Production PDFDocument108 pagesCH.8 Energy Production PDFAashna pandyaNo ratings yet
- Assigning Oxidation NumberDocument10 pagesAssigning Oxidation NumberUserrrrrbistaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Placement Chemistry TestDocument15 pagesAdvanced Placement Chemistry TestBobNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law Problems SolvedDocument2 pagesHess's Law Problems SolvedTjrjfjdjNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Learning Task 2-1: Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument4 pagesChemical Bonding Learning Task 2-1: Statement or Answers The QuestionJerome Fresado100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Basic Atomic Theory: Key PointsDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Basic Atomic Theory: Key PointsDaahirshiiq MadoobeNo ratings yet
- SL Score ! /30: Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: BondingDocument7 pagesSL Score ! /30: Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bondingraja_tanukuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document84 pagesChapter 8Hafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems on Net Ionic EquationsDocument3 pagesPractice Problems on Net Ionic EquationsZainabNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Assignment 1 - SCH4U h5, Chemistry, 12, UniversityDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Assignment 1 - SCH4U h5, Chemistry, 12, UniversityAnonymous iadge07t0% (3)
- Chapter 11Document4 pagesChapter 11John Christian De LeonNo ratings yet
- ResonanceDocument3 pagesResonanceAltaf RatherNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Notes - Avogadro & The MoleDocument5 pages3.1 Notes - Avogadro & The MoleRoddyNo ratings yet
- Topic 7-17 Practice Questions Key 1 2Document8 pagesTopic 7-17 Practice Questions Key 1 2Isaline GurneNo ratings yet
- Polyurethane ChemistryDocument15 pagesPolyurethane Chemistryyoga nayagi punichelvana100% (1)
- Naming Compounds Practice WorksheetDocument5 pagesNaming Compounds Practice Worksheetd4ddY chiLLNo ratings yet
- Examview 2009 2010 Sch4c Unit 3 (Org) Test Exam PrepDocument4 pagesExamview 2009 2010 Sch4c Unit 3 (Org) Test Exam Prepabebaw matebuNo ratings yet
- Trends worksheet answersDocument3 pagesTrends worksheet answersFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ether MCQsDocument22 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Ether MCQsShypackofcheetosNo ratings yet
- Answers CH 6 Review PDFDocument4 pagesAnswers CH 6 Review PDFMinson Sim100% (1)
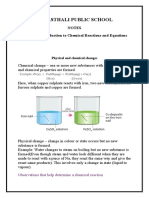
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolPlatinum Gaming Warrior100% (1)
- General Chemistry Che 101: Prof. Moavin Islam PHD Ficorr Mim Ceng (Mvi)Document88 pagesGeneral Chemistry Che 101: Prof. Moavin Islam PHD Ficorr Mim Ceng (Mvi)Irfanul HoqueNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument6 pagesSolutionsSelma BahyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument22 pagesChemical Kinetics Multiple Choice QuestionsMohamed MegahedNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass 11 Physics Important QuestionsIshar ravaniNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Phase Diagrams PracticeDocument10 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Phase Diagrams PracticeKyla BaysaNo ratings yet
- 11 Sample Papers Chemistry 1Document5 pages11 Sample Papers Chemistry 1Abhipsa Priyadarsini SahuNo ratings yet
- DPS Ruby Park Block Test II 2019-20 Class XI ChemistryDocument6 pagesDPS Ruby Park Block Test II 2019-20 Class XI ChemistrySoham NagNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document32 pagesWa0010.Tanvi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism Principles and Theories: Consequences Affect BehaviorDocument18 pagesBehaviorism Principles and Theories: Consequences Affect BehaviorLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Perspectives On LearningDocument4 pagesPerspectives On LearningLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Learning & The BrainDocument7 pagesLearning & The BrainLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Plant Roots Structure and FunctionsDocument2 pagesPlant Roots Structure and FunctionsLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- (PSYCH 153) Handout 10 - Goal Setting and Goal StrivingDocument4 pages(PSYCH 153) Handout 10 - Goal Setting and Goal StrivingLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions PacketsDocument9 pagesOxidation Reduction Reactions Packetsrachana rupereeNo ratings yet
- Psych 153Document11 pagesPsych 153Lara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- (PSYCH 153) Handout 10 - Goal Setting and Goal StrivingDocument4 pages(PSYCH 153) Handout 10 - Goal Setting and Goal StrivingLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Practice NieDocument2 pagesPractice Nieridah_686No ratings yet
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic MotivationDocument6 pagesIntrinsic and Extrinsic MotivationLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Identifying Laboratory Equipment: Holt Chemistry Textbook Laboratory Equipment (For Modeling and Demonstration)Document9 pagesIdentifying Laboratory Equipment: Holt Chemistry Textbook Laboratory Equipment (For Modeling and Demonstration)Lara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Biosummative 3Document3 pagesBiosummative 3Lara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Cell structures and organelles experimentDocument4 pagesCell structures and organelles experimentEinor AbadNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 LE 2 ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio 11 LE 2 ReviewerLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: M. R. Naimi-JamalDocument69 pagesGeneral Chemistry: M. R. Naimi-JamalJohn Labilles Jr.No ratings yet
- The Quality of Light Used by The Microscope Depends On The Parts Below The StageDocument4 pagesThe Quality of Light Used by The Microscope Depends On The Parts Below The StageLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- BIOSUMMATIVE4Document7 pagesBIOSUMMATIVE4Lara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- BIOSUMMATIVE4Document7 pagesBIOSUMMATIVE4Lara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Can We Know the Universe? Carl SaganDocument2 pagesCan We Know the Universe? Carl SaganPolyjuice PotionNo ratings yet
- 02 Pirsig - On Scientific Method PDFDocument4 pages02 Pirsig - On Scientific Method PDFSeulgi JeonNo ratings yet
- ORG LAB Recrystallization2009 PDFDocument12 pagesORG LAB Recrystallization2009 PDFAnnaReyesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Plant EmbryosDocument13 pagesGrowth and Development of Plant EmbryosLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Le1 1Document6 pagesLe1 1Lara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Abduction, Reason, and ScienceDocument12 pagesAbduction, Reason, and ScienceLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 General Chemistry 1 Electron Configuration and Chemical PeriodicityDocument9 pagesChem 16 General Chemistry 1 Electron Configuration and Chemical PeriodicityLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions PacketsDocument9 pagesOxidation Reduction Reactions Packetsrachana rupereeNo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent ProblemsDocument6 pagesLimiting Reagent ProblemsFarisDonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Chemical EquilibriumDocument52 pagesChapter 15 Chemical EquilibriumLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure NotesDocument14 pagesQuantum Theory and Atomic Structure NotesLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet